【VUE3】setup语法糖使用记录
一、定义data
//定义data
//vue2
<script>
export default {
data(){
retrun{
aa:""
}
}
}
</script>
//Vue3 通过 ref 和 rective 代替以前的 data 语法,在setup语法糖中直接使用,无需return 出去
<script setup>
//首先需要引入
import { ref , reactive } from "vue"
//定义一个数据
const aa = ref("") //ref(false) //ref([])//ref({})
//查看或者修改的时候需要在数后面加一个value。
console.log(aa.value)
aa.value = 1
//reactive 主要是用来处理复杂的数据类型,比如对象和数组。
//所以当你传递的是非对象时,页面不会发生响应
//错误示范
// let error = reactive(err)
//正确示范
let right = reactive({
name:"张三"
})
//修改值得时候
right.name = "李四"
</script>
二、computed 使用
与vue2不同的是,Vue3需要引入相关内容
<template>
<div class="box">
<!-- 在上方调用即可,结果为169 -->
{{add}}
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { computed, ref } from "vue";
let num1 = ref(13);
let num2 = ref(13); // 设置个变量接收
let add = computed(() => {
return num1.value * num2.value;
});
</script>
三、watch监听
使用watch也需要引入,使用方式与vue2相差不大,不同的是,监听多个属性的时候,要写多个watch。
import { watch } from "vue"
watch(() => brand.brand, (newVal) => {
console.log(newVal)
})
}, { deep: true,immediate:true }
)
如果写到一起的话,就会出现其中一个值变化,下面的方法都会触发,不能独立监听。
watch(()=>[user.value, password.value],([newUser, newPassword],[oldUser, oldPassword])=>{
console.log('我是新的user值'+newUser);
console.log('我是旧的的user值'+oldUser);
console.log('我是新的pass值'+newPassword);
console.log('我是旧的的pass值'+oldPassword);
})
四、组件之间传参
在vue3中有setup语法糖,所以我们引入子组件之后无需注册,可以直接使用,子组件也不需要命名
<template>
<UpgradePopUpVue/>
</template>
<script setup>
import UpgradePopUpVue from "@/components/UpgradePopUp.vue"
</script>
组件之间传参
/// defineProps传参(父传子)
//父组件
<child word="我是父组件传过来的内容"></child>
//子组件
<script>
import { defineProps } from "vue"
const props = defineProps({
word:String
})
console.log(props) // Proxy {word: '我是父组件传过来的内容'}
</script>
// defineEmits传值(子传父)
//子组件
<template>
<button @click="clickFun">点击给父组件传话</button>
</template>
<script>
import { defineEmits } from "vue"
const emit = defineEmits(["getWord"])
const clickFun = () => {
emit('getWordChild','我是子组件,给父组件传一句话')
}
</script>
//父组件
<template>
<child @getWordChild="getWord"></child>
</template>
<script setup>
import child from "./child"
const getWord = (val) => {
console.log(val)//我是子组件,给父组件传一句话
}
</script>
父子组件的双向绑定
1、通过prop向下传递, emit向上传递。
1)父组件通过props向子组件传递内容
2)子组件通过emit向父组件传递信息
3)父组件接受子组件(通过emit)传过来的数据,修改自己的内容
4)子组件在通过watch去监听父组件的props传递内容的改变
//父组件
<template>
<div>
<child :value='value' @getChildData='getChildData'></child>
来自子组件的数据:<span>{{value}}</span>
<div/>
</template>
<script>
data() {
return {
value: '父组件的数据'
}
},
methods:{
getChildData(v){
this.value = v
}
}
</script>
//子组件child
<template>
<input v-model='childValue' @input='childInputChange'></input>
</template>
<script>
props:{
value:{
type:String,//在props接受父组件传递数据
default:''
}
},
data(){
return {
childValue:this.value
}
},
watch:{
value(){
this.childValue = this.value //监听父组件的数据,同步更新子组件数据
}
},
methods:{
childInputChange(){
this.$emit('getChildData',this.childValue) // 通过emit触发getChildData,将子组件数据传递给父组件
}
</script>
在vue2中双向绑定,v-model相当于绑定了value prop并触发input事件
//父组件
<template>
<div>
<child v-model='value'></child>
// 等价于
<child :value='value' @childValueChange = "val=>{ value = val }"></child>
父子组件同步的数据:<span>{{value}}</span>
<div/>
</template>
<script>
data() {
return {
value: '父组件的数据'
}
}
</script>
//子组件child
<template>
<input type="text" v-model="childValue" @input="childInputChange"/>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "child",
model: { // 定义model
prop: 'fatherValue', // 父组件v-model绑定的值传递给props中的fatherValue
event: 'childValueChange'
// 通过emit触发childValueChange将内部值传递给父组件v-model绑定的值
},
props: {
fatherValue: String // 接受父组件传递的值
},
data(){
return {
childValue: this.fatherValue// 关联值
}
},
methods: {
childInputChange(){
// 通过$emit触发childValueChange(model内定义)事件,将内部值传递给给父组件
this.$emit('childValueChange', this.childValue)
}
}
}
</script>
在 3.x 中,自定义组件上的 v-model 相当于传递了 modelValue prop 并接收抛出的 update:modelValue 事件:
子组件
<template>
<div>
<input v-model="sea" @input="valChange(sea)" />
</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import { defineComponent, ref, watch } from 'vue'
export default defineComponent({
name: 'ChildComp',
props: {
modelValue: { // 父组件 v-model 没有指定参数名,则默认是 modelValue
type: String,
default: ''
}
},
setup (props, { emit }) {
// input初始化
const sea = ref(props.modelValue)
// 因为props.modelValue是非引用类型,改变时,需要监听,对sea重新赋值
watch(() => props.modelValue, () => { sea.value = props.modelValue })
// 数据双向绑定
function valChange (e: string) {
emit('update:modelValue', e)
}
return {
sea,
valChange
}
}
})
</script>
//父组件
<template>
<div>
<!-- v-model 没有指定参数名时,子组件默认参数名是modelValue -->
<ChildComp v-model="search" />
<h1>{{ search }}</h1>
</div>
</template>ddimport { defineComponent, ref } from 'vue'
import ChildComp from '../components/ChildComp'
s
export default defineComponent({
name: 'Index',
components: {
ChildComp
},
setup () {
const search = ref('')
return {
search
}
}
})
</script>
父组件调用子组件的方法或者获取数据 defineExpose
如果组件使用了setup语法糖,那么组件方法啥的默认的就是关闭的。需要将你要调用的方法暴露出去,父组件才可以使用。就要用到defineExpose ,还有就是vue2中用到的ref
话不多说,上代码
//子组件
<template>
....省略
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref, defineExpose} from "vue"
const chooseModel = ref("all")
const selects = (v, type) => {
chooseModel.value = “change”
}
defineExpose({
chooseModel,
selects
})
</script >
//父组件
<template>
<child ref="childComponent"/>
</template>
<script setup>
import child from "./child"
import { ref } from "vue"
const childComponent = ref()
console.log(childComponent .value.chooseModel) //打印子组件的值
childComponent .value.selects("1","dsa") //调用子组件的方法
</script >
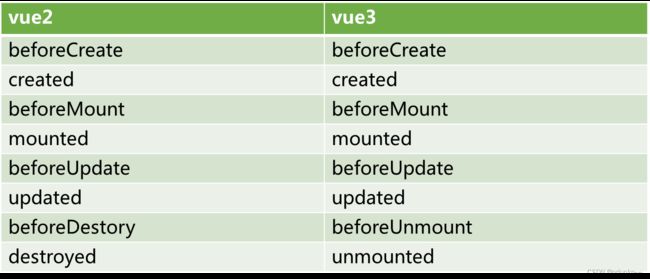
五、生命周期
与vue2不同的是 销毁变成了beforeUnmount,unmounted.其余的都是一致的。
setup相当于生命周期的 beforeCreate 和 created。所以在setup里面们可以直接定义内容