eureka服务注册与发现机制
无服务注册中心
问题描述:
- 接口系统服务器不固定,随时可能增删机器
- 接口调用方法无法知晓服务具体的IP和Port地址.(除非手工调整接口调用者的代码)
Eureka的作用
流程说明:
服务提供者启动时:定时向EurekaServer注册自己的服务信息(服务名、IP、端口…等等)
服务消费者启动时:后台定时拉取EurekaServer中存储的服务信息.
使用Eureka
创建springboot工程
pom文件
springboot版本
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parentartifactId>
<version>2.1.4.RELEASEversion>
parent>
引入eureka-server和web jar包
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloudgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-serverartifactId>
dependency>
SpringCloudEurekaApplication
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.server.EnableEurekaServer;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaServer //启用eureka-server
public class SpringCloudEurekaApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringCloudEurekaApplication.class, args);
}
}
application.yml
spring:
application:
name: eureka-peer
server:
port: 10000
eureka:
instance:
hostname: dev
instance-id: dev
client:
# 不获取注册表信息
fetch-registry: false
# 不向EurekaServer进行注册,因为它自己就是服务
register-with-eureka: false
service-url:
# 一个服务的时候就是当前的地址加上端口和/eureka/
defaultZone: http://localhost:10000/eureka/
server:
#设置 如果同步没有数据等待时长 默认 5分
wait-time-in-ms-when-sync-empty: 0
#设为false,关闭自我保护,默认true
enable-self-preservation: true
#Peer Node信息的定时更新,默认值为600s,即10min,同步eureka-server上的节点信息
peer-eureka-nodes-update-interval-ms: 10000
service-url zone的概念
zone就相当于一个一个的地区,使多地的机房优先调用当前地域机房的服务
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-BnWz2tAy-1580803636677)(http://note.youdao.com/yws/res/8652/WEBRESOURCEdc56894f7a0ce4746368ac6ef7a78417)]application配置
eureka.client.availability-zones.beijing:zone-1 eureka.client.service-url.zone1=http://localhost:10001/eureka这样配置之后,如果consumer配置的也是这个zone就会向这个zone查找服务,如果找不到服务,才回去去其他zone查找服务
启动服务
启动服务,http://localhost:10000/
创建服务和消费者
Hello服务1
pom文件
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloudgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-clientartifactId>
dependency>
HelloDemoPeer1Application
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.EnableEurekaClient;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaClient
@RestController
public class HelloDemoPeer1Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(HelloDemoPeer1Application.class, args);
}
@GetMapping("")
public Object index() {
String str = "这是服务端1返回的应答";
return new String(str);
}
}
application.yml
server:
port: 8001
spring:
application:
#当做服务名称,不区分大小写
name: helloserver
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://127.0.0.1:10000/eureka/
启动服务查看eureka dashboard
新服务实例
Hello服务2
修改
HelloDemoPeer1Application
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.EnableEurekaClient;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaClient
@RestController
public class HelloDemoPeer1Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(HelloDemoPeer1Application.class, args);
}
@GetMapping("")
public Object index() {
String str = "这是服务端2返回的应答";
return new String(str);
}
}
application.yml
server:
port: 8002
spring:
application:
#当做服务名称,不区分大小写
name: helloserver
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://127.0.0.1:10000/eureka/
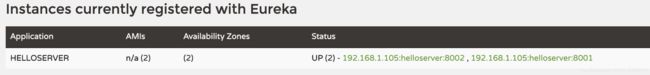
启动服务查看eureka dashboard
当前已经启动了两个服务实例
customer-demo
CustomerDemoApplication
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.LoadBalanced;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.EnableEurekaClient;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaClient
@RestController
public class CustomerDemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(CustomerDemoApplication.class, args);
}
@Bean
// 负载均衡
@LoadBalanced
public RestTemplate template(){
return new RestTemplate();
}
}
application.yml
server:
port: 8083
spring:
application:
name: consumer-demo
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone : http://127.0.0.1:10000/eureka/
启动服务查看eureka dashboard
服务注册成功
访问hello服务
CustomerController
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
@RestController
public class CustomerController {
@Autowired
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
@GetMapping("index")
public Object getIndex(){
// 可以直接使用服务的名称:HELLOSERVER进行访问,不区分大小写
return restTemplate.getForObject("http://HELLOSERVER/",String.class,"");
}
}
访问http://localhost:8083/index
多次访问,返回不同服务的响应,这是由于配置了@LoadBalanced默认轮询所有服务
Eureka核心知识
- 启动时服务如何注册到Eureka的?
- 服务端如何保存这些信息?
- 消费者如何根据服务名称发现服务实例?
- 如何构建高可用的eureka集群?
- 心跳和服务剔除机制是什么?
- eureka自我保护模式是什么?
服务注册流程
启动时通过后台任务,注册到EurekaServer,内容包含有:服务名、IP、端口
| 名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| eureka.instance.instanceId | 实例唯一ID |
| eureka.client.serviceUrl | Eureka客户端的地址 |
| eureka.client.registerWithEureka | 是否注册到eureka上 |
| eureka.client.fetchRegistry | 是否拉取服务 |
推测EurekaServer中存放的是一个map,key为serviceId,value为一个object对象包含服务的信息
按照以上思路,需要在EurekaClient中拼装服务对象并在启动的时候注册到EurekaServer中
1.找到springboot自动装配文件,看看在启动的时候装配了哪些信息
spring.factories
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.config.EurekaClientConfigServerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.config.EurekaDiscoveryClientConfigServiceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.EurekaClientAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.cloud.netflix.ribbon.eureka.RibbonEurekaAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.EurekaDiscoveryClientConfiguration
org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.BootstrapConfiguration=\
org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.config.EurekaDiscoveryClientConfigServiceBootstrapConfiguration
查看Client的Configuration EurekaClientAutoConfiguration
初始化了一个实例
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = ApplicationInfoManager.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT)
@org.springframework.cloud.context.config.annotation.RefreshScope
@Lazy
public ApplicationInfoManager eurekaApplicationInfoManager(
EurekaInstanceConfig config) {
InstanceInfo instanceInfo = new InstanceInfoFactory().create(config);
return new ApplicationInfoManager(config, instanceInfo);
}
查看create方法
public InstanceInfo create(EurekaInstanceConfig config) {
...
}
此方法通过EurekaInstanceConfig这个类的对象创建一个InstanceInfo的对象
查看EurekaInstanceConfig
public interface EurekaInstanceConfig {
...
}
此方法是一个接口,那么我们查找相关的实现类
// 这个类获取在配置文件中以eureka.instance开头的信息,并设置没有定义的信息的默认值
@ConfigurationProperties("eureka.instance")
public class EurekaInstanceConfigBean
implements CloudEurekaInstanceConfig, EnvironmentAware {
private static final String UNKNOWN = "unknown";
private HostInfo hostInfo;
private InetUtils inetUtils;
/**
* Default prefix for actuator endpoints.
*/
private String actuatorPrefix = "/actuator";
/**
* Get the name of the application to be registered with eureka.
*/
private String appname = UNKNOWN;
...
}
2.装配的信息是如何发送到EurekaServer
同样还是在EurekaClientAutoConfiguration
@Bean(destroyMethod = "shutdown")
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = EurekaClient.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT)
@org.springframework.cloud.context.config.annotation.RefreshScope
@Lazy
public EurekaClient eurekaClient(ApplicationInfoManager manager,//加载了包含装配信息的对象
EurekaClientConfig config, EurekaInstanceConfig instance,
@Autowired(required = false) HealthCheckHandler healthCheckHandler) {
// If we use the proxy of the ApplicationInfoManager we could run into a
// problem
// when shutdown is called on the CloudEurekaClient where the
// ApplicationInfoManager bean is
// requested but wont be allowed because we are shutting down. To avoid this
// we use the
// object directly.
ApplicationInfoManager appManager;
if (AopUtils.isAopProxy(manager)) {
appManager = ProxyUtils.getTargetObject(manager);
}
else {
appManager = manager;
}
//将对象传递到CloudEurekaClient的构造方法中返回
CloudEurekaClient cloudEurekaClient = new CloudEurekaClient(appManager,
config, this.optionalArgs, this.context);
cloudEurekaClient.registerHealthCheck(healthCheckHandler);
return cloudEurekaClient;
}
查看CloudEurekaClient的构造方法
public CloudEurekaClient(ApplicationInfoManager applicationInfoManager,
EurekaClientConfig config, AbstractDiscoveryClientOptionalArgs<?> args,
ApplicationEventPublisher publisher) {
//调用了父类的构造方法
super(applicationInfoManager, config, args);
this.applicationInfoManager = applicationInfoManager;
this.publisher = publisher;
this.eurekaTransportField = ReflectionUtils.findField(DiscoveryClient.class,
"eurekaTransport");
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(this.eurekaTransportField);
}
查看父类的构造方法
public DiscoveryClient(ApplicationInfoManager applicationInfoManager, final EurekaClientConfig config, AbstractDiscoveryClientOptionalArgs args) {
this(applicationInfoManager, config, args, new Provider<BackupRegistry>() {
...
});
}
查看this()构造方法
DiscoveryClient(ApplicationInfoManager applicationInfoManager, EurekaClientConfig config, AbstractDiscoveryClientOptionalArgs args,
Provider<BackupRegistry> backupRegistryProvider) {
...
try {
// default size of 2 - 1 each for heartbeat and cacheRefresh
scheduler = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(2,
new ThreadFactoryBuilder()
.setNameFormat("DiscoveryClient-%d")
.setDaemon(true)
.build());
//心跳检测定时任务
heartbeatExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
1, clientConfig.getHeartbeatExecutorThreadPoolSize(), 0, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>(),
new ThreadFactoryBuilder()
.setNameFormat("DiscoveryClient-HeartbeatExecutor-%d")
.setDaemon(true)
.build()
); // use direct handoff
//注册表缓存信息刷新任务
cacheRefreshExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
1, clientConfig.getCacheRefreshExecutorThreadPoolSize(), 0, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>(),
new ThreadFactoryBuilder()
.setNameFormat("DiscoveryClient-CacheRefreshExecutor-%d")
.setDaemon(true)
.build()
); // use direct handoff
...
} catch (Throwable e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to initialize DiscoveryClient!", e);
}
...
// finally, init the schedule tasks (e.g. cluster resolvers, heartbeat, instanceInfo replicator, fetch
initScheduledTasks();
...
}
查看initScheduledTasks方法
private void initScheduledTasks() {
// 如果为eurekaclient默认为true,获取注册表信息
if (clientConfig.shouldFetchRegistry()) {
...
scheduler.schedule(
new TimedSupervisorTask(
"cacheRefresh",
scheduler,
cacheRefreshExecutor,
registryFetchIntervalSeconds,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
expBackOffBound,
// 获取注册表信息方法
new CacheRefreshThread()
),
registryFetchIntervalSeconds, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
// 如果为eurekaclient默认为true,发送心跳
if (clientConfig.shouldRegisterWithEureka()) {
...
// Heartbeat timer
scheduler.schedule(
new TimedSupervisorTask(
"heartbeat",
scheduler,
heartbeatExecutor,
renewalIntervalInSecs,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
expBackOffBound,
// 发送心跳方法
new HeartbeatThread()
),
renewalIntervalInSecs, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
...
} else {
logger.info("Not registering with Eureka server per configuration");
}
}
查看如何获取注册表服务信息
class CacheRefreshThread implements Runnable {
public void run() {
refreshRegistry();
}
}
@VisibleForTesting ①
void refreshRegistry() {
...
// 获取远程EurekaServer的注册信息,并更新本地缓存
boolean success = fetchRegistry(remoteRegionsModified);
...
}
查看发送心跳
private class HeartbeatThread implements Runnable {
public void run() {
// 除了这个方法并无其他有意义的方法
if (renew()) {
lastSuccessfulHeartbeatTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
}
}
查看renew方法
boolean renew() {
...
// 如果没找到这个服务就调用注册方法
if (httpResponse.getStatusCode() == Status.NOT_FOUND.getStatusCode()) {
...
// 注册方法
boolean success = register();
if (success) {
instanceInfo.unsetIsDirty(timestamp);
}
return success;
}
// 如果服务已经存在了直接返回成功
return httpResponse.getStatusCode() == Status.OK.getStatusCode();
...
}
查看register方法
boolean register() throws Throwable {
...
// 将实例信息instanceInfo注册到EurekaServer
httpResponse = eurekaTransport.registrationClient.register(instanceInfo);
return httpResponse.getStatusCode() == Status.NO_CONTENT.getStatusCode(); ②
}
服务端如何保存这些信息
客户端启动后会去调用http,将服务实例放在Server内部一个Map对象中存储,获取时直接去拿
| 名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| enableSelfPreservation | 关闭自我保护机制 |
| waitTimeInMsWhenSyncEmpty | 如果同步没有数据等待时长 |
| peerEurekaNodesUpdateIntervalMs | 同步注册表信息时间间隔 |
官网API地址:https://github.com/Netflix/eureka/wiki/Eureka-REST-operations
API介绍
| Operation | HTTP action | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Register new application instance | POST /eureka/v2/apps/appID | Input: JSON/XML payload HTTP Code: 204 on success |
| De-register application instance | DELETE /eureka/v2/apps/appID/instanceID | HTTP Code: 200 on success |
| Send application instance heartbeat | PUT /eureka/v2/apps/appID/instanceID | HTTP Code: * 200 on success * 404 if instanceID doesn’t exist |
| Query for all instances | GET /eureka/v2/apps | HTTP Code: 200 on success Output: JSON/XML |
| Query for all appID instances | GET /eureka/v2/apps/appID | HTTP Code: 200 on success Output: JSON/XML |
| Query for a specific appID/instanceID | GET /eureka/v2/apps/appID/instanceID | HTTP Code: 200 on success Output: JSON/XML |
| Query for a specific instanceID | GET /eureka/v2/instances/instanceID | HTTP Code: 200 on success Output: JSON/XML |
| Take instance out of service | PUT /eureka/v2/apps/appID/instanceID/status?value=OUT_OF_SERVICE | HTTP Code: * 200 on success * 500 on failure |
| Move instance back into service (remove override) | DELETE /eureka/v2/apps/appID/instanceID/status?value=UP (The value=UP is optional, it is used as a suggestion for the fallback status due to removal of the override) | HTTP Code: * 200 on success * 500 on failure |
| Update metadata | PUT /eureka/v2/apps/appID/instanceID/metadata?key=value | HTTP Code: * 200 on success * 500 on failure |
| Query for all instances under a particular vip address | GET /eureka/v2/vips/vipAddress | * HTTP Code: 200 on success Output: JSON/XML * 404 if the vipAddress does not exist. |
| Query for all instances under a particular secure vip address | GET /eureka/v2/svips/svipAddress | * HTTP Code: 200 on success Output: JSON/XML * 404 if the svipAddress does not exist. |
客户端如何发送API
继续查看register方法看看具体是调用的哪个API
// 但是registrationClient是一个接口有三个实现类
httpResponse = eurekaTransport.registrationClient.register(instanceInfo);
这个时候我们使用查看源码的方法之一,在对应的三个实现类中打断点;看最后是进入到哪个方法中
运行的是AbstractJerseyEurekaHttpClient
@Override
public EurekaHttpResponse<Void> register(InstanceInfo info) {
String urlPath = "apps/" + info.getAppName();
ClientResponse response = null;
try {
Builder resourceBuilder =
// Jersey RESTful 框架是开源的RESTful框架 亚马逊平台用的比较多,比较老
jerseyClient.resource(serviceUrl).path(urlPath).getRequestBuilder();
addExtraHeaders(resourceBuilder);
response = resourceBuilder
.header("Accept-Encoding", "gzip")
.type(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_TYPE)
.accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
.post(ClientResponse.class, info);
return anEurekaHttpResponse(response.getStatus()).headers(headersOf(response)).build();
} finally {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Jersey HTTP POST {}/{} with instance {}; statusCode={}", serviceUrl, urlPath, info.getId(),
response == null ? "N/A" : response.getStatus());
}
if (response != null) {
response.close();
}
}
}
通过阅读源码可知最后调用的是
| Operation | HTTP action | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Register new application instance | POST /eureka/v2/apps/appID | Input: JSON/XML payload HTTP Code: 204 on success |
服务端如何接收
1.找到springboot自动装配文件,看看在启动的时候装配了哪些信息
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.server.EurekaServerAutoConfiguration
在EurekaServerAutoConfiguration中找到如下代码
/**
* Register the Jersey filter.
* @param eurekaJerseyApp an {@link Application} for the filter to be registered
* @return a jersey {@link FilterRegistrationBean}
*/
@Bean
public FilterRegistrationBean jerseyFilterRegistration(
javax.ws.rs.core.Application eurekaJerseyApp) {
FilterRegistrationBean bean = new FilterRegistrationBean();
bean.setFilter(new ServletContainer(eurekaJerseyApp));
bean.setOrder(Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE);
bean.setUrlPatterns(
Collections.singletonList(EurekaConstants.DEFAULT_PREFIX + "/*"));
return bean;
}
但是已然无法继续追踪下去,这个时候我们需要使用阅读源码的第二个方法加log
在配置文件中添加如下代码
logging:
level:
org:
springframework:
cloud: debug
com:
netflix: debug
启动server,然后启动client,查看server的log信息
2020-02-02 16:36:28.648 DEBUG 25686 --- [io-10000-exec-2] c.n.eureka.resources.InstanceResource : Found (Renew): HELLOSERVER - 192.168.1.105:helloserver:8002; reply status=200
根据API文档和log信息,查看InstanceResource
| Operation | HTTP action | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Register new application instance | POST /eureka/v2/apps/appID | Input: JSON/XML payload HTTP Code: 204 on success |
发现这个方法是用来获取instance信息的
private final PeerAwareInstanceRegistry registry;
private final EurekaServerConfig serverConfig;
private final String id;
private final ApplicationResource app;
/**
* Get requests returns the information about the instance's
* {@link InstanceInfo}.
*
* @return response containing information about the the instance's
* {@link InstanceInfo}.
*/
@GET
public Response getInstanceInfo() {
// 返回的InstanceInfo对象是registry对象的getInstanceByAppAndId通过app.getName()和id获取
InstanceInfo appInfo = registry
.getInstanceByAppAndId(app.getName(), id);
if (appInfo != null) {
logger.debug("Found: {} - {}", app.getName(), id);
return Response.ok(appInfo).build();
} else {
logger.debug("Not Found: {} - {}", app.getName(), id);
return Response.status(Status.NOT_FOUND).build();
}
}
id就是一个字符串,查看app类,ApplicationResource
@Produces({"application/xml", "application/json"})
public class ApplicationResource {
...
@GET
public Response getApplication(@PathParam("version") String version,
@HeaderParam("Accept") final String acceptHeader,
@HeaderParam(EurekaAccept.HTTP_X_EUREKA_ACCEPT) String eurekaAccept) {
...
}
@Path("{id}")
public InstanceResource getInstanceInfo(@PathParam("id") String id) {
return new InstanceResource(this, id, serverConfig, registry);
}
@POST
@Consumes({"application/json", "application/xml"})
public Response addInstance(InstanceInfo info,
@HeaderParam(PeerEurekaNode.HEADER_REPLICATION) String isReplication) {
...
}
...
}
可以看到@GET,@POST等方法,根据Jersey框架,我们应该到ApplicationsResource中继续查找
@Path("/{version}/apps")
@Produces({"application/xml", "application/json"})
public class ApplicationsResource {
...
@Path("{appId}")
public ApplicationResource getApplicationResource(
@PathParam("version") String version,
@PathParam("appId") String appId) {
CurrentRequestVersion.set(Version.toEnum(version));
// 返回的是ApplicationResource对象
return new ApplicationResource(appId, serverConfig, registry);
}
...
}
Jersey根据@Path层级下发请求到不同的Resource处理
知道了如何处理,我们再查看PeerAwareInstanceRegistry,看是如何进行注册的
public interface PeerAwareInstanceRegistry extends InstanceRegistry {
...
void register(InstanceInfo info, boolean isReplication);
...
}
发现了register方法,我们可以根据注册方法,看最后信息是否被保存到map中
PeerAwareInstanceRegistry有两个实现类
点开其中一个实现类InstanceRegistry
@Override
public void register(final InstanceInfo info, final boolean isReplication) {
handleRegistration(info, resolveInstanceLeaseDuration(info), isReplication);
super.register(info, isReplication);
}
发现调用的super的register方法,继续跟进
public class PeerAwareInstanceRegistryImpl extends AbstractInstanceRegistry implements PeerAwareInstanceRegistry {
...
@Override
public void register(final InstanceInfo info, final boolean isReplication) {
int leaseDuration = Lease.DEFAULT_DURATION_IN_SECS;
if (info.getLeaseInfo() != null && info.getLeaseInfo().getDurationInSecs() > 0) {
leaseDuration = info.getLeaseInfo().getDurationInSecs();
}
super.register(info, leaseDuration, isReplication);
replicateToPeers(Action.Register, info.getAppName(), info.getId(), info, null, isReplication);
}
...
}
发现调用的是PeerAwareInstanceRegistryImpl的register方法,也就是PeerAwareInstanceRegistry的另一个实现类
继续跟进super.register
public abstract class AbstractInstanceRegistry implements InstanceRegistry {
...
private final ConcurrentHashMap<String, Map<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>>> registry = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Map<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>>>();
...
public void register(InstanceInfo registrant, int leaseDuration, boolean isReplication) {
...
gMap = registry.putIfAbsent(registrant.getAppName(), gNewMap);
...
}
...
}
将服务注册信息放入了registry中,而registry实际上是一个ConcurrentHashMap。
证实了服务信息就是存放再Map中的。
消费者服务发现
启动时通过后台定时任务,定期从EurekaServer拉取服务信息,缓存到消费者本地内存中。
根据上文线索直接查看DiscoveryClient
//注册表缓存信息刷新任务
cacheRefreshExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
1, clientConfig.getCacheRefreshExecutorThreadPoolSize(), 0, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>(),
new ThreadFactoryBuilder()
.setNameFormat("DiscoveryClient-CacheRefreshExecutor-%d")
.setDaemon(true)
.build()
); // use direct handoff
这部分上文提到过,不再赘述
高可用集群
在eureka的高可用状态下,这些注册中心是对等的,他们会互相将注册在自己的实例同步给其他的注册中心
程序演示
spring-cloud-eureka 项目
修改application文件
# 通过不同的profiles启动三个EurekaServer实例
spring:
profiles:
active: dev
---
spring:
application:
name: eureka-peer
profiles: dev
server:
port: 10000
eureka:
instance:
hostname: dev
instance-id: dev
client:
fetch-registry: false
register-with-eureka: false
# 需要在此处配置三个EurekaServer的地址
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:10000/eureka/,http://localhost:10001/eureka/,http://localhost:10002/eureka/
server:
wait-time-in-ms-when-sync-empty: 0
enable-self-preservation: true
peer-eureka-nodes-update-interval-ms: 10000
logging:
level:
org:
springframework:
cloud: debug
com:
netflix: debug
---
spring:
profiles: dev1
application:
name: eureka-peer2
server:
port: 10001
eureka:
instance:
hostname: dev1
instance-id: dev1
client:
fetch-registry: false
register-with-eureka: false
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:10000/eureka/,http://localhost:10001/eureka/,http://localhost:10002/eureka/
server:
wait-time-in-ms-when-sync-empty: 0
enable-self-preservation: true
peer-eureka-nodes-update-interval-ms: 10000
---
spring:
profiles: dev2
application:
name: eureka-peer3
server:
port: 10002
eureka:
instance:
hostname: dev2
instance-id: dev2
client:
fetch-registry: false
register-with-eureka: false
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:10000/eureka/,http://localhost:10001/eureka/,http://localhost:10002/eureka/
server:
wait-time-in-ms-when-sync-empty: 0
enable-self-preservation: true
peer-eureka-nodes-update-interval-ms: 10000
---
—为分隔符
在EurekaClient中不做修改还是只填写一个地址
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://127.0.0.1:10000/eureka/
启动Server
server 10000
server 10001
server 10002
启动EurekaClient服务,看EurekaClient服务是否在三个EurekaServer上都注册成功
server 10000
server 10001
server 10002

可以看到,即使只配置其中一个EurekaServer的地址,其他的节点也会同步到注册信息。
如果EurekaClient配置的EurekaServer地址的服务宕机还是会出现注册服务失败的情况,我们可以像EurekaServer一样配置EurekaClient的地址
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://127.0.0.1:10000/eureka/,http://127.0.0.1:10001/eureka/,http://127.0.0.1:10002/eureka/
如果第一个EurekaServer的服务地址失效,会向其他的服务地址发送注册请求。
高可用原理源码
查看EurekaServerAutoConfiguration,了解是如何维护多服务节点信息的
// 看在初始化的时候,都加载了哪些上下文,应该把我们在配置文件中配置的多个EurekaServer的地址加载进去
@Bean
public EurekaServerContext eurekaServerContext(ServerCodecs serverCodecs,
PeerAwareInstanceRegistry registry, PeerEurekaNodes peerEurekaNodes) {
return new DefaultEurekaServerContext(this.eurekaServerConfig, serverCodecs,
registry, peerEurekaNodes, this.applicationInfoManager);
}
查看DefaultEurekaServerContext
@Singleton
public class DefaultEurekaServerContext implements EurekaServerContext {
...
@PostConstruct
@Override
public void initialize() {
logger.info("Initializing ...");
// EurekaServer服务节点启动
peerEurekaNodes.start();
try {
registry.init(peerEurekaNodes);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
logger.info("Initialized");
}
...
}
查看peerEurekaNodes.start方法
public void start() {
// 循环运行
taskExecutor = Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor(
new ThreadFactory() {
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
Thread thread = new Thread(r, "Eureka-PeerNodesUpdater");
thread.setDaemon(true);
return thread;
}
}
);
// 更新当前存活的节点
updatePeerEurekaNodes(resolvePeerUrls());
Runnable peersUpdateTask = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
// 更新当前存活的节点
updatePeerEurekaNodes(resolvePeerUrls());
} catch (Throwable e) {
logger.error("Cannot update the replica Nodes", e);
}
}
};
// 添加更新任务
taskExecutor.scheduleWithFixedDelay(
peersUpdateTask,
serverConfig.getPeerEurekaNodesUpdateIntervalMs(),
serverConfig.getPeerEurekaNodesUpdateIntervalMs(),
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS
);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new IllegalStateException(e);
}
for (PeerEurekaNode node : peerEurekaNodes) {
logger.info("Replica node URL: {}", node.getServiceUrl());
}
}
可以看到是通过定时任务更新当前可用服务列表的信息
查看resolvePeerUrls方法
protected List<String> resolvePeerUrls() {
InstanceInfo myInfo = applicationInfoManager.getInfo();
String zone = InstanceInfo.getZone(clientConfig.getAvailabilityZones(clientConfig.getRegion()), myInfo);
// 从配置文件获取配置的服务列表信息
List<String> replicaUrls = EndpointUtils
.getDiscoveryServiceUrls(clientConfig, zone, new EndpointUtils.InstanceInfoBasedUrlRandomizer(myInfo));
// 移除自己的信息
int idx = 0;
while (idx < replicaUrls.size()) {
if (isThisMyUrl(replicaUrls.get(idx))) {
replicaUrls.remove(idx);
} else {
idx++;
}
}
return replicaUrls;
}
resolvePeerUrls方法就是用来获取其他可用节点地址的
再查看updatePeerEurekaNodes方法,此方法就是给定新的副本URL集,销毁不再可用的
protected void updatePeerEurekaNodes(List<String> newPeerUrls) {
if (newPeerUrls.isEmpty()) {
logger.warn("The replica size seems to be empty. Check the route 53 DNS Registry");
return;
}
Set<String> toShutdown = new HashSet<>(peerEurekaNodeUrls);
toShutdown.removeAll(newPeerUrls);
Set<String> toAdd = new HashSet<>(newPeerUrls);
toAdd.removeAll(peerEurekaNodeUrls);
if (toShutdown.isEmpty() && toAdd.isEmpty()) { // No change
return;
}
// Remove peers no long available
List<PeerEurekaNode> newNodeList = new ArrayList<>(peerEurekaNodes);
if (!toShutdown.isEmpty()) {
logger.info("Removing no longer available peer nodes {}", toShutdown);
int i = 0;
while (i < newNodeList.size()) {
PeerEurekaNode eurekaNode = newNodeList.get(i);
if (toShutdown.contains(eurekaNode.getServiceUrl())) {
newNodeList.remove(i);
eurekaNode.shutDown();
} else {
i++;
}
}
}
// Add new peers
if (!toAdd.isEmpty()) {
logger.info("Adding new peer nodes {}", toAdd);
for (String peerUrl : toAdd) {
newNodeList.add(createPeerEurekaNode(peerUrl));
}
}
this.peerEurekaNodes = newNodeList;
this.peerEurekaNodeUrls = new HashSet<>(newPeerUrls);
}
注册信息同步原理解析
注册信息同步源码
根据前文的分析找到一下API,查看EurekaServer之间是如何通过对等协议进行信息同步的
| Operation | HTTP action | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Register new application instance | POST /eureka/v2/apps/appID | Input: JSON/XML payload HTTP Code: 204 on success |
public class ApplicationResource {
...
@POST
@Consumes({"application/json", "application/xml"})
public Response addInstance(InstanceInfo info,
@HeaderParam(PeerEurekaNode.HEADER_REPLICATION) String isReplication) {
...
registry.register(info, "true".equals(isReplication));
return Response.status(204).build(); // 204 to be backwards compatible
}
...
}
查看register方法
@Override
public void register(final InstanceInfo info, final boolean isReplication) {
...
super.register(info, leaseDuration, isReplication);
replicateToPeers(Action.Register, info.getAppName(), info.getId(), info, null, isReplication);
}
super.register方法前文已经分析过,查看replicateToPeers方法
private void replicateToPeers(Action action, String appName, String id,
InstanceInfo info /* optional */,
InstanceStatus newStatus /* optional */, boolean isReplication) {
Stopwatch tracer = action.getTimer().start();
try {
...
// If it is a replication already, do not replicate again as this will create a poison replication
// 如果是注册信息备份的请求就不继续执行,如果不是就继续执行
if (peerEurekaNodes == Collections.EMPTY_LIST || isReplication) {
return;
}
for (final PeerEurekaNode node : peerEurekaNodes.getPeerEurekaNodes()) {
// If the url represents this host, do not replicate to yourself.
if (peerEurekaNodes.isThisMyUrl(node.getServiceUrl())) {
continue;
}
// 备份实例到每个服务
replicateInstanceActionsToPeers(action, appName, id, info, newStatus, node);
}
} finally {
tracer.stop();
}
}
replicateInstanceActionsToPeers 调用服务的注册方法
private void replicateInstanceActionsToPeers(Action action, String appName,
String id, InstanceInfo info, InstanceStatus newStatus,
PeerEurekaNode node) {
...
switch (action) {
...
case Register:
node.register(info);
break;
...
}
}
继续跟踪register方法
public void register(final InstanceInfo info) throws Exception {
long expiryTime = System.currentTimeMillis() + getLeaseRenewalOf(info);
batchingDispatcher.process(
taskId("register", info),
// 备份任务,replicateInstanceInfo(见下方构造函数)设置为true
new InstanceReplicationTask(targetHost, Action.Register, info, null, true) {
public EurekaHttpResponse<Void> execute() {
return replicationClient.register(info);
}
},
expiryTime
);
}
查看InstanceReplicationTask
protected InstanceReplicationTask(String peerNodeName,
Action action,
InstanceInfo instanceInfo,
InstanceStatus overriddenStatus,
boolean replicateInstanceInfo) {
super(peerNodeName, action);
this.appName = instanceInfo.getAppName();
this.id = instanceInfo.getId();
this.instanceInfo = instanceInfo;
this.overriddenStatus = overriddenStatus;
this.replicateInstanceInfo = replicateInstanceInfo;
}
设置为true之后
registry.register(info, "true".equals(isReplication));
接收的值就为true,这样我们在执行replicateToPeers方法时就不会继续向其他server发送注册信息
EurekaClient注册没有发送isReplication参数,所以值为null,null通过"true".equals(isReplication)判断的结果就为false,通过在server debug可以获取这个值
心跳和服务剔除机制是什么
心跳:客户端定期发送心跳请求包到EurekaServer
一旦出现心跳长时间没有发送,那么Eureka会采用剔除机制,将服务实例改为Down状态
源码解析
查看EurekaServerInitializerConfiguration服务初始化配置类
@Override
public void start() {
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
// TODO: is this class even needed now?
eurekaServerBootstrap.contextInitialized(
EurekaServerInitializerConfiguration.this.servletContext);
log.info("Started Eureka Server");
publish(new EurekaRegistryAvailableEvent(getEurekaServerConfig()));
EurekaServerInitializerConfiguration.this.running = true;
publish(new EurekaServerStartedEvent(getEurekaServerConfig()));
}
catch (Exception ex) {
// Help!
log.error("Could not initialize Eureka servlet context", ex);
}
}
}).start();
}
查看contextInitialized方法
public void contextInitialized(ServletContext context) {
try {
initEurekaEnvironment();
// 初始化服务上下文
initEurekaServerContext();
context.setAttribute(EurekaServerContext.class.getName(), this.serverContext);
}
catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("Cannot bootstrap eureka server :", e);
throw new RuntimeException("Cannot bootstrap eureka server :", e);
}
}
查看initEurekaServerContext方法
protected void initEurekaServerContext() throws Exception {
...
this.registry.openForTraffic(this.applicationInfoManager, registryCount);
...
}
查看openForTraffic方法
@Override
public void openForTraffic(ApplicationInfoManager applicationInfoManager, int count) {
super.openForTraffic(applicationInfoManager,
count == 0 ? this.defaultOpenForTrafficCount : count);
}
查看super.openForTraffic方法
@Override
public void openForTraffic(ApplicationInfoManager applicationInfoManager, int count) {
...
// 设置实例都为UP状态
applicationInfoManager.setInstanceStatus(InstanceStatus.UP);
// post初始化
super.postInit();
}
查看updateRenewsPerMinThreshold方法
protected void updateRenewsPerMinThreshold() {
// 计算numberOfRenewsPerMinThreshold
this.numberOfRenewsPerMinThreshold = (int) (this.expectedNumberOfClientsSendingRenews
* (60.0 /
// 未配置 Defaults is 30 seconds.
serverConfig.getExpectedClientRenewalIntervalSeconds())
// 未配置 Defaults is 0.85.
* serverConfig.getRenewalPercentThreshold());
}
默认值
/** * The interval with which clients are expected to send their heartbeats. > Defaults to 30 * seconds. If clients send heartbeats with different frequency, say, > every 15 seconds, then * this parameter should be tuned accordingly, otherwise, self-preservation won't work as * expected. * * @return time in seconds indicating the expected interval */ int getExpectedClientRenewalIntervalSeconds();@Override public double getRenewalPercentThreshold() { return configInstance.getDoubleProperty( namespace + "renewalPercentThreshold", 0.85).get(); }
查看super.postInit方法
protected void postInit() {
renewsLastMin.start();
if (evictionTaskRef.get() != null) {
evictionTaskRef.get().cancel();
}
// 设置剔除任务
evictionTaskRef.set(new EvictionTask());
evictionTimer.schedule(evictionTaskRef.get(),
serverConfig.getEvictionIntervalTimerInMs(),
serverConfig.getEvictionIntervalTimerInMs());
}
根据名称,我们查看驱逐任务EvictionTask
class EvictionTask extends TimerTask {
...
@Override
public void run() {
...
evict(compensationTimeMs);
...
}
...
}
继续查看evict方法
public void evict(long additionalLeaseMs) {
// 是否开启lease expiration
if (!isLeaseExpirationEnabled()) {
logger.debug("DS: lease expiration is currently disabled.");
return;
}
// 我们首先收集所有过期的物品,以随机顺序将其逐出。对于大型驱逐集,
// 如果我们不这样做,我们可能会在自我保护开始之前就淘汰整个应用程序。通过将其随机化,
// 影响应该均匀地分布在所有应用程序中。
List<Lease<InstanceInfo>> expiredLeases = new ArrayList<>();
for (Entry<String, Map<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>>> groupEntry : registry.entrySet()) {
Map<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>> leaseMap = groupEntry.getValue();
if (leaseMap != null) {
for (Entry<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>> leaseEntry : leaseMap.entrySet()) {
Lease<InstanceInfo> lease = leaseEntry.getValue();
if (lease.isExpired(additionalLeaseMs) && lease.getHolder() != null) {
expiredLeases.add(lease);
}
}
}
}
// To compensate for GC pauses or drifting local time, we need to use current registry size as a base for
// triggering self-preservation. Without that we would wipe out full registry.
int registrySize = (int) getLocalRegistrySize();
int registrySizeThreshold = (int) (registrySize * serverConfig.getRenewalPercentThreshold());
int evictionLimit = registrySize - registrySizeThreshold;
int toEvict = Math.min(expiredLeases.size(), evictionLimit);
if (toEvict > 0) {
logger.info("Evicting {} items (expired={}, evictionLimit={})", toEvict, expiredLeases.size(), evictionLimit);
Random random = new Random(System.currentTimeMillis());
for (int i = 0; i < toEvict; i++) {
// Pick a random item (Knuth shuffle algorithm)
int next = i + random.nextInt(expiredLeases.size() - i);
Collections.swap(expiredLeases, i, next);
Lease<InstanceInfo> lease = expiredLeases.get(i);
String appName = lease.getHolder().getAppName();
String id = lease.getHolder().getId();
EXPIRED.increment();
logger.warn("DS: Registry: expired lease for {}/{}", appName, id);
// 循环删除
internalCancel(appName, id, false);
}
}
}
查看isLeaseExpirationEnabled方法
@Override
public boolean isLeaseExpirationEnabled() {
// 配置文件中配置的Eureka的自我保护机制,默认开启为true,根据逻辑关闭之后允许剔除服务
if (!isSelfPreservationModeEnabled()) {
// The self preservation mode is disabled, hence allowing the instances to expire.
return true;
}
// 或者通过下面的判断才可以剔除服务,判断就是为了保证Eureka在健康状态,不会因为网络分区而错误的剔除正确的服务
return numberOfRenewsPerMinThreshold > 0 && getNumOfRenewsInLastMin() > numberOfRenewsPerMinThreshold;
}
查看internalCancel方法
protected boolean internalCancel(String appName, String id, boolean isReplication) {
try {
read.lock();
CANCEL.increment(isReplication);
Map<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>> gMap = registry.get(appName);
Lease<InstanceInfo> leaseToCancel = null;
if (gMap != null) {
// 通过remove移除服务信息
leaseToCancel = gMap.remove(id);
}
synchronized (recentCanceledQueue) {
recentCanceledQueue.add(new Pair<Long, String>(System.currentTimeMillis(), appName + "(" + id + ")"));
}
InstanceStatus instanceStatus =
// 通过remove移除服务信息
overriddenInstanceStatusMap.remove(id);
if (instanceStatus != null) {
logger.debug("Removed instance id {} from the overridden map which has value {}", id, instanceStatus.name());
}
if (leaseToCancel == null) {
CANCEL_NOT_FOUND.increment(isReplication);
logger.warn("DS: Registry: cancel failed because Lease is not registered for: {}/{}", appName, id);
return false;
} else {
leaseToCancel.cancel();
InstanceInfo instanceInfo = leaseToCancel.getHolder();
String vip = null;
String svip = null;
if (instanceInfo != null) {
// 事件类型为DELETED
instanceInfo.setActionType(ActionType.DELETED);
recentlyChangedQueue.add(new RecentlyChangedItem(leaseToCancel));
instanceInfo.setLastUpdatedTimestamp();
vip = instanceInfo.getVIPAddress();
svip = instanceInfo.getSecureVipAddress();
}
// 在其他Server中取消这个服务
invalidateCache(appName, vip, svip);
logger.info("Cancelled instance {}/{} (replication={})", appName, id, isReplication);
return true;
}
} finally {
read.unlock();
}
}
自我保护机制
启用自我保护机制,首页输出红字警告
默认情况下,如果EurekaServer在一定时间内没有接收到某个微服务实例的心跳,EurekaServer将注销该实例(默认为90秒)。但是当网络分区故障发生时,微服务与EurekaServer之前无法正常通信,以上行为可能变得非常危险–因为微服务本身其实是健康的,此时本不应该注销这个微服务。
Eureka通过"自我保护模式"来解决这个问题–当EurekaServer节点在短时间内丢失过多客户端时(可能发生了网络分区故障),那么这个节点就会进入自我保护模式。一旦进入该模式,EurekaServer就会保护服务注册表中的信息,不再删除服务注册表中的数据(也就是不会注销任何微服务)。当网络故障恢复后,该EurekaServer节点会自动退出自我保护模式。
即上文isLeaseExpirationEnabled方法中的
numberOfRenewsPerMinThreshold > 0 && getNumOfRenewsInLastMin() > numberOfRenewsPerMinThreshold;
综上,自我保护模式是一种应对网络异常的安全保护措施。它的架构哲学是宁可同时保留所有微服务(健康的微服务和不健康的微服务都会保留),也不盲目注销任何健康的微服务。使用自我保护模式,可以让Eureka集群更加健壮、稳定。
在Eureka中可以使用eureka.server.enable-self-preservation=false,禁用自我保护模式。
最后
Eureka由于自我保护机制并不能确保注册的微服务是一定可以用的,所以SpringCloud体系中提供了Hystrix来进一步保证服务的高可用。
① 提醒这个为了测试才放宽了方法的访问限制
VisibleForTesting
②Status.NO_CONTENT.getStatusCode()等于204,对于一些提交到服务器处理的数据,只需要返回是否成功的情况下,可以考虑使用状态码204来作为返回信息,从而省掉多余的数据传输
意思等同于请求执行成功,但是没有数据,浏览器不用刷新页面.也不用导向新的页面。如何理解这段话呢。还是通过例子来说明吧,假设页面上有个form,提交的url为http-204.htm,提交form,正常情况下,页面会跳转到http-204.htm,但是如果http-204.htm的相应的状态码是204,此时页面就不会发生转跳,还是停留在当前页面。另外对于a标签,如果链接的页面响应码为204,页面也不会发生跳转。
③c.n.e.registry 为文件夹缩写c,n等为首字母
项目地址:https://gitee.com/cjx940216/springcloud/tree/master/eureka