LeetCode刷题复盘笔记:打爆二叉树(续二)(最大、最小深度,节点个数,平衡二叉树)
在此非常感谢“代码随想录”的通俗易懂的总结,昨天前天打了10个,今天继续打!
(致敬叶师傅和李小龙)
“我不害怕曾经练过一万种踢法的人,但我害怕一种踢法练过一万次的人”(by 叶师傅的徒弟Bruce Lee)
![]()
今天继续打5道,加油,冲冲冲!
具体题目
题目1:104. 二叉树的最大深度
题目描述:
给定一个二叉树,找出其最大深度。
二叉树的深度为根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例:
给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]

返回它的最大深度 3
「这道题目使用前序遍历、后序遍历以及层序遍历都可以,但只是使用单纯中序遍历不行,因为中序遍历会把某些节点的左右孩子翻转了两次,但是可以把中序遍历稍微改动一下即可!」
C++代码
方法一、递归方法(规范写法)
class Solution {
public:
int getDepth(TreeNode* Node){ //确定递归函数的参数和返回值
if(Node==NULL) return 0;//终止条件
int leftDepth=getDepth(Node->left);//单层递归的逻辑
int rightDepth=getDepth(Node->right);
return 1+max(leftDepth,rightDepth);//返回当前节点左右子树的最大深度(+1是为了包括当前节点这一层)
}
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
return getDepth(root);
}
};
方法二、递归方法(简便写法)
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if(root==NULL) return 0;
return 1+max(maxDepth(root->left),maxDepth(root->right));
}
};
方法三、迭代方法(层序遍历模板应用)
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if(root==NULL) return 0;
queue<TreeNode*> que;
que.push(root);
int Depth=0;
while(!que.empty()){
int size=que.size();
Depth++;
for(int i=0;i<size;++i){
TreeNode* cur=que.front();
que.pop();
if(cur->left) que.push(cur->left);
if(cur->right) que.push(cur->right);
}
}
return Depth;
}
};
题目2:559. N 叉树的最大深度
题目描述:
给定一个 N 叉树,找到其最大深度。
最大深度是指从根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点总数。
N 叉树输入按层序遍历序列化表示,每组子节点由空值分隔(请参见示例)。
示例 1:
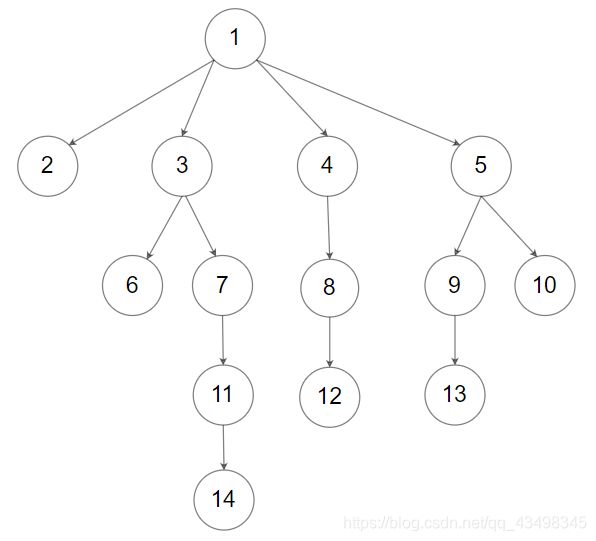
输入:root = [1,null,3,2,4,null,5,6]
输出:3
输入:root = [1,null,2,3,4,5,null,null,6,7,null,8,null,9,10,null,null,11,null,12,null,13,null,null,14]
输出:5
C++代码:
方法一、递归方法(最开始方法:空间复杂度有待优化!)
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(Node* root) {
if(root==NULL) return 0;
int size=root->children.size();
int Depth[10000];
int maxcount=0;
for(int i=0;i<size;++i){
Depth[i]=maxDepth(root->children[i]);
if(Depth[i]>maxcount) maxcount=Depth[i];
}
return 1+maxcount;
}
};
方法二、递归简便方法(方法一优化)
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(Node* root) {
if(root==NULL) return 0;
int size=root->children.size();
int maxcount=0;
for(int i=0;i<size;++i){
maxcount=max(maxcount,maxDepth(root->children[i]));
}
return 1+maxcount;
}
};
方法三、迭代方法(层序遍历)
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(Node* root) {
if(root==NULL) return 0;
queue<Node*> que;
que.push(root);
int maxcount=0;
while(!que.empty()){
int size=que.size();
maxcount++;
for(int i=0;i<size;++i){
Node* cur=que.front();
que.pop();
int levelsize=cur->children.size();
for(int j=0;j<levelsize;++j){
que.push(cur->children[j]);
}
}
}
return maxcount;
}
};
题目3:111. 二叉树的最小深度
题目描述:
给定一个二叉树,找出其最小深度。
最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。
说明:叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出:2
示例 2:
输入:root = [2,null,3,null,4,null,5,null,6]
输出:5
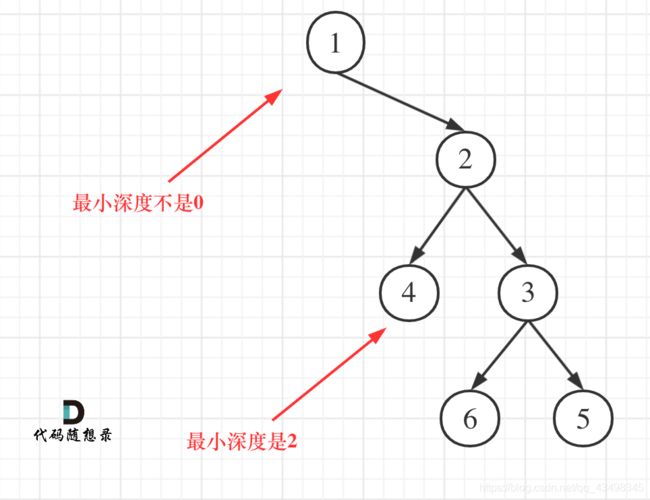
最小深度可有一个误区,如图:
这就重新审题了,题目中说的是:「最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。」,注意是「叶子节点」。
所有不能直接照搬求最大深度的思路:
而是,如果左子树为空,右子树不为空,说明最小深度是 1 + 右子树的深度。
反之,右子树为空,左子树不为空,最小深度是 1 + 左子树的深度。最后如果左右子树都不为空,返回左右子树深度最小值 + 1 。
C++代码:
方法一、递归方法
class Solution {
public:
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if(root==NULL) return 0;
if(!root->left && root->right) return minDepth(root->right)+1;
if(!root->right && root->left) return minDepth(root->left)+1;
return min(minDepth(root->left),minDepth(root->right))+1;
}
};
方法二、迭代方法(层序遍历)
class Solution {
public:
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if(root==NULL) return 0;
queue<TreeNode*> que;
que.push(root);
int flag=0;
int Depth=0;
while(!que.empty()){
int size=que.size();
Depth++;
for(int i=0;i<size;++i){
TreeNode* cur=que.front();
que.pop();
if(cur->left) que.push(cur->left);
if(cur->right) que.push(cur->right);
if(!cur->left && !cur->right) {
flag=1;break;
}
}
if(flag) break;
}
return Depth;
}
};
题目4:222. 完全二叉树的节点个数
题目描述:
给你一棵 完全二叉树 的根节点 root ,求出该树的节点个数。
完全二叉树 的定义如下:在完全二叉树中,除了最底层节点可能没填满外,其余每层节点数都达到最大值,并且最下面一层的节点都集中在该层最左边的若干位置。若最底层为第 h 层,则该层包含 1~ 2^h 个节点。
示例 1:
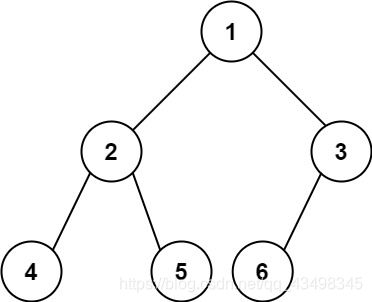
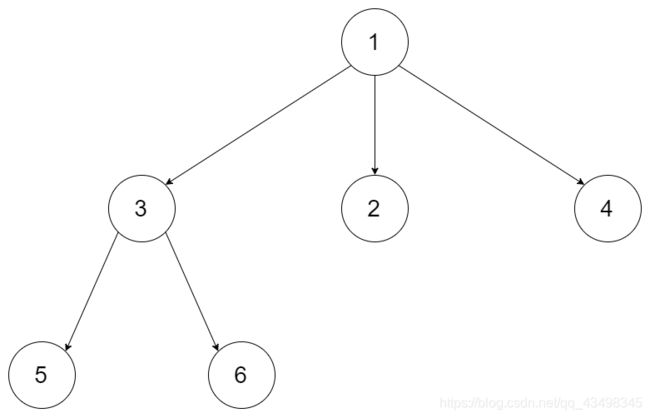
输入:root = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
输出:6
示例 2:
输入:root = []
输出:0
示例 3:
输入:root = [1]
输出:1
C++代码:
方法一、递归方法
class Solution {
public:
int countNodes(TreeNode* root) {
if(root==NULL) return 0;
return 1+countNodes(root->left)+countNodes(root->right);
}
};
方法二、迭代之层序遍历
class Solution {
public:
int countNodes(TreeNode* root) {
if(root==NULL) return 0;
queue<TreeNode*> que;
que.push(root);
int result=0;
while(!que.empty()){
int size=que.size();
result+=size;
for(int i=0;i<size;++i){
TreeNode* cur=que.front();
que.pop();
if(cur->left) que.push(cur->left);
if(cur->right) que.push(cur->right);
}
}
return result;
}
};
题目5:110. 平衡二叉树
题目描述:
给定一个二叉树,判断它是否是高度平衡的二叉树
本题中,一棵高度平衡二叉树定义为:
一个二叉树每个节点 的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过 1
示例 1:
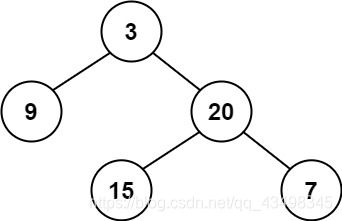
输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出:true
输入:root = [1,2,2,3,3,null,null,4,4]
输出:false
示例 3:
输入:root = []
输出:true
C++代码:
递归方法
class Solution {
public:
int getDepth(TreeNode* Node){
if(Node==NULL) return 0;
if(getDepth(Node->left)==-1) return -1;
if(getDepth(Node->right)==-1) return -1;
return abs(getDepth(Node->left)-getDepth(Node->right))>1?-1:max(getDepth(Node->left),getDepth(Node->right))+1;
}
bool isBalanced(TreeNode* root) {
if(getDepth(root)==-1) return false;
else return true;
}
};
总结
二叉树
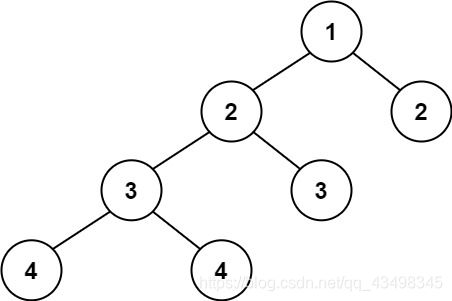
二叉树节点的深度:指从根节点到该节点的最长简单路径边的条数。
二叉树节点的高度:指从该节点到叶子节点的最长简单路径边的条数。
但leetcode中强调的深度和高度很明显是按照节点来计算的,如图:
关于根节点的深度究竟是1 还是 0,不同的地方有不一样的标准,leetcode的题目中都是以节点为一度,即根节点深度是1。
欢迎大家扫码关注本人公众号:编程复盘与思考随笔
(关注后可以免费获得本人在csdn发布的资源源码)