c#winform线程间操作UI的五种方法
经常因为需要在线程间操作UI而头疼,总结了一下,记录出来,以后方便查阅。
以下代码,展示在一个窗体内,线程接到消息后(当前时间字符串),使窗体的UI发生改变。分别使用五种不同的方法。
方法一:
通过设置窗体属性,取消线程间的安全检查。(最简单,最省事,也是最不负责任的一种)。
代码:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace winform线程间操作UI的五种方法
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
Control.CheckForIllegalCrossThreadCalls = false;//取消线程间的安全检查
}
public bool bTest = false; //测试执行一次线程里面的函数
public string sTip;
Thread thrRecv;
private void Form1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
thrRecv = new Thread(ReceiveMessage);
thrRecv.IsBackground = true;
thrRecv.Start();
}
public void ReceiveMessage()
{
while (true)
{
if (bTest)
{
sTip = System.DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyy-mm-dd HH:mm:ss");
textBox1.Text = sTip;
}
}
}
private void checkBox1_CheckedChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
bTest = checkBox1.Checked ? true : false;
}
private void Form1_FormClosing(object sender, FormClosingEventArgs e)
{
thrRecv.Abort();
}
}
}
运行效果:

分析:
这种方法,可能会导致不安全,不推荐使用。
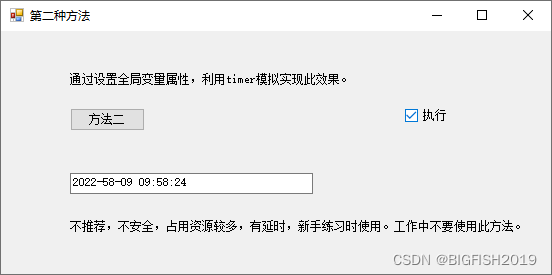
方法二:
通过设置全局变量属性,利用timer模拟实现此效果。
代码:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace winform线程间操作UI的五种方法
{
public partial class Form2 : Form
{
public Form2()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
}
public bool bTest = false; //测试执行一次线程里面的函数
public string sTip;
private void Form2_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Thread thrRecv = new Thread(ReceiveMessage);
thrRecv.IsBackground = true;
thrRecv.Start();
timer1.Start();
}
private void checkBox1_CheckedChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
bTest = checkBox1.Checked ? true : false;
}
public void ReceiveMessage()
{
while (true)
{
if (bTest)
{
sTip = System.DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyy-mm-dd HH:mm:ss");
}
}
}
private void timer1_Tick(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
textBox1.Text = sTip;
}
}
}
此方法的原理是,当接收线程接收到消息后,将消息赋值到一个全局变量上,同时timer一直在运行textBox1.Text = sTip;
运行效果:
分析:
这种方法,不推荐使用,占用资源过多,并且根据timer时间设置的不同会有不同的延时。
方法三:
通过winform自带的backgroundworker取代thread进行异步操作。
代码:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace winform线程间操作UI的五种方法
{
public partial class Form3 : Form
{
public Form3()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
public bool bTest = false; //测试执行一次线程里面的函数
public string sTip; //UI显示的内容
public int iCount = 0;
private void Form3_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
backgroundWorker2.WorkerReportsProgress = true;
backgroundWorker2.RunWorkerAsync();
}
private void checkBox1_CheckedChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
bTest = checkBox1.Checked ? true : false;
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
//backgroundWorker1.RunWorkerAsync();
MessageBox.Show("测试界面卡顿");
}
private void backgroundWorker2_DoWork(object sender, DoWorkEventArgs e)
{
while(true)
{
if (bTest)
{
iCount++;
sTip = System.DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyy-mm-dd HH:mm:ss");
backgroundWorker2.ReportProgress(50, sTip);
Thread.Sleep(1); //需要休眠,要不然界面卡顿
}
}
}
private void backgroundWorker2_ProgressChanged(object sender, ProgressChangedEventArgs e)
{
textBox1.Text = e.UserState.ToString();
}
private void Form3_Shown(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
//backgroundWorker2.RunWorkerAsync();
}
}
}
上面代码的原理就是,把对UI的操作放到了backgroundworker2_progresschanged方法中进行,winform自带的backgroundworker不会受到影响,可以对UI进行操作。
运行效果:

分析:
这种方法,不推荐使用,虽然并没有什么不好的。但是就是感觉特别挫,因为只局限于winform,到了其它的地方,还不是得用thread来实现,使用这种方法解决问题,治标不治本。
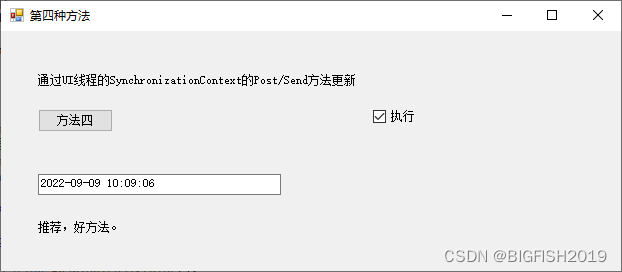
方法四:
通过UI线程的SynchronizationContext的Post/Send方法更新。
代码:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace winform线程间操作UI的五种方法
{
public partial class Form4 : Form
{
SynchronizationContext SyncContext = null;
public bool bTest = false; //测试执行一次线程里面的函数
public string sTip;
public Form4()
{
InitializeComponent();
SyncContext = SynchronizationContext.Current;
}
private void Form4_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Thread thrRecv = new Thread(ReceiveMessage);
thrRecv.IsBackground = true;
thrRecv.Start();
}
public void ReceiveMessage()
{
while (true)
{
if (bTest)
{
sTip = System.DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyy-mm-dd HH:mm:ss");
SyncContext.Post(change, sTip);
Thread.Sleep(1);
}
}
}
private void change(object str)
{
textBox1.Text = str.ToString();
}
private void checkBox1_CheckedChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
bTest = checkBox1.Checked ? true : false;
}
}
}
原理是,在线程执行过程中,需要更新到UI控件上的数据不再直接更新,而是通过UI线程上下文的Post/Send方法,将数据以异步/同步消息的形式发送到UI线程的消息队列;UI线程收到该消息后,根据消息是异步消息还是同步消息来决定通过异步/同步的方式调用SetTextSafePost方法直接更新自己的控件了。
在本质上,向UI线程发送的消息并不是简单数据,而是一条委托调用命令。效果图如下
分析:
这种方法,推荐使用,是不错的解决问题的好方法。
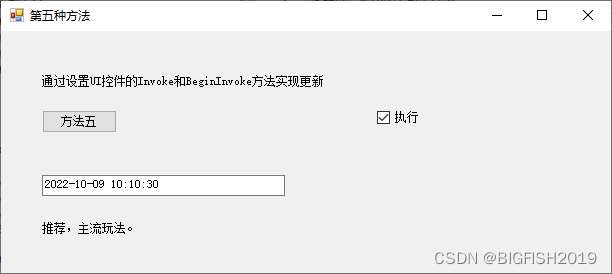
方法五:
通过设置UI控件的Invoke和BeginInvoke方法实现更新。
代码如下:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace winform线程间操作UI的五种方法
{
public partial class Form5 : Form
{
delegate void Change(string text);
public bool bTest = false; //测试执行一次线程里面的函数
public string sTip;
public Form5()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void Form5_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Thread thrRecv = new Thread(ReceiveMessage);
thrRecv.IsBackground = true;
thrRecv.Start();
}
private void Settext(string text)
{
textBox1.Text = text;
}
private void ReceiveMessage()
{
while (true)
{
if (bTest)
{
sTip = System.DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyy-mm-dd HH:mm:ss");
this.BeginInvoke(new Change(Settext), sTip);
Thread.Sleep(1);
}
}
}
private void checkBox1_CheckedChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
bTest = checkBox1.Checked ? true : false;
}
}
}
这个方法是目前跨线程更新UI使用的主流方法,使用控件的Invoke/BegainInvoke方法,将委托转到UI线程上调用,实现线程安全的更新。
总结
总结,多线程间会经常使用到委托,对委托的理解十分关键。
参考
https://www.cnblogs.com/weifeng123/p/13734999.html