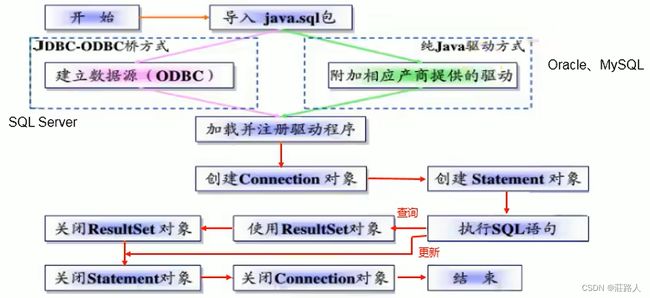
【JDBC】连接MySQL数据库实现增删改查
文章目录
- 一、JDBC编写步骤
- 二、数据库连接——Connection
-
- 2.1 连接要素
-
- 2.1.1 Driver接口实现类
- 2.1.2 URL
- 2.1.3 用户名和密码
- 2.2 建立连接
-
- 2.2.1 改进
- 三、数据库操作——Statement
-
- 3.1 Statement简介
- 3.2 使用Statement进行数据更新
-
- 3.2.1 简单更新
- 3.2.2 通用更新操作的实现
- 3.3 ResultSet获取查询结果
-
- 3.3.1 简单查询
- 3.3.2 通用查询操作的实现
一、JDBC编写步骤
ODBC(Open Database Connectivity,开放式数据库连接),是微软在Windows平台下推出的。使用者在程序中只需要调用ODBC,由ODBC驱动程序将调用转换成对特定数据库的调用请求
二、数据库连接——Connection
2.1 连接要素
2.1.1 Driver接口实现类
在pom.xml中maven导入依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>mysqlgroupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-javaartifactId>
<version>8.0.12version>
dependency>
MySQL5↓:用com.mysql.jdbc.Driver的Driver实现类
MySQL5↑:用com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver的Driver实现类
2.1.2 URL
驱动程序管理器通过URL选择正确的驱动程序以建立数据库连接
通常为:协议:子协议:子名称【例:jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/database1】
- 协议:JDBC的URL就是jdbc
- 子协议:用于标识数据库驱动程序
- 子名称:用于标识数据库的方法。用于定位数据库,其中包含主机名(服务端的ip地址),端口号,数据库名
MySQL8.0连接时需要指定时区以及是否进行SSL连接,例:jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/zlr?serverTimezone=GMT&useSSL=false
2.1.3 用户名和密码
数据库的用户名和密码,可以封装在Properties中
2.2 建立连接
// 加载Driver
Driver driver = new com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver();
// 基本信息:URL
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/zlr?serverTimezone=GMT";
// 基本信息:用户名,密码
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.setProperty("user","root");
properties.setProperty("password","password");
// 获取连接
Connection connection = driver.connect(url,properties);
2.2.1 改进
- 不指定具体使用的数据库Driver,修改Driver的时候不用修改源码,用反射读取配置文件来生成对应的Driver
Class driverClass = Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
Driver driver = (Driver) driverClass.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance();
- 通过注册驱动的方式,用DriverManager包装Driver并获取连接
// 注册Driver
DriverManager.registerDriver(driver);
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/zlr?serverTimezone=GMT";
String user = "root";
String password = "password";
// 获取连接
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,password);
-
只加载驱动,不需显式地注册驱动
原因:com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver源码中的静态代码块已经执行了注册驱动的操作
// 加载Driver
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
// 基本信息
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/zlr?serverTimezone=GMT";
String user = "root";
String password = "password";
// 获取连接
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,password);
- 将配置信息写入配置文件中通过读取获得
// 读取配置文件
InputStream is = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties");
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(is);
String url = properties.getProperty("url");
String user = properties.getProperty("user");
String password = properties.getProperty("password");
String driverClassStr = properties.getProperty("driverClass");
// 加载驱动
Class driverClass = Class.forName(driverClassStr);
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,password);
三、数据库操作——Statement
3.1 Statement简介
在java.sql包下有三个接口定义了对数据库调用的不同方式:
- Statement:用于执行静态SQL语句并返回它所生成结果的对象
弊端:需要拼写sql语句,存在SQL注入的问题
例:String sql = “SELECT user,password FROM user_table WHERE USER = ‘’”+user+“’ AND password = '”+password+“‘;’”
在输入user和password后,拼接过程中可以注入SQL语句截断某些判断条件达成恒等式完成登录
为避免上述问题可以使用PreparedStatement取代Statement进行使用
-
PreparedStatement:SQL语句被预编译并存储在此对象中,可使用此对象多次高效地执行该语句
- 能操作Blob数据,Statement做不到
- 可实现更高效的批量操作
-
CallableStatement:执行SQL存储
3.2 使用Statement进行数据更新
3.2.1 简单更新
// 待执行的sql语句 ?:占位符
String sql = "insert into users(name,password)values(?,?)";
// 使用前面获得的Connection对象,预编译sql语句,返回PreparedStatement的实例
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
// 填充占位符 【索引从1开始】
preparedStatement.setString(1,"User1Name");
preparedStatement.setString(2,"User1Password");
// 执行操作
preparedStatement.execute();
// 关闭资源
preparedStatement.close();
connection.close();
3.2.2 通用更新操作的实现
若想使用多种不同的更新语句更新数据:
delete from users where id = ?
update users set name = ? , password = ? where id =
insert into users (name,password) values( ? , ? )
可以使用如下方法实现通用的查询操作:
public void update(String sql,Object ... args) {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
try {
// 获取Connection【省略】
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
// 根据输入参数的多少填充占位符
preparedStatement.setObject(i+1,args[i]);
}
preparedStatement.execute();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
// 执行资源关闭操作【省略】
}
}
3.3 ResultSet获取查询结果
3.3.1 简单查询
创建的数据库的数据有三个属性,分别是id(int),name(varchar(127)),password(varchar(255))
新建一个User类将数据封装成对象,含有id,name,password三个属性,根据返回的ResultSet将其填充
// ?:占位符
String sql = "select * from users where name = ? ";
// 预编译sql语句,返回PreparedStatement的实例
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
// 填充占位符【注意索引从1开始】
preparedStatement.setString(1,"zlr");
// 执行并返回结果集
ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
// 处理结果集
// next():若下一条有数据则返回true,指针下移;若下一条无数据则返回false
if(resultSet.next()){
int userId = resultSet.getInt(1);
String userName = resultSet.getString(2);
String userPassword = resultSet.getString(3);
//封装成对象
User u = new User(userId,userName,userPassword);
System.out.println(u);
}
// 关闭资源
preparedStatement.close();
connection.close();
resultSet.close();
3.3.2 通用查询操作的实现
若想使用多种不同的查询语句查询数据:
select id,name from users where name = ?
select name from users where id = ?
select id from users where name = ? and password = ?
可以使用如下方法实现通用的查询操作:
User类对应的属性必须与数据库中表的属性名相同
若要查询多行可以考虑使用while+集合的方式
public User queryForUsers(String sql,Object ... args){
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
// 获取Connection【省略】
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
// 根据输入参数的多少填充占位符
preparedStatement.setObject(i+1,args[i]);
}
resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
// 获取ResultSet的元数据
ResultSetMetaData rsmd = resultSet.getMetaData();
// 获取ResultSet的列数
int columCount = rsmd.getColumnCount();
if(resultSet.next()){
// 先用空参构造器生成User对象,之后将获取到的属性使用set方法填充
User u = new User();
// 处理结果集一行数据的每个列
for (int i = 0; i < columCount; i++) {
// 获取当前列的值
Object columnValue = resultSet.getObject(i+1);
// 获取当前列的列名
String columnName = rsmd.getColumnName(i+1);
// 通过反射,给User对象指定的columnName属性赋值为columnValue
Field field = User.class.getDeclaredField(columnName);
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(u,columnValue);
}
return u;
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
// 执行资源关闭操作【省略】
}
return null;
}
上述方法中使用getColumnName()的方式获取列名,再使用反射来设置属性,存在局限性
当表的字段名与类的属性名不一致时:
1.声明sql时,使用类的属性名来命名字段的别名
例如:表的字段名:user_id,user_name,user_password 类的属性名:id,name,password
则应使用:select user_name name, user_password password from users where user_id = 1 ;
2.使用getColumnLable()方法代替getColumnName()
作用:获取当前列的别名:若无别名则获得当前列的列名