Linux shell编程学习笔记13:文件测试运算
Linux Shell 脚本编程和其他编程语言一样,支持算数、关系、布尔、逻辑、字符串、文件测试等多种运算。前面几节我们依次研究了 Linux shell编程 中的 字符串运算、算术运算、关系运算、布尔运算 和 逻辑运算,今天我们来研究 Linux shell编程中的文件测试运算。
一、文件测试运算符说明
| 操作符 | 说明 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| -b file | 检测文件是否是块设备文件,如果是,则返回 true。 | block |
| -c file | 检测文件是否是字符设备文件,如果是,则返回 true。 | char |
| -d file | 检测文件是否是目录,如果是目录,则返回 true。 | directory |
| -f file | 检测文件是否是普通文件(既不是目录,也不是设备文件),如果是,则返回 true。 | file |
| -g file | 检测文件是否设置了 SGID 位,如果是,则返回 true。 | set Group ID |
| -k file | 检测文件是否设置了粘着位(Sticky Bit),如果是,则返回 true。 | |
| -p file | 检测文件是否是有名管道,如果是,则返回 true。 | name pipe |
| -u file | 检测文件是否设置了 SUID 位,如果是,则返回 true。 | Set User ID |
| -r file | 检测文件是否可读,如果是,则返回 true。 | readonly |
| -w file | 检测文件是否可写,如果是,则返回 true。 | writeable |
| -x file | 检测文件是否可执行,如果是,则返回 true。 | excecutable |
| -s file | 检测文件是否不为空(文件大小是否大于0),不为空返回 true。 | space |
| -e file | 检测文件(包括目录)是否存在,如果是,则返回 true。 | exist |
| -S file | 检测文件是否 socket | socket |
| -L file | 检测文件是否存在并且是一个符号链接 | link |
二、文件测试运算实例
为了进行文件测试实例演示,我们使用文件 /init 和 根目录 / 来作为操作对象。
我们先用ls -l 命令查看文件 /init 的详细属性:
user @ host: / $ ls -l init
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 492 Apr 12 2023 init
user @ host : / $
ls -l 命令返回信息中的第一列共有10个字符,可以分个部分:
第一个部分是文件类型,由第1个字符表示,它可能是下列值之一:
- :表示普通文件
d :表示目录
l :表示符号链接
c :表示字符设备文件
b :表示块设备文件
s :表示套接字文件
p :表示管道文件
第二部分表示访问权限,包括第2-第10个字符,以3个字符为一组,共分为3组,第一组由前三个字符组成,表示所有者的权限,第二组由中间三个字符组成,表示所属组的权限,第三组由最后三个字符,表示其他用户的权限。每个字符的含义如下:
r :表示读取权限
w :表示写入权限
x :表示执行权限
- :表示没有对应权限
由命令返回结果可以看出,\init 是一个文件,文件所有者具有读取(r)写入(w)执行(x)权限,所属组和其他用户具有读取(r)和执行(x)权限。
我们再用ls -ld 命令查看 / 的详细属性:
user @ host : / $ ls -ld /
drwxr-xr-x 17 root root 380 Apr 12 2023 //
由命令返回结果可以看出,\ 是一个目录,目录所有者具有读取(r)写入(w)执行(x)权限,所属组和其他用户具有读取(r)和执行(x)权限。
(一)检测文件是否是块设备文件
user @ host : / $ f="/init"
user @ host : / $ if[-b $f ]; then echo "$f is a block file"; else echo "$f is not a block file"; fi
/init is not a block file
user @ host : / $
可见 /init 不是块设备文件
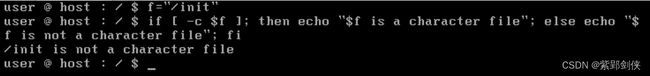
(二)检测文件是否是字符设备文件
user @ host : / $ f="/init"
user @ host : / $ if [-c $f]; then echo "$f is a character file"; else echo "$f is not a character filel"; fi
/init is not a character file
user @ host : / $
可见 \init 不是字符设备文件。
(三)检测文件是否是目录
user @ host : / $ f="/init"
user @ host : / $ if [-d $f ]; then echo"$f is a directory"; else echo "$f is not a directory"; fi
/init is not a directory
user @ host : / $
user @ host : / $ f="//"
user @ host : / $ if [ -d $f ];then echo "$f is a directory"; else echo "$f is not a directory";fi
// is a directory
user @ host : / $ f="/"
user @ host : / $ if [ -d $f ]; then echo "$f is a directory"; else echo "$f is not a directory"; fi
/ is a directory
user @ host : / $
可见,/ 是一个目录,而不是文件。
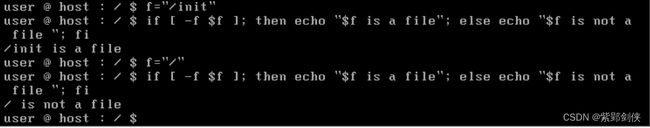
(四)检测文件是否是普通文件
user @ host : / $ f="/init"
user @ host : / $ if [-f $f ]; then echo"$f is a file"; else echo "$f is not a file"; fi
/init is a file
user @ host : / $ f="/"
user @ host : / $ if [ -d $f ]; then echo "$f is a file"; else echo "$f is not a file"; fi
/ is not a fle
user @ host : / $
可见,/init是一个文件,/ 不是一个文件。
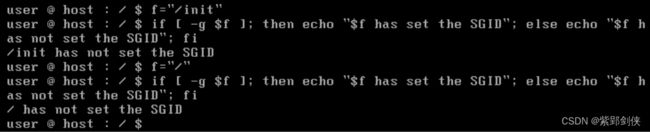
(五)检测文件是否设置了 SGID 位
user @ host : / $ f="/init"
user @ host : / $ if [ -g $f ];then echo "$f has set the SGID"; else echo "$f has not set the SGID "; fi
/init has not set the SGID
user @ host : / $ f="/"
user @ host : / $ if [ -g $f ];then echo "$f has set the SGID"; else echo "$f has not set the SGID "; fi
/ has not set the SGID
user @ host : / $
可见 /init 和 / 都没有设置SGID。
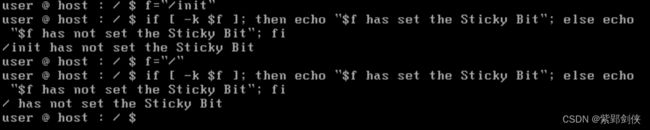
(六)检测文件是否设置了粘着位(Sticky Bit)
user @ host : / $ f="/init"
user @ host : / $ if [ -k $f ];then echo "$f has set the Sticky Bit"; else echo "$f has not set the Sticky Bit"; fi
/init has not set the Sticky Bit
user @ host : / $ f="/"
user @ host : / $ if [ -k $f ];then echo "$f has set the Sticky Bit"; else echo "$f has not set the Sticky Bit"; fi
/ has not set the Sticky Bit
user @ host : / $
可见 /init 和 / 都没有设置粘着位(Sticky Bit)
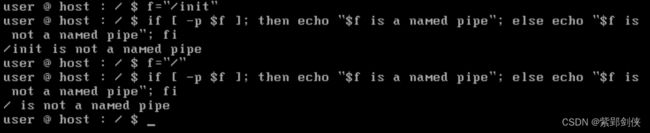
(七)检测文件是否是有名管道
user @ host : / $ f="/init"
user @ host : / $ if [ -p $f ];then echo "$f is a named pipe "; else echo "$f is not a named pipe"; fi
/init is not a named pipe
user @ host : / $ f="/"
user @ host : / $ if [ -p $f ];then echo "$f is a named pipe "; else echo "$f is not a named pipe"; fi
/ is not a named pipe
user @ host : / $
可见 /init 和 / 都不是有名管道。
(八)检测文件是否设置了 SUID 位
user @ host : / $ f="/init"
user @ host : / $ if [ -u $f ];then echo "$f has set the SUID"; else echo "$f has not set the SUID"; fi
/init has not set the SUID
user @ host : / $ f="/"
user @ host : / $ if [ -u $f ];then echo "$f has set the SUID"; else echo "$f has not set the SUID"; fi
/ is has not set the SUID
user @ host : / $
可见 /init 和 / 都没有设置 SUID 位
(九)检测文件是否可读
user @ host : / $ f="/init"
user @ host : / $ if [ -r $f ]; then echo "$f is readable"; else echo "$f is not readable"; fi
/init is readable
user@host:/ $
可见 /init是可以读取的。
(十)检测文件是否可写
user @ host : / $ f="/ init"
user @ host : / $ if [ -w $f ];then echo "$f is writable"; else echo "$f is not writable"; fi
/init is not writable
user @ host : / $ f="/"
user @ host : / $ if [ -w $f ];then echo "$f is writable"; else echo "$f is not writable"; fi
/ is not writable
user @ host : / $
可见 /init 和 / 都不可写入。
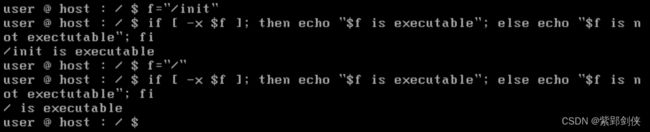
(十一)检测文件是否可执行
user @ host : / $ f="/init"
user @ host : / $ if [ -x $f ];then echo "$f is executable"; else echo "$f is not executable"; fi
/init is executable
user @ host : / $ f="/"
user @ host : / $ if [ -x $f ];then echo "$f is executable"; else echo "$f is not executable"; fi
/ is executable
user @ host : / $
可见 /init 和 / 都可以执行。
(十二)检测文件是否不为空(文件大小是否大于0)
user @ host : / $ f="/init"
user @ host : / $ if [ -s $f ];then echo "$f is not space"; else echo "$f is space"; fi
/init is not space
可见 /init 不为空。
我们可以用cat命令查看 /init的内容:
(十三)检测文件(包括目录)是否存在
user @ host : / $ f="/init"
user @ host : / $ if [ -e $f ];then echo "$f exists"; else echo "$f does not exist"; fi
/init exists
user @ host : / $ f="/"
user @ host : / $ if [ -e $f ];then echo "$f exists"; else echo "$f does not exist"; fi
/ exists
user @ host : / $ if [ -e null ];then echo "$f exists"; else echo "$f does not exist"; fi
/ exists
user @ host : / $ if [ -e nil ];then echo "$f exists"; else echo "$f does not exist"; fi
/ exists
user @ host : / $ if [ -e /dev/null ];then echo "$f exists"; else echo "$f does not exist"; fi
/ exists
user @ host : / $ f="/dev/null"
user @ host : / $ if [ -e $f ];then echo "$f exists"; else echo "$f does not exist"; fi
/dev/null exists

可见 /init 和 / 以及 /dev/null 都存在。
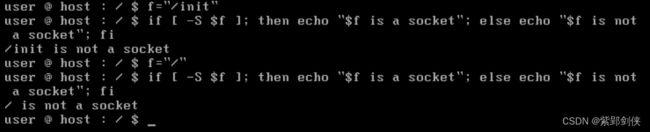
(十四)检测文件是否 socket
user @ host : / $ f="/init"
user @ host : / $ if [ -S $f ];then echo "$f is a socket"; else echo "$f is not a socket"; fi
/init is not a socket
user @ host : / $ f="/"
user @ host : / $ if [ -S $f ];then echo "$f is a socket"; else echo "$f is not a socket"; fi
/ is not a socket
(十五)检测文件是否存在并且是一个符号链接
user @ host : / $ f="/init"
user @ host : / $ if [ -L $f ];then echo "$f is a link"; else echo "$f is not a link"; fi
/init is not a link
user @ host : / $ f="/"
user @ host : / $ if [ -L $f ];then echo "$f is a link"; else echo "$f is not a link"; fi
/ is not a link