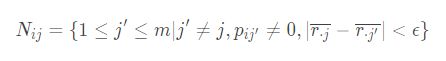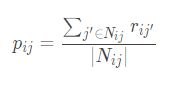51-60天
第 51 天: kNN 分类器
- 两种距离度量.
- 数据随机分割方式.
- 间址的灵活使用: trainingSet 和 testingSet 都是整数数组, 表示下标.
- arff 文件的读取. 需要 weka.jar 包.
- 求邻居.
- 投票.
代码如下:
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Random;
import weka.core.*;
public class KnnClassification {
public static final int MANHATTAN = 0;
public static final int EUCLIDEAN = 1;
public int distanceMeasure = EUCLIDEAN;
public static final Random random = new Random();
int numNeighbors = 7;
Instances dataset;
int[] trainingSet;
int[] testingSet;
int[] predictions;
public KnnClassification(String paraFilename) {
try {
FileReader fileReader = new FileReader(paraFilename);
dataset = new Instances(fileReader);
// The last attribute is the decision class.
dataset.setClassIndex(dataset.numAttributes() - 1);
fileReader.close();
} catch (Exception ee) {
System.out.println("Error occurred while trying to read \'" + paraFilename
+ "\' in KnnClassification constructor.\r\n" + ee);
System.exit(0);
} // Of try
}// Of the first constructor
public static int[] getRandomIndices(int paraLength) {
int[] resultIndices = new int[paraLength];
// Step 1. Initialize.
for (int i = 0; i < paraLength; i++) {
resultIndices[i] = i;
} // Of for i
// Step 2. Randomly swap.
int tempFirst, tempSecond, tempValue;
for (int i = 0; i < paraLength; i++) {
// Generate two random indices.
tempFirst = random.nextInt(paraLength);
tempSecond = random.nextInt(paraLength);
// Swap.
tempValue = resultIndices[tempFirst];
resultIndices[tempFirst] = resultIndices[tempSecond];
resultIndices[tempSecond] = tempValue;
} // Of for i
return resultIndices;
}// Of getRandomIndices
public void splitTrainingTesting(double paraTrainingFraction) {
int tempSize = dataset.numInstances();
int[] tempIndices = getRandomIndices(tempSize);
int tempTrainingSize = (int) (tempSize * paraTrainingFraction);
trainingSet = new int[tempTrainingSize];
testingSet = new int[tempSize - tempTrainingSize];
for (int i = 0; i < tempTrainingSize; i++) {
trainingSet[i] = tempIndices[i];
} // Of for i
for (int i = 0; i < tempSize - tempTrainingSize; i++) {
testingSet[i] = tempIndices[tempTrainingSize + i];
} // Of for i
}// Of splitTrainingTesting
public void predict() {
predictions = new int[testingSet.length];
for (int i = 0; i < predictions.length; i++) {
predictions[i] = predict(testingSet[i]);
} // Of for i
}// Of predict
public int predict(int paraIndex) {
int[] tempNeighbors = computeNearests(paraIndex);
int resultPrediction = simpleVoting(tempNeighbors);
return resultPrediction;
}// Of predict
public double distance(int paraI, int paraJ) {
int resultDistance = 0;
double tempDifference;
switch (distanceMeasure) {
case MANHATTAN:
for (int i = 0; i < dataset.numAttributes() - 1; i++) {
tempDifference = dataset.instance(paraI).value(i) - dataset.instance(paraJ).value(i);
if (tempDifference < 0) {
resultDistance -= tempDifference;
} else {
resultDistance += tempDifference;
} // Of if
} // Of for i
break;
case EUCLIDEAN:
for (int i = 0; i < dataset.numAttributes() - 1; i++) {
tempDifference = dataset.instance(paraI).value(i) - dataset.instance(paraJ).value(i);
resultDistance += tempDifference * tempDifference;
} // Of for i
break;
default:
System.out.println("Unsupported distance measure: " + distanceMeasure);
}// Of switch
return resultDistance;
}// Of distance
public double getAccuracy() {
// A double divides an int gets another double.
double tempCorrect = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < predictions.length; i++) {
if (predictions[i] == dataset.instance(testingSet[i]).classValue()) {
tempCorrect++;
} // Of if
} // Of for i
return tempCorrect / testingSet.length;
}// Of getAccuracy
/
public int[] computeNearests(int paraCurrent) {
int[] resultNearests = new int[numNeighbors];
boolean[] tempSelected = new boolean[trainingSet.length];
double tempDistance;
double tempMinimalDistance;
int tempMinimalIndex = 0;
// Select the nearest paraK indices.
for (int i = 0; i < numNeighbors; i++) {
tempMinimalDistance = Double.MAX_VALUE;
for (int j = 0; j < trainingSet.length; j++) {
if (tempSelected[j]) {
continue;
} // Of if
tempDistance = distance(paraCurrent, trainingSet[j]);
if (tempDistance < tempMinimalDistance) {
tempMinimalDistance = tempDistance;
tempMinimalIndex = j;
} // Of if
} // Of for j
resultNearests[i] = trainingSet[tempMinimalIndex];
tempSelected[tempMinimalIndex] = true;
} // Of for i
System.out.println("The nearest of " + paraCurrent + " are: " + Arrays.toString(resultNearests));
return resultNearests;
}// Of computeNearests
/**
************************************
* Voting using the instances.
*
* @param paraNeighbors
* The indices of the neighbors.
* @return The predicted label.
************************************
*/
public int simpleVoting(int[] paraNeighbors) {
int[] tempVotes = new int[dataset.numClasses()];
for (int i = 0; i < paraNeighbors.length; i++) {
tempVotes[(int) dataset.instance(paraNeighbors[i]).classValue()]++;
} // Of for i
int tempMaximalVotingIndex = 0;
int tempMaximalVoting = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < dataset.numClasses(); i++) {
if (tempVotes[i] > tempMaximalVoting) {
tempMaximalVoting = tempVotes[i];
tempMaximalVotingIndex = i;
} // Of if
} // Of for i
return tempMaximalVotingIndex;
}// Of simpleVoting
public static void main(String args[]) {
KnnClassification tempClassifier = new KnnClassification("D:/data/iris.arff");
tempClassifier.splitTrainingTesting(0.8);
tempClassifier.predict();
System.out.println("The accuracy of the classifier is: " + tempClassifier.getAccuracy());
}// Of main
}// Of class KnnClassification
今天停电,暂时只把代码抄完,而且缺少weka.jar 包,目前还不能运行。
第 52 天: kNN 分类器 (续)
重新实现 computeNearests, 仅需要扫描一遍训练集, 即可获得 k kk 个邻居. 提示: 现代码与插入排序思想相结合.
增加 setDistanceMeasure() 方法.
增加 setNumNeighors() 方法.
新增代码如下:
// setDistanceMeasure方法
/**
* @Description: 选择距离计算方式
* @Param: [paraType:0 or 1]
* @return: void
*/
public void setDistanceMeasure(int paraType) {
if (paraType == 0) {
distanceMeasure = MANHATTAN;
} else if (paraType == 1) {
distanceMeasure = EUCLIDEAN;
} else {
System.out.println("Wrong Distance Measure!!!");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
KnnClassification tempClassifier = new KnnClassification("F:\\研究生\\研0\\学习\\Java_Study\\data_set\\iris.arff");
tempClassifier.setDistanceMeasure(1);
tempClassifier.splitTrainingTesting(0.8);
tempClassifier.predict();
System.out.println("The accuracy of the classifier is: " + tempClassifier.getAccuracy());
}
//setNumNeighors方法
/**
* @Description: 设置邻居数量
* @Param: [paraNumNeighbors]
* @return: void
*/
public void setNumNeighbors(int paraNumNeighbors) {
if (paraNumNeighbors > dataset.numInstances()) {
System.out.println("The number of neighbors is bigger than the number of dataset!!!");
return;
}
numNeighbors = paraNumNeighbors;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
KnnClassification tempClassifier = new KnnClassification("F:\\研究生\\研0\\学习\\Java_Study\\data_set\\iris.arff");
tempClassifier.setDistanceMeasure(1);
tempClassifier.setNumNeighbors(8);
tempClassifier.splitTrainingTesting(0.8);
tempClassifier.predict();
System.out.println("The accuracy of the classifier is: " + tempClassifier.getAccuracy());
}
Day53: kNN 分类器 (续)
- 增加 weightedVoting() 方法, 距离越短话语权越大. 支持两种以上的加权方式.
- 实现 leave-one-out 测试.
代码如下:
//weightedVoting
public int weightedVoting(int paraCurrent, int[] paraNeighbors) {
double[] tempVotes = new double[dataset.numClasses()];
//计算各类型出现的次数
double tempDistance;
//a越大,b越小,效果越好
int a = 2, b = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < paraNeighbors.length; i++) {
tempDistance = distance(paraCurrent, paraNeighbors[i]);
tempVotes[(int) dataset.instance(paraNeighbors[i]).classValue()]
+= getWeightedNum(a, b, tempDistance);
}
int tempMaximalVotingIndex = 0;
double tempMaximalVoting = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < dataset.numClasses(); i++) {
if (tempVotes[i] > tempMaximalVoting) {
tempMaximalVoting = tempVotes[i];
tempMaximalVotingIndex = i;
}
}
return tempMaximalVotingIndex;
}
//getWeightedNum
public double getWeightedNum(int a, int b, double paraDistance) {
return b / (paraDistance + a);
}
public void leave_one_out() {
//留一法交叉验证
int tempSize = dataset.numInstances();
int[] tempIndices = getRandomIndices(tempSize);
double tempCorrect = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < tempSize; i++) {
trainingSet = new int[tempSize - 1];
testingSet = new int[1];
int tempIndex = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < tempSize; j++) {
if (j == i) {
continue;
}
trainingSet[tempIndex++] = tempIndices[j];
}
testingSet[0] = tempIndices[i];
this.predict();
if (predictions[0] == dataset.instance(testingSet[0]).classValue()) {
tempCorrect++;
}
}
System.out.println("The accuracy is:" + tempCorrect / tempSize);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
KnnClassification tempClassifier = new KnnClassification("D:\\data\\iris.arff");
tempClassifier.setDistanceMeasure(0);
tempClassifier.setNumNeighbors(5);
tempClassifier.splitTrainingTesting(0.8);
tempClassifier.predict();
System.out.println("The accuracy of the classifier is: " + tempClassifier.getAccuracy());
//测试
System.out.println("\r\n-------leave_one_out-------");
tempClassifier.leave_one_out();
}第 54 天: 基于 M-distance 的推荐
原理:
M-distance, 就是根据平均分来计算两个用户 (或项目) 之间的距离.
令项目j的平均分为x.j;采用 item-based recommendation,则第 j 个项目关于第 i 个用户的邻居项目集合为:
第 i 个用户对 j 个项目的评分预测为
代码如下:
package machinelearning.knn;
/**
* Recommendation with M-distance.
* @author Fan Min [email protected].
*/
import java.io.*;
public class MBR {
/**
* Default rating for 1-5 points.
*/
public static final double DEFAULT_RATING = 3.0;
/**
* The total number of users.
*/
private int numUsers;
/**
* The total number of items.
*/
private int numItems;
/**
* The total number of ratings (non-zero values)
*/
private int numRatings;
/**
* The predictions.
*/
private double[] predictions;
/**
* Compressed rating matrix. User-item-rating triples.
*/
private int[][] compressedRatingMatrix;
/**
* The degree of users (how many item he has rated).
*/
private int[] userDegrees;
/**
* The average rating of the current user.
*/
private double[] userAverageRatings;
/**
* The degree of users (how many item he has rated).
*/
private int[] itemDegrees;
/**
* The average rating of the current item.
*/
private double[] itemAverageRatings;
/**
* The first user start from 0. Let the first user has x ratings, the second
* user will start from x.
*/
private int[] userStartingIndices;
/**
* Number of non-neighbor objects.
*/
private int numNonNeighbors;
/**
* The radius (delta) for determining the neighborhood.
*/
private double radius;
/**
*************************
* Construct the rating matrix.
*
* @param paraRatingFilename
* the rating filename.
* @param paraNumUsers
* number of users
* @param paraNumItems
* number of items
* @param paraNumRatings
* number of ratings
*************************
*/
public MBR(String paraFilename, int paraNumUsers, int paraNumItems, int paraNumRatings) throws Exception {
// Step 1. Initialize these arrays
numItems = paraNumItems;
numUsers = paraNumUsers;
numRatings = paraNumRatings;
userDegrees = new int[numUsers];
userStartingIndices = new int[numUsers + 1];
userAverageRatings = new double[numUsers];
itemDegrees = new int[numItems];
compressedRatingMatrix = new int[numRatings][3];
itemAverageRatings = new double[numItems];
predictions = new double[numRatings];
System.out.println("Reading " + paraFilename);
// Step 2. Read the data file.
File tempFile = new File(paraFilename);
if (!tempFile.exists()) {
System.out.println("File " + paraFilename + " does not exists.");
System.exit(0);
} // Of if
BufferedReader tempBufReader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(tempFile));
String tempString;
String[] tempStrArray;
int tempIndex = 0;
userStartingIndices[0] = 0;
userStartingIndices[numUsers] = numRatings;
while ((tempString = tempBufReader.readLine()) != null) {
// Each line has three values
tempStrArray = tempString.split(",");
compressedRatingMatrix[tempIndex][0] = Integer.parseInt(tempStrArray[0]);
compressedRatingMatrix[tempIndex][1] = Integer.parseInt(tempStrArray[1]);
compressedRatingMatrix[tempIndex][2] = Integer.parseInt(tempStrArray[2]);
userDegrees[compressedRatingMatrix[tempIndex][0]]++;
itemDegrees[compressedRatingMatrix[tempIndex][1]]++;
if (tempIndex > 0) {
// Starting to read the data of a new user.
if (compressedRatingMatrix[tempIndex][0] != compressedRatingMatrix[tempIndex - 1][0]) {
userStartingIndices[compressedRatingMatrix[tempIndex][0]] = tempIndex;
} // Of if
} // Of if
tempIndex++;
} // Of while
tempBufReader.close();
double[] tempUserTotalScore = new double[numUsers];
double[] tempItemTotalScore = new double[numItems];
for (int i = 0; i < numRatings; i++) {
tempUserTotalScore[compressedRatingMatrix[i][0]] += compressedRatingMatrix[i][2];
tempItemTotalScore[compressedRatingMatrix[i][1]] += compressedRatingMatrix[i][2];
} // Of for i
for (int i = 0; i < numUsers; i++) {
userAverageRatings[i] = tempUserTotalScore[i] / userDegrees[i];
} // Of for i
for (int i = 0; i < numItems; i++) {
itemAverageRatings[i] = tempItemTotalScore[i] / itemDegrees[i];
} // Of for i
}// Of the first constructor
/**
*************************
* Set the radius (delta).
*
* @param paraRadius
* The given radius.
*************************
*/
public void setRadius(double paraRadius) {
if (paraRadius > 0) {
radius = paraRadius;
} else {
radius = 0.1;
} // Of if
}// Of setRadius
/**
*************************
* Leave-one-out prediction. The predicted values are stored in predictions.
*
* @see predictions
*************************
*/
public void leaveOneOutPrediction() {
double tempItemAverageRating;
// Make each line of the code shorter.
int tempUser, tempItem, tempRating;
System.out.println("\r\nLeaveOneOutPrediction for radius " + radius);
numNonNeighbors = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < numRatings; i++) {
tempUser = compressedRatingMatrix[i][0];
tempItem = compressedRatingMatrix[i][1];
tempRating = compressedRatingMatrix[i][2];
// Step 1. Recompute average rating of the current item.
tempItemAverageRating = (itemAverageRatings[tempItem] * itemDegrees[tempItem] - tempRating)
/ (itemDegrees[tempItem] - 1);
// Step 2. Recompute neighbors, at the same time obtain the ratings
// Of neighbors.
int tempNeighbors = 0;
double tempTotal = 0;
int tempComparedItem;
for (int j = userStartingIndices[tempUser]; j < userStartingIndices[tempUser + 1]; j++) {
tempComparedItem = compressedRatingMatrix[j][1];
if (tempItem == tempComparedItem) {
continue;// Ignore itself.
} // Of if
if (Math.abs(tempItemAverageRating - itemAverageRatings[tempComparedItem]) < radius) {
tempTotal += compressedRatingMatrix[j][2];
tempNeighbors++;
} // Of if
} // Of for j
// Step 3. Predict as the average value of neighbors.
if (tempNeighbors > 0) {
predictions[i] = tempTotal / tempNeighbors;
} else {
predictions[i] = DEFAULT_RATING;
numNonNeighbors++;
} // Of if
} // Of for i
}// Of leaveOneOutPrediction
/**
*************************
* Compute the MAE based on the deviation of each leave-one-out.
*
* @author Fan Min
*************************
*/
public double computeMAE() throws Exception {
double tempTotalError = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < predictions.length; i++) {
tempTotalError += Math.abs(predictions[i] - compressedRatingMatrix[i][2]);
} // Of for i
return tempTotalError / predictions.length;
}// Of computeMAE
/**
*************************
* Compute the MAE based on the deviation of each leave-one-out.
*
* @author Fan Min
*************************
*/
public double computeRSME() throws Exception {
double tempTotalError = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < predictions.length; i++) {
tempTotalError += (predictions[i] - compressedRatingMatrix[i][2])
* (predictions[i] - compressedRatingMatrix[i][2]);
} // Of for i
double tempAverage = tempTotalError / predictions.length;
return Math.sqrt(tempAverage);
}// Of computeRSME
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
MBR tempRecommender = new MBR("D:/data/movielens-943u1682m.txt", 943, 1682, 100000);
for (double tempRadius = 0.2; tempRadius < 0.6; tempRadius += 0.1) {
tempRecommender.setRadius(tempRadius);
tempRecommender.leaveOneOutPrediction();
double tempMAE = tempRecommender.computeMAE();
double tempRSME = tempRecommender.computeRSME();
System.out.println("Radius = " + tempRadius + ", MAE = " + tempMAE + ", RSME = " + tempRSME
+ ", numNonNeighbors = " + tempRecommender.numNonNeighbors);
} // Of for tempRadius
} catch (Exception ee) {
System.out.println(ee);
} // Of try
}// Of main
}// Of class MBR
这几天停电挺难受的,一直没能理解透彻代码
第55天:基于 M-distance 的推荐 (续)
昨天实现的是 item-based recommendation. 今天自己来实现一下 user-based recommendation. 只需要在原有基础上增加即可.
新增代码:
public void leaveOneOutPredictionBasedOnUsers() {
double tempUserAverageRating;
// Make each line of the code shorter.
int tempUser, tempItem, tempRating;
System.out.println("\r\nleaveOneOutPredictionBasedOnUsers for radius " + radius);
numNonNeighbors = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < numRatings; i++) {
tempUser = compressedRatingMatrix[i][0];
tempItem = compressedRatingMatrix[i][1];
tempRating = compressedRatingMatrix[i][2];
// 重新计算当前项的平均分(把当前项的评分去除后的)
tempUserAverageRating = (userAverageRatings[tempUser] * userDegrees[tempUser] - tempRating)
/ (userDegrees[tempUser] - 1);
// 重新计算邻居,同时获得邻居的评分
int tempNeighbors = 0;
double tempTotal = 0;
//根据该用户的评分去预测
for (int j = 0; j < numUsers; j++) {
if (tempUser == j) {
continue;
}
if (Math.abs(tempUserAverageRating - userAverageRatings[j]) < radius) {
tempTotal += userAverageRatings[j];
tempNeighbors++;
}
}
// 根据邻居的平均值预测
if (tempNeighbors > 0) {
predictions[i] = tempTotal / tempNeighbors;
} else {
predictions[i] = DEFAULT_RATING;
numNonNeighbors++;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
MBR tempRecommender = new MBR("D:data\movielens943u1682m.txt", 943, 1682, 100000);
System.out.println("\r\n-------leave_one_out-------");
for (double tempRadius = 0.2; tempRadius < 0.6; tempRadius += 0.1) {
tempRecommender.setRadius(tempRadius);
tempRecommender.leaveOneOutPrediction();
double tempMAE = tempRecommender.computeMAE();
double tempRSME = tempRecommender.computeRSME();
System.out.println("Radius = " + tempRadius + ", MAE = " + tempMAE + ", RSME = " + tempRSME
+ ", numNonNeighbors = " + tempRecommender.numNonNeighbors);
}
System.out.println("\r\n-------leave_one_out_BasedOnUsers-------");
for (double tempRadius = 0.2; tempRadius < 0.6; tempRadius += 0.1) {
tempRecommender.setRadius(tempRadius);
tempRecommender.leaveOneOutPredictionBasedOnUsers();
double tempMAE = tempRecommender.computeMAE();
double tempRSME = tempRecommender.computeRSME();
System.out.println("Radius = " + tempRadius + ", MAE = " + tempMAE + ", RSME = " + tempRSME
+ ", numNonNeighbors = " + tempRecommender.numNonNeighbors);
}
} catch (Exception ee) {
System.out.println(ee);
}
}
第 56 天: kMeans 聚类
kMeans 是最常用的聚类算法.
kMeans 聚类需要中心点收敛时结束. 偷懒使用了 Arrays.equals()
数据集为 iris, 所以最后一个属性没使用. 如果对于没有决策属性的数据集, 需要进行相应修改.
数据没有归一化.
getRandomIndices() 和 kMeans 的完全相同, 拷贝过来. 本来应该写在 SimpleTools.java 里面的, 代码不多, 为保证独立性就放这里了.
distance() 和 kMeans 的相似, 注意不要用决策属性, 而且参数不同. 第 2 个参数为实数向量, 这是类为中心可能为虚拟的, 而中心点那里并没有对象.
代码如下:
package days51-60;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Random;
import weka.core.Instances;
public class KMeans {
/**
* Manhattan distance.
*/
public static final int MANHATTAN = 0;
/**
* Euclidean distance.
*/
public static final int EUCLIDEAN = 1;
/**
* The distance measure.
*/
public int distanceMeasure = EUCLIDEAN;
/**
* A random instance;
*/
public static final Random random = new Random();
/**
* The data.
*/
Instances dataset;
/**
* The number of clusters.
*/
int numClusters = 2;
/**
* The clusters.
*/
int[][] clusters;
/**
*******************************
* The first constructor.
*
* @param paraFilename
* The data filename.
*******************************
*/
public KMeans(String paraFilename) {
dataset = null;
try {
FileReader fileReader = new FileReader(paraFilename);
dataset = new Instances(fileReader);
fileReader.close();
} catch (Exception ee) {
System.out.println("Cannot read the file: " + paraFilename + "\r\n" + ee);
System.exit(0);
} // Of try
}// Of the first constructor
/**
*******************************
* A setter.
*******************************
*/
public void setNumClusters(int paraNumClusters) {
numClusters = paraNumClusters;
}// Of the setter
/**
*********************
* Get a random indices for data randomization.
*
* @param paraLength
* The length of the sequence.
* @return An array of indices, e.g., {4, 3, 1, 5, 0, 2} with length 6.
*********************
*/
public static int[] getRandomIndices(int paraLength) {
int[] resultIndices = new int[paraLength];
// Step 1. Initialize.
for (int i = 0; i < paraLength; i++) {
resultIndices[i] = i;
} // Of for i
// Step 2. Randomly swap.
int tempFirst, tempSecond, tempValue;
for (int i = 0; i < paraLength; i++) {
// Generate two random indices.
tempFirst = random.nextInt(paraLength);
tempSecond = random.nextInt(paraLength);
// Swap.
tempValue = resultIndices[tempFirst];
resultIndices[tempFirst] = resultIndices[tempSecond];
resultIndices[tempSecond] = tempValue;
} // Of for i
return resultIndices;
}// Of getRandomIndices
/**
*********************
* The distance between two instances.
*
* @param paraI
* The index of the first instance.
* @param paraArray
* The array representing a point in the space.
* @return The distance.
*********************
*/
public double distance(int paraI, double[] paraArray) {
int resultDistance = 0;
double tempDifference;
switch (distanceMeasure) {
case MANHATTAN:
for (int i = 0; i < dataset.numAttributes() - 1; i++) {
tempDifference = dataset.instance(paraI).value(i) - paraArray[i];
if (tempDifference < 0) {
resultDistance -= tempDifference;
} else {
resultDistance += tempDifference;
} // Of if
} // Of for i
break;
case EUCLIDEAN:
for (int i = 0; i < dataset.numAttributes() - 1; i++) {
tempDifference = dataset.instance(paraI).value(i) - paraArray[i];
resultDistance += tempDifference * tempDifference;
} // Of for i
break;
default:
System.out.println("Unsupported distance measure: " + distanceMeasure);
}// Of switch
return resultDistance;
}// Of distance
/**
*******************************
* Clustering.
*******************************
*/
public void clustering() {
int[] tempOldClusterArray = new int[dataset.numInstances()];
tempOldClusterArray[0] = -1;
int[] tempClusterArray = new int[dataset.numInstances()];
Arrays.fill(tempClusterArray, 0);
double[][] tempCenters = new double[numClusters][dataset.numAttributes() - 1];
// Step 1. Initialize centers.
int[] tempRandomOrders = getRandomIndices(dataset.numInstances());
for (int i = 0; i < numClusters; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < tempCenters[0].length; j++) {
tempCenters[i][j] = dataset.instance(tempRandomOrders[i]).value(j);
} // Of for j
} // Of for i
int[] tempClusterLengths = null;
while (!Arrays.equals(tempOldClusterArray, tempClusterArray)) {
System.out.println("New loop ...");
tempOldClusterArray = tempClusterArray;
tempClusterArray = new int[dataset.numInstances()];
// Step 2.1 Minimization. Assign cluster to each instance.
int tempNearestCenter;
double tempNearestDistance;
double tempDistance;
for (int i = 0; i < dataset.numInstances(); i++) {
tempNearestCenter = -1;
tempNearestDistance = Double.MAX_VALUE;
for (int j = 0; j < numClusters; j++) {
tempDistance = distance(i, tempCenters[j]);
if (tempNearestDistance > tempDistance) {
tempNearestDistance = tempDistance;
tempNearestCenter = j;
} // Of if
} // Of for j
tempClusterArray[i] = tempNearestCenter;
} // Of for i
// Step 2.2 Mean. Find new centers.
tempClusterLengths = new int[numClusters];
Arrays.fill(tempClusterLengths, 0);
double[][] tempNewCenters = new double[numClusters][dataset.numAttributes() - 1];
// Arrays.fill(tempNewCenters, 0);
for (int i = 0; i < dataset.numInstances(); i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < tempNewCenters[0].length; j++) {
tempNewCenters[tempClusterArray[i]][j] += dataset.instance(i).value(j);
} // Of for j
tempClusterLengths[tempClusterArray[i]]++;
} // Of for i
// Step 2.3 Now average
for (int i = 0; i < tempNewCenters.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < tempNewCenters[0].length; j++) {
tempNewCenters[i][j] /= tempClusterLengths[i];
} // Of for j
} // Of for i
System.out.println("Now the new centers are: " + Arrays.deepToString(tempNewCenters));
tempCenters = tempNewCenters;
} // Of while
// Step 3. Form clusters.
clusters = new int[numClusters][];
int[] tempCounters = new int[numClusters];
for (int i = 0; i < numClusters; i++) {
clusters[i] = new int[tempClusterLengths[i]];
} // Of for i
for (int i = 0; i < tempClusterArray.length; i++) {
clusters[tempClusterArray[i]][tempCounters[tempClusterArray[i]]] = i;
tempCounters[tempClusterArray[i]]++;
} // Of for i
System.out.println("The clusters are: " + Arrays.deepToString(clusters));
}// Of clustering
/**
*******************************
* Clustering.
*******************************
*/
public static void testClustering() {
KMeans tempKMeans = new KMeans("D:/data/iris.arff");
tempKMeans.setNumClusters(3);
tempKMeans.clustering();
}// Of testClustering
/**
*************************
* A testing method.
*************************
*/
public static void main(String arags[]) {
testClustering();
}// Of main
}// Of class KMeans
运行有问题:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: weka/core/Instances
at days51_60.KnnClassification.
at days51_60.KnnClassification.main(KnnClassification.java:249)
Caused by: java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: weka.core.Instances
at java.base/jdk.internal.loader.BuiltinClassLoader.loadClass(BuiltinClassLoader.java:606)
at java.base/jdk.internal.loader.ClassLoaders$AppClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoaders.java:168)
at java.base/java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoader.java:522)
... 2 more
待解决
第 57 天: kMeans 聚类 (续)
任务:
获得虚拟中心后, 换成与其最近的点作为实际中心, 再聚类.
修改代码如下:
//当前临时实际中心点与平均中心点的距离
double[] tempNearestDistanceArray = new double[numClusters];
//当前距离平均中心最近的实际点
double[][] tempActualCenters = new double[numClusters][dataset.numAttributes() - 1];
Arrays.fill(tempNearestDistanceArray, Double.MAX_VALUE);
for (int i = 0; i < dataset.numInstances(); i++) {
//用当前数据去与其分类的中心比较距离
if (tempNearestDistanceArray[tempClusterArray[i]] > distance(i, tempCenters[tempClusterArray[i]])) {
tempNearestDistanceArray[tempClusterArray[i]] = distance(i, tempCenters[tempClusterArray[i]]);
//暂时存储当前距离平均中心最近的实际点
for (int j = 0; j < dataset.numAttributes() - 1; j++) {
tempActualCenters[tempClusterArray[i]][j] = dataset.instance((i)).value(j);
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < tempNewCenters.length; i++) {
tempNewCenters[i] = tempActualCenters[i];
}
System.out.println("Now the new centers are: " + Arrays.deepToString(tempNewCenters));
tempCenters = tempNewCenters;
}第 58 天: 符号型数据的 NB 算法
任务:
Naive Bayes 是一种用后验概率公式推导出的算法. 它有一个独立性假设, 从数学上看起来不靠谱. 但从机器学习效果来说是不错的.
所有的程序都在今天列出, 但今天只研究符号型数据的分类. 为此, 可以只抄符号型数据相关的方法 (从 main() 开始有选择性地抄), 明天再抄数值型数据处理算法.
必须自己举一个小的例子 (如 10 个对象, 3 个条件属性, 2 个类别) 来辅助理解.
需要查阅相关基础知识.
需要理解三维数组每个维度的涵义: The conditional probabilities for all classes over all attributes on all values. 注意到三维数组不是规则的, 例如, 不同属性的属性值个数可能不同.
这里使用同样的数据进行训练和测试. 如果要划分训练集和测试集, 可参考 kNN 代码.
代码如下:
package days51_60;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.util.Arrays;
import weka.core.*;
/**
* The Naive Bayes algorithm.
*
* @author Fan Min [email protected].
*/
public class NaiveBayes {
/**
*************************
* An inner class to store parameters.
*************************
*/
private class GaussianParamters {
double mu;
double sigma;
public GaussianParamters(double paraMu, double paraSigma) {
mu = paraMu;
sigma = paraSigma;
}// Of the constructor
public String toString() {
return "(" + mu + ", " + sigma + ")";
}// Of toString
}// Of GaussianParamters
/**
* The data.
*/
Instances dataset;
/**
* The number of classes. For binary classification it is 2.
*/
int numClasses;
/**
* The number of instances.
*/
int numInstances;
/**
* The number of conditional attributes.
*/
int numConditions;
/**
* The prediction, including queried and predicted labels.
*/
int[] predicts;
/**
* Class distribution.
*/
double[] classDistribution;
/**
* Class distribution with Laplacian smooth.
*/
double[] classDistributionLaplacian;
/**
* The conditional probabilities for all classes over all attributes on all
* values.
*/
double[][][] conditionalProbabilities;
/**
* The conditional probabilities with Laplacian smooth.
*/
double[][][] conditionalProbabilitiesLaplacian;
/**
* The Guassian parameters.
*/
GaussianParamters[][] gaussianParameters;
/**
* Data type.
*/
int dataType;
/**
* Nominal.
*/
public static final int NOMINAL = 0;
/**
* Numerical.
*/
public static final int NUMERICAL = 1;
/**
********************
* The constructor.
*
* @param paraFilename
* The given file.
********************
*/
public NaiveBayes(String paraFilename) {
dataset = null;
try {
FileReader fileReader = new FileReader(paraFilename);
dataset = new Instances(fileReader);
fileReader.close();
} catch (Exception ee) {
System.out.println("Cannot read the file: " + paraFilename + "\r\n" + ee);
System.exit(0);
} // Of try
dataset.setClassIndex(dataset.numAttributes() - 1);
numConditions = dataset.numAttributes() - 1;
numInstances = dataset.numInstances();
numClasses = dataset.attribute(numConditions).numValues();
}// Of the constructor
/**
********************
* Set the data type.
********************
*/
public void setDataType(int paraDataType) {
dataType = paraDataType;
}// Of setDataType
/**
********************
* Calculate the class distribution with Laplacian smooth.
********************
*/
public void calculateClassDistribution() {
classDistribution = new double[numClasses];
classDistributionLaplacian = new double[numClasses];
double[] tempCounts = new double[numClasses];
for (int i = 0; i < numInstances; i++) {
int tempClassValue = (int) dataset.instance(i).classValue();
tempCounts[tempClassValue]++;
} // Of for i
for (int i = 0; i < numClasses; i++) {
classDistribution[i] = tempCounts[i] / numInstances;
classDistributionLaplacian[i] = (tempCounts[i] + 1) / (numInstances + numClasses);
} // Of for i
System.out.println("Class distribution: " + Arrays.toString(classDistribution));
System.out.println(
"Class distribution Laplacian: " + Arrays.toString(classDistributionLaplacian));
}// Of calculateClassDistribution
/**
********************
* Calculate the conditional probabilities with Laplacian smooth. ONLY scan
* the dataset once. There was a simpler one, I have removed it because the
* time complexity is higher.
********************
*/
public void calculateConditionalProbabilities() {
conditionalProbabilities = new double[numClasses][numConditions][];
conditionalProbabilitiesLaplacian = new double[numClasses][numConditions][];
// Allocate space
for (int i = 0; i < numClasses; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < numConditions; j++) {
int tempNumValues = (int) dataset.attribute(j).numValues();
conditionalProbabilities[i][j] = new double[tempNumValues];
conditionalProbabilitiesLaplacian[i][j] = new double[tempNumValues];
} // Of for j
} // Of for i
// Count the numbers
int[] tempClassCounts = new int[numClasses];
for (int i = 0; i < numInstances; i++) {
int tempClass = (int) dataset.instance(i).classValue();
tempClassCounts[tempClass]++;
for (int j = 0; j < numConditions; j++) {
int tempValue = (int) dataset.instance(i).value(j);
conditionalProbabilities[tempClass][j][tempValue]++;
} // Of for j
} // Of for i
// Now for the real probability with Laplacian
for (int i = 0; i < numClasses; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < numConditions; j++) {
int tempNumValues = (int) dataset.attribute(j).numValues();
for (int k = 0; k < tempNumValues; k++) {
conditionalProbabilitiesLaplacian[i][j][k] = (conditionalProbabilities[i][j][k]
+ 1) / (tempClassCounts[i] + numClasses);
} // Of for k
} // Of for j
} // Of for i
System.out.println(Arrays.deepToString(conditionalProbabilities));
}// Of calculateConditionalProbabilities
/**
********************
* Calculate the conditional probabilities with Laplacian smooth.
********************
*/
public void calculateGausssianParameters() {
gaussianParameters = new GaussianParamters[numClasses][numConditions];
double[] tempValuesArray = new double[numInstances];
int tempNumValues = 0;
double tempSum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < numClasses; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < numConditions; j++) {
tempSum = 0;
// Obtain values for this class.
tempNumValues = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < numInstances; k++) {
if ((int) dataset.instance(k).classValue() != i) {
continue;
} // Of if
tempValuesArray[tempNumValues] = dataset.instance(k).value(j);
tempSum += tempValuesArray[tempNumValues];
tempNumValues++;
} // Of for k
// Obtain parameters.
double tempMu = tempSum / tempNumValues;
double tempSigma = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < tempNumValues; k++) {
tempSigma += (tempValuesArray[k] - tempMu) * (tempValuesArray[k] - tempMu);
} // Of for k
tempSigma /= tempNumValues;
tempSigma = Math.sqrt(tempSigma);
gaussianParameters[i][j] = new GaussianParamters(tempMu, tempSigma);
} // Of for j
} // Of for i
System.out.println(Arrays.deepToString(gaussianParameters));
}// Of calculateGausssianParameters
/**
********************
* Classify all instances, the results are stored in predicts[].
********************
*/
public void classify() {
predicts = new int[numInstances];
for (int i = 0; i < numInstances; i++) {
predicts[i] = classify(dataset.instance(i));
} // Of for i
}// Of classify
/**
********************
* Classify an instances.
********************
*/
public int classify(Instance paraInstance) {
if (dataType == NOMINAL) {
return classifyNominal(paraInstance);
} else if (dataType == NUMERICAL) {
return classifyNumerical(paraInstance);
} // Of if
return -1;
}// Of classify
/**
********************
* Classify an instances with nominal data.
********************
*/
public int classifyNominal(Instance paraInstance) {
// Find the biggest one
double tempBiggest = -10000;
int resultBestIndex = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < numClasses; i++) {
double tempPseudoProbability = Math.log(classDistributionLaplacian[i]);
for (int j = 0; j < numConditions; j++) {
int tempAttributeValue = (int) paraInstance.value(j);
// Laplacian smooth.
tempPseudoProbability += Math
.log(conditionalProbabilities[i][j][tempAttributeValue]);
} // Of for j
if (tempBiggest < tempPseudoProbability) {
tempBiggest = tempPseudoProbability;
resultBestIndex = i;
} // Of if
} // Of for i
return resultBestIndex;
}// Of classifyNominal
/**
********************
* Classify an instances with numerical data.
********************
*/
public int classifyNumerical(Instance paraInstance) {
// Find the biggest one
double tempBiggest = -10000;
int resultBestIndex = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < numClasses; i++) {
double tempPseudoProbability = Math.log(classDistributionLaplacian[i]);
for (int j = 0; j < numConditions; j++) {
double tempAttributeValue = paraInstance.value(j);
double tempSigma = gaussianParameters[i][j].sigma;
double tempMu = gaussianParameters[i][j].mu;
tempPseudoProbability += -Math.log(tempSigma) - (tempAttributeValue - tempMu)
* (tempAttributeValue - tempMu) / (2 * tempSigma * tempSigma);
} // Of for j
if (tempBiggest < tempPseudoProbability) {
tempBiggest = tempPseudoProbability;
resultBestIndex = i;
} // Of if
} // Of for i
return resultBestIndex;
}// Of classifyNumerical
/**
********************
* Compute accuracy.
********************
*/
public double computeAccuracy() {
double tempCorrect = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < numInstances; i++) {
if (predicts[i] == (int) dataset.instance(i).classValue()) {
tempCorrect++;
} // Of if
} // Of for i
double resultAccuracy = tempCorrect / numInstances;
return resultAccuracy;
}// Of computeAccuracy
/**
*************************
* Test nominal data.
*************************
*/
public static void testNominal() {
System.out.println("Hello, Naive Bayes. I only want to test the nominal data.");
String tempFilename = "D:/data/mushroom.arff";
NaiveBayes tempLearner = new NaiveBayes(tempFilename);
tempLearner.setDataType(NOMINAL);
tempLearner.calculateClassDistribution();
tempLearner.calculateConditionalProbabilities();
tempLearner.classify();
System.out.println("The accuracy is: " + tempLearner.computeAccuracy());
}// Of testNominal
/**
*************************
* Test numerical data.
*************************
*/
public static void testNumerical() {
System.out.println(
"Hello, Naive Bayes. I only want to test the numerical data with Gaussian assumption.");
String tempFilename = "D:/data/iris.arff";
NaiveBayes tempLearner = new NaiveBayes(tempFilename);
tempLearner.setDataType(NUMERICAL);
tempLearner.calculateClassDistribution();
tempLearner.calculateGausssianParameters();
tempLearner.classify();
System.out.println("The accuracy is: " + tempLearner.computeAccuracy());
}// Of testNominal
/**
*************************
* Test this class.
*
* @param args
* Not used now.
*************************
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
testNominal();
testNumerical();
}// Of main
}// Of class NaiveBayes
运行有错待解决:
第 59 天: 数值型数据的 NB 算法
- 今天把数值型数据处理的代码加上去.
- 假设所有属性的属性值都服从高斯分布. 也可以做其它假设.
- 将概率密度当成概率值直接使用 Bayes 公式.
- 可以看到, 数值型数据的处理并不会比符号型的复杂.
代码如下:
/**
* @Description: 数值型数据分类
* @Param: [paraInstance]
* @return: int
*/
public int classifyNumerical(Instance paraInstance) {
// 找到最大的一个
double tempBiggest = -10000;
int resultBestIndex = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < numClasses; i++) {
double tempPseudoProbability = Math.log(classDistributionLaplacian[i]);
for (int j = 0; j < numConditions; j++) {
double tempAttributeValue = paraInstance.value(j);
double tempSigma = gaussianParameters[i][j].sigma;
double tempMu = gaussianParameters[i][j].mu;
tempPseudoProbability += -Math.log(tempSigma) - (tempAttributeValue - tempMu)
* (tempAttributeValue - tempMu) / (2 * tempSigma * tempSigma);
}
if (tempBiggest < tempPseudoProbability) {
tempBiggest = tempPseudoProbability;
resultBestIndex = i;
}
}
return resultBestIndex;
}
/**
* @Description: 数值型数据测试
* @Param: []
* @return: void
*/
public static void testNumerical() {
System.out.println(
"Hello, Naive Bayes. I only want to test the numerical data with Gaussian assumption.");
String tempFilename = "F:\\研究生\\研0\\学习\\Java_Study\\data_set\\iris.arff";
NaiveBayes tempLearner = new NaiveBayes(tempFilename);
tempLearner.setDataType(NUMERICAL);
tempLearner.calculateClassDistribution();
tempLearner.calculateGausssianParameters();
tempLearner.classify();
System.out.println("The accuracy is: " + tempLearner.computeAccuracy());
}