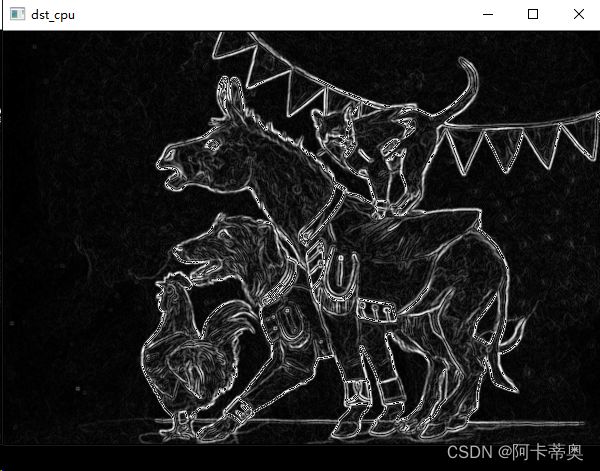
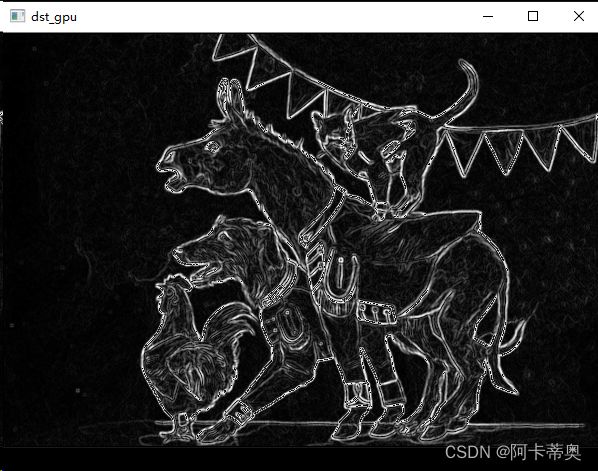
CUDA学习笔记3——图像卷积实现
分别采用GPU、CPU对图像进行sobel滤波处理
#include