粘包和半包问题及解决办法
粘包问题是指数据在传输时,在一条消息中读取到了另一条消息的部分数据,这种现象就叫做粘包。
半包问题是指数据在传输时,接收端只收到了部分数据,而非完整的数据,就叫做半包。
产生粘包和半包问题原因:
这些问题发生在 TCP/IP 协议中,因为 TCP 是面向连接的传输协议,它是以“流”的形式传输数据的,而“流”数据是没有明确的开始和结尾边界的,所以就会出现粘包问题。
大部分情况下我们都把粘包问题和半包问题看成同一个问题
问题代码演示
- 服务器端用来接收消息
- 客户端用来发送一段固定的消息。
通过输出服务器端接收到的信息来观察粘包问题。服务器端代码实现如下:
package com.nien.test.sticky;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
/**
* @author ally-coding
* @Date: 2023/10/16 23:47
* @Project cetc_test
* @Description: 粘包服务器端测试
*/
public class ServSocket {
private static final int BYTE_LENGTH = 20;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(8888);
//获取客户端连接
Socket clientSocker = serverSocket.accept();
//得到客户端发送的流对象
try(InputStream inputStream = clientSocker.getInputStream()){
while(true){
//循环获取客户端发送的信息
byte[] bytes = new byte[BYTE_LENGTH];
// 读取客户端发送的信息
int count = inputStream.read(bytes, 0, BYTE_LENGTH);
if(count>0){
System.out.println("接受到客户端的信息是:"+new String(bytes));
}
count=0;
}
}
}
}
客户端代码:
package com.nien.test.sticky;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.Socket;
/**
* @author ally-coding
* @Date: 2023/10/16 23:54
* @Project cetc_test
* @Description: 粘包客户端端测试
*/
public class ClientSocket {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Socket socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1",8888);
final String message = "Hello world!";
try(OutputStream outputStream = socket.getOutputStream()){
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
outputStream.write(message.getBytes());
}
}
}
}
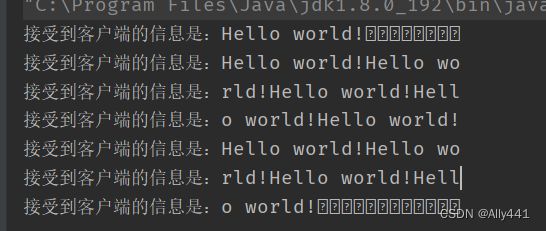
执行结果如下所示。
可以明显看出,服务器端发生了粘包问题。
解决办法
1.发送方和接收方固定发送数据的大小,当字符长度不够时用空字符弥补,有了固定大小之后就知道每条消息的具体边界了,这样就没有粘包的问题了; 2.在 TCP 协议的基础上封装一层自定义数据协议,在自定义数据协议中,包含数据头(存储数据的大小)和数据的具体内容,这样服务端得到数据之后,通过解析数据头就可以知道数据的具体长度了,也就没有粘包的问题了; 3.以特殊的字符结尾,比如以“\n”结尾,这样我们就知道数据的具体边界了,从而避免了粘包问题(推荐方案)
方法1 固定发送数据的大小
代码实现:
服务端代码:
package com.nien.test.sticky.solver1;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
/**
* @author ally-coding
* @Date: 2023/10/17 0:40
* @Project cetc_test
* @Description: 粘包问题解决1-服务端
*/
public class Server1 {
private static final int BYTE_LENGTH = 1024;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(9091);
//获取客户端连接
Socket clientSocker = serverSocket.accept();
//得到客户端发送的流对象
try(InputStream inputStream = clientSocker.getInputStream()){
while(true){
//循环获取客户端发送的信息
byte[] bytes = new byte[BYTE_LENGTH];
// 读取客户端发送的信息
int count = inputStream.read(bytes, 0, BYTE_LENGTH);
if(count>0){
System.out.println("接受到客户端的信息是:"+new String(bytes).trim());
}
count=0;
}
}
}
}
客户端代码:
package com.nien.test.sticky.solver1;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.Socket;
/**
* @author ally-coding
* @Date: 2023/10/17 0:40
* @Project cetc_test
* @Description: 粘包问题解决1-客户端
*/
public class Client1 {
private static final int BYTE_LENGTH=1024;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Socket socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1",9091);
final String messgae = "Hello world!";
try(OutputStream outputStream = socket.getOutputStream()){
byte[] bytes = new byte[BYTE_LENGTH];
int idx = 0;
for (byte b : messgae.getBytes()){
bytes[idx] = b;
idx++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
outputStream.write(bytes, 0, BYTE_LENGTH);
}
}
}
}
执行结果如下所示。
虽然这种方式可以解决粘包问题,但这种固定数据大小的传输方式,当数据量比较小时会使用空字符来填充,所以会额外的增加网络传输的负担。
方法2 在 TCP 协议的基础上封装一层自定义数据协议
步骤1 编写一个消息封装类 2编写客户端 3编写服务器
1.编写消息封装类代码:
package com.nien.test.sticky.solver2;
import com.sun.org.apache.regexp.internal.RE;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.text.NumberFormat;
/**
* @author ally-coding
* @Date: 2023/10/17 0:52
* @Project cetc_test
* @Description: 消息封装类
*/
public class SocketPacket {
static final int HEAD_SIZE=8;
/**
* 将协议封装为:协议头 + 协议体
* @param content
* @return
*/
public byte[] toBytes(String content){
//协议体 byte数据
byte[] bodyByte = content.getBytes();
int bodyByteLength = bodyByte.length;
// 最终封装对象
byte[] result = new byte[HEAD_SIZE + bodyByteLength];
// 借助 NumberFormat 将 int 转换为 byte[]
NumberFormat numberFormat = NumberFormat.getNumberInstance();
numberFormat.setMinimumIntegerDigits(HEAD_SIZE);
numberFormat.setGroupingUsed(false);
//协议头 byte数组
byte[] headByte = numberFormat.format(bodyByteLength).getBytes();
// 封装协议头
System.arraycopy(headByte, 0, result, 0, HEAD_SIZE);
// 封装协议体
System.arraycopy(bodyByte,0, result, HEAD_SIZE, bodyByteLength);
return result;
}
/**
* 获取消息头的内容(也就是消息体的长度)
* @param inputStream
* @return
* @throws IOException
*/
public int getHeader(InputStream inputStream) throws IOException {
int result = 0;
byte[] bytes = new byte[HEAD_SIZE];
inputStream.read(bytes, 0, HEAD_SIZE);
//得到消息体的字节长度
result = Integer.valueOf(new String(bytes));
return result;
}
}
2.编写客户端代码
package com.nien.test.sticky.solver2;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.util.Random;
/**
* @author ally-coding
* @Date: 2023/10/17 1:30
* @Project cetc_test
* @Description: 客户端
*/
public class Client2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Socket socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1",9093);
String[] message = {"Hello world","Hello java"};
SocketPacket socketPacket = new SocketPacket();
try(OutputStream outputStream = socket.getOutputStream()){
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
String msg = message[new Random().nextInt(message.length)];
byte[] bytes = socketPacket.toBytes(msg);
outputStream.write(bytes, 0, bytes.length);
outputStream.flush();
}
}
}
}
3.编写服务端
package com.nien.test.sticky.solver2;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* @author ally-coding
* @Date: 2023/10/17 9:19
* @Project cetc_test
* @Description: 服务器端 使用线程池来处理每个客户端的业务请求
*/
public class Server2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(9093);
// 获取客户端连接
Socket clientSocket = serverSocket.accept();
// 用线程池处理更多的客户端
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(100,150,100,
TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(1000));
threadPoolExecutor.submit(()->{
//客户端消息处理
processMessage(clientSocket);
});
}
private static void processMessage(Socket clientSocket){
// Socket 封装对象
SocketPacket socketPacket = new SocketPacket();
// 获取客户端发送的消息对象
try(InputStream inputStream = clientSocket.getInputStream()) {
while (true){
// 获取消息头(也就是消息体的长度)
int bodyLength = socketPacket.getHeader(inputStream);
// 消息体 byte 数组
byte[] bodyBytes = new byte[bodyLength];
// 每次实际读取字节数
int readCount = 0;
// 消息体赋值下标
int bodyIndex = 0;
// 循环接收消息头中定义的长度
while (bodyIndex<=(bodyLength-1) &&
(readCount = inputStream.read(bodyBytes, bodyIndex, bodyLength))!= -1){
bodyIndex += readCount;
}
bodyIndex=0;
// 成功接收到客户端的消息并打印
System.out.println("接收到客户端的信息:" + new String(bodyBytes));
}
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
}
运行结果如下所示。
此方法虽然可以解决粘包问题,但消息的设计和代码的实现复杂度比较高,所以也不是理想的解决方案。
方法3 以特殊的字符结尾
代码实现:
服务器代码:
package com.nien.test.sticky.solver3;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* @author ally-coding
* @Date: 2023/10/18 0:40
* @Project cetc_test
* @Description:
*/
public class Server3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(9092);
// 获取客户端连接
Socket clientSocket = serverSocket.accept();
// 使用线程池处理更多的客户端
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(100,150,100,
TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(1000));
threadPool.submit(()->{
//消息处理
processMessage(clientSocket);
});
}
/**
* 消息处理
* @param clientSocket
*/
private static void processMessage(Socket clientSocket){
// 获取客户端发送的消息流对象
try(BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(clientSocket.getInputStream()))) {
while (true){
// 按行读取客户端发送的消息
String msg = bufferedReader.readLine();
if(msg!=null){
System.out.println("接收到客户端的信息:" + msg);
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
客户端代码:
package com.nien.test.sticky.solver3;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.net.Socket;
/**
* @author ally-coding
* @Date: 2023/10/18 0:40
* @Project cetc_test
* @Description:
*/
public class Client3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 启动 Socket 并尝试连接服务器
Socket socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 9092);
String message = "Hi,Java."; // 发送消息
try (BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(
new OutputStreamWriter(socket.getOutputStream()))) {
// 给服务器端发送 10 次消息
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
// 注意:结尾的 \n 不能省略,它表示按行写入
bufferedWriter.write(message + "\n");
// 刷新缓冲区(此步骤不能省略)
bufferedWriter.flush();
}
}
}
}
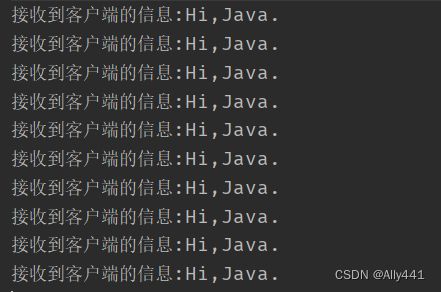
执行结果如下图所示。
该方法最大优点是实现简单,但存在一定的局限性,比如当一条消息中间如果出现了结束符就会造成半包的问题,所以如果是复杂的字符串要对内容进行编码和解码处理,这样才能保证结束符的正确性。