使用Python进行钻石价格分析
钻石是最昂贵的宝石之一。钻石的质量通常以其重量(克拉)、净度、颜色和切工来评估。重量越大、净度越高、色彩纯净、切工精细的钻石价格也越高。其中,4C标准是衡量钻石质量的国际标准,即克拉(Carat)、净度(Clarity)、颜色(Color)和切工(Cut)。
钻石价格分析
为了根据钻石的属性来分析钻石的价格,我们首先需要一个包含钻石价格的数据集。
这里有一个Kaggle上数据集地址:https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/shivam2503/diamonds,其中包含有关钻石的信息,例如:
- Carat
- Cut
- Colour
- Clarity
- Depth
- Table
- Price
- Size
导入必要的Python库和数据集:
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import plotly.express as px
import plotly.graph_objects as go
data = pd.read_csv("diamonds.csv")
print(data.head())
输出
Unnamed: 0 carat cut color clarity depth table price x y \
0 1 0.23 Ideal E SI2 61.5 55.0 326 3.95 3.98
1 2 0.21 Premium E SI1 59.8 61.0 326 3.89 3.84
2 3 0.23 Good E VS1 56.9 65.0 327 4.05 4.07
3 4 0.29 Premium I VS2 62.4 58.0 334 4.20 4.23
4 5 0.31 Good J SI2 63.3 58.0 335 4.34 4.35
z
0 2.43
1 2.31
2 2.31
3 2.63
4 2.75
此数据集包含未命名列。在进一步处理之前删除此列:
data = data.drop("Unnamed: 0",axis=1)
现在让我们开始分析钻石价格。先来分析一下克拉数和钻石价格之间的关系,看看克拉数是如何影响钻石价格的:
figure = px.scatter(data_frame = data, x="carat",
y="price", size="depth",
color= "cut", trendline="ols")
figure.show()
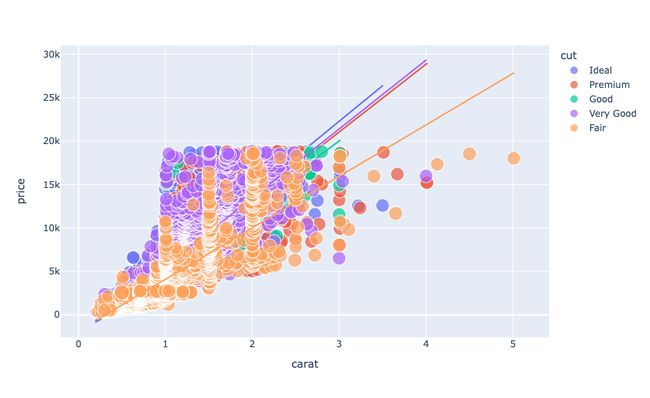
我们可以看到克拉数和钻石价格之间的线性关系。这意味着克拉数越高,价格越高。
现在,通过计算钻石的大小(长度x宽度x高度)向该数据集添加一个新列:
data["size"] = data["x"] * data["y"] * data["z"]
print(data)
输出
carat cut color clarity depth table price x y z \
0 0.23 Ideal E SI2 61.5 55.0 326 3.95 3.98 2.43
1 0.21 Premium E SI1 59.8 61.0 326 3.89 3.84 2.31
2 0.23 Good E VS1 56.9 65.0 327 4.05 4.07 2.31
3 0.29 Premium I VS2 62.4 58.0 334 4.20 4.23 2.63
4 0.31 Good J SI2 63.3 58.0 335 4.34 4.35 2.75
... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
53935 0.72 Ideal D SI1 60.8 57.0 2757 5.75 5.76 3.50
53936 0.72 Good D SI1 63.1 55.0 2757 5.69 5.75 3.61
53937 0.70 Very Good D SI1 62.8 60.0 2757 5.66 5.68 3.56
53938 0.86 Premium H SI2 61.0 58.0 2757 6.15 6.12 3.74
53939 0.75 Ideal D SI2 62.2 55.0 2757 5.83 5.87 3.64
size
0 38.202030
1 34.505856
2 38.076885
3 46.724580
4 51.917250
... ...
53935 115.920000
53936 118.110175
53937 114.449728
53938 140.766120
53939 124.568444
[53940 rows x 11 columns]
现在让我们来看看钻石的大小与其价格之间的关系:
figure = px.scatter(data_frame = data, x="size",
y="price", size="size",
color= "cut", trendline="ols")
figure.show()
- 优质切工钻石比其他钻石相对较大
- 所有类型的钻石的大小和它们的价格之间都有线性关系
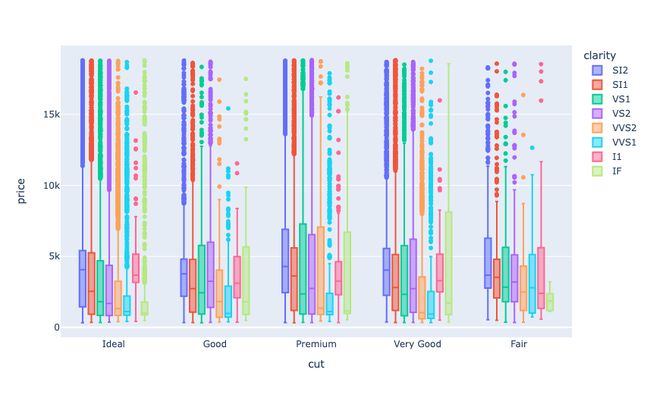
现在让我们来看看所有类型的钻石的价格,根据它们的颜色:
fig = px.box(data, x="cut",
y="price",
color="color")
fig.show()
fig = px.box(data,
x="cut",
y="price",
color="clarity")
fig.show()
correlation = data.corr()
print(correlation["price"].sort_values(ascending=False))
输出
price 1.000000
carat 0.921591
size 0.902385
x 0.884435
y 0.865421
z 0.861249
table 0.127134
depth -0.010647
Name: price, dtype: float64
钻石价格预测
现在,将通过使用上述钻石价格分析中的所有必要信息来预测钻石价格。
在继续之前,转换切割列的值,因为钻石的切割类型是预测钻石价格的一个有价值的特征。要使用此列,我们需要将其分类值转换为数值。下面是我们如何将其转换为数字功能:
data["cut"] = data["cut"].map({"Ideal": 1,
"Premium": 2,
"Good": 3,
"Very Good": 4,
"Fair": 5})
现在,让我们将数据分为训练集和测试集:
#splitting data
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
x = np.array(data[["carat", "cut", "size"]])
y = np.array(data[["price"]])
xtrain, xtest, ytrain, ytest = train_test_split(x, y,
test_size=0.10,
random_state=42)
训练一个机器学习模型来完成钻石价格预测的任务:
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor
model = RandomForestRegressor()
model.fit(xtrain, ytrain)
下面是我们如何使用机器学习模型来预测钻石的价格:
print("Diamond Price Prediction")
a = float(input("Carat Size: "))
b = int(input("Cut Type (Ideal: 1, Premium: 2, Good: 3, Very Good: 4, Fair: 5): "))
c = float(input("Size: "))
features = np.array([[a, b, c]])
print("Predicted Diamond's Price = ", model.predict(features))
输出
Diamond Price Prediction
Carat Size: 0.60
Cut Type (Ideal: 1, Premium: 2, Good: 3, Very Good: 4, Fair: 5): 2
Size: 40
Predicted Diamond's Price = [937.13946429]
总结
因此,这就是如何使用Python进行钻石价格分析和预测的任务。根据钻石价格分析,我们可以说优质钻石的价格和尺寸都高于其他类型的钻石。