Flink转换算子
文章目录
-
-
- 映射(map)
- 过滤(filter)
- 扁平映射(flatMap)
- 聚合算子(Aggregation)
-
- 按键分区(keyBy)+简单聚合
- 归约聚合(reduce)
- 用户自定义函数(UDF)
-
- 函数类
- 匿名函数(Lambda表达式)
- 富函数类(Rich Function Classes)
- 物理分区(Physical Partitioning)
-
映射(map)
基于DataStream调用map()方法就可以进行转换处理,方法需要传入的参数是接口MapFunction的实现,返回类型是 SingleOutputStreamOperator,继承于DataStream
import org.apache.flink.api.common.functions.MapFunction;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.DataStreamSource;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.SingleOutputStreamOperator;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.environment.StreamExecutionEnvironment;
public class TransformMapTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
env.setParallelism(1);
//从元素中读取数据
DataStreamSource<Event> stream = env.fromElements(
new Event("Mary", "./home", 1000L),
new Event("Bob", "./cart", 2000L)
);
//进行转换计算,提取user字段
//使用自定类,实现MapFunction接口
SingleOutputStreamOperator<String> result1 = stream.map(new MyMappper());
//2.使用匿名类实现MapFunction接口
SingleOutputStreamOperator<String> result2 = stream.map(new MapFunction<Event, String>() {
@Override
public String map(Event event) throws Exception {
return event.user;
}
});
//3.传入Lambda表达式
SingleOutputStreamOperator<String> result3 = stream.map(data -> data.user);
result1.print();
result2.print();
result3.print();
env.execute();
}
//自定义MapFunction
public static class MyMappper implements MapFunction<Event,String>{
@Override
public String map(Event event) throws Exception {
return event.user;
}
}
}
过滤(filter)
实现FilterFunction接口,重写filter()方法,返回true则元素正常输出,若为false则被过滤
import org.apache.flink.api.common.functions.FilterFunction;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.DataStreamSource;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.SingleOutputStreamOperator;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.environment.StreamExecutionEnvironment;
public class TransformFilterTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
env.setParallelism(1);
//从元素中读取数据
DataStreamSource<Event> stream = env.fromElements(
new Event("Mary", "./home", 1000L),
new Event("Bob", "./cart", 2000L),
new Event("Alice","./prod?id=100",3000L)
);
//1.传入一个实现了FilterFunction的类对象
SingleOutputStreamOperator<Event> result1 = stream.filter(new MyFilter());
//2.传入一个匿名类实现FilterFunction接口
SingleOutputStreamOperator<Event> result2 = stream.filter(new FilterFunction<Event>() {
@Override
public boolean filter(Event event) throws Exception {
return event.user.equals("Bob");
}
});
//3.传入Lambda表达式
SingleOutputStreamOperator<Event> result3 = stream.filter(data -> data.user.equals("Alice"));
result1.print();
result2.print();
result3.print();
env.execute();
}
private static class MyFilter implements FilterFunction<Event> {
@Override
public boolean filter(Event event) throws Exception {
return event.user.equals("Mary");
}
}
}
扁平映射(flatMap)
flatMap操作
将数据流中整体拆分成个体使用。消费一个元素,产生0到多个元素,flatMap是扁平化和映射两步操作的结合。对接口FlatMapFunction的实现,重写flatmap方法,通过收集器Collector来指定输出
import org.apache.flink.api.common.functions.FlatMapFunction;
import org.apache.flink.api.common.typeinfo.TypeHint;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.DataStreamSource;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.SingleOutputStreamOperator;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.environment.StreamExecutionEnvironment;
import org.apache.flink.util.Collector;
public class TransformFlatMapTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
env.setParallelism(1);
//从元素中读取数据
DataStreamSource<Event> stream = env.fromElements(
new Event("Mary", "./home", 1000L),
new Event("Bob", "./cart", 2000L),
new Event("Alice", "./prod?id=100", 3000L)
);
//1.传入一个实现了FlatMapFunction的类对象
SingleOutputStreamOperator result1 = stream.flatMap(new MyFlatMap());
//2.传入Lambda表达式
SingleOutputStreamOperator<String> result2 = stream.flatMap((Event event, Collector<String> out) -> {
if (event.user.equals("Mary"))
out.collect(event.url);
else if (event.user.equals("Bob")) {
out.collect(event.user);
out.collect(event.url);
out.collect(event.timestamp.toString());
}
}).returns(new TypeHint<String>() {});
result1.print("1");
result2.print("2");
// result3.print();
env.execute();
}
//实现一个自定义的FlatMapFunction
private static class MyFlatMap implements FlatMapFunction<Event, String> {
@Override
public void flatMap(Event event, Collector<String> collector) throws Exception {
collector.collect(event.user);
collector.collect(event.url);
collector.collect(event.timestamp.toString());
}
}
}
聚合算子(Aggregation)
按键分区(keyBy)+简单聚合
通过计算key的hash值来对分区数进行取模实现,key如果是POJO需要重新hashcode方法。
keyBy()方法需要传入一个参数,这个参数指定了一个或一组key。有很多不同的方法来指定key:对于Tuple数据类型,指定字段的位置或者多个位置的组合;对于POJO类型,指定字段的名称(String);传入Lambda表达式或者实现一个键选择器(KeySelector)
keyBy()方法返回一个KeyedStream,继承于DataStream。有了按键分区的数据流KeyedStream,可进行聚合操作,内置的有:
sum()、min()、max()、minBy()、maxBy()
min,minBy的区别:min只计算指定字段的最小值,其他字段会保留最初第一个数据的值,而minBy会返回包含字段最小值的整条数据。
指定字段的方式有两种:指定位置、指定名称
import org.apache.flink.api.java.functions.KeySelector;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.DataStreamSource;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.environment.StreamExecutionEnvironment;
public class TransformSimpleAggTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
env.setParallelism(1);
//从元素中读取数据
DataStreamSource<Event> stream = env.fromElements(
new Event("Mary", "./home", 1000L),
new Event("Bob", "./cart", 2000L),
new Event("Alice", "./prod?id=100", 3000L),
new Event("Bob", "./prod?id=1", 3300L),
new Event("Bob", "./home", 3500L),
new Event("Alice", "./prod?id=200", 3200L),
new Event("Bob", "./prod?id=2", 3800L),
new Event("Bob", "./prod?id=3", 4200L)
);
//按键分组之后进行聚合,提取当前用户最后一次访问数据
stream.keyBy(new KeySelector<Event, String>() {
@Override
public String getKey(Event value) throws Exception {
return value.user;
}
}).max("timestamp").print("max: ");
stream.keyBy(data -> data.user).maxBy("timestamp").print("maxBy: ");
env.execute();
}
}
归约聚合(reduce)
调用KeyedStream的reduce方法,实现ReduceFunction接口。在流处理的底层实现过程中,实际是将中间“合并的结果”作为任务的一个状态保存起来的,之后每来一个新的数据,就和之前的聚合状态做归约。
public interface ReduceFunction<T> extends Function, Serializable {
T reduce(T value1, T value2) throws Exception;
}
import org.apache.flink.api.common.functions.MapFunction;
import org.apache.flink.api.common.functions.ReduceFunction;
import org.apache.flink.api.java.tuple.Tuple2;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.DataStreamSource;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.SingleOutputStreamOperator;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.environment.StreamExecutionEnvironment;
public class TransformReduceTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
env.setParallelism(1);
//从元素中读取数据
DataStreamSource<Event> stream = env.fromElements(
new Event("Mary", "./home", 1000L),
new Event("Bob", "./cart", 2000L),
new Event("Alice", "./prod?id=100", 3000L),
new Event("Bob", "./prod?id=1", 3300L),
new Event("Alice", "./prod?id=200", 3200L),
new Event("Bob", "./home", 3500L),
new Event("Bob", "./prod?id=2", 3800L),
new Event("Bob", "./prod?id=3", 4200L)
);
// 1.统计每个用户的访问频次
SingleOutputStreamOperator<Tuple2<String, Long>> clicksByUser = stream.map(new MapFunction<Event, Tuple2<String, Long>>() {
@Override
public Tuple2<String, Long> map(Event value) throws Exception {
return Tuple2.of(value.user, 1L);
}
}).keyBy(data -> data.f0).reduce(new ReduceFunction<Tuple2<String, Long>>() {
@Override
public Tuple2<String, Long> reduce(Tuple2<String, Long> value1, Tuple2<String, Long> value2) throws Exception {
return Tuple2.of(value1.f0, value1.f1 + value2.f1);
}
});
//2.选取当前最活跃的用户
SingleOutputStreamOperator<Tuple2<String, Long>> result = clicksByUser.keyBy(data -> "key").reduce(new ReduceFunction<Tuple2<String, Long>>() {
@Override
public Tuple2<String, Long> reduce(Tuple2<String, Long> value1, Tuple2<String, Long> value2) throws Exception {
return value1.f1 > value2.f1 ? value1 : value2;
}
});
result.print();
env.execute();
}
}
用户自定义函数(UDF)
函数类
对于大部分操作而言,都需要传入一个用户自定义函数,实现相关操作的接口。Flink暴露了所有UDF函数的接口,具体实现的方式为接口或者抽象类,如MapFunction、FilterFunction、ReduceFunction等。
匿名函数(Lambda表达式)
Flink的所有算子都可以适应Lambda表达式的方式来进行编码,但当Lambda表达式使用Java的泛型时,我们需要显示的声明类型信息,使用returns(new TypeHint
富函数类(Rich Function Classes)
所有Flink函数类都有其Rich版本。富函数类一般是以抽象类的形式出现,如:RichMapFunction、RichFilterFunction、 RichReduceFunction 等。
富函数类有比常规的函数类提供更多、更丰富的功能,可以获取运行环境的上下文,并拥有一些生命周期方法。
- open()方法:Rich Function的初始化方法,开启一个算子的生命周期,当一个算子的实际工作方法如map()或者filter()方法被调用之前,open()会首先被调用。像文件IO的创建、数据库连接的创建、配置文件的读取等这样一次性的工作,都适合在open()方法中完成
- close()方法:生命周期中的最后一个调用的方法
另外,富函数类提供了getRuntimeContext()方法,可以获取到运行时上下文的一些信息,例如程序执行的并行度、任务名称、状态。
import org.apache.flink.api.common.functions.RichMapFunction;
import org.apache.flink.configuration.Configuration;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.DataStreamSource;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.environment.StreamExecutionEnvironment;
public class TransformRichFunctionTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
env.setParallelism(1);
//从元素中读取数据
DataStreamSource<Event> stream = env.fromElements(
new Event("Mary", "./home", 1000L),
new Event("Bob", "./cart", 2000L),
new Event("Alice", "./prod?id=100", 3000L),
new Event("Bob", "./prod?id=1", 3300L),
new Event("Alice", "./prod?id=200", 3200L),
new Event("Bob", "./home", 3500L),
new Event("Bob", "./prod?id=2", 3800L),
new Event("Bob", "./prod?id=3", 4200L)
);
stream.map(new MyRichMapper()).print();
env.execute();
}
//实现一个自定义的富函数类
private static class MyRichMapper extends RichMapFunction<Event,Integer>{
@Override
public void open(Configuration parameters) throws Exception {
super.open(parameters);
System.out.println("open生命周期被调用 " + getRuntimeContext().getIndexOfThisSubtask() + "号任务启动");
}
@Override
public Integer map(Event value) throws Exception {
return value.url.length();
}
@Override
public void close() throws Exception {
super.close();
System.out.println("close生命周期被调用 " + getRuntimeContext().getIndexOfThisSubtask() + "号任务结束");
}
}
}
物理分区(Physical Partitioning)
有时我们需要手动控制数据分配策略:当发送数据倾斜时,系统无法自动加载,我们需要重新进行负载均衡,将数据流较为平均地发送到下游任务操作分区中取。常见的物理分区策略有:随机分配(Random)、轮询分配(Round-Robin)、重缩放(Rescale)、广播(Broadcast)
1、随机分区
洗牌,调用shuffle()方法,将数据随机均匀地分配到下游算子的并行任务中
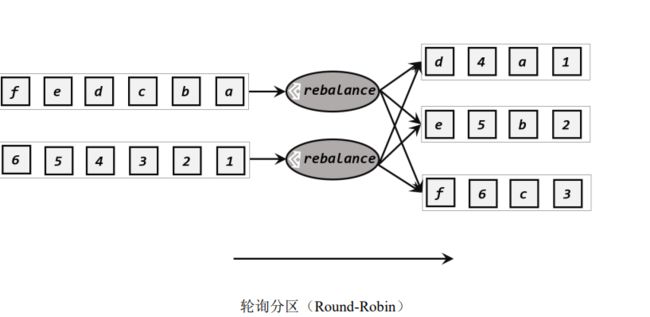
2、轮询分区
发牌,调用rebalance()方法,按照先后顺序将数据依次均匀地分发到下游的并行任务中
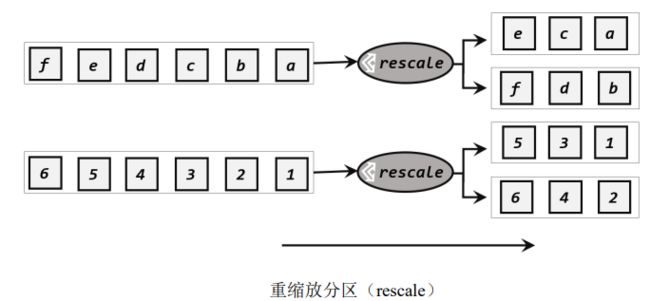
3、重缩放分区
调用rescale()方法,底层使用Round-Robin算法进行轮询。rebalance是每个发牌人面向所有人发牌,而rescale是分成小团体,发牌人只给自己团体内所有人轮流发牌。
当下游任务数量是上游任务数量的整数倍时,rescale的效率会明显更高:
- rebalance是所有分区数据的“重新平衡”,当TaskManager数据量较多时,这种跨节点的网络传输必然影响效率;配置合适数量的task slot,用rescale的方式进行“举报重缩放”,让数据只在当前TaskManager的多个slot之间重新分配,从而避免网络传输带来的损耗
- 底层实现来看,resbalance会真的所有上游任务和所有上游任务之间建立通信信道,笛卡尔积;rescale仅仅针对每一个任务和下游对应部分任务之间建立通信信道。
4、广播
调用broadcast()方法,数据再不同的分区都保留一份,将输入数据复制并发送到下游算子的所有并行任务中
5、全局分区
调用global()方法,将所有的输入流数据都发送到下游算子的第一个并行子任务中,强行让下游任务并行度为1,需谨慎使用,给程序造成很大压力
6、自定义分区
调用partitionCustom()方法,传入两个参数,第一个是自定义分区器(Partitioner),第二个是应用分区器的字段
import org.apache.flink.api.common.functions.Partitioner;
import org.apache.flink.api.java.functions.KeySelector;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.DataStreamSource;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.environment.StreamExecutionEnvironment;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.functions.source.RichParallelSourceFunction;
public class TransformPartitionTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
env.setParallelism(1);
//从元素中读取数据
DataStreamSource<Event> stream = env.fromElements(
new Event("Mary", "./home", 1000L),
new Event("Bob", "./cart", 2000L),
new Event("Alice", "./prod?id=100", 3000L),
new Event("Bob", "./prod?id=1", 3300L),
new Event("Alice", "./prod?id=200", 3200L),
new Event("Bob", "./home", 3500L),
new Event("Bob", "./prod?id=2", 3800L),
new Event("Bob", "./prod?id=3", 4200L)
);
//1. 随机分区
//stream.shuffle().print().setParallelism(4);
//2. 轮询分区
//stream.rebalance().print().setParallelism(4);
//3.rescale重缩放分区
env.addSource(new RichParallelSourceFunction<Integer>() {
@Override
public void run(SourceContext<Integer> ctx) throws Exception {
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
// 将奇偶数分别发送到0号和1号并行分区
if (i % 2 == getRuntimeContext().getIndexOfThisSubtask()){
ctx.collect(i);
}
}
}
@Override
public void cancel() {
}
}).setParallelism(2).
// rescale().
// print().
setParallelism(4);
//4.广播
// stream.broadcast().print().setParallelism(4);
//5.全局分区
//stream.global().print().setParallelism(4);
//6.自定义重分区
env.fromElements(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8).partitionCustom(new Partitioner<Integer>() {
@Override
public int partition(Integer key, int numPartitions) {
return key % 2;
}
}, new KeySelector<Integer, Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer getKey(Integer value) throws Exception {
return value;
}
}).print().setParallelism(4);
env.execute();
}
}