【论文阅读】RAL2020: UFOMap An Efficient Probabilistic 3D Mapping Framework That Embraces the Unknown
Last edited time: March 31, 2023 1:30 PM
-
Reference and prenotes
Paper link:https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9158399
Code link:https://github.com/UnknownFreeOccupied/ufomap
1. Motivation
主要是针对octomap的,framework去做对比和实验
- octomap 对于unknown space并没有进行表示,叶节点状态主要是 是否被占据的概率;而是这对于planning的碰检来说很重要
- 操作octomap是比较耗时而且有限的操作
Contribution
- 显示的进行 unknown space的表达
- 加速查找过程:Indicator values for the inner nodes summarizing the state of children for faster state based queries
- 加速traversal:Morton codes for faster traversal of the octree
- 给八叉树加了一种快速的raycasting方式:A fast ray casting approach for integrating data into the octree
-
voxel hashing:voxblox
Voxblox builds on [13] where they use a spatial hashing scheme and allocate blocks of fixed size when needed
-
octree-based: OctoMap
octomap对比于voxblox 可以更节约内存 or a fixed grid structure 保存在不同分辨率下的八叉树内
2. Method
ufomap基于octomap来看: 每一个node都有一个占据值 去标识是否 occupancy/free/unknown 保存的是log-odds occupancy value
A probabilistic occupancy value is used in order to better handle sensor noise and dynamic environments
与octomap相同的是,每一个node有的是它所有children中的最大占据值,方便路径规划
-
但是octomap中我记得unknown的节点其实是空的(被剪掉的) 为了节约memory的操作,其实也不算 本身其不做 只是为了 memory save的原因 而不做吧?
nope duberg大哥说 即使是空的 octomap 还是给了pointer,一个pointer是8个bits,所以他们只是空了 剪掉了 但是pointer没剪掉 所以这就是为什么下面实验中 ufomap可以省空间的原因,因为ufomap是一个pointer到一个array 里面是children 看下面framework介绍 因为这个问题是我看完全文问的
2.1 Framework
UFOMap 保存三个 indicators i f , i u , i a i_f,i_u,i_a if,iu,ia
-
前两个指示 这个是否是free/unknown,而被占据的不需要再单独给出一个 因为有 occupancy value;
注意,当更新Octree时 indicator values 也会随着树向上传播 propagated upwards
-
最后一个则是判断所有children是否是一样的,主要是在自动pruning被禁止时 可以有相同的功能
自动pruning 意味着当数据被删除或者插入数据时,octree会自动pruned,而禁止他的主要原因是 我们想同时进行读取、插入和删除数据
而此 indicators 也可以提高 traversing 整个树的效率,比如当我们仅寻找unknown space的时候
问题区
-
indicator values 和 occupancy values不是同一个东西?
不是 indicator 是 0/1 occupancy value是一个float值
-
这里的 pruning 被禁止 可以有相同的功能是指?人为去判断是否要进行嘛?
[原文: i a i_a ia is useful in cases where automatic pruning has been disabled, but you still want the same behavior as if it were enabled. ]
是的 原文里 有 同时进行访问 插入 删除的时候 会禁止,这种情况下 就由 我们手动指定什么时候做 prune
-
pruned 操作在 code 中的体现?
不用管 用就行了
-
[原文:The third indicator, ia, indicates whether all of a node’s children are the same. ] 这里的判断是否是一样的是指 前面两个 indicators嘛?还是指 free/occupancy/unknown
感觉是的… 确认一下吧
MK: 根据Fig 2图c感觉应该就是(~if) | (~iu)。图里没给if iu都是0的情况,但ia=1应该不需要找children了,而if iu都是0说明全occupied,应该还要找到d_max为止
2.2 Node
A. State 节点状态
OctoMap 的节点状态 如下表示:
state ( n ) = { unknown if n is null pointer occupied if t o ≤ occ ( n ) free else. \operatorname{state}(n)= \begin{cases}\text { unknown } & \text { if } n \text { is null pointer } \\ \text { occupied } & \text { if } t_o \leq \operatorname{occ}(n) \\ \text { free } & \text { else. }\end{cases} state(n)=⎩ ⎨ ⎧ unknown occupied free if n is null pointer if to≤occ(n) else.
- occ(n) 表示了 node n的occupancy value
- t o t_o to 表示OctoMap里的阈值 value超过这个值 则意味着 occupied
而 UFOMap 里的节点状态 进行了一点扩充 加入了另一个 t f t_f tf 阈值 来只是如果超过小于此 则说明是free状态
state ( n ) = { unknown if t f ≤ occ ( n ) ≤ t o occupied if t o < occ ( n ) free if t f > occ ( n ) \operatorname{state}(n)= \begin{cases}\text { unknown } & \text { if } t_f \leq \operatorname{occ}(n) \leq t_o \\ \text { occupied } & \text { if } t_o<\operatorname{occ}(n) \\ \text { free } & \text { if } t_f>\operatorname{occ}(n)\end{cases} state(n)=⎩ ⎨ ⎧ unknown occupied free if tf≤occ(n)≤to if to<occ(n) if tf>occ(n)
比如 设定 tf = 0.1 to=0.9,节点本身只有在确定自己是被占据/free的时候 才给状态 否则就是未知,这对于 exploration和reconstruction的任务 可以快速定位到 unknown 进行处理
再比如 设定 tf=0.5 to=0.9 则意味着 exploration algorithm 可以将注意力集中在 occupancy 区域. meaning you would target higher certainty about the occupied space.
-
tf=0.5 to=0.9的时候 为什么是 [meaning you would target higher certainty about the occupied space.] 主要是对occ的判断只和 to有关 to=0.9是不变的,只是说变unknown的条件更严格了吧?
是的 因为前面的是 tf=0.1 to=0.9 所以是对free和occupied都 严格; tf=0.5 to=0.9的画 就是只对occupied严格了,duberg说他应该写一个only
B. Types
OctoMap: inner nodes and inner leaf nodes
UFOMap: inner nodes, inner leaf nodes, and leaf nodes. [多了一个leaf node]
以下为详细的解释:
- inner nodes 是指所有 有 children 的 nodes,一个inner node里面包含:
- log-odds occupancy value
- three indicators [在前面提到的 i f , i u , i a i_f,i_u,i_a if,iu,ia ]
- 一个指向其children的指针数组 [a pointer to an array of its children]
- inner leaf nodes,和上面那个完全相同,不通电在于 inner nodes 没有children 也就是 child pointer是一个空的指针 【这是OctoMap里面仅存在的leaf node】
- leaf nodes 仅存储 log-odd value 对比 inner leaf node, leaf node 不可能会有children
下图是三个nodes的展示:

(b, c) 是 UFOMap的哈:
- 从c顶端可以看到的 是 inner nodes 具有:log-odds value, indicators, 指向child pointer
- 然后往下第二层,没有children 指针的那些都是 inner leaf nodes
- 再往下最后一层 只有occupancy value是 leaf node
-
那这个inner leaf nodes存在的意义是?
名字 进行区分
-
这两句话 inner leaf node 和 leaf node都没有 children不是矛盾的嘛?
- the inner leaf nodes have no children, meaning the child pointer is a null pointer
- Compared to an inner leaf node, it is not possible for a leaf node to have children.
【我感觉是 区别应该是 是否有 indicators】
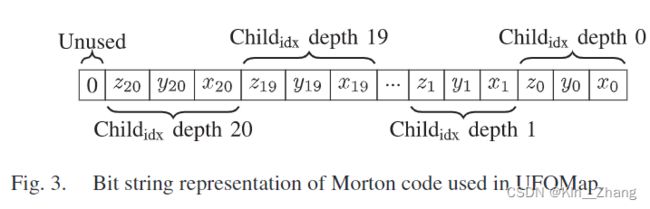
2.3 Morton codes
参考文献[15] 中文博客有一些解释:莫顿码:莫顿码是将多维数据转化为一维数据的编码
-
首先将 笛卡尔坐标系的 点云 c = ( c x , c y , c z ) ∈ R 3 c = (c_x,c_y,c_z) \in \R^3 c=(cx,cy,cz)∈R3 转到 octree node的index tuple k = ( k x , k y , k z ) ∈ N 0 3 k=(k_x,k_y,k_z) \in \N^3_0 k=(kx,ky,kz)∈N03 ,其中 k的计算为:
k j = ⌊ c j res ⌋ + 2 d max − 1 k_j=\left\lfloor\frac{c_j}{\text { res }}\right\rfloor+2^{d_{\max }-1} kj=⌊ res cj⌋+2dmax−1
-
如下图所示的通过交错表示 kj 的位,可以为 一个点云坐标闯进对应的 莫顿码 m
-
然后可以从根节点向下遍历到这个节点,原文 From the root node it is then possible to traverse down to the node by simply looking at the three bits of m m m that corresponds to the depth of the child and moving to that child
-
代码中 这里 右移 又左移 不就没有了定位到那个depth了嘛?
using code_t = uint64_t; using depth_t = uint8_t; /*! * @brief Return the code at a specified depth * * @param depth The depth of the code * @return Code The code at the specified depth */ constexpr Code toDepth(depth_t depth) const { code_t temp = 3 * depth; return Code((code_ >> temp) << temp, depth); // (code_ >> temp) << temp }因为 右移左移 可以有设0,当然ufomap2.0【还没发布】已经做了更聪明的方式
举个例子 [1111 1111] 经过 右移三位是 [1111 1],然后左移三位[1111 1000] 所以还是有区别的
2.4 Integrating Point Cloud
终于 讲完了 不擅长的部分 虽然遗留的问题好像还是有点多 … 等等 问问duberg吧 作者在身边的好处就是这个 hhh
这一部分主要就是怎么根据点云进行生成occupancy value了,一共有三种方法 每一种都比前一种更快,但是更快的
-
参考 [17] 对于每一个点! trace a ray 减少从 传感器出发点 到 终点hit point之间所有grid的occupancy value,然后hit point的地方 占用值增加 【Same in OctoMap】
-
对于点先进行离散化 如果多个点落在同一个grid里 对这一个grid只做一次 ray casting 【Same in OctoMap】
-
Fast Discrete: ray casting 和 离散化 是在八叉树的不同深度进行的
- 简单的 ray marching 步长固定 为 深度 d d d 对应的分辨率
- Ray marching步骤一直执行到 n n n 的节点 [原文: Ray marching is performed untilnnodes, at thatresolution, away from the end node.]
- 从这里开始 我们会在 lower depth 进行ray marching 直到我们到达 depth 0 也就是 leaf node depth,但是不同于上面的固定步长,这里我们切换到方法二的ray casting
其中 d 和 n 是可以调节的参数 用来平衡 效果和速度;举两个极端的例子:
- d = 0的时候 也就是 在 leaf node 上的分辨率 也就是最小分辨率 那么就是方法二的
- n = 0的时候 则是 只有在d的空间才会被赋值,比如 下图 f中 是不是橙色点后面还有紫色区域(free space)
- 更多例子见下图

其中为了 补偿 occupancy value在方法三 遇到 larger surface 下降的情况,the clearing 会有一个因子 1 2 d + 1 \frac{1}{2d+1} 2d+11
在所有方法中 occupancy grid都是以最高分辨率进行的更新,因此三种ray方案在occupancy 下 几乎是一样的 如上图四的比较
问题区
-
Ray marching is performed until n nodes, at that resolution, away from the end node. 远离end node是什么意思? 不太懂
是指 这个分辨率 还没到 end node 也就是leaf node
3. Experiments
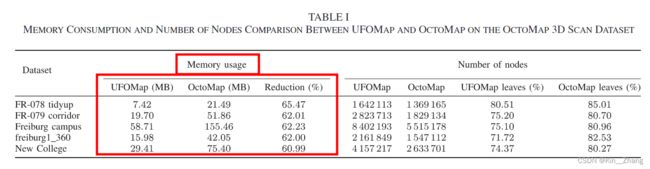
首先是关于区分 inner leaf node 和 leaf node ,因为OctoMap里面 他们都是一个 inner leaf node
从 [5] 中 我们得知 大多数 octree node 在OctoMap 里都是 inner leaf node [80-85%] 而在UFOMap里面 因为我们再次做了区分,所以这个值下降了71-81%,也就是说大部分节点 其实是leaf node,通过UFOMap的再次划分 即使是我们的树节点总数增加的情况下,也可以明显减少内存使用量 对比OctoMap 减少了三倍 【参考问题 ① 】
-
① 这个内存减少 如果 inner leaf node里面只存了log-odd value 再加上一个空指针 并不会耗多少memeory吧?所以减少的不是因为 我们把 inner leaf node区分开了吧? !!问一下duberg
因为实际上的octomap上存的虽然是空指针 但是一个指针 8bits, 即使空的 9*8=72,但是ufomap只需要一个pointer,也就是8个bits,然后指针指向children array开头,而octomap需要先做一个pointer指向parent的指针位置 然后再指向找到想到的那个children的pointer
图五则是不同的 ray 方案 也就是 2.4里提到的:

这里则是不同的操作的时间对比 主要和OctoMap对比

Other words
妙啊,然后有 作者Duberg 再旁边解释 也太爽了 hhhh 当然里面的解释还是我转述的哈,如果有啥不对的 不是Duberg哥的锅 是我的理解的锅
Duberg 大哥和我说 不用看内在代码 用就行了,寻思着 我写的C++技巧过多 你可能陷进去了
最后 February 22, 2023 更新一下用UFOMap做下游任务的一系列paper 现在ufomap的文档还没更新 所以使用者都是由作者手把手教学 hhh 等后面文档更新了 可能使用的人可以开始变得更多
- 天明哥的 SLAM 开源了:SLICT: Multi-Input Multi-Scale Surfel-Based Lidar-Inertial Continuous-Time Odometry and Mapping
- Duberg在1.0的基础上做了 planning 工作 UFOExplorer:UFOExplorer: Fast and Scalable Sampling-Based Exploration With a Graph-Based Planning Structure
- 本人小试… 还在进行中 等后面来更新
赠人点赞 手有余香 ;正向回馈 才能更好开放记录 hhh