【yolov8目标检测】使用yolov8训练自己的数据集
目录
准备数据集
python安装yolov8
配置yaml
从0开始训练
从预训练模型开始训练
准备数据集
首先得准备好数据集,你的数据集至少包含images和labels,严格来说你的images应该包含训练集train、验证集val和测试集test,不过为了简单说明使用步骤,其中test可以不要,val和train可以用同一个,因此我这里只用了一个images
其中images装的是图片数据,labels装的是与图片一一对应同名的yolo格式txt,即类别号,经过归一化的中心x和y坐标以及宽和高
python安装yolov8
然后我们开始准备yolov8,使用python的API的话就比较简单,首先安装一下yolov8
用pip的话安装的话
pip install ultralytics使用pycharm安装的话
配置yaml
安装完了之后,差不多就可以开始了,我们首先看看官方给的代码
from ultralytics import YOLO
# Load a model
model = YOLO("yolov8n.yaml") # build a new model from scratch
model = YOLO("yolov8n.pt") # load a pretrained model (recommended for training)
# Use the model
model.train(data="coco128.yaml", epochs=3) # train the model
metrics = model.val() # evaluate model performance on the validation set
results = model("https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg") # predict on an image
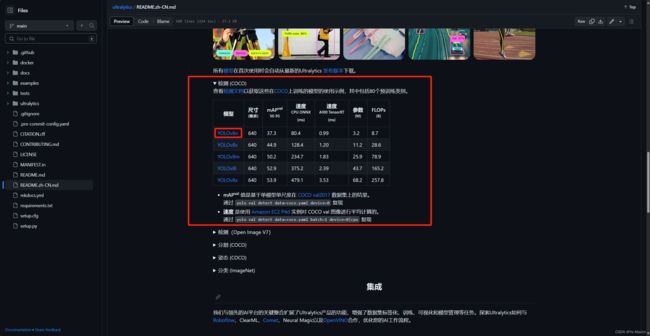
path = model.export(format="onnx") # export the model to ONNX format其中迷惑的是yolov8n.yaml、yolov8n.pt和coco128.yaml这几个文件,yolov8n.yaml是yolov8的配置,yolov8n.pt是预训练的模型,coco128.yaml是coco数据集的配置参数
因此如果我们想要训练自己的模型的话,需要修改一下配置文件,首先到GitHub上下载yolov8n.yaml和coco128.yaml下来,这两个文件的位置有可能会变,所以最好在仓库上直接搜索
大概长这样,你也可以自己创建,然后把内容复制进去
yolov8n.yaml
# Ultralytics YOLO , AGPL-3.0 license
# YOLOv8 object detection model with P3-P5 outputs. For Usage examples see https://docs.ultralytics.com/tasks/detect
# Parameters
nc: 80 # number of classes
scales: # model compound scaling constants, i.e. 'model=yolov8n.yaml' will call yolov8.yaml with scale 'n'
# [depth, width, max_channels]
n: [0.33, 0.25, 1024] # YOLOv8n summary: 225 layers, 3157200 parameters, 3157184 gradients, 8.9 GFLOPs
s: [0.33, 0.50, 1024] # YOLOv8s summary: 225 layers, 11166560 parameters, 11166544 gradients, 28.8 GFLOPs
m: [0.67, 0.75, 768] # YOLOv8m summary: 295 layers, 25902640 parameters, 25902624 gradients, 79.3 GFLOPs
l: [1.00, 1.00, 512] # YOLOv8l summary: 365 layers, 43691520 parameters, 43691504 gradients, 165.7 GFLOPs
x: [1.00, 1.25, 512] # YOLOv8x summary: 365 layers, 68229648 parameters, 68229632 gradients, 258.5 GFLOPs
# YOLOv8.0n backbone
backbone:
# [from, repeats, module, args]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [64, 3, 2]] # 0-P1/2
- [-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]] # 1-P2/4
- [-1, 3, C2f, [128, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]] # 3-P3/8
- [-1, 6, C2f, [256, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]] # 5-P4/16
- [-1, 6, C2f, [512, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [1024, 3, 2]] # 7-P5/32
- [-1, 3, C2f, [1024, True]]
- [-1, 1, SPPF, [1024, 5]] # 9
# YOLOv8.0n head
head:
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']]
- [[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P4
- [-1, 3, C2f, [512]] # 12
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']]
- [[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P3
- [-1, 3, C2f, [256]] # 15 (P3/8-small)
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]]
- [[-1, 12], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P4
- [-1, 3, C2f, [512]] # 18 (P4/16-medium)
- [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]]
- [[-1, 9], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P5
- [-1, 3, C2f, [1024]] # 21 (P5/32-large)
- [[15, 18, 21], 1, Detect, [nc]] # Detect(P3, P4, P5)coco128.yaml
# Ultralytics YOLO , AGPL-3.0 license
# COCO128 dataset https://www.kaggle.com/ultralytics/coco128 (first 128 images from COCO train2017) by Ultralytics
# Example usage: yolo train data=coco128.yaml
# parent
# ├── ultralytics
# └── datasets
# └── coco128 ← downloads here (7 MB)
# Train/val/test sets as 1) dir: path/to/imgs, 2) file: path/to/imgs.txt, or 3) list: [path/to/imgs1, path/to/imgs2, ..]
path: ../datasets/coco128 # dataset root dir
train: images/train2017 # train images (relative to 'path') 128 images
val: images/train2017 # val images (relative to 'path') 128 images
test: # test images (optional)
# Classes
names:
0: person
1: bicycle
2: car
3: motorcycle
4: airplane
5: bus
6: train
7: truck
8: boat
9: traffic light
10: fire hydrant
11: stop sign
12: parking meter
13: bench
14: bird
15: cat
16: dog
17: horse
18: sheep
19: cow
20: elephant
21: bear
22: zebra
23: giraffe
24: backpack
25: umbrella
26: handbag
27: tie
28: suitcase
29: frisbee
30: skis
31: snowboard
32: sports ball
33: kite
34: baseball bat
35: baseball glove
36: skateboard
37: surfboard
38: tennis racket
39: bottle
40: wine glass
41: cup
42: fork
43: knife
44: spoon
45: bowl
46: banana
47: apple
48: sandwich
49: orange
50: broccoli
51: carrot
52: hot dog
53: pizza
54: donut
55: cake
56: chair
57: couch
58: potted plant
59: bed
60: dining table
61: toilet
62: tv
63: laptop
64: mouse
65: remote
66: keyboard
67: cell phone
68: microwave
69: oven
70: toaster
71: sink
72: refrigerator
73: book
74: clock
75: vase
76: scissors
77: teddy bear
78: hair drier
79: toothbrush
# Download script/URL (optional)
download: https://ultralytics.com/assets/coco128.zip然后修改yolov8n.yaml,把nc的数值改成你的数据集的类别数,我这里的数据集只有乌骨鸡和狮头鹅两个
# Ultralytics YOLO , AGPL-3.0 license
# YOLOv8 object detection model with P3-P5 outputs. For Usage examples see https://docs.ultralytics.com/tasks/detect
# Parameters
nc: 2 # number of classes
scales: # model compound scaling constants, i.e. 'model=yolov8n.yaml' will call yolov8.yaml with scale 'n'
# [depth, width, max_channels]
n: [0.33, 0.25, 1024] # YOLOv8n summary: 225 layers, 3157200 parameters, 3157184 gradients, 8.9 GFLOPs
s: [0.33, 0.50, 1024] # YOLOv8s summary: 225 layers, 11166560 parameters, 11166544 gradients, 28.8 GFLOPs
m: [0.67, 0.75, 768] # YOLOv8m summary: 295 layers, 25902640 parameters, 25902624 gradients, 79.3 GFLOPs
l: [1.00, 1.00, 512] # YOLOv8l summary: 365 layers, 43691520 parameters, 43691504 gradients, 165.7 GFLOPs
x: [1.00, 1.25, 512] # YOLOv8x summary: 365 layers, 68229648 parameters, 68229632 gradients, 258.5 GFLOPs
# YOLOv8.0n backbone
backbone:
# [from, repeats, module, args]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [64, 3, 2]] # 0-P1/2
- [-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]] # 1-P2/4
- [-1, 3, C2f, [128, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]] # 3-P3/8
- [-1, 6, C2f, [256, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]] # 5-P4/16
- [-1, 6, C2f, [512, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [1024, 3, 2]] # 7-P5/32
- [-1, 3, C2f, [1024, True]]
- [-1, 1, SPPF, [1024, 5]] # 9
# YOLOv8.0n head
head:
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']]
- [[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P4
- [-1, 3, C2f, [512]] # 12
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']]
- [[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P3
- [-1, 3, C2f, [256]] # 15 (P3/8-small)
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]]
- [[-1, 12], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P4
- [-1, 3, C2f, [512]] # 18 (P4/16-medium)
- [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]]
- [[-1, 9], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P5
- [-1, 3, C2f, [1024]] # 21 (P5/32-large)
- [[15, 18, 21], 1, Detect, [nc]] # Detect(P3, P4, P5)
然后修改coco128.yaml,我把文件名也改成了data.yaml,path改成images和labels的上一级目录地址,train改成训练集相对于path的地址,val也是改成验证集的相对于path的地址,我这里训练集和验证集用的是同一个嘿嘿嘿,然后把test注释掉,因为我没用测试集,还有就是names那里改成你的训练集的类别名,并把多余的类别删掉
# Ultralytics YOLO , AGPL-3.0 license
# COCO128 dataset https://www.kaggle.com/ultralytics/coco128 (first 128 images from COCO train2017) by Ultralytics
# Example usage: yolo train data=coco128.yaml
# parent
# ├── ultralytics
# └── datasets
# └── coco128 ← downloads here (7 MB)
# Train/val/test sets as 1) dir: path/to/imgs, 2) file: path/to/imgs.txt, or 3) list: [path/to/imgs1, path/to/imgs2, ..]
path: C:/Users/Yezi/Desktop/人工智能实训/HW2/data # dataset root dir
train: images # train images (relative to 'path') 128 images
val: images # val images (relative to 'path') 128 images
#test: # test images (optional)
# Classes
names:
0: goose
1: chicken这样子就配置好了
然后开始训练
从0开始训练
下面是从0开始训练的过程
其实训练的代码就两行
model = YOLO("yolov8n.yaml") # build a new model from scratch
model.train(data="data.yaml", epochs=5) # train the model不过从0开始训练的效果并不好,下面是我自己的测试代码,由于我电脑比较烂,GPU摆不上用场,所以只能用cpu训练
from ultralytics import YOLO
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
model = YOLO("yolov8n.yaml") # build a new model from scratch
model.train(data="data.yaml", epochs=30, device='cpu') # train the model
model.val(data="data.yaml")
results = model(r"C:\Users\Yezi\Desktop\人工智能实训\HW2\data\images\00909.jpg") # predict on an image
plt.imshow(results[0].plot())
plt.show()
results = model(r"C:\Users\Yezi\Desktop\人工智能实训\HW2\data\images\100318.jpg") # predict on an image
plt.imshow(results[0].plot())
plt.show()
从预训练模型开始训练
官方推荐用预训练好的模型开始训练
首先下载一个官方预训练好的模型
我这里下载的是yolov8n
然后使用预训练模型训练我的数据集
from ultralytics import YOLO
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
model=YOLO("yolov8n.pt")
model.train(data="data.yaml", epochs=30, device='cpu') # train the model
model.val(data="data.yaml")
results = model(r"C:\Users\Yezi\Desktop\人工智能实训\HW2\data\images\00909.jpg") # predict on an image
plt.imshow(results[0].plot())
plt.show()
results = model(r"C:\Users\Yezi\Desktop\人工智能实训\HW2\data\images\100318.jpg") # predict on an image
plt.imshow(results[0].plot())
plt.show()
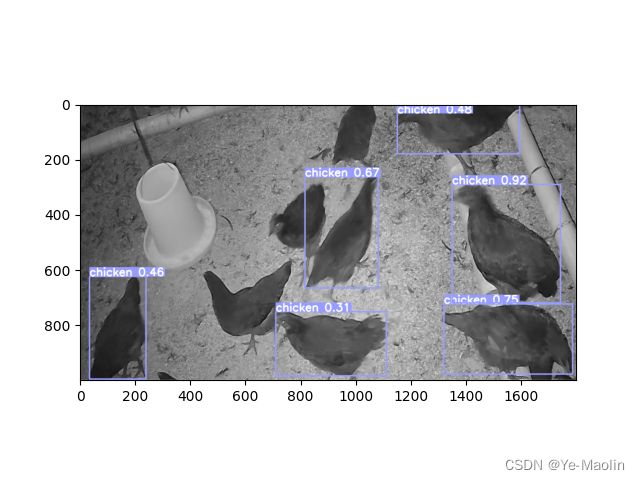
乌骨鸡的效果是这样的
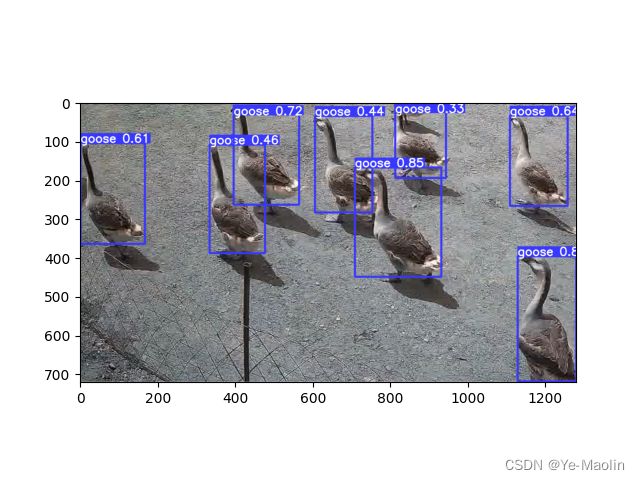
狮头鹅的效果是这样的