若依前后端分离版源码分析-前端头像上传后传递到后台以及在服务器上存储和数据库存储设计
场景
使用若依前后端分离版本时,分析其头像上传机制。
可作为续参考学习。
注:
博客:
https://blog.csdn.net/badao_liumang_qizhi
关注公众号
霸道的程序猿
获取编程相关电子书、教程推送与免费下载。
实现
首先是前端,登录成功点击个人中心
对应的代码为
![]()
个人中心
布局设置
退出登录
这里的img就是右上角的头像图片,这里的的src属性后面讲。
然后点击个人中心时,跳转到user/profile/index.vue,这里的头像引用的头像组件并且传递user对象参数。
个人信息
-
这里传递的user是从后台数据库查询的用户数据
created() {
this.getUser();
},
methods: {
getUser() {
getUserProfile().then(response => {
this.user = response.data;
this.roleGroup = response.roleGroup;
this.postGroup = response.postGroup;
});
}
}
在个人信息页面加载完成就请求后台获取数据。
请求后台的数据是调用的getUserProfile,此方法是调用数据的接口方法
// 查询用户个人信息
export function getUserProfile() {
return request({
url: '/system/user/profile',
method: 'get'
})
}
请求的后台接口
@GetMapping
public AjaxResult profile()
{
LoginUser loginUser = tokenService.getLoginUser(ServletUtils.getRequest());
SysUser user = loginUser.getUser();
AjaxResult ajax = AjaxResult.success(user);
ajax.put("roleGroup", userService.selectUserRoleGroup(loginUser.getUsername()));
ajax.put("postGroup", userService.selectUserPostGroup(loginUser.getUsername()));
return ajax;
}
后台接口中在通过token的服务类获取登录的用户的相关信息,然后返回给前端。
前面讲讲上面获取的登录用户的信息传递给用户头像组件,通过如下方式
然后来到用户头像组件,页面效果为
此组件对应的代码为
![点击上传头像]()
![]()
上传
提 交
在此组件中用到了图片裁剪组件vue-cropper并且其自带的预览效果,然后图片上传使用了
el-upload。
在此组件中接收上面传递过来的用户信息参数
props: {
user: {
type: Object
}
},
但是接收到的用户信息在此组件中并没有使用,对于裁剪图片的url使用的是
img: store.getters.avatar, //裁剪图片的地址
store来源外部js
import store from "@/store";
在外部js中
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import app from './modules/app'
import user from './modules/user'
import tagsView from './modules/tagsView'
import permission from './modules/permission'
import settings from './modules/settings'
import getters from './getters'
Vue.use(Vuex)
const store = new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
app,
user,
tagsView,
permission,
settings
},
getters
})
export default store
使用的是Vuex的Store作为缓存。
而且在此组件中也没有调用后台接口获取头像
created(){
this.getUserAvator();
},
methods: {
//查询数据库获取用户头像
getUserAvator(){
},
方法为空,具体可以根据自己的需要去决定是否请求后台数据获取头像。
这里是直接从缓存中直接取值,缓存中的值是在登录的是后请求后台接口直接获取用户的头像信息并存入缓存。
在登录页面Login.vue中,点击登录对应的方法中
handleLogin() {
this.$refs.loginForm.validate(valid => {
if (valid) {
this.loading = true;
if (this.loginForm.rememberMe) {
Cookies.set("username", this.loginForm.username, { expires: 30 });
Cookies.set("password", encrypt(this.loginForm.password), { expires: 30 });
Cookies.set('rememberMe', this.loginForm.rememberMe, { expires: 30 });
} else {
Cookies.remove("username");
Cookies.remove("password");
Cookies.remove('rememberMe');
}
this.$store
.dispatch("Login", this.loginForm)
.then(() => {
this.$router.push({ path: this.redirect || "/" });
})
.catch(() => {
this.loading = false;
this.getCode();
});
}
});
}
验证并且存储用户名密码等操作后通过
this.$store
.dispatch("Login", this.loginForm)
调用store下的modules下的user.js下Login
actions: {
// 登录
Login({ commit }, userInfo) {
const username = userInfo.username.trim()
const password = userInfo.password
const code = userInfo.code
const uuid = userInfo.uuid
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
login(username, password, code, uuid).then(res => {
setToken(res.token)
commit('SET_TOKEN', res.token)
resolve()
}).catch(error => {
reject(error)
})
})
},
然后在权限验证的permission.js中
import router from './router'
import store from './store'
import { Message } from 'element-ui'
import NProgress from 'nprogress'
import 'nprogress/nprogress.css'
import { getToken } from '@/utils/auth'
NProgress.configure({ showSpinner: false })
const whiteList = ['/login', '/auth-redirect', '/bind', '/register']
router.beforeEach((to, from, next) => {
NProgress.start()
if (getToken()) {
/* has token*/
if (to.path === '/login') {
next({ path: '/' })
NProgress.done()
} else {
if (store.getters.roles.length === 0) {
// 判断当前用户是否已拉取完user_info信息
store.dispatch('GetInfo').then(res => {
// 拉取user_info
const roles = res.roles
store.dispatch('GenerateRoutes', { roles }).then(accessRoutes => {
// 测试 默认静态页面
// store.dispatch('permission/generateRoutes', { roles }).then(accessRoutes => {
// 根据roles权限生成可访问的路由表
router.addRoutes(accessRoutes) // 动态添加可访问路由表
next({ ...to, replace: true }) // hack方法 确保addRoutes已完成
})
})
.catch(err => {
store.dispatch('FedLogOut').then(() => {
Message.error(err)
next({ path: '/' })
})
})
} else {
next()
// 没有动态改变权限的需求可直接next() 删除下方权限判断 ↓
// if (hasPermission(store.getters.roles, to.meta.roles)) {
// next()
// } else {
// next({ path: '/401', replace: true, query: { noGoBack: true }})
// }
// 可删 ↑
}
}
} else {
// 没有token
if (whiteList.indexOf(to.path) !== -1) {
// 在免登录白名单,直接进入
next()
} else {
next(`/login?redirect=${to.fullPath}`) // 否则全部重定向到登录页
NProgress.done()
}
}
})
router.afterEach(() => {
NProgress.done()
})
又执行了拉取登录用户信息的方法,在拉取用户信息的方法中
// 获取用户信息
GetInfo({ commit, state }) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
getInfo(state.token).then(res => {
const user = res.user
if (res.roles && res.roles.length > 0) { // 验证返回的roles是否是一个非空数组
commit('SET_ROLES', res.roles)
commit('SET_PERMISSIONS', res.permissions)
} else {
commit('SET_ROLES', ['ROLE_DEFAULT'])
}
commit('SET_NAME', user.userName)
commit('SET_AVATAR', avatar)
resolve(res)
}).catch(error => {
reject(error)
})
})
},
将用户头像存储进缓存中,通过
commit('SET_AVATAR', avatar)
而这里的获取用户头像的路径的方法是如下,这里修改过
判断从后台查询的头像路径是否为空,如果为空的话则使用默认图片。
const avatar = (user.avatar == "" || !user ) ? require("@/assets/image/profile.jpg") : process.env.VUE_APP_BASE_API + user.avatar;
这就是为什么在进行上传头像时能在缓存中取到头像。
然后点击上面的上传按钮执行的方法
// 上传图片
uploadImg() {
this.$refs.cropper.getCropBlob(data => {
let formData = new FormData();
formData.append("avatarfile", data);
uploadAvatar(formData).then(response => {
if (response.code === 200) {
this.open = false;
debugger
this.options.img = process.env.VUE_APP_BASE_API + response.imgUrl;
store.commit('SET_AVATAR', this.options.img);
this.msgSuccess("修改成功");
}
this.visible = false;
});
首先将图片上传到服务器,然后上传成功后将返回的头像的路径存在缓存中。
调用了上传头像的接口方法uploadAvator
// 用户头像上传
export function uploadAvatar(data) {
return request({
url: '/system/user/profile/avatar',
method: 'post',
data: data
})
}
来到上传照片对应的后台接口
@PostMapping("/avatar")
public AjaxResult avatar(@RequestParam("avatarfile") MultipartFile file) throws IOException
{
if (!file.isEmpty())
{
LoginUser loginUser = tokenService.getLoginUser(ServletUtils.getRequest());
String avatar = FileUploadUtils.upload(RuoYiConfig.getAvatarPath(), file);
if (userService.updateUserAvatar(loginUser.getUsername(), avatar))
{
AjaxResult ajax = AjaxResult.success();
ajax.put("imgUrl", avatar);
// 更新缓存用户头像
loginUser.getUser().setAvatar(avatar);
tokenService.setLoginUser(loginUser);
return ajax;
}
}
return AjaxResult.error("上传图片异常,请联系管理员");
}
在后台接口中首先是使用Token的service获取当前登录的用户。
然后调用文件上传工具类的文件上传方法upload,参数为在application.yml中设置的上传文件的路径和文件。
RuoYiConfig.getAvatarPath()中
public static String getAvatarPath()
{
return getProfile() + "/avatar";
}
调用getProfile方法并且拼接一个avatar路径。
在方法getProfile中
public static String getProfile()
{
return profile;
}
返回profile节点的值
/** 上传路径 */
private static String profile;
此配置类使用了注解就可以获取到application.yml中配置的profile节点所对应的配置内容
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "ruoyi")
public class RuoYiConfig
{
/** 项目名称 */
private String name;
/** 版本 */
private String version;
/** 版权年份 */
private String copyrightYear;
/** 实例演示开关 */
private boolean demoEnabled;
/** 上传路径 */
private static String profile;
最终获取的是下面配置的D:ruoyi/uploadPath路径
再回到上面的upload方法
public static final String upload(String baseDir, MultipartFile file) throws IOException
{
try
{
return upload(baseDir, file, MimeTypeUtils.DEFAULT_ALLOWED_EXTENSION);
}
catch (Exception e)
{
throw new IOException(e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
此方法是根据文件路径进行上传,文件路径已经在上面进行指定。
其中又调用了upload方法,第三个参数是用来指定文件的后缀名
public static final String[] DEFAULT_ALLOWED_EXTENSION = {
// 图片
"bmp", "gif", "jpg", "jpeg", "png",
// word excel powerpoint
"doc", "docx", "xls", "xlsx", "ppt", "pptx", "html", "htm", "txt",
// 压缩文件
"rar", "zip", "gz", "bz2",
// pdf
"pdf" };
在上传的方法中
/**
* 文件上传
*
* @param baseDir 相对应用的基目录
* @param file 上传的文件
* @param extension 上传文件类型
* @return 返回上传成功的文件名
* @throws FileSizeLimitExceededException 如果超出最大大小
* @throws FileNameLengthLimitExceededException 文件名太长
* @throws IOException 比如读写文件出错时
* @throws InvalidExtensionException 文件校验异常
*/
public static final String upload(String baseDir, MultipartFile file, String[] allowedExtension)
throws FileSizeLimitExceededException, IOException, FileNameLengthLimitExceededException,
InvalidExtensionException
{
int fileNamelength = file.getOriginalFilename().length();
if (fileNamelength > FileUploadUtils.DEFAULT_FILE_NAME_LENGTH)
{
throw new FileNameLengthLimitExceededException(FileUploadUtils.DEFAULT_FILE_NAME_LENGTH);
}
assertAllowed(file, allowedExtension);
String fileName = extractFilename(file);
File desc = getAbsoluteFile(baseDir, fileName);
file.transferTo(desc);
String pathFileName = getPathFileName(baseDir, fileName);
return pathFileName;
}
首先是进行文件长度的判断,这里是指定的100
然后通过assertAllowed对文件大小进行校验,具体实现方法
/**
* 文件大小校验
*
* @param file 上传的文件
* @return
* @throws FileSizeLimitExceededException 如果超出最大大小
* @throws InvalidExtensionException
*/
public static final void assertAllowed(MultipartFile file, String[] allowedExtension)
throws FileSizeLimitExceededException, InvalidExtensionException
{
long size = file.getSize();
if (DEFAULT_MAX_SIZE != -1 && size > DEFAULT_MAX_SIZE)
{
throw new FileSizeLimitExceededException(DEFAULT_MAX_SIZE / 1024 / 1024);
}
String fileName = file.getOriginalFilename();
String extension = getExtension(file);
if (allowedExtension != null && !isAllowedExtension(extension, allowedExtension))
{
if (allowedExtension == MimeTypeUtils.IMAGE_EXTENSION)
{
throw new InvalidExtensionException.InvalidImageExtensionException(allowedExtension, extension,
fileName);
}
else if (allowedExtension == MimeTypeUtils.FLASH_EXTENSION)
{
throw new InvalidExtensionException.InvalidFlashExtensionException(allowedExtension, extension,
fileName);
}
else if (allowedExtension == MimeTypeUtils.MEDIA_EXTENSION)
{
throw new InvalidExtensionException.InvalidMediaExtensionException(allowedExtension, extension,
fileName);
}
else
{
throw new InvalidExtensionException(allowedExtension, extension, fileName);
}
}
}
然后调用extractFilename对文件名进行编码,具体实现
/**
* 编码文件名
*/
public static final String extractFilename(MultipartFile file)
{
String fileName = file.getOriginalFilename();
String extension = getExtension(file);
fileName = DateUtils.datePath() + "/" + encodingFilename(fileName) + "." + extension;
return fileName;
}
这其中获取文件名和扩展名再调用工具类生成一个日期路径,比如下面的示例2018/08/08
/**
* 日期路径 即年/月/日 如2018/08/08
*/
public static final String datePath() {
Date now = new Date();
return DateFormatUtils.format(now, "yyyy/MM/dd");
}
encodingFilename:
/**
* 编码文件名
*/
private static final String encodingFilename(String fileName)
{
fileName = fileName.replace("_", " ");
fileName = Md5Utils.hash(fileName + System.nanoTime() + counter++);
return fileName;
}
其中又调用了工具类的hash方法和获取当前时间的纳秒并且加上一个递增的计数变量。
private static int counter = 0;
在hash方法中
public static String hash(String s)
{
try
{
return new String(toHex(md5(s)).getBytes("UTF-8"), "UTF-8");
}
catch (Exception e)
{
log.error("not supported charset...{}", e);
return s;
}
}
完整的MD5加密工具类Md5Utils代码
package com.ruoyi.common.utils.security;
import java.security.MessageDigest;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
/**
* Md5加密方法
*
* @author ruoyi
*/
public class Md5Utils
{
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(Md5Utils.class);
private static byte[] md5(String s)
{
MessageDigest algorithm;
try
{
algorithm = MessageDigest.getInstance("MD5");
algorithm.reset();
algorithm.update(s.getBytes("UTF-8"));
byte[] messageDigest = algorithm.digest();
return messageDigest;
}
catch (Exception e)
{
log.error("MD5 Error...", e);
}
return null;
}
private static final String toHex(byte hash[])
{
if (hash == null)
{
return null;
}
StringBuffer buf = new StringBuffer(hash.length * 2);
int i;
for (i = 0; i < hash.length; i++)
{
if ((hash[i] & 0xff) < 0x10)
{
buf.append("0");
}
buf.append(Long.toString(hash[i] & 0xff, 16));
}
return buf.toString();
}
public static String hash(String s)
{
try
{
return new String(toHex(md5(s)).getBytes("UTF-8"), "UTF-8");
}
catch (Exception e)
{
log.error("not supported charset...{}", e);
return s;
}
}
}
再回到上面文件上传的具体方法upload中对文件名称进行编码后
调用获取文件绝对路径的方法
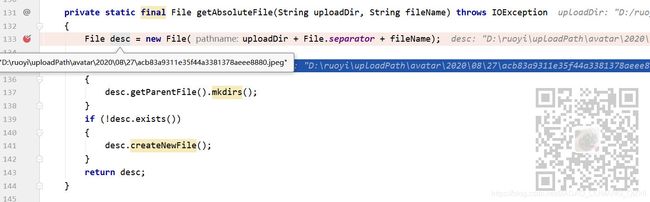
File desc = getAbsoluteFile(baseDir, fileName);
此方法实现
private static final File getAbsoluteFile(String uploadDir, String fileName) throws IOException
{
File desc = new File(uploadDir + File.separator + fileName);
if (!desc.getParentFile().exists())
{
desc.getParentFile().mkdirs();
}
if (!desc.exists())
{
desc.createNewFile();
}
return desc;
}
此时获取的文件的绝对路径类似如下
然后将上传的文件转换成指定的绝对路径的文件,就能将上传的文件存储到服务器上指定的文件路径。
file.transferTo(desc);
然后需要将相对路径返回给前端,所以调用
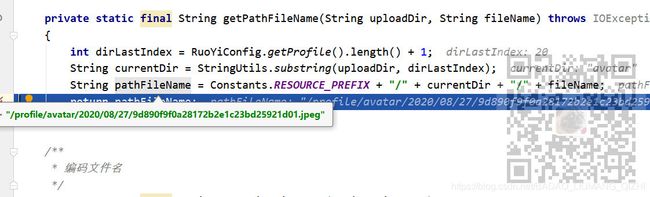
String pathFileName = getPathFileName(baseDir, fileName);
就可以获取上传后头像的相对路径,此方法的实现为
private static final String getPathFileName(String uploadDir, String fileName) throws IOException
{
int dirLastIndex = RuoYiConfig.getProfile().length() + 1;
String currentDir = StringUtils.substring(uploadDir, dirLastIndex);
String pathFileName = Constants.RESOURCE_PREFIX + "/" + currentDir + "/" + fileName;
return pathFileName;
}
首先获取的是配置的上传文件的路径的路径的长度加上1,在将绝对路径按此进行截取,只取后面的部分。
然后获取常量类中的资源映射路径的前缀
/**
* 资源映射路径 前缀
*/
public static final String RESOURCE_PREFIX = "/profile";
这样获取相对路径为
这样的话就能将服务器上需要请求的图片的路径获取到。再回到头像上传的接口中。
String avatar = FileUploadUtils.upload(RuoYiConfig.getAvatarPath(), file);
if (userService.updateUserAvatar(loginUser.getUsername(), avatar))
{
AjaxResult ajax = AjaxResult.success();
ajax.put("imgUrl", avatar);
// 更新缓存用户头像
loginUser.getUser().setAvatar(avatar);
tokenService.setLoginUser(loginUser);
return ajax;
}
获取了头像地址,将此头像的地址更新到数据库中存储。然后将此头像地址存储进缓存中并且返回给前端。
在数据库中将上面的头像路径进行存储
后台将头像的路径返回给前端后
// 上传图片
uploadImg() {
this.$refs.cropper.getCropBlob(data => {
let formData = new FormData();
formData.append("avatarfile", data);
uploadAvatar(formData).then(response => {
if (response.code === 200) {
this.open = false;
debugger
this.options.img = process.env.VUE_APP_BASE_API + response.imgUrl;
var path = this.options.img;
console.log(this.options.img);
store.commit('SET_AVATAR', this.options.img);
this.msgSuccess("修改成功");
}
this.visible = false;
});
});
},
前端获取并拼接一个配置的请求url的前缀
this.options.img = process.env.VUE_APP_BASE_API + response.imgUrl;
后台获取的路径
最终前端需要的路径为
然后将其存储进缓存中,所以这张头像的路径就是
/dev-api/profile/avatar/2020/08/27/a2869bfe4c34c5eac14211dd0d24c0db.jpeg
为什么前端通过这就能获取到后台的这张照片。
在前端项目的vue.config.js中,配置的请求代理,
devServer: {
host: '0.0.0.0',
port: port,
proxy: {
// detail: https://cli.vuejs.org/config/#devserver-proxy
[process.env.VUE_APP_BASE_API]: {
target: `http://localhost:8080`,
changeOrigin: true,
pathRewrite: {
['^' + process.env.VUE_APP_BASE_API]: ''
}
}
},
disableHostCheck: true
},
所有前端的指定的ip加端口加配置的接口前缀(这里是/dev-api)都会被代理到http://localhost:8080
所以这里的前端请求的/dev-api/profile/avatar/2020/08/27/a2869bfe4c34c5eac14211dd0d24c0db.jpeg
就被代理到
http://localhost:8080/profile/avatar/2020/08/27/a2869bfe4c34c5eac14211dd0d24c0db.jpeg
浏览器中可以直接对此头像文件进行访问
那么在后端是怎样对这个资源请求进行处理的。
在后台项目的com.ruoyi.framework.config下的ResourcesConfig使用此配置类配置静态资源映射
package com.ruoyi.framework.config;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.InterceptorRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.ResourceHandlerRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;
import com.ruoyi.common.constant.Constants;
import com.ruoyi.framework.interceptor.RepeatSubmitInterceptor;
/**
* 通用配置
*
* @author ruoyi
*/
@Configuration
public class ResourcesConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer
{
@Autowired
private RepeatSubmitInterceptor repeatSubmitInterceptor;
@Override
public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry)
{
/** 本地文件上传路径 */
registry.addResourceHandler(Constants.RESOURCE_PREFIX + "/**").addResourceLocations("file:" + RuoYiConfig.getProfile() + "/");
/** swagger配置 */
registry.addResourceHandler("swagger-ui.html").addResourceLocations("classpath:/META-INF/resources/");
registry.addResourceHandler("/webjars/**").addResourceLocations("classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/");
}
/**
* 自定义拦截规则
*/
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry)
{
registry.addInterceptor(repeatSubmitInterceptor).addPathPatterns("/**");
}
}
通过重写addResourceHandlers
registry.addResourceHandler(Constants.RESOURCE_PREFIX + "/**").addResourceLocations("file:" + RuoYiConfig.getProfile() + "/");
就可以将上面的请求映射为服务器上本地的路径。
还有就是在前端请求静态资源时将权限验证放开,即运行匿名访问。
在com.ruoyi.framework.config下的SecurityConfig中对此请求的url配置为允许匿名访问。
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity httpSecurity) throws Exception
{
httpSecurity
// CRSF禁用,因为不使用session
.csrf().disable()
// 认证失败处理类
.exceptionHandling().authenticationEntryPoint(unauthorizedHandler).and()
// 基于token,所以不需要session
.sessionManagement().sessionCreationPolicy(SessionCreationPolicy.STATELESS).and()
// 过滤请求
.authorizeRequests()
// 对于登录login 验证码captchaImage 允许匿名访问
.antMatchers("/login", "/captchaImage").anonymous()
.antMatchers(
HttpMethod.GET,
"/*.html",
"/**/*.html",
"/**/*.css",
"/**/*.js"
).permitAll()
.antMatchers("/profile/**").anonymous()
配置类完整代码
package com.ruoyi.framework.config;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.http.HttpMethod;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.AuthenticationManager;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.authentication.builders.AuthenticationManagerBuilder;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.method.configuration.EnableGlobalMethodSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter;
import org.springframework.security.config.http.SessionCreationPolicy;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter;
import com.ruoyi.framework.security.filter.JwtAuthenticationTokenFilter;
import com.ruoyi.framework.security.handle.AuthenticationEntryPointImpl;
import com.ruoyi.framework.security.handle.LogoutSuccessHandlerImpl;
/**
* spring security配置
*
* @author ruoyi
*/
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true, securedEnabled = true)
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter
{
/**
* 自定义用户认证逻辑
*/
@Autowired
private UserDetailsService userDetailsService;
/**
* 认证失败处理类
*/
@Autowired
private AuthenticationEntryPointImpl unauthorizedHandler;
/**
* 退出处理类
*/
@Autowired
private LogoutSuccessHandlerImpl logoutSuccessHandler;
/**
* token认证过滤器
*/
@Autowired
private JwtAuthenticationTokenFilter authenticationTokenFilter;
/**
* 解决 无法直接注入 AuthenticationManager
*
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
@Bean
@Override
public AuthenticationManager authenticationManagerBean() throws Exception
{
return super.authenticationManagerBean();
}
/**
* anyRequest | 匹配所有请求路径
* access | SpringEl表达式结果为true时可以访问
* anonymous | 匿名可以访问
* denyAll | 用户不能访问
* fullyAuthenticated | 用户完全认证可以访问(非remember-me下自动登录)
* hasAnyAuthority | 如果有参数,参数表示权限,则其中任何一个权限可以访问
* hasAnyRole | 如果有参数,参数表示角色,则其中任何一个角色可以访问
* hasAuthority | 如果有参数,参数表示权限,则其权限可以访问
* hasIpAddress | 如果有参数,参数表示IP地址,如果用户IP和参数匹配,则可以访问
* hasRole | 如果有参数,参数表示角色,则其角色可以访问
* permitAll | 用户可以任意访问
* rememberMe | 允许通过remember-me登录的用户访问
* authenticated | 用户登录后可访问
*/
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity httpSecurity) throws Exception
{
httpSecurity
// CRSF禁用,因为不使用session
.csrf().disable()
// 认证失败处理类
.exceptionHandling().authenticationEntryPoint(unauthorizedHandler).and()
// 基于token,所以不需要session
.sessionManagement().sessionCreationPolicy(SessionCreationPolicy.STATELESS).and()
// 过滤请求
.authorizeRequests()
// 对于登录login 验证码captchaImage 允许匿名访问
.antMatchers("/login", "/captchaImage").anonymous()
.antMatchers(
HttpMethod.GET,
"/*.html",
"/**/*.html",
"/**/*.css",
"/**/*.js"
).permitAll()
.antMatchers("/profile/**").anonymous()
.antMatchers("/common/download**").anonymous()
.antMatchers("/common/download/resource**").anonymous()
.antMatchers("/swagger-ui.html").anonymous()
.antMatchers("/swagger-resources/**").anonymous()
.antMatchers("/webjars/**").anonymous()
.antMatchers("/*/api-docs").anonymous()
.antMatchers("/druid/**").anonymous()
// 除上面外的所有请求全部需要鉴权认证
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.headers().frameOptions().disable();
httpSecurity.logout().logoutUrl("/logout").logoutSuccessHandler(logoutSuccessHandler);
// 添加JWT filter
httpSecurity.addFilterBefore(authenticationTokenFilter, UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class);
}
/**
* 强散列哈希加密实现
*/
@Bean
public BCryptPasswordEncoder bCryptPasswordEncoder()
{
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
/**
* 身份认证接口
*/
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception
{
auth.userDetailsService(userDetailsService).passwordEncoder(bCryptPasswordEncoder());
}
}
由此实现了整个前后端头像上传与存储于查询和映射的全过程。