Spring系列综合
目录
- 1 Spring介绍
- 2 Spring核心技术
- 3 Spring入门案例
-
- 3.1 Spring jar包下载(了解)
- 3.2 通过mven方式导入jar包
- 3.3 编辑application.xml文件
- 3.4 编辑测试类
- 4 Spring核心技术IOC
-
- 4.1 什么是IOC
- 4.2 IOC实现原理
- 5 Spring创建对象方式
-
- 5.1 静态工厂模式
-
- 5.1.1 编辑静态工厂类
- 5.1.2 编辑静态工厂配置文件
- 5.1.3 编辑测试类
- 5.2 实例工厂
-
- 5.2.1 编辑实例工厂
- 5.2.2 编辑xml配置文件
- 5.2.3 编辑测试类
- 5.3 spring工厂模式(通用)
-
- 5.3.1 编辑spring工厂
- 5.3.2 编辑xml配置文件
- 5.3.3 配置测试类
- 6 关于单例多例模式说明
-
- 6.1 单例/多例模式说明
- 6.2 编辑xml配置文件
- 6.3 编辑测试代码
- 6.4 懒加载配置
-
- 6.4.1 xml文件配置
- 6.5 spring对象初始化/销毁方法
-
- 6.5.1 编辑xml配置文件
- 6.5.2 编辑测试类内容
- 6.5.3 执行效果
- 7 IOC-DI(Dependency Injection,简称DI)
-
- 7.1 常规注入方式
- 7.2 Spring Set赋值
-
- 7.2.1 编辑xml配置文件
- 7.2.2 编辑POJO对象
- 7.2.3 编辑测试类
- 7.3 构造方法赋值
-
- 7.3.1 编辑xml配置文件
- 7.3.2 测试方法
- 7.3.3 测试结果
- 7.4 特殊字符赋值
-
- 7.4.1 编辑xml配置文件
- 7.4.2 测试结果
- 7.5 对象引用赋值
-
- 7.5.1 编辑Dog对象
- 7.5.2 编辑xml配置文件
- 7.5.3 测试结果
- 7.5 安装lombok插件
-
- 7.5.1 安装插件
- 7.5.2 添加依赖包
- 7.5.3 使用注解优化
- 7.6 MVC结构
-
- 7.6.1 编辑POJO
- 7.6.2 编辑UserDao
- 7.6.3 编辑UserService
- 7.6.4 编辑UserController
- 7.6.5 编辑application配置文件
- 7.7 扩展内容(内部bean)
- 7.8 集合属性抽取(util)
-
- 7.8.1 编辑头标签
- 7.8.2 编辑xml配置文件
- 8 自动装配
-
- 8.1 编辑POJO对象
-
- 8.1.1 定义Dog对象
- 8.1.2 定义User对象
- 8.1.3 编辑自动装配
- 9 引入外部文件为属性赋值
-
- 9.1 定义数据源对象
- 9.2 常规方式赋值
- 9.3 引入第三方配置为属性赋值
-
- 9.3.1 编辑pro配置文件
- 9.3.2 编辑xml配置文件
- 9.3.3 编辑测试类
- 10 Spring中注解形式
-
- 10.1 常用注解
- 10.2 开启注解标签
- 10.3 注解引用
- 10.4 注解测试代码
- 10.5 关于注解包扫描扩展
- 10.6 Spring属性注入
-
- 10.6.1 常用注解说明
- 10.6.2 @Autowired使用
- 10.6.3 @Qualifier使用
- 10.6.4 @Resource使用
- 10.6.5 @Value注解使用
- 10.7 纯注解开发
-
- 10.7.1 编辑配置类
- 10.7.2 编辑测试类
- 11 Spring-AOP机制
- 11.1 AOP介绍
- 11.2 事物控制代码(铺垫)
-
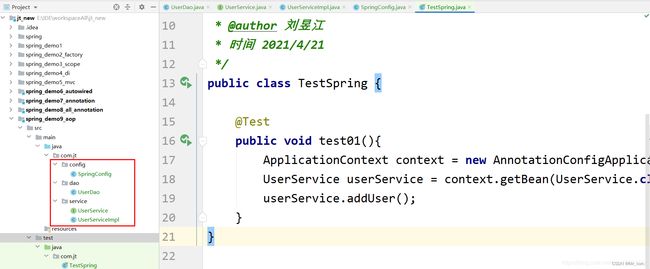
- 11.2.1 代码结构/测试方法
- 11.2.2 编辑配置类
- 11.2.3 编辑Service/Dao
- 11.2.4编辑测试代码
- 11.3 静态代理
-
- 11.3.1 代理模式实现步骤
- 11.3.2 配置代理对象
- 11.3.3 编辑测试类
- 11.4 动态代理
-
- 11.4.1 动态代理分类
- 11.5 JDK动态代理实现
-
- 11.5.1 编辑代理对象
- 11.5.2 编辑测试代码
- 12 Spring AOP
-
- 12.1 AOP介绍
- 12.2 AOP中专业术语(难点)
- 12.3 通知类型
- 12.4 切入点表达式
- 12.5 引入jar包
- 12.6 编辑AOP文件
- 12.7 编辑配置类
- 12.8 编辑测试类
1 Spring介绍
Spring框架是一个开放源代码的J2EE应用程序框架,由Rod Johnson发起,是针对bean的生命周期进行管理的轻量级容器(lightweight container)。
Spring解决了开发者在J2EE开发中遇到的许多常见的问题,提供了功能强大IOC、AOP及Web MVC等功能。Spring可以单独应用于构筑应用程序,也可以和Struts、Webwork、Tapestry等众多Web框架组合使用,并且可以与 Swing等桌面应用程序AP组合。因此, Spring不仅仅能应用于JEE应用程序之中,也可以应用于桌面应用程序以及小应用程序之中。Spring框架主要由七部分组成,分别是 Spring Core、 Spring AOP、 Spring ORM、 Spring DAO、Spring Context、 Spring Web和 Spring Web MVC。
2 Spring核心技术
- IOC/DI
- AOP
3 Spring入门案例
3.1 Spring jar包下载(了解)
官网: https://repo.spring.io/release/org/springframework/spring/5.3.6/ 地址
3.2 通过mven方式导入jar包
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0modelVersion>
<groupId>com.jt.newgroupId>
<artifactId>spring_demo1artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOTversion>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-coreartifactId>
<version>5.3.6version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-beansartifactId>
<version>5.3.6version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-contextartifactId>
<version>5.3.6version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-expressionartifactId>
<version>5.3.6version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-logginggroupId>
<artifactId>commons-loggingartifactId>
<version>1.2version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junitgroupId>
<artifactId>junitartifactId>
<version>4.12version>
dependency>
dependencies>
project>
3.3 编辑application.xml文件
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="user" class="com.jt.pojo.User">bean>
beans>
3.4 编辑测试类
4 Spring核心技术IOC
4.1 什么是IOC
控制反转(Inversion of Control,缩写为IoC),是面向对象编程中的一种设计原则,可以用来减低计算机代码之间的耦合度。其中最常见的方式叫做依赖注入(Dependency Injection,简称DI),还有一种方式叫“依赖查找”(Dependency Lookup)。通过控制反转,对象在被创建的时候,由一个调控系统内所有对象的外界实体将其所依赖的对象的引用传递给它。也可以说,依赖被注入到对象中。
- 概念: 将对象创建的权利交给Spring容器管理,由容器控制对象的生命周期.
- 作用: 降低代码之间的耦合性
4.2 IOC实现原理
- 解析xml配置文件
- 通过反射机制 实例化对象.
- 由spring容器管理对象的生命周期
5 Spring创建对象方式
5.1 静态工厂模式
5.1.1 编辑静态工厂类
package com.jt.factory;
import java.util.Calendar;
/**
* @author 刘昱江
* 时间 2021/4/20
*/
public class staticFactory {
//通过静态工厂实例化对象
public static Calendar getInstance(){
return Calendar.getInstance();
}
}
5.1.2 编辑静态工厂配置文件
<!--静态工厂方法-->
<bean id="calendar1" class="com.jt.factory.staticFactory" factory-method="getInstance"/>
5.1.3 编辑测试类
/*通过静态工厂获取数据 要求方法必须为static配置*/
@Test
public void staticFactory(){
//如果省略不写,默认是application.xml
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application.xml");
Calendar calendar = context.getBean("calendar1",Calendar.class);
System.out.println(calendar.getTime());
}
5.2 实例工厂
5.2.1 编辑实例工厂
package com.jt.factory;
import java.util.Calendar;
/**
* @author 刘昱江
* 时间 2021/4/20
*/
public class InstanceFactory {
public Calendar getCalendar(){
return Calendar.getInstance();
}
}
5.2.2 编辑xml配置文件
<bean id="instanceFactory" class="com.jt.factory.InstanceFactory">bean>
<bean id="calendar2" factory-bean="instanceFactory" factory-method="getCalendar">bean>
5.2.3 编辑测试类
@Test
public void instanceFactory(){
//如果省略不写,默认是application.xml
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application.xml");
Calendar calendar = context.getBean("calendar2",Calendar.class);
System.out.println(calendar.getTime());
}
5.3 spring工厂模式(通用)
5.3.1 编辑spring工厂
package com.jt.factory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.FactoryBean;
import java.util.Calendar;
/**
* @author 刘昱江
* 时间 2021/4/20
*/
public class SpringFactory implements FactoryBean<Calendar> {
@Override
public Calendar getObject() throws Exception {
return Calendar.getInstance();
}
@Override
public Class<?> getObjectType() {
return Calendar.class;
}
//是否为单例模式 默认为true
@Override
public boolean isSingleton() {
return true;
}
}
5.3.2 编辑xml配置文件
<bean id="calendar3" class="com.jt.factory.SpringFactory">bean>
5.3.3 配置测试类
/**
* 更加通用的工厂模式
*/
@Test
public void SpringFactory(){
//如果省略不写,默认是application.xml
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application.xml");
Calendar calendar = context.getBean("calendar3",Calendar.class);
System.out.println(calendar.getTime());
}
6 关于单例多例模式说明
6.1 单例/多例模式说明
- 单例: 在Spring容器中,有且只有一份对象.并且默认通过构造方法实例化对象
- 多例: 需要时创建,并且将创建好的对象赋值给调用者.
6.2 编辑xml配置文件
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="user" class="com.jt.pojo.User" scope="prototype">bean>
beans>
6.3 编辑测试代码
@Test
public void test01(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application.xml");
User user1 = context.getBean("user", User.class);
User user2 = context.getBean("user", User.class);
user1.addUser();
}
6.4 懒加载配置
6.4.1 xml文件配置
<bean id="user" class="com.jt.pojo.User" lazy-init="true">bean>
6.5 spring对象初始化/销毁方法
6.5.1 编辑xml配置文件
<bean id="user" class="com.jt.pojo.User" init-method="init" destroy-method="destroy">bean>
6.5.2 编辑测试类内容
package com.jt.pojo;
/**
* @author 刘昱江
* 时间 2021/4/20
*/
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String name;
public User(){
System.out.println("通过构造方法创建对象");
}
public void init(){
//一般调用初始化方法 为属性赋值(一般多为对象)
this.id = 1000;
this.name = "spring案例测试";
System.out.println("调用初始化方法");
}
public void addUser(){
System.out.println("新增用户"+id+":"+name);
}
public void destroy(){
//设置对象的销毁方法,一般都是为了释放资源
this.id = null;
this.name = null;
System.out.println("调用对象的销毁方法");
}
}
6.5.3 执行效果
7 IOC-DI(Dependency Injection,简称DI)
7.1 常规注入方式
//常规为属性赋值
@Test
public void test01(){
//1.构造方法赋值
User user = new User(1,"天上有星星");
System.out.println(user);
//2.set方法赋值
User user2 = new User();
user2.setId(2);
user2.setName("下上有羊羊");
System.out.println(user2);
}
7.2 Spring Set赋值
7.2.1 编辑xml配置文件
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="user" class="com.jt.pojo.User">
<property name="id" value="100">property>
<property name="name" value="小花花">property>
bean>
beans>
7.2.2 编辑POJO对象
package com.jt.pojo;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* @author 刘昱江
* 时间 2021/4/20
*/
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Set set;
private List list;
private Map map;
private Properties pro;
//快捷鍵 alt+insert
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Set<String> getSet() {
return set;
}
public void setSet(Set set) {
this.set = set;
}
public List getList() {
return list;
}
public void setList(List list) {
this.list = list;
}
public Map getMap() {
return map;
}
public void setMap(Map map) {
this.map = map;
}
public Properties getPro() {
return pro;
}
public void setPro(Properties pro) {
this.pro = pro;
}
public User(){
}
public User(Integer id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
public User(Integer id, String name, Set set, List list, Map map, Properties pro) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.set = set;
this.list = list;
this.map = map;
this.pro = pro;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", set=" + set +
", list=" + list +
", map=" + map +
", pro=" + pro +
'}';
}
}
7.2.3 编辑测试类
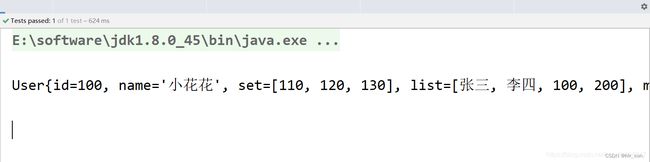
//set方法赋值
@Test
public void consUser(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application.xml");
User user = context.getBean(User.class);
System.out.println(user);
}
7.3 构造方法赋值
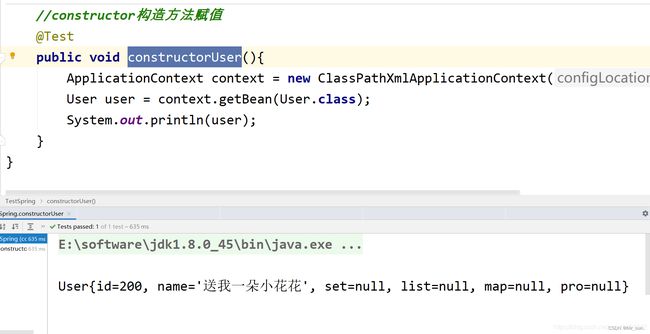
7.3.1 编辑xml配置文件
<bean id="user" class="com.jt.pojo.User">
<constructor-arg name="id" value="200">constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="name" value="送我一朵小花花">constructor-arg>
bean>
7.3.2 测试方法
//constructor构造方法赋值
@Test
public void constructorUser(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application.xml");
User user = context.getBean(User.class);
System.out.println(user);
}
7.3.3 测试结果
7.4 特殊字符赋值
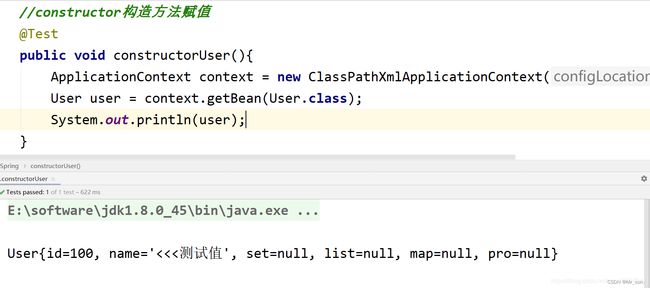
7.4.1 编辑xml配置文件
<bean id="user" class="com.jt.pojo.User">
<constructor-arg name="id" value="100">constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="name">
<value>value>
constructor-arg>
bean>
7.4.2 测试结果
7.5 对象引用赋值
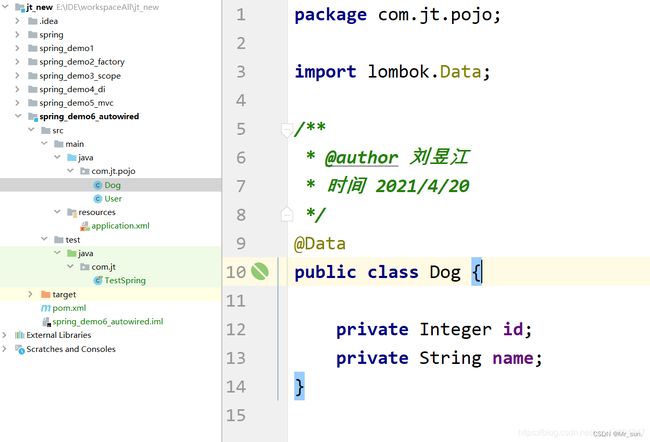
7.5.1 编辑Dog对象
package com.jt.pojo;
/**
* @author 刘昱江
* 时间 2021/4/20
*/
public class Dog {
private String name;
//添加无参构造方法
public Dog(){
}
public Dog(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Dog{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
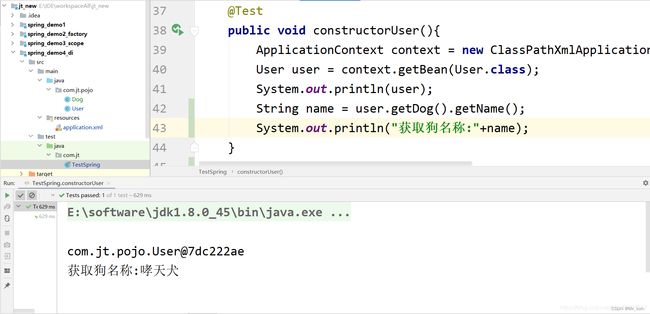
7.5.2 编辑xml配置文件
<bean id="user" class="com.jt.pojo.User">
<constructor-arg name="id" value="100">constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="name">
<value>value>
constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="dog" ref="dog">constructor-arg>
bean>
<bean id="dog" class="com.jt.pojo.Dog">
<property name="name" value="哮天犬">property>
bean>
7.5.3 测试结果
7.5 安装lombok插件
7.5.1 安装插件
7.5.2 添加依赖包
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombokgroupId>
<artifactId>lombokartifactId>
<version>1.18.20version>
<scope>providedscope>
dependency>
7.5.3 使用注解优化
/**
* @author 刘昱江
* 时间 2021/4/20
*/
@Data //动态get/set方法
@Accessors(chain = true)
@NoArgsConstructor //添加无参构造
@AllArgsConstructor //添加全参构造
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String name;
}
7.6 MVC结构
7.6.1 编辑POJO
/**
* @author 刘昱江
* 时间 2021/4/20
*/
@Data //动态get/set方法
@Accessors(chain = true)
@NoArgsConstructor //添加无参构造
@AllArgsConstructor //添加全参构造
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String name;
}
7.6.2 编辑UserDao
/**
* @author 刘昱江
* 时间 2021/4/20
*/
public class UserDao {
public void addUser(User user){
System.out.println("新增用户:"+user.getName());
}
}
7.6.3 编辑UserService
/**
* @author 刘昱江
* 时间 2021/4/20
*/
@Data
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{
private UserDao userDao;
@Override
public void addUser(User user) {
userDao.addUser(user);
}
}
7.6.4 编辑UserController
package com.jt.controller;
import com.jt.pojo.User;
import com.jt.service.UserService;
import lombok.Data;
/**
* @author 刘昱江
* 时间 2021/4/20
*/
@Data
public class UserController {
private UserService userService;
private User user;
public void addUser(){
userService.addUser(user);
}
}
7.6.5 编辑application配置文件
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="user" class="com.jt.pojo.User">
<property name="id" value="100">property>
<property name="name" value="安琪拉">property>
bean>
<bean id="userDao" class="com.jt.dao.UserDao">bean>
<bean id="userService" class="com.jt.service.UserServiceImpl">
<property name="userDao" ref="userDao">property>
bean>
<bean id="userController" class="com.jt.controller.UserController">
<property name="userService" ref="userService">property>
<property name="user" ref="user">property>
bean>
beans>
7.7 扩展内容(内部bean)
<bean id="dept" class="com.jt.pojo.Dept">
<property name="id" value="101">property>
<property name="name" value="财务部">property>
<property name="user">
<bean id="user" class="com.jt.pojo.User">
<property name="name" value="项思醒">property>
bean>
property>
bean>
7.8 集合属性抽取(util)
7.8.1 编辑头标签
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util.xsd
">
7.8.2 编辑xml配置文件
之后通过ref属性进行引用
<util:list id="list">
<value>1value>
<value>2value>
<ref bean="user">ref>
util:list>
8 自动装配
8.1 编辑POJO对象
8.1.1 定义Dog对象
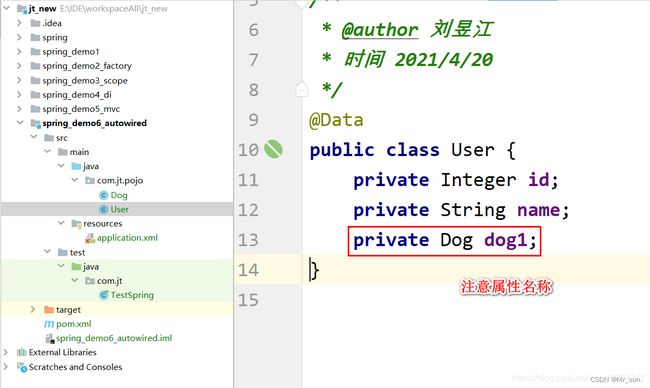
8.1.2 定义User对象
8.1.3 编辑自动装配
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="user" class="com.jt.pojo.User" autowire="byType">
<property name="id" value="101">property>
<property name="name" value="小天天">property>
bean>
<bean id="dog" class="com.jt.pojo.Dog">
<property name="id" value="100">property>
<property name="name" value="旺财">property>
bean>
beans>
9 引入外部文件为属性赋值
9.1 定义数据源对象
package com.jt.db;
import lombok.Data;
/**
* @author 刘昱江
* 时间 2021/4/20
*/
@Data
public class DataSource {
private String driverName;
private String url;
private String username;
private String password;
}
9.2 常规方式赋值
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.jt.db.DataSource">
<property name="driverName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver">property>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db">property>
<property name="username" value="root">property>
<property name="password" value="root">property>
bean>
9.3 引入第三方配置为属性赋值
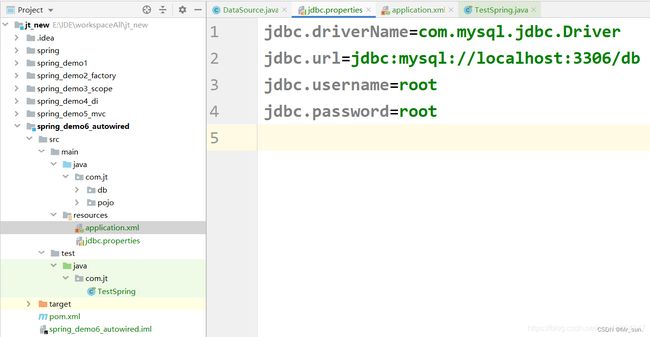
9.3.1 编辑pro配置文件
jdbc.driverName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=root
9.3.2 编辑xml配置文件
注意头标签写法
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-util.xsd">
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:/jdbc.properties"/>
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.jt.db.DataSource">
<property name="driverName" value="${jdbc.driverName}">property>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}">property>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}">property>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}">property>
bean>
9.3.3 编辑测试类
@Test
public void test02(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application.xml");
DataSource dataSource = context.getBean(DataSource.class);
System.out.println(dataSource);
}
10 Spring中注解形式
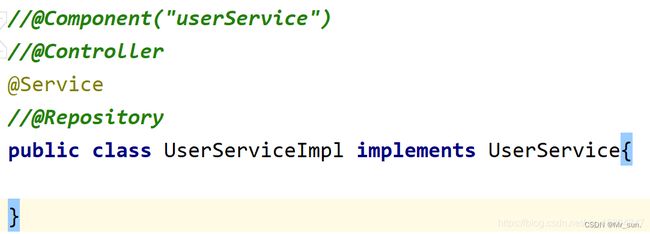
10.1 常用注解
默认时 自动将bean的Id首字母小写
@Component(“userService”)
@Controller
@Service
@Repository
10.2 开启注解标签
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-util.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.jt"/>
beans>
10.3 注解引用
10.4 注解测试代码
package com.jt;
import com.jt.service.UserService;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
/**
* @author 刘昱江
* 时间 2021/4/20
*/
public class TestSpring {
/**
* 获取注解定义的对象
*/
@Test
public void test01(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application.xml");
UserService userService = context.getBean(UserService.class);
System.out.println(userService);
}
}
10.5 关于注解包扫描扩展
<context:component-scan base-package="com.jt" >
<context:exclude-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"/>
context:component-scan>
10.6 Spring属性注入
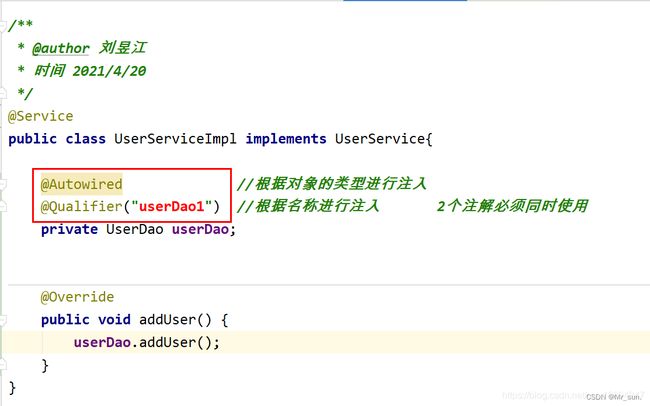
10.6.1 常用注解说明
1.@Autowired 根据对象的类型进行注入
2.@Qualifier(“userDao”) 根据属性的名称进行注入
3.@Resource 根据属性和类型进行注入
10.6.2 @Autowired使用
10.6.3 @Qualifier使用
10.6.4 @Resource使用
Resource 注解 可以通过类型和name名称进行注入.
关于Resource注解的说明, @Resource注解不是Spring原生提供的,所以兼容性上有待考量 ,spring建议使用原生注解.
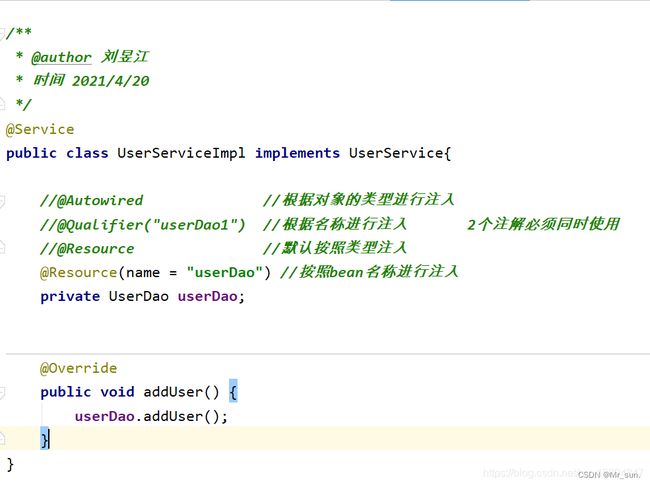
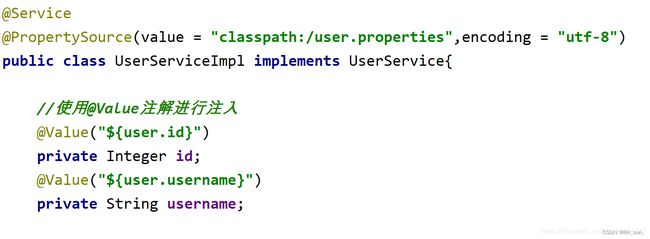
10.6.5 @Value注解使用
10.7 纯注解开发
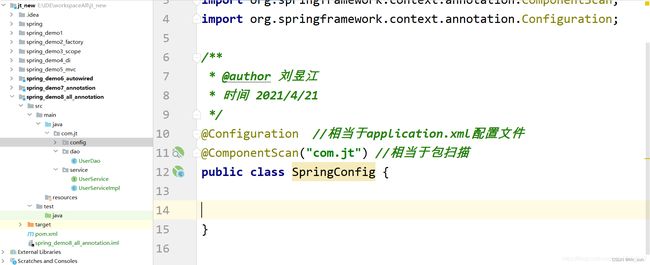
10.7.1 编辑配置类
10.7.2 编辑测试类
public class TestSpring {
//采用纯注解的方式开发 实现类对象发生变化
@Test
public void test01(){
ApplicationContext context =
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
UserService userService = context.getBean(UserService.class);
userService.addUser();
}
}
11 Spring-AOP机制
11.1 AOP介绍
在软件业,AOP为Aspect Oriented Programming的缩写,意为:面向切面编程,通过预编译方式和运行期间动态代理实现程序功能的统一维护的一种技术。AOP是OOP的延续,是软件开发中的一个热点,也是Spring框架中的一个重要内容,是函数式编程的一种衍生范型。利用AOP可以对业务逻辑的各个部分进行隔离,从而使得业务逻辑各部分之间的耦合度降低,提高程序的可重用性,同时提高了开发的效率。
AOP主要作用: 在不修改原有代码的条件下 对方法进行扩展
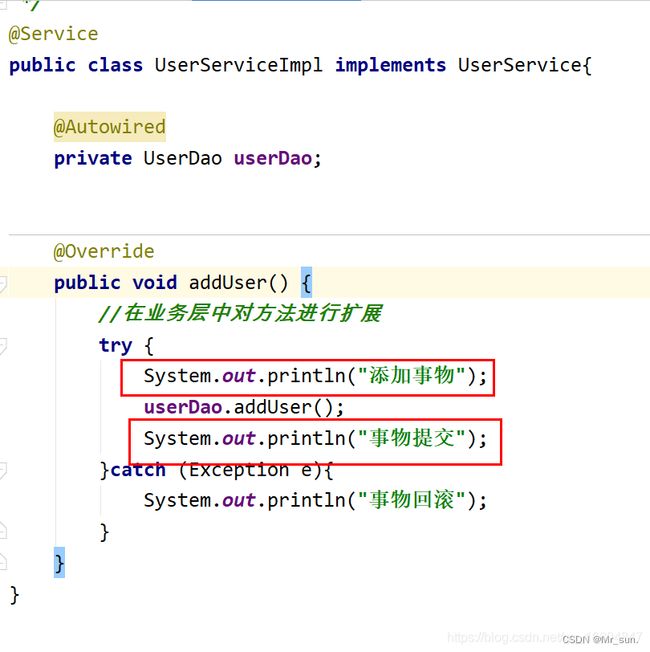
11.2 事物控制代码(铺垫)
11.2.1 代码结构/测试方法
11.2.2 编辑配置类
11.2.3 编辑Service/Dao
11.2.4编辑测试代码
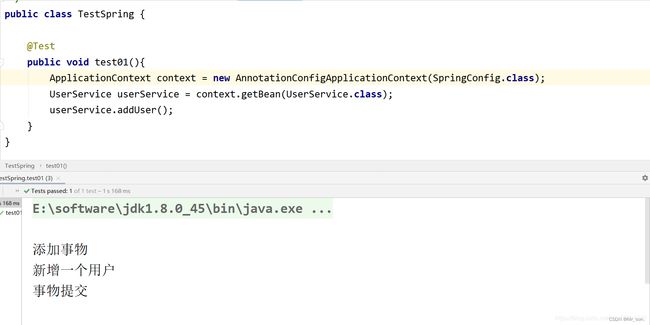
发现问题: 业务代码和事物代码紧紧的耦合在一起. 如何优化?
11.3 静态代理
11.3.1 代理模式实现步骤
1.代理对象要求与被代理者实现相同的接口
2.代理对象完成功能的扩展
3.用户调用实现业务(让用户感觉起来和原始对象一样)
11.3.2 配置代理对象
11.3.3 编辑测试类
public class TestSpring {
//通过bean的Id获取对象
@Test
public void test01(){
ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
UserService userService = (UserService) context.getBean("userService");
userService.addUser();
}
}
11.4 动态代理
11.4.1 动态代理分类
- JDK动态代理 要求代理对象实现与被代理者相同的接口
- CGLIB动态代理 代理对象是被代理者的子类 (了解)
11.5 JDK动态代理实现
11.5.1 编辑代理对象
package com.jt.proxy;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
/**
* @author 刘昱江
* 时间 2021/4/22
*/
public class JDKDynamicProxy {
public static Object getObject(Object target){
/**
* 参数说明:
* 参数1: 类加载器
* 参数2: 目标对象的接口数组
* 参数3: 调用处理器执行
*/
ClassLoader classLoader = target.getClass().getClassLoader();
Class[] interfaces = target.getClass().getInterfaces();
Object proxy = Proxy.newProxyInstance(classLoader, interfaces, new InvocationHandler() {
//当代理对象调用方法时,回调该方法
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
Object result = null;
try {
System.out.println("数据库事物开始");
//执行回调方法
result = method.invoke(target, args);
System.out.println("数据库事物提交");
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("事物回滚");
}
return result;
}
});
//将代理对象返回
return proxy;
}
}
11.5.2 编辑测试代码
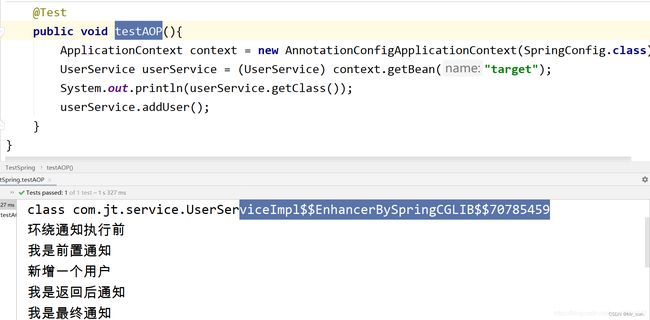
//JDK动态代理测试案例
@Test
public void testJDKProxy(){
ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
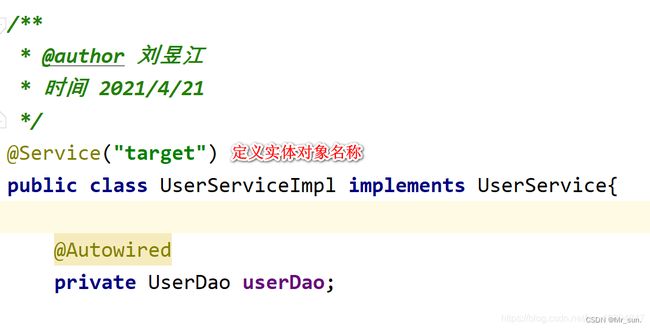
//通过容器获取目标对象
UserService userService = (UserService) context.getBean("target");
//传入目标对象
System.out.println("我是目标对象:"+userService.getClass());
//获取代理对象
UserService userServiceProxy = (UserService) JDKDynamicProxy.getObject(userService);
System.out.println("我是代理对象:"+userServiceProxy.getClass());
//通过代理对象实现方法扩展
userServiceProxy.addUser();
}
12 Spring AOP
12.1 AOP介绍
在软件业,AOP为Aspect Oriented Programming的缩写,意为:面向切面编程,通过预编译方式和运行期间动态代理实现程序功能的统一维护的一种技术。AOP是OOP的延续,是软件开发中的一个热点,也是Spring框架中的一个重要内容,是函数式编程的一种衍生范型。利用AOP可以对业务逻辑的各个部分进行隔离,从而使得业务逻辑各部分之间的耦合度降低,提高程序的可重用性,同时提高了开发的效率。
总结: Spring中的AOP 利用代理对象在不修改源代码的条件下,对方法进行扩展.
12.2 AOP中专业术语(难点)
1).连接点: 用户可以被扩展的方法
2).切入点: 用户实际扩展的方法
3).通知: 扩展方法的具体实现
4).切面: 将通知应用到切入点的过程
12.3 通知类型
1).before通知 目标方法执行前执行
2).afterRrturning 通知 目标方法执行之后执行
3).afterThrowing 通知 目标方法报错时执行
4).after通知 目标方法执行之后 最后执行
5).around通知 目标方法执行前后都要执行
12.4 切入点表达式
1). bean(bean的Id号) 按照bean匹配
2). within(包名.类名) 可以使用通配符
3). execution(返回值类型 包名.类名.方法名(参数列表))
4). @annotation(包名.注解名称)
12.5 引入jar包
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-aopartifactId>
<version>5.3.6version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-aspectsartifactId>
<version>5.3.6version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectjgroupId>
<artifactId>aspectjrtartifactId>
<version>1.9.6version>
dependency>
12.6 编辑AOP文件
package com.jt.aop;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @author 刘昱江
* 时间 2021/4/22
*/
@Component //将对象交给Spring容器管理
@Aspect //标识AOP切面
@Order(1) //通过order 控制切面执行顺序 数值越小越先执行
public class TransactionAop {
//1.定义通知方法
@Pointcut("bean(target)")
public void pointCut(){
System.out.println("我是切入点表达式");
}
//2.定义前置通知
@Before("pointCut()")
public void before1(){
System.out.println("我是前置通知");
}
@AfterReturning("pointCut()")
public void afterReturn(){
System.out.println("我是返回后通知");
}
@AfterReturning("pointCut()")
public void after(){
System.out.println("我是最终通知");
}
@Around("pointCut()")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("环绕通知执行前");
Object object = joinPoint.proceed();
System.out.println("环绕通知执行后");
return object;
}
}