深度学习日记——卷积神经网络
一、加载数据集
选择FashionMnist数据集作为训练的样本数据集。
import torch.nn as nn
import torch
import torch.utils.data.dataloader as dataloader
from torchvision import datasets, transforms
def dataAugment(size):
"""
数据增强方法
:return transform_1:训练集数据增强
:return transform_2:测试集数据增强
"""
'''
transform_1 = transforms.Compose([transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(), transforms.Grayscale(), transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize(0.5, 0.5)])
transform_2 = transforms.Compose([transforms.ToTensor(), transforms.Normalize(0.5, 0.5)])
'''
transform_1 = transforms.Compose([transforms.Resize(size), transforms.ToTensor()])
transform_2 = transforms.Compose([transforms.Resize(size), transforms.ToTensor()])
return transform_1, transform_2
def loadData(path, batch_size, size=24):
"""
加载数据
:param size: 图片大小
:param batch_size: batch_size
:param path: 数据集路径
:return: 返回训练数据集
"""
transform_train, transform_test = dataAugment(size)
mnist_train = datasets.FashionMNIST(root=path, train=True, download=False, transform=transform_train)
mnist_test = datasets.FashionMNIST(root=path, train=False, download=False, transform=transform_test)
data_train = dataloader.DataLoader(mnist_train, batch_size, shuffle=True)
data_test = dataloader.DataLoader(mnist_test, batch_size, shuffle=True)
return data_train, data_test
def evaluate_accuracy(data_iter, net):
"""
统计测试集精度
:param data_iter:数据集
:param net: 模型
:return: 精度
"""
acc_num, n = 0.0, 0
device = torch.device('cuda:0' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
with torch.no_grad():
# 评估模式
net.eval()
for x, y in data_iter:
if isinstance(net, nn.Module):
x, y = x.to(device), y.to(device)
acc_num += (net(x).argmax(dim=1) == y).float().sum().item()
n += y.shape[0]
return acc_num / n
def train(net, optim, data_train, data_test, epochs, loss,scheduler):
"""
训练网络
:param scheduler: 学习率衰减
:param epochs: 轮数
:param data_test: 测试数据集
:param data_train: 训练数据集
:param optim: 优化器
:param loss: 损失函数
:param net: 网络模型
:return:
"""
# 使用Gpu训练
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
net.to(device)
for epoch in range(epochs):
# 训练模式
net.train()
acc_sum, loss_sum, n = 0.0, 0.0, 0
for x, y in data_train:
x, y = x.to(device), y.to(device)
out = net(x)
ls = loss(out, y)
optim.zero_grad()
ls.backward()
optim.step()
scheduler.step()
loss_sum += ls.item()
t=out.argmax(dim=1)
acc_sum += (out.argmax(dim=1) == y).float().sum().item()
n += y.shape[0]
test_acc = evaluate_accuracy(data_test, net)
print(
'epoch:%d,train_loss:%.6f,train_acc:%.6f,test_acc:%.6f' % (epoch + 1, loss_sum / n, acc_sum / n, test_acc))二、AlexNet
优点:AlexNet跟LeNet结构类似,但使⽤了更多的卷积层和更⼤的参数空间来拟合⼤规模数据集 ImageNet。它是浅层神经⽹络和深度神经⽹络的分界线。
import torch.nn as nn
class AlexNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_channel=1, output_channel=10):
"""
定义网络结构
:param input_channel: 输入通道
:param output_channel: 输出通道
"""
super().__init__()
'''# 原始的AlexNet结构 输入图片为(227,227,3)
self.conv1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(input_channel, 96, 11, 4, 0), # 输出为(96,55,55) (227-11)/4+1=55 28-5+1=24
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(3, 2) # 输出(96,27,27) (55-3)/2+1=27
)
self.conv2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(96, 256, 5, 1, 2), # 输出(128,27,27)(27-5+4)/1+1=27
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(3, 2) # 输出(256,13,13) (27-3)/2+1=13
)
self.conv3 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(256, 384, 3, 1, 1), # 输出(384,13,13)(13-3+2)/1+1=13
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(384, 384, 3, 1, 1), # 输出(384,13,13)(13-3+2)/1+1=13
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(384, 256, 3, 1, 1), # 输出(256,13,13)(13-3+2)/1+1=13
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(3, 2) # 输出(256,6,6) (13-3)/2+1=6
)
self.classifier = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(256 * 6 * 6, 4096),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(0.5),
nn.Linear(4096, 4096),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(0.5),
nn.Linear(4096, output_channel)
)'''
# 输入为(24,24)
self.conv1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(input_channel,16, 3, 1, 1), # 输出为(16,24,24) (24-3+2)/1+1=24
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2) # 输出(96,12,12) (24-2)/2+1=12
)
self.conv2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(16, 32, 3, 1, 1), # 输出(32,12,12)(12-3+2)/1+1=12
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2) # 输出(32,6,6) (12-2)/2+1=6
)
self.conv3 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(32, 64, 3, 1, 1), # 输出(64,6,6)(6-3+2)/1+1=6
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(64, 64, 3, 1, 1), # 输出(64,6,6)(6-3+2)/1+1=6
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2) # 输出(64,3,3) (6-2)/2+1=3
)
self.classifier = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(64 * 3 * 3, 1024),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(0.5),
nn.Linear(1024, 256),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(0.5),
nn.Linear(256, output_channel)
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.conv2(x)
x = self.conv3(x)
# x的形状为(256,3,3),需要将x的数据展平输入全连接层
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
out = self.classifier(x)
return out三、VGG
VGG块的组成规律是:连续使⽤数个相同的填充为1、窗⼝形状为 的卷积层后接上⼀个步幅为2、 窗⼝形状为 的最⼤池化层。卷积层保持输⼊的⾼和宽不变,⽽池化层则对其减半。
对于给定的感受野(与输出有关的输⼊图⽚的局部⼤⼩),采⽤堆积的⼩卷积核优于采⽤⼤的卷积核,因为可以增加⽹络深度来保证学习更复杂的模式,⽽且代价还⽐较⼩(参数更少)。
import torch.nn as nn
from addData import loadData,train
import torch
class FlattenLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
def forward(self, x):
return x.view(x.shape[0], -1)
def vgg_block(num_conv, input_chanel, output_channel):
"""
vgg_block 用于生成vgg_block
:param num_conv: 该模块需要的卷积层的数量
:param input_chanel: 输入通道
:param output_channel: 输出通道
:return: 返回该模块
"""
# 记录该模块的网络情况
blk = []
for i in range(num_conv):
if i == 0:
# 该模块第一层网络
blk.append(nn.Conv2d(input_chanel, output_channel, 3, 1, 1))
else:
# 该模块之后的网络
blk.append(nn.Conv2d(output_channel, output_channel, 3, 1, 1))
blk.append(nn.ReLU())
blk.append(nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2))
return nn.Sequential(*blk)
def vgg(conv_arg, fc_features, fc_hidden_units):
net = nn.Sequential()
# 添加网络
for i, (conv_num, input_chanel, output_chanel) in enumerate(conv_arg):
net.add_module("vgg_block_" + str(i + 1), vgg_block(conv_num, input_chanel, output_chanel))
net.add_module("fc", nn.Sequential(
FlattenLayer(),
nn.Linear(fc_features, fc_hidden_units),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(0.5),
nn.Linear(fc_hidden_units, fc_hidden_units),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(0.5),
nn.Linear(fc_hidden_units, 10)
))
return net
if __name__ == '__main__':
path = "./Datasets/FashionMNIST"
batch_size = 128
lr = 0.01
epoch = 50
size = 64
input_channel = 1
out_channel = 10
data_train, data_test = loadData(path, batch_size, size)
# 若输入为(224,224)的话 经过5个maxpool变成 224/32=7
# conv_arg = ((2, 1, 64), (2, 64, 128), (3, 128, 256), (3, 256, 512), (3, 512, 512)) #生成vgg16
conv_arg = ((1, 1, 64), (1, 64, 128), (2, 128, 256), (2, 256, 512), (2, 512, 512)) #vgg11
# 经过5个vgg_block, 宽⾼会减半5次, 变成 224/32 = 7
fc_features = 512 * 2 * 2 # c * w * h
fc_hidden_units = 512 # 任意
net = vgg(conv_arg, fc_features, fc_hidden_units)
print(net)
optim = torch.optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr)
loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
scheduler = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.MultiStepLR(optim, milestones=[25, 50], gamma=0.1)
train(net, optim, data_train, data_test, epoch, loss, scheduler)
四、NiN
NiN使⽤ 1x1卷积层来替代全连接层,从⽽使空间信息能够⾃然传递到后⾯的层中去。(使用1x1卷积核可以保证特征图的长宽不变但是可以减少维度从而压缩数据量,例如:一个(96,10,10)的数据用10个1x1卷积核可以变成(10,10,10)的数据)
另外,该网络舍弃了传统的全连接层,利用1x1卷积层来替代全连接层,通过全局均值池化作为输出的判断依据。
优点:
- NiN重复使⽤由卷积层和代替全连接层的卷积层构成的NiN块来构建深层⽹络。
- NiN去除了容易造成过拟合的全连接输出层,⽽是将其替换成输出通道数等于标签类别数的NiN 块和全局平均池化层
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from addData import loadData,train
import torch
class GlobalAvgPool2d(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
def forward(self, x):
# print(x.size()[2:])
return F.avg_pool2d(x,x.size()[2:])
class FlattenLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
def forward(self, x):
return x.view(x.shape[0], -1)
def nin_block(input_channel, output_channel, kernel_size, stride, padding=0):
"""
生成NiN模块
:param padding: 填充
:param stride: 步长
:param kernel_size: 卷积核大小
:param input_channel: 输入通道
:param output_channel: 输出通道
:return: 返回模块
"""
blk = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(input_channel, output_channel, kernel_size, stride, padding),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(output_channel, output_channel, 1, 1), # Nin网络通过选用1x1的卷积核保持长、宽不变,通过降低数据的维度来达到减少数据的目的
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(output_channel, output_channel, 1, 1),
nn.ReLU()
)
return blk
def Nin(input_chanel, output_channel):
"""
创建Nin网络
:param input_chanel: 输入通道
:param output_channel: 输出通道
:return: 模型
"""
net = nn.Sequential(
nin_block(input_chanel, 96, 11, 4, 0),
nn.MaxPool2d(3, 2),
nin_block(96, 256, 5, 1, 2),
nn.MaxPool2d(3, 2),
nin_block(256, 384, 3, 1, 1),
nn.MaxPool2d(3, 2),
nn.Dropout(0.5),
nin_block(384, output_channel, 3, 1, 1), # 输出为(1,10,5,5)
GlobalAvgPool2d(), # (1,10,1,1)
# 将四维的输出转成⼆维的输出,其形状为(批量⼤⼩, 10)
FlattenLayer()
)
return net
if __name__ == '__main__':
path = "./Datasets/FashionMNIST"
batch_size = 128
lr = 0.01
epoch = 50
size = 224
input_channel = 1
out_channel = 10
data_train, data_test = loadData(path, batch_size, size)
net=Nin(input_channel,out_channel)
print(net)
optim = torch.optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr)
loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
scheduler = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.MultiStepLR(optim, milestones=[25, 50], gamma=0.1)
train(net, optim, data_train, data_test, epoch, loss, scheduler)五、GoogleNet
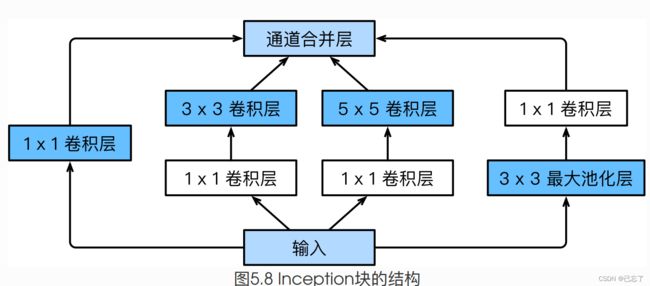
GoogLeNet中的基础卷积块叫作Inception块,Inception块⾥有4条并⾏的线路。前3条线路使⽤窗⼝⼤⼩分别是 、 和 的卷积层来抽取不同空间尺⼨下的信息,其中中间2个线路会对输⼊先做 卷积来减少输⼊通道数,以降低模型复杂度。第四条线路则使⽤ 最⼤池化层,后接 卷积层来改变通道数。4条 线路都使⽤了合适的填充来使输⼊与输出的⾼和宽⼀致。最后我们将每条线路的输出在通道维上连结, 并输⼊接下来的层中去。
优点:
- Inception块相当于⼀个有4条线路的⼦⽹络。它通过不同窗⼝形状的卷积层和最⼤池化层来并⾏抽取信息,并使⽤ 卷积层减少通道数从⽽降低模型复杂度。
- GoogLeNet将多个设计精细的Inception块和其他层串联起来。其中Inception块的通道数分配 之⽐是在ImageNet数据集上通过⼤量的实验得来的。
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from addData import loadData,train
"""
GoogleNet:使用多分支网络结构
"""
class GlobalAvgPool2d(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
def forward(self, x):
# print(x.size()[2:])
return F.avg_pool2d(x,x.size()[2:])
class FlattenLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
def forward(self, x):
return x.view(x.shape[0], -1)
class Inception(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,input_channel,c1,c2,c3,c4):
"""
:param input_channel: 输入通道
:param c1: 线路一的输出层
:param c2: 线路二的输出参数
:param c3: 线路三的输出参数
:param c4: 线路四的输出参数
"""
super().__init__()
# 线路一:通过一层一个1x1卷积核的卷积层
self.c1 = nn.Conv2d(input_channel,c1,1,1)
# 线路二:先过一层一个1x1卷积核的卷积层,再通过一个3x3卷积核的卷积层
self.c2_1 = nn.Conv2d(input_channel,c2[0],1,1)
self.c2_2 = nn.Conv2d(c2[0],c2[1],3,1,1)
# 线路三:先过一层一个1x1卷积核的卷积层,再通过一个5x5卷积核的卷积层
self.c3_1 = nn.Conv2d(input_channel, c3[0], 1, 1)
self.c3_2 = nn.Conv2d(c3[0], c3[1], 5, 1, 2)
# 线路四:先过一层一个3x3的最大池化层,再通过一个1x1卷积核的卷积层
self.c4_1 = nn.MaxPool2d(3,1,1)
self.c4_2 = nn.Conv2d(input_channel, c4, 1, 1)
def forward(self,x):
c1_out = F.relu(self.c1(x))
c2_out = F.relu(self.c2_2(F.relu(self.c2_1(x))))
c3_out = F.relu(self.c3_2(F.relu(self.c3_1(x))))
c4_out = F.relu(self.c4_2(self.c4_1(x)))
# 在维度通道上连结输出
return torch.cat((c1_out,c2_out,c3_out,c4_out),dim=1)
def GoogleNet(input_channel,output_channel):
"""
GoogleNet本身由5个模块组成
:return:
"""
# 第⼀模块使⽤⼀个64通道的7x7卷积层
block_1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(input_channel, 64, 7, 2, 3),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(3, 2, 1)
)
# 第二个模块使⽤2个卷积层:⾸先是64通道的1x1卷积层,然后是将通道增⼤3倍的3x3卷积层。它对应Inception块中的第⼆条线路。
block_2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(64, 64, 1),
nn.Conv2d(64, 192, 3, 1, 1),
nn.MaxPool2d(3, 2, 1)
)
# 第三个模块串联 2 个完整的 Inception 块
# 第一个Inception:模块参数为64+128+32+32=256
# 第二个Inception:模块参数为128+192+96+32=480
block_3 = nn.Sequential(
Inception(192, 64, (96, 128), (16, 32), 32),
Inception(256, 128, (128, 192), (32, 96), 64),
nn.MaxPool2d(3, 2, 1)
)
# 第四个模块串联了5个Inception块
# 第一个Inception:模块参数为192+208+48+64=512
# 第二个Inception:模块参数为160+224+64+64=512
# 第三个Inception:模块参数为128+256+64+64=512
# 第四个Inception:模块参数为112+288+64+64=512
# 第五个Inception:模块参数为256+320+128+126=832
block_4 = nn.Sequential(
Inception(480,192,(96,208),(16,48),64),
Inception(512, 160, (112, 224), (24, 64), 64),
Inception(512, 128, (128, 256), (24, 64), 64),
Inception(512, 112, (144, 288), (32, 64), 64),
Inception(528, 256, (160, 320), (32, 128), 128),
nn.MaxPool2d(3,2,1)
)
# 第五个模块串联2个Inception模块
# 第一个Inception:模块参数为256+320+128+128=832
# 第二个Inception:模块参数为384+384+128+128=1024
block_5 = nn.Sequential(
Inception(832, 256, (160, 320), (32, 128), 128),
Inception(832, 384, (192, 384), (48, 128), 128),
GlobalAvgPool2d()
)
net = nn.Sequential(
block_1,
block_2,
block_3,
block_4,
block_5,
FlattenLayer(),
nn.Linear(1024,output_channel)
)
return net
if __name__=='__main__':
'''net=GoogleNet(1,10)
X = torch.rand(1, 1, 96, 96)
for blk in net.children():
X = blk(X)
print('output shape: ', X.shape)'''
path = "./Datasets/FashionMNIST"
batch_size = 128
lr = 0.01
epoch = 10
size = 96
input_channel = 1
out_channel = 10
data_train, data_test = loadData(path, batch_size, size)
net = GoogleNet(input_channel,out_channel)
print(net)
optim = torch.optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr)
loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
scheduler = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.MultiStepLR(optim, milestones=[25, 50], gamma=0.1)
train(net, optim, data_train, data_test, epoch, loss, scheduler)