词法分析器【编译原理】
实验内容:
基于TEST语言设计相应的词法输入器并且输出二元组
实验目的:
1、理解词法分析器的基本功能
2、理解简单的词法规则的描述方法
3、理解状态转化图及其实现
4、能够编写简单的词法分析器
实验原理:
根据DFA构造词法分析程序
1、直接编程的词法分析程序
(1)、适合词法比较简单的、手工实现、比较精简,分析速度快
(2)、与要识别的语言单词密切相关,一旦词法规则发生变化,则要重新编写程序
(3)、通过程序的控制流转移来完成对输入字符的响应,程序中的每一条语句都要与识别的单词符号有关
2、表驱动的词法分析程序
(1)、一种典型的数据与操作的分离的工作模式,控制程序不变;不同的词法分析器实质上是构造不同的分析表
(2)、为词法分析程序的自动生成提供了极大的方便
(3)、程序比较复杂,分析速度慢一些
实验内容:
1、输入:源文件字符序列s
任务:识别单词符号;滤过空格、注释等
依据:TEST语言的词法规则
输出:字符流(单词)、错误信息
2、本实验我设计的词法分析器:
(1)、能够识别出保留字、标识符、单分符、双分符、常量
(2)、利用表驱动法识别注释并且滤过注释
(3)、错误处理,能够连续查错并且能够指明错误类型
主要实现了三种错误的查找:
非法字符(@、¥等)
大小写敏感问题(保留字大小写错误例如INT a 但对于int INT不报错,只会识别为标识符)
标识符以数字开头的错误
实验代码:
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include
#include
#include
#define NUM 15
using namespace std;
FILE* f_in;
FILE* f_out;
char f1_name[100];
char f2_name[100];
char keyWord[NUM][20] = { "default","if", "else","for","while","do","int","read","write","float","switch","case","break","function","call" }; //保留字
char token[15]; //识别的单词
char token_num; //记录单词长度
char ch; //单词的首个字符
int row; //记录程序编译行数
char tmp[15];
int flag1; //用于标志换行后可能产生错误
int flag2; //区别标识符和保留字大小写敏感
int flag3;
int flag = 0;
char(*keyword)[20] = keyWord;
char* string;
void compile();
int compile_word();
void sort(char(*a)[20]);
int binary_S(char(*a)[20], char* string);
int main() {
sort(keyWord);
printf("请输入要编译的文件名字:");
scanf("%s", f1_name);
f_in = fopen(f1_name, "r");
printf("请输入要将编译结果存入的文件名字:");
scanf("%s", f2_name);
f_out = fopen(f2_name, "w");
compile();
fclose(f_in);
fclose(f_out);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//用冒泡法将保留字数组排序(根据ASCII码)
void sort(char(*a)[20]) {
char tmp[20];
for (int i = 0;i < NUM;i++) {
for (int j = i + 1;j < NUM;j++) {
if (strcmp(a[j], a[i]) < 0) {
for (int k = 0;k < 20;k++) {
tmp[k] = a[i][k];
a[i][k] = a[j][k];
a[j][k] = tmp[k];
}
}
}
}
}
//对数组进行折半查找
int binary_S(char(*a)[20], char* string) {
int low = 0;
int high = NUM-1;
while (low <= high) {
int middle = (low + high) / 2;
if (strcmp(string, a[middle]) == 0) {
return middle;
}
else if (strcmp(string, a[middle]) < 0) {
high = middle - 1;
}
else {
low = middle + 1;
}
}
return -1;
}
void bqd() {
//状态2
switch (ch)
{
case '*': ch = getc(f_in); //转到状态3
//状态3
s3:while (ch != '*') {
ch = getc(f_in);
if (ch == EOF) {
printf("ERROR: the error place is in the %d row.注释错误\n", row + 1);
return;
}
} //状态3循环
switch (ch)
{
case '*':ch = getc(f_in); //转到状态4
//状态4
while (ch == '*') ch = getc(f_in); //状态4循环
switch (ch)
{
case '/':ch = getc(f_in);
printf("注释正确\n");
fprintf(f_out, "注释正确\n");
return; //状态5结束
default:goto s3; //转到状态3
}
default: goto end;
}
default:
printf("单分符\t%s\n", token); //状态6
goto end;
}
end:return;
}
int compile_word() {
//将识别的单词数组初始化
for (int i = 0;i < 15;i++) {
token[i] = NULL;
tmp[i] = NULL;
}
token_num = 0;
flag1 = 0;
flag2 = 0;
flag3 = 0;
//处理空格
while ((ch == ' ') || (ch == '\n')) {
if (ch == '\n') {
row++;
flag1 = 1;
}
ch = getc(f_in);
}
if ((ch >= 'a' && ch <= 'z') || (ch >= 'A' && ch <= 'Z')) { //输入可能是标识符或者保留字
//组成一个单词
while ((ch >= 'a' && ch <= 'z') || (ch >= 'A' && ch <= 'Z') || (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9')) {
token[token_num++] = ch;
ch = getc(f_in);
}
if (flag1 == 1) {
for (int j = 0;j < token_num;j++) {
tmp[j] = token[j];
if (token[j] >= 'A' && token[j] <= 'Z') {
tmp[j] = tmp[j] + 32; //大写转换为小写
flag2 = 1;
}
}
}
token[token_num++] = '\0';
//比对保留字
for (int i = 0;i < NUM;i++) {
if (flag1 == 1 && flag2 == 1) {
if (binary_S(keyWord, tmp)!=-1) {
return -3; //大小写敏感
}
}
if (binary_S(keyWord, token)!=-1) { //匹配到某个保留字
return 1;
}
}
return 2; //关键字ID
}
else if (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') { //输入的是常量NUM(整型)
//组成一个单词
while ((ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') || ch == '.') { //扩展为浮点型
token[token_num++] = ch;
ch = getc(f_in);
while((ch >= 'a' && ch <= 'z') || (ch >= 'A' && ch <= 'Z')) {
ch = getc(f_in);
flag3 = 1;
}
}
if (flag3 != 1) {
return 3;
} //常量
else return -4; //非法单词
}
else { //输入为纯单分符
token[token_num++] = ch;
switch (ch)
{
//单分符为4 双分界符为5
case '*':
ch = getc(f_in);
return 4;
case '+':
ch = getc(f_in);
if (ch == '+') {
token[token_num++] = ch;
ch = getc(f_in);
return 5;
}
else {
return 4;
} //可以扩展为++
case '-':
ch = getc(f_in);
return 4; //可以扩展为--
case '(':
ch = getc(f_in);
return 4;
case ')':
ch = getc(f_in);
return 4;
case '{':
ch = getc(f_in);
return 4;
case '}':
ch = getc(f_in);
return 4;
case ',':
ch = getc(f_in);
return 4;
case ';':
ch = getc(f_in);
return 4;
case '"':
ch = getc(f_in);
return 4;
case '/':
ch = getc(f_in);
return 4;
case '>':
ch = getc(f_in);
//读下个字符看看是不是双分符
if (ch == '=') {
token[token_num++] = ch;
ch = getc(f_in);
return 5;
}
else {
return 4;
}
case '<':
ch = getc(f_in);
//读下个字符看看是不是双分符
if (ch == '=') {
token[token_num++] = ch;
ch = getc(f_in);
return 5;
}
else {
return 4;
}
case '!':
ch = getc(f_in);
//读下个字符看看是不是双分符
if (ch == '=') {
token[token_num++] = ch;
ch = getc(f_in);
return 5;
}
else {
return 4;
}
case ':':
ch = getc(f_in);
return 4;
case '=':
ch = getc(f_in);
//读下个字符看看是不是双分符
if (ch == '=') {
token[token_num++] = ch;
ch = getc(f_in);
return 5;
}
else {
return 4;
}
case EOF:return -1; //文件结尾符号
default: //错误没有匹配
ch = getc(f_in);
return -2;
}
}
}
int INT;
void compile() {
int state; //记录编译状态
int error[100]; //记录错误行数
printf("编译结果:\n");
printf("类别值\t自身值\n");
//读取文件第一个字符
ch = getc(f_in);
while (1) {
if (ch != '/') {
state = compile_word();
if (state == -1) {
break;
}
switch (state)
{
case 1:
printf("%s\t%s\n", token, token);
fprintf(f_out, "%s\t%s\n", token, token);
break;
case 2: {
printf("ID\t%s\n", token);
fprintf(f_out, "ID\t%s\n", token);}
break;
case 3:
printf("NUM\t%s\n", token);
fprintf(f_out,"NUM\t%s\n", token);
break;
case 4:
printf("%s\t%s\n", token, token);
fprintf(f_out, "%s\t%s\n", token, token);
break;
case 5:
printf("%s\t%s\n", token, token);
fprintf(f_out, "%s\t%s\n", token, token);
break;
case -2:
printf("ERROR: the error place is in the %d row. You have entered illegal characters\n", row + 1);
fprintf(f_out, "ERROR: the error place is in the %d row. You have entered illegal characters\n", row + 1);
break;
case -3:
printf("ERROR: the error place is in the %d row. You should enter lowercase (%s)\n", row + 1, tmp);
fprintf(f_out, "ERROR: the error place is in the %d row. You should enter lowercase (%s)\n", row + 1, tmp);
break;
case -4:
printf("ERROR: the error place is in the %d row. You cannot start a word with a number\n", row + 1);
fprintf(f_out, "ERROR: the error place is in the %d row. You cannot start a word with a number\n", row + 1);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
else
{
ch = getc(f_in);
bqd();
}
}
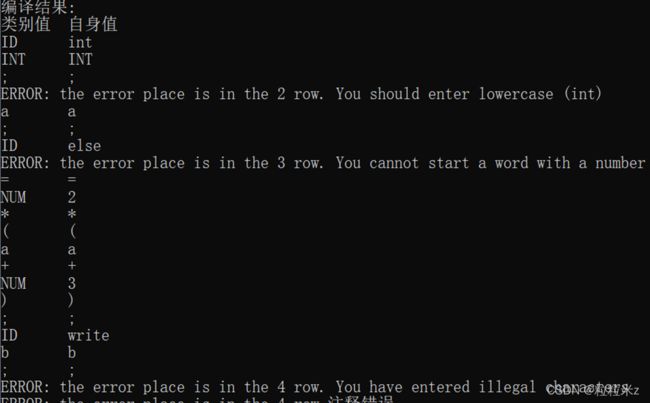
} 测试数据:
实验结果: