【卷积神经网络系列】六、GoogLeNet复现(Pytorch实现)
目录
- 参考:
- 一、GoogLeNet-V1
-
- 1. 搭建神经网络结构
-
- (1)定义基本的卷积:卷积+激活函数
- (2)类`Inception`定义了 Inception 模块的网络结构
- (3)类`InceptionAux`定义了辅助分类器模块的结构,辅助分类器只在训练的时候使用
- (4)整体网络结构
- 2. 将定义好的网络结构搭载到GPU/CPU,并定义优化器
- 3.绘图参数列表
- 4.训练函数
- 5.测试函数
- 6.训练过程
- 二、GoogLeNet-V2
-
-
- (1)定义基本的卷积:卷积+激活函数
- (2)定义带BN的卷积:卷积+BN+ReLu6
- (3)InceptionV2-A 模块结构:
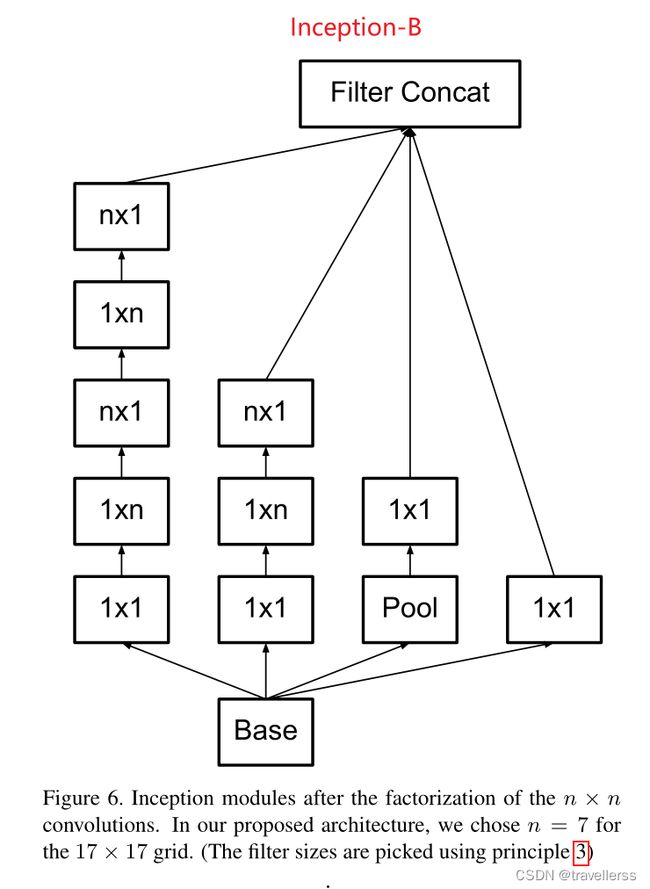
- (4)InceptionV2-B 模块结构:
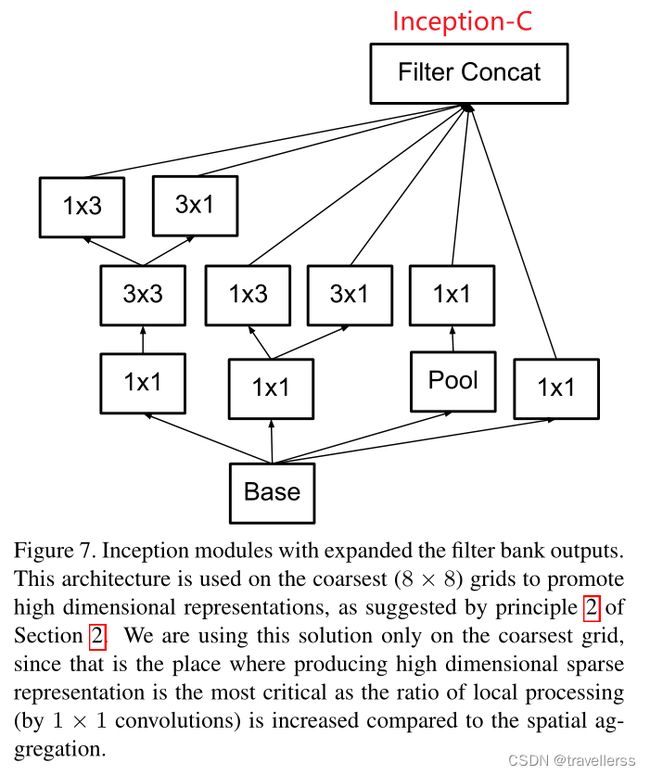
- (5)InceptionV2-C 模块结构:
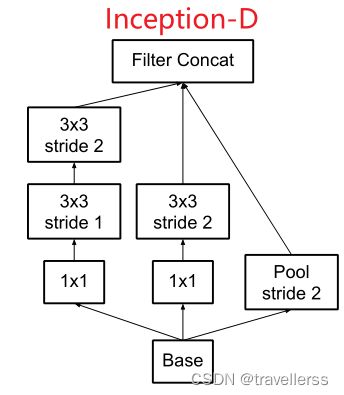
- (6)InceptionV2-D 模块结构:
- (7)完整的 GoogLeNetV2 网络结构:
-
- 三、GoogLeNet-V4
-
- 1. 搭建神经网络结构
-
- (1)定义基本的卷积:卷积+激活函数
- (2)定义带BN的卷积:卷积+BN+ReLu
- (3)Stem
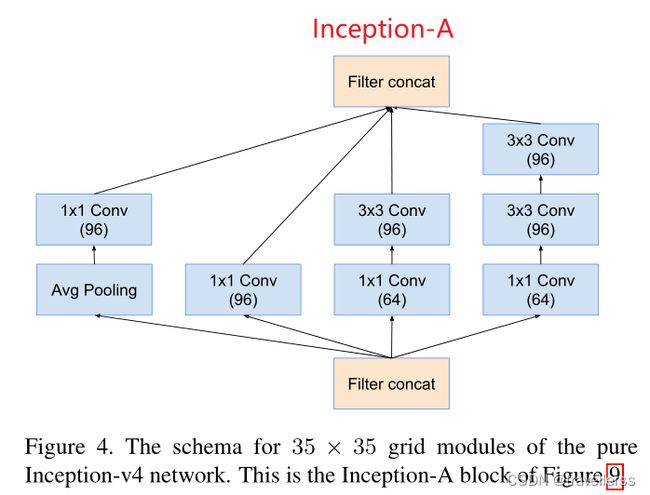
- (4)Inception-A:
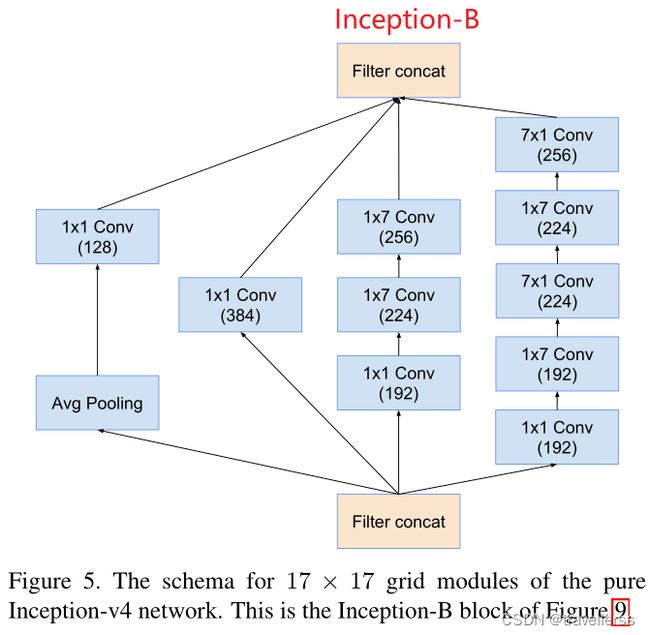
- (5)Inception-B:
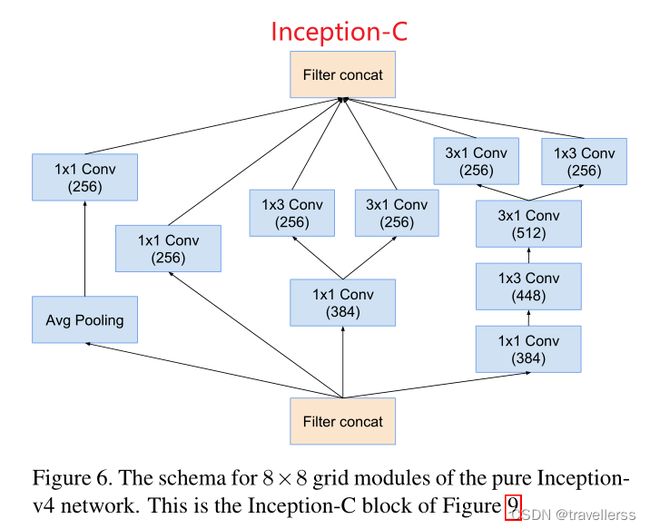
- (6)Inception-C:
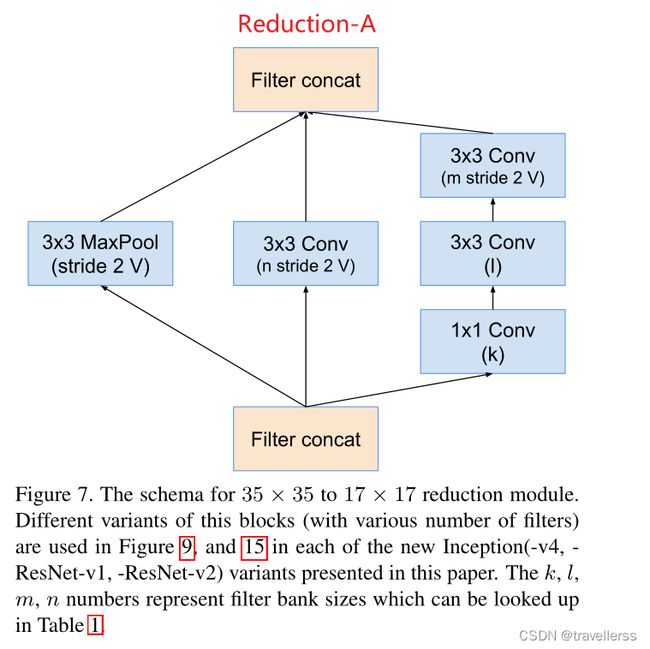
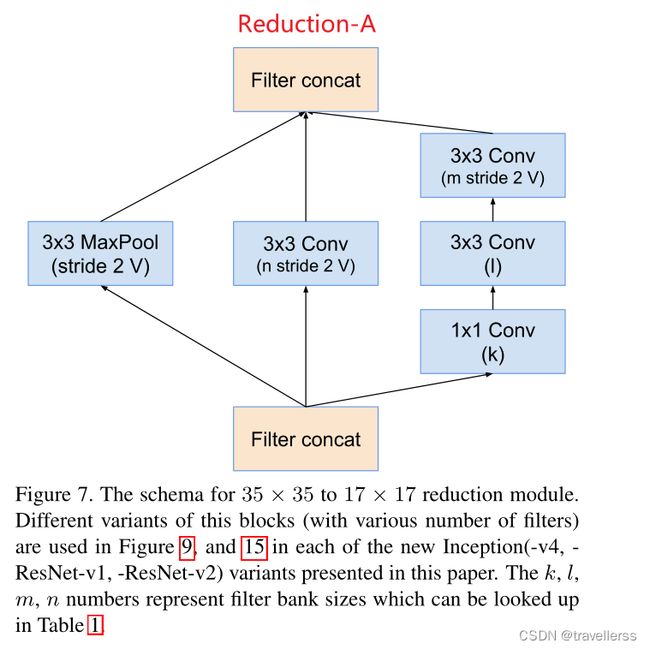
- (7)Reduction-A:
- (8)Reduction-B:
- (9)整体网络结构:
- 2. 将定义好的网络结构搭载到GPU/CPU,并定义优化器
- 3. 绘图参数
- 4. 训练函数
- 5. 测试函数
- 6. 训练过程
- 7. 保存模型并测试
- 8. 下载在服务器上训练好的模型参数,在测试集上验证精度
- 四、GoogLeNet-ResNet-V1
-
-
- (1)定义基本的卷积:卷积+激活函数
- (2)定义带BN的卷积:卷积+BN+ReLu
- (3)Steam:
- (4)Inception-A
- (5)Inception-B
- (6)Inception-C
- (7)Reduction-A:
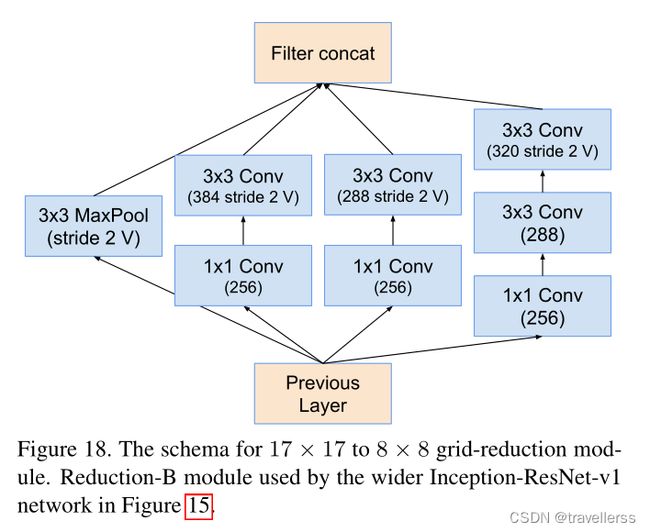
- (8)Reduction-B:
- (9)整体网络结构:
-
- 五、GoogLeNet-ResNet-V2
-
-
- (1)定义基本的卷积:卷积+激活函数
- (2)定义带BN的卷积:卷积+BN+ReLu
- (3)Stem
- (4)Inception-A
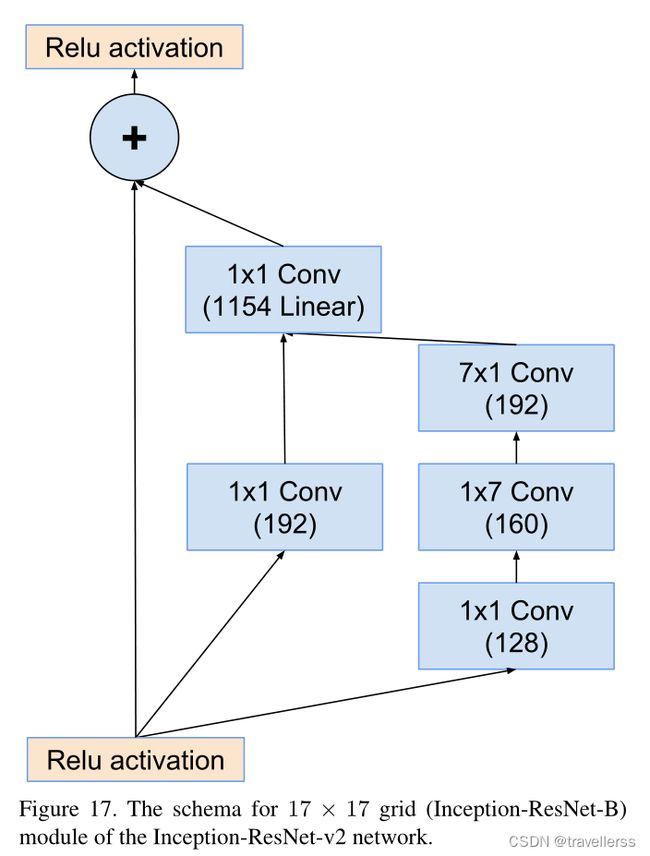
- (5)Inception-B
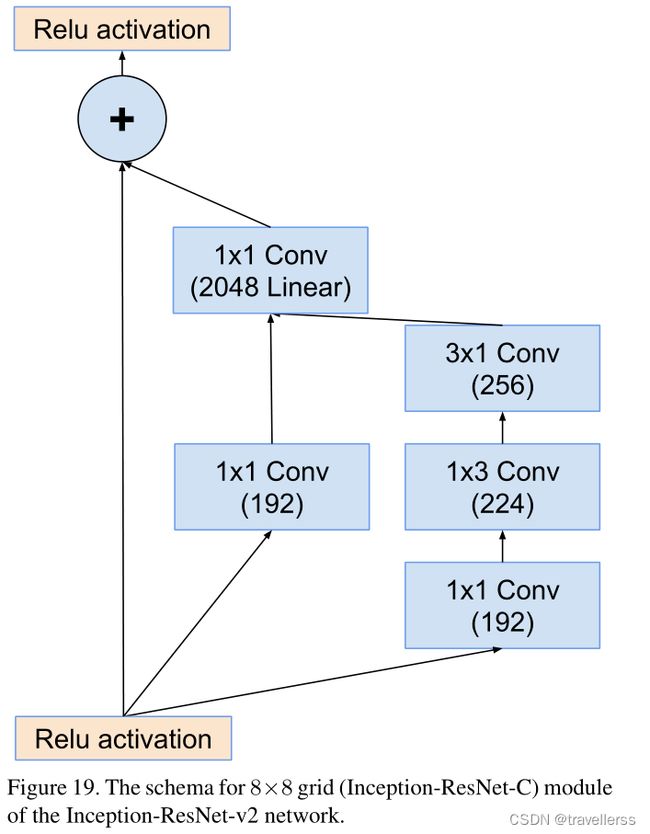
- (6)Inception-C
- (7)Reduction-A:
- (8)Reduction-B:
- (9)整体网络结构:
-
参考:
基于PyTorch实现Inception-v4, Inception-ResNet-v1, Inception-ResNet-v2亲身实践
一、GoogLeNet-V1
1. 搭建神经网络结构
(1)定义基本的卷积:卷积+激活函数
class BasicConv2d(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, **kwargs):
super(BasicConv2d, self).__init__()
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, **kwargs)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv(x)
x = self.relu(x)
return x
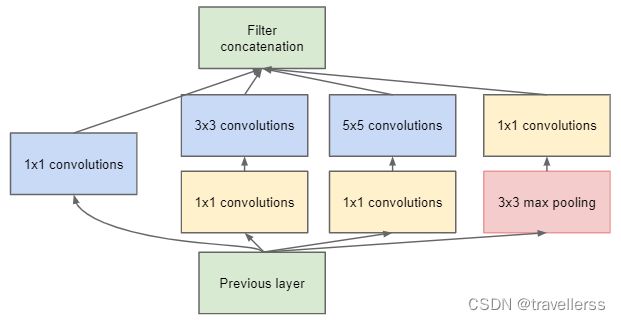
(2)类Inception定义了 Inception 模块的网络结构
class Inception(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, ch1x1, ch3x3red, ch3x3, ch5x5red, ch5x5, pool_proj):
"""
Args:
in_channels: 整个Inception的输入维度
ch1x1: 分支1(1x1卷积核)的out_channels
ch3x3red: 分支2(3x3卷积核)的in_channels
ch3x3: 分支2(3x3卷积核)的out_channels
ch5x5red: 分支3(5x5卷积核)的in_channels
ch5x5: 分支3(5x5卷积核)的out_channels
pool_proj: 分支4(1x1卷积核)的out_channels
"""
super(Inception, self).__init__()
# 分支1 -> 1x1
self.branch1 = BasicConv2d(in_channels, ch1x1, kernel_size=1)
# 分支2 -> 1x1 -> 3x3
self.branch2 = nn.Sequential(
BasicConv2d(in_channels, ch3x3red, kernel_size=1),
BasicConv2d(ch3x3red, ch3x3, kernel_size=3, padding=1) # 保证输出大小等于输入大小
)
# 分支3 -> 1x1 -> 5x5
self.branch3 = nn.Sequential(
BasicConv2d(in_channels, ch5x5red, kernel_size=1),
BasicConv2d(ch5x5red, ch5x5, kernel_size=5, padding=2) # 保证输出大小等于输入大小
)
# 分支4 -> 3x3 -> 1x1
self.branch4 = nn.Sequential(
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1), # 保证输出大小等于输入大小
BasicConv2d(in_channels, pool_proj, kernel_size=1) # 1x1的卷积核,输入为in_channels,输出为pool_proj
)
def forward(self, x):
branch1 = self.branch1(x)
branch2 = self.branch2(x)
branch3 = self.branch3(x)
branch4 = self.branch4(x)
outputs = [branch1, branch2, branch3, branch4]
# 拼接向量(从维度1开始拼接,维度0是batch)
return torch.cat(outputs, 1)
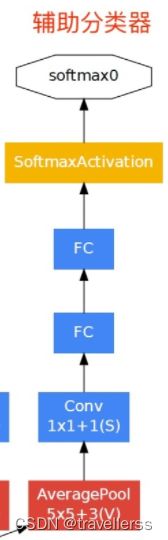
(3)类InceptionAux定义了辅助分类器模块的结构,辅助分类器只在训练的时候使用
- 下图是辅助分类器 aux1 的结构图,aux2 结构与 aux1 完全相同。
class InceptionAux(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, num_classes):
super(InceptionAux, self).__init__()
self.averagePool = nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=5, stride=3)
self.conv = BasicConv2d(in_channels, 128, kernel_size=1) # output[batch, 128, 4, 4]
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(2048, 1024)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(1024, num_classes)
def forward(self, x):
# aux1: N x 512 x 14 x 14, aux2: N x 528 x 14 x 14
x = self.averagePool(x)
# aux1: N x 512 x 4 x 4, aux2: N x 528 x 4 x 4
x = self.conv(x)
# N x 128 x 4 x 4
x = torch.flatten(x, 1)
x = F.dropout(x, 0.5, training=self.training)
# N x 2048
x = F.relu(self.fc1(x), inplace=True)
x = F.dropout(x, 0.5, training=self.training)
# N x 1024
x = self.fc2(x)
# N x num_classes
return x
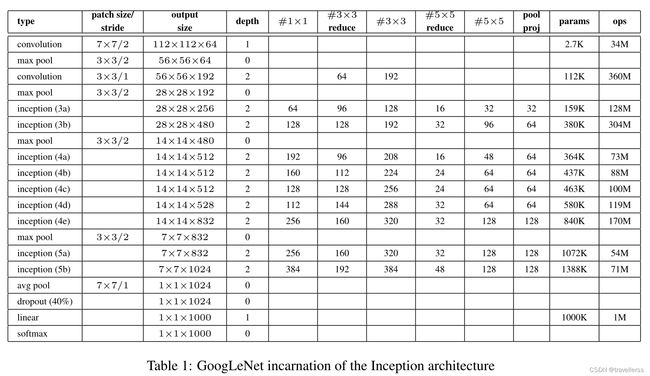
(4)整体网络结构
class GoogLeNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes=2, aux_logits=True, init_weights=False):
super(GoogLeNet, self).__init__()
self.aux_logits = aux_logits
# 输入为224x224x3 -> 输出为112x112x64
self.conv1 = BasicConv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3)
# 输入为112x112x64 -> 输出为56x56x64
# 当ceil_mode = true时,将保存不足为kernel_size大小的数据保存,自动补足NAN至kernel_size大小;
self.maxpool1 = nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=2, ceil_mode=True)
# 1x1的卷积核(带ReLu),增加非线性
self.conv2 = BasicConv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=1)
# 3x3的卷积核(带ReLu),输入为56x56x64 -> 输出为56x56x192
self.conv3 = BasicConv2d(64, 192, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
# 输入为56x56x192 -> 输出为28x28x192
self.maxpool2 = nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=2, ceil_mode=True)
# 输入为28x28x192 -> 输出为28x28x(64+128+32+32=256)
self.inception3a = Inception(192, 64, 96, 128, 16, 32, 32)
# 输入为28x28x256 -> 输出为28x28x(128+192+96+64=480)
self.inception3b = Inception(256, 128, 128, 192, 32, 96, 64)
# 输入为28x28x480 -> 输出为14x14x480
self.maxpool3 = nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=2, ceil_mode=True)
# 输入为14x14x480 -> 输出为14x14x(192+208+48+64=512)
self.inception4a = Inception(480, 192, 96, 208, 16, 48, 64)
# 输入为14x14x512 -> 输出为14x14x(160+224+64+64=512)
self.inception4b = Inception(512, 160, 112, 224, 24, 64, 64)
# 输入为14x14x512 -> 输出为14x14x(128+256+64+64=512)
self.inception4c = Inception(512, 128, 128, 256, 24, 64, 64)
# 输入为14x14x512 -> 输出为14x14x(112+288+64+64=528)
self.inception4d = Inception(512, 112, 144, 288, 32, 64, 64)
# 输入为14x14x528 -> 输出为14x14x(256+320+128+128=832)
self.inception4e = Inception(528, 256, 160, 320, 32, 128, 128)
# 输入为14x14x832 -> 输出为7x7x832
self.maxpool4 = nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=2, ceil_mode=True)
# 输入为7x7x832 -> 输出为7x7x(256+320+128+128=832)
self.inception5a = Inception(832, 256, 160, 320, 32, 128, 128)
# 输入为7x7x832 -> 输出为7x7x(384+384+128+128=1024)
self.inception5b = Inception(832, 384, 192, 384, 48, 128, 128)
# 是否需要辅助分类器
if self.aux_logits:
self.aux1 = InceptionAux(512, num_classes)
self.aux2 = InceptionAux(528, num_classes)
# 输入为7x7x1024 -> 输出为1x1x1024
self.avgpool = nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=7, stride=1)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(0.4)
self.fc = nn.Linear(1024, num_classes)
# 如果需要初始化参数,则调用函数
if init_weights:
self._initialize_weights()
def forward(self, x):
#------ 输入块 ------#
# N x 3 x 224 x 224
x = self.conv1(x)
# N x 64 x 112 x 112
x = self.maxpool1(x)
# N x 64 x 56 x 56
x = self.conv2(x)
# N x 64 x 56 x 56
x = self.conv3(x)
# N x 192 x 56 x 56
x = self.maxpool2(x)
#------ Inception 4a/4b ------#
# N x 192 x 28 x 28
x = self.inception3a(x)
# N x 256 x 28 x 28
x = self.inception3b(x)
# N x 480 x 28 x 28
x = self.maxpool3(x)
# N x 480 x 14 x 14
x = self.inception4a(x)
#------ 辅助分类器 1 ------#
# N x 512 x 14 x 14
if self.training and self.aux_logits: # eval model lose this layer
aux1 = self.aux1(x)
#------ Inception 4b/4c/4d ------#
x = self.inception4b(x)
# N x 512 x 14 x 14
x = self.inception4c(x)
# N x 512 x 14 x 14
x = self.inception4d(x)
#------ 辅助分类器 2 ------#
# N x 528 x 14 x 14
if self.training and self.aux_logits: # eval model lose this layer
aux2 = self.aux2(x)
#------ Inception 4e/5a/5b ------#
x = self.inception4e(x)
# N x 832 x 14 x 14
x = self.maxpool4(x)
# N x 832 x 7 x 7
x = self.inception5a(x)
# N x 832 x 7 x 7
x = self.inception5b(x)
# N x 1024 x 7 x 7
#------ 输出块 ------#
x = self.avgpool(x)
# N x 1024 x 1 x 1
x = torch.flatten(x, 1)
# N x 1024
x = self.dropout(x)
x = self.fc(x)
# N x 1000 (num_classes)
if self.training and self.aux_logits: # 测试时不需要辅助分类器
return x, aux2, aux1
return x
# 初始化参数
def _initialize_weights(self):
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
if m.bias is not None:
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
nn.init.normal_(m.weight, 0, 0.01)
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
2. 将定义好的网络结构搭载到GPU/CPU,并定义优化器
#创建模型,部署gpu
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
model = GoogLeNet(num_classes=2, aux_logits=True, init_weights=True)
model.to(device)
#定义优化器
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.0001)
3.绘图参数列表
# 训练次数
epoch = 10
# 绘图所用
plt_epoch = [] # 横坐标,训练次数
Train_Loss = [] # 训练损失
Train_Accuracy = [] # 训练精度
Test_Loss = [] # 测试损失
Test_Accuracy = [] # 测试精度
4.训练函数
def train_runner(model, epoch):
#训练模型, 启用 BatchNormalization 和 Dropout, 将BatchNormalization和Dropout置为True
model.train()
total = 0 # 总样本数量
correct =0.0 # 每轮epoch分类正确样本数量
epoch_avg_loss = 0.0 # 每轮epoch的平均损失
#enumerate迭代已加载的数据集,同时获取数据和数据下标
for batch_idx, data in enumerate(trainloader, 0):
batch_avg_loss = 0.0 # 每个batch的平均损失
inputs, labels = data # 解包
inputs, labels = inputs.to(device), labels.to(device) # 把模型部署到device上
optimizer.zero_grad() # 梯度清零
logits, aux_logits2, aux_logits1 = model(inputs) # 保存训练结果
#计算损失和
loss0 = criterion(logits, labels) # 主分类器
loss1 = criterion(aux_logits1, labels) # 辅助分类器1
loss2 = criterion(aux_logits2, labels) # 辅助分类器2
loss = loss0 + loss1 * 0.3 + loss2 * 0.3 # 权重加和
#dim=1表示返回每一行的最大值对应的列下标
predict = logits.argmax(dim=1) #获取最大概率的预测结果
total += labels.size(0) # 总样本数
correct += (predict == labels).sum().item() # 统计正确分类样本个数
epoch_avg_loss += loss.item() # 把每轮epoch的损失累加
batch_avg_loss += loss.item() # 累加每100个batch的损失
loss.backward() # 反向传播
optimizer.step() # 更新参数
# 每100个batch进行一次loss输出
if batch_idx % 100 == 99:
print('[epoch:%d, batch_idx:%5d] batch_avg_loss: %.6f' % (epoch, batch_idx+1, batch_avg_loss/100))
batch_avg_loss = 0.0
# 这里train_batchsize是64,向上取整,所有小数都是向着数值更大的方向取整
batch_num = math.ceil(total/64)
# 每完成一次训练epoch,打印当前平均Loss和精度
epoch_avg_loss /= batch_num
print("Train Epoch{} \t epoch_avg_loss: {:.6f}, accuracy: {:.6f}%".format(epoch, epoch_avg_loss, 100*(correct/total)))
# 加入列表,以便于绘图
Train_Loss.append(epoch_avg_loss)
Train_Accuracy.append(correct/total)
5.测试函数
def test_runner(model):
#模型验证, 必须要写, 否则只要有输入数据, 即使不训练, 它也会改变权值
#因为调用eval()将不启用 BatchNormalization 和 Dropout, BatchNormalization和Dropout置为False
model.eval()
#统计模型正确率, 设置初始值
correct = 0.0
test_loss = 0.0
total = 0
#torch.no_grad将不会计算梯度, 也不会进行反向传播
with torch.no_grad():
for data, label in testloader:
data, label = data.to(device), label.to(device)
output = model(data)
test_loss += criterion(output, label).item()
predict = output.argmax(dim=1)
#计算正确数量
total += label.size(0)
correct += (predict == label).sum().item()
# # 每完成一次训练epoch,打印当前平均Loss和精度
test_loss /= total
#计算损失值和精度
print("test_avarage_loss: {:.6f}, accuracy: {:.6f}%".format(test_loss, 100*(correct/total)))
# 加入列表,以便于绘图
Test_Loss.append(test_loss)
Test_Accuracy.append(correct/total)
6.训练过程
if __name__ == '__main__':
print("start_time",time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S',time.localtime(time.time())))
for epoch in range(1, epoch+1):
plt_epoch.append(epoch)
train_runner(model, epoch)
test_runner(model)
print("end_time: ",time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S',time.localtime(time.time())),'\n')
print('Finished Training')
plt.subplot(2,2,1), plt.plot(plt_epoch, Train_Loss), plt.title('Train_Loss'), plt.grid()
plt.subplot(2,2,2), plt.plot(plt_epoch, Train_Accuracy), plt.title('Train_Accuracy'), plt.grid()
plt.subplot(2,2,3), plt.plot(plt_epoch, Test_Loss), plt.title('Test_Loss'), plt.grid()
plt.subplot(2,2,4), plt.plot(plt_epoch, Test_Accuracy), plt.title('Test_Accuracy'), plt.grid()
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
二、GoogLeNet-V2
(1)定义基本的卷积:卷积+激活函数
- ReLU6是在ReLU的基础上,限制正值的上限6。
class BasicConv2d(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, **kwargs):
super(BasicConv2d, self).__init__()
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, **kwargs)
self.relu = nn.ReLU6(inplace=True)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv(x)
x = self.relu(x)
return x
(2)定义带BN的卷积:卷积+BN+ReLu6
class ConvBNReLU(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, **kwargs):
super(ConvBNReLU, self).__init__()
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, **kwargs)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
self.relu = nn.ReLU6(inplace=True)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv(x)
x = self.bn(x)
x = self.relu(x)
return x
(3)InceptionV2-A 模块结构:
class InceptionV2_A(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels_1red, out_channels_1, out_channels_2red, out_channels_2, out_channels_3, out_channels_4):
"""
Args:
in_channels: 整个Inception的输入维度
out_channels_1red: 分支1(1x1卷积核)的out_channels
out_channels_1: 分支1(3x3卷积核)的out_channels
out_channels_2red: 分支2(1x1卷积核)的out_channels
out_channels_2: 分支2(3x3卷积核)的out_channels
out_channels_3: 分支3(1x1卷积核)的out_channels
out_channels_4: 分支4(1x1卷积核)的out_channels
"""
super(InceptionV2_A, self).__init__()
# 分支1:(1x1->3x3->3x3)
self.branch1 = nn.Sequential(
ConvBNReLU(in_channels, out_channels_1red, kernel_size=1),
ConvBNReLU(out_channels_1red, out_channels_1, kernel_size=3, padding=1), # 保证输出大小等于输入大小
ConvBNReLU(out_channels_1, out_channels_1, kernel_size=3, padding=1) # 保证输出大小等于输入大小
)
# 分支2:(1x1->3x3)
self.branch2 = nn.Sequential(
ConvBNReLU(in_channels, out_channels_2red, kernel_size=1),
ConvBNReLU(out_channels_2red, out_channels_2, kernel_size=3, padding=1) # 保证输出大小等于输入大小
)
# 分支3:(MaxPool->1x1)
self.branch3 = nn.Sequential(
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
ConvBNReLU(in_channels, out_channels_3, kernel_size=1) # 保证输出大小等于输入大小
)
# 分支4(1x1)
self.branch4 = ConvBNReLU(in_channels, out_channels_4, kernel_size=1)
def forward(self, x):
branch1 = self.branch1(x)
branch2 = self.branch2(x)
branch3 = self.branch3(x)
branch4 = self.branch4(x)
outputs = [branch1, branch2, branch3, branch4]
return torch.cat(outputs, 1)
(4)InceptionV2-B 模块结构:
class InceptionV2_B(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels_1red, out_channels_1, out_channels_2red, out_channels_2, out_channels_3, out_channels_4):
"""
Args:
in_channels: 整个Inception的输入维度
out_channels_1red: 分支1(1x1卷积核)的out_channels
out_channels_1: 分支1(3x1卷积核)的out_channels
out_channels_2red: 分支2(1x1卷积核)的out_channels
out_channels_2: 分支2(3x1卷积核)的out_channels
out_channels_3: 分支3(1x1卷积核)的out_channels
out_channels_4: 分支4(1x1卷积核)的out_channels
"""
super(InceptionV2_B, self).__init__()
# 分支1:(1x1->1x3->3x1->1x3->3x1)
self.branch1 = nn.Sequential(
ConvBNReLU(in_channels, out_channels_1red, kernel_size=1),
# 使用1x3卷积核时,需要分别设置padding,以保证WxH不发生改变
ConvBNReLU(out_channels_1red, out_channels_1red, kernel_size=[1,3], padding=[0,1]),
ConvBNReLU(out_channels_1red, out_channels_1red, kernel_size=[3,1], padding=[1,0]),
ConvBNReLU(out_channels_1red, out_channels_1red, kernel_size=[1,3], padding=[0,1]),
ConvBNReLU(out_channels_1red, out_channels_1, kernel_size=[3,1], padding=[1,0])
)
# 分支2:(1x1->1x3->3x1)
self.branch2 = nn.Sequential(
ConvBNReLU(in_channels, out_channels_2red, kernel_size=1),
ConvBNReLU(out_channels_2red, out_channels_2red, kernel_size=[1,3], padding=[0,1]),
ConvBNReLU(out_channels_2red, out_channels_2, kernel_size=[3,1], padding=[1,0])
)
# 分支3:(MaxPool->1x1)
self.branch3 = nn.Sequential(
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
ConvBNReLU(in_channels, out_channels_3, kernel_size=1)
)
# 分支4:(1x1)
self.branch4 = ConvBNReLU(in_channels, out_channels_4, kernel_size=1)
def forward(self, x):
branch1 = self.branch1(x)
branch2 = self.branch2(x)
branch3 = self.branch3(x)
branch4 = self.branch4(x)
outputs = [branch1, branch2, branch3, branch4]
return torch.cat(outputs, 1)
(5)InceptionV2-C 模块结构:
class InceptionV2_C(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels_1red, out_channels_1, out_channels_2red, out_channels_2, out_channels_3, out_channels_4):
"""
Args:
in_channels: 整个Inception的输入维度
out_channels_1red: 分支1(1x1卷积核)的out_channels
out_channels_1: 分支1(1x3与3x1卷积核)的out_channels
out_channels_2red: 分支2(1x1卷积核)的out_channels
out_channels_2: 分支2(1x3与3x1卷积核)的out_channels
out_channels_3: 分支3(1x1卷积核)的out_channels
out_channels_4: 分支4(1x1卷积核)的out_channels
"""
super(InceptionV2_C, self).__init__()
# 分支1:(1x1->3x3->两个分支:①1x3;②3x1)
self.branch1_conv1x1 = ConvBNReLU(in_channels, out_channels_1red, kernel_size=1)
self.branch1_conv3x3 = ConvBNReLU(out_channels_1red, out_channels_1, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
self.branch1_conv1x3 = ConvBNReLU(out_channels_1, out_channels_1, kernel_size=[1,3], padding=[0,1])
self.branch1_conv3x1 = ConvBNReLU(out_channels_1, out_channels_1, kernel_size=[3,1], padding=[1,0])
# 分支2:(1x1->两个分支:①1x3;②3x1)
self.branch2_conv1x1 = ConvBNReLU(in_channels, out_channels_2red, kernel_size=1)
self.branch2_conv1x3 = ConvBNReLU(out_channels_2red, out_channels_2, kernel_size=[1,3],padding=[0,1])
self.branch2_conv3x1 = ConvBNReLU(out_channels_2red, out_channels_2, kernel_size=[3,1],padding=[1,0])
# 分支3:(MaxPool->1x1)
self.branch3 = nn.Sequential(
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
ConvBNReLU(in_channels, out_channels_3, kernel_size=1)
)
# 分支4:(1x1)
self.branch4 = ConvBNReLU(in_channels, out_channels_4, kernel_size=1)
def forward(self, x):
# 分支1
branch1_tmp = self.branch1_conv1x1(x)
branch1_tmp = self.branch1_conv3x3(branch1_tmp)
branch1 = torch.cat([self.branch1_conv1x3(branch1_tmp), self.branch1_conv3x1(branch1_tmp)], dim=1)
# 分支2
branch2_tmp = self.branch2_conv1x1(x)
branch2 = torch.cat([self.branch2_conv1x3(branch2_tmp), self.branch2_conv3x1(branch2_tmp)], dim=1)
# 分支3
branch3 = self.branch3(x)
# 分支4
branch4 = self.branch4(x)
outputs = [branch1, branch2, branch3, branch4]
return torch.cat(outputs, 1)
(6)InceptionV2-D 模块结构:
class InceptionV2_D(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels_1red, out_channels_1, out_channels_2red, out_channels_2):
super(InceptionV2_D, self).__init__()
# 分支1:(1x1->3x3->3x3)
self.branch1 = nn.Sequential(
ConvBNReLU(in_channels, out_channels_1red, kernel_size=1),
ConvBNReLU(out_channels_1red, out_channels_1, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
ConvBNReLU(out_channels_1, out_channels_1, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)
)
# 分支2:(1x1->3x3)
self.branch2 = nn.Sequential(
ConvBNReLU(in_channels, out_channels_2red, kernel_size=1),
ConvBNReLU(out_channels_2red, out_channels_2, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)
)
# 分支3:(1x1)
self.branch3 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)
def forward(self, x):
branch1 = self.branch1(x)
branch2 = self.branch2(x)
branch3 = self.branch3(x)
outputs = [branch1, branch2, branch3]
return torch.cat(outputs, 1)
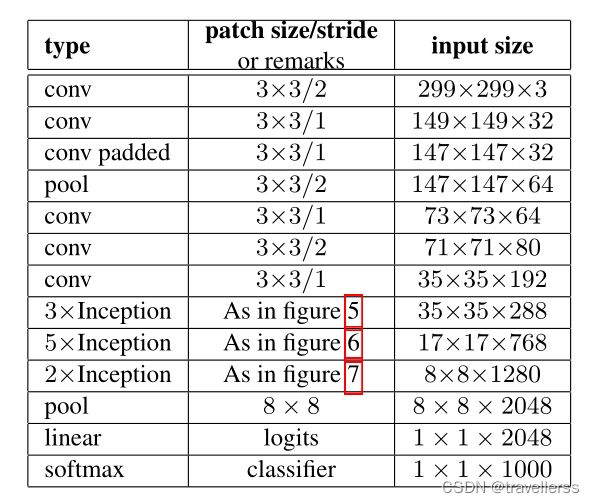
(7)完整的 GoogLeNetV2 网络结构:
class GoogLeNetV2(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes=2, init_weights=False):
super(GoogLeNetV2, self).__init__()
# 输入299x299x3 -> 输出149x149x32
self.conv1 = ConvBNReLU(3, 32, kernel_size=3, stride=2)
# 输入149x149x32 -> 输出147x147x32
self.conv2 = ConvBNReLU(32, 32, kernel_size=3, stride=1)
# 输入147x147x32 -> 输出147x147x64
self.conv3 = ConvBNReLU(32, 64, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=2)
# 输入147x147x64 -> 输出73x73x64
self.maxpool1 = nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=2)
# 输入73x73x64 -> 输出71x71x80
self.conv4 = ConvBNReLU(64, 80, kernel_size=3, stride=1)
# 输入71x71x80 -> 输出35x35x192
self.conv5 = ConvBNReLU(80, 192, kernel_size=3, stride=2)
# 输入35x35x192 -> 输出35x35x288
self.conv6 = BasicConv2d(192, 288, kernel_size=1)
# 输入35x35x288 -> 输出17x17x288
self.maxpool2 = nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=2)
# 输入17x17x288 -> 输出17x17x(128+96+64+64=352)
self.inceptionA1 = InceptionV2_A(288, 96, 128, 96, 96, 64, 64)
# 输入17x17x352 -> 输出17x17x(256+128+96+128=608)
self.inceptionA2 = InceptionV2_A(352, 256, 256, 128, 128, 96, 128)
# 输入17x17x608 -> 输出17x17x(320+224+96+128=768)
self.inceptionA3 = InceptionV2_A(608, 256, 320, 128, 224, 96, 128)
# 输入17x17x768 -> 输出17x17x(384+256+96+128=864)
self.inceptionB1 = InceptionV2_B(768, 128, 384, 128, 256, 96, 128)
# 输入17x17x864 -> 输出17x17x(320+320+96+128=864)
self.inceptionB2 = InceptionV2_B(864, 256, 320, 160, 320, 96, 128)
# 输入17x17x864 -> 输出17x17x(272+368+96+128=864)
self.inceptionB3 = InceptionV2_B(864, 256, 272, 192, 368, 96, 128)
# 输入17x17x864 -> 输出17x17x(368+368+96+128=960)
self.inceptionB4 = InceptionV2_B(864, 256, 368, 192, 368, 96, 128)
# 输入17x17x960 -> 输出17x17x(496+400+128+256=1280)
self.inceptionB5 = InceptionV2_B(960, 320, 496, 256, 400, 128, 256)
# 输入17x17x1280 -> 输出8x8x1280
self.maxpool3 = nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=2)
# 输入8x8x1280 -> 输出(384x2+256x2+128+256=1664)
self.inceptionC1 = InceptionV2_C(1280, 512, 384, 384, 256, 128, 256)
# 输入8x8x1664 -> 输出8x8x(216x2+192x2+80+128=1024)
self.inceptionC2 = InceptionV2_C(1664, 512, 216, 192, 192, 80, 128)
# 输出部分:平均池化->全连接层
self.avgpool = nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=8, stride=1)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(0.5)
self.fc = nn.Linear(1024, num_classes)
if init_weights:
self._initialize_weights()
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.conv2(x)
x = self.conv3(x)
x = self.maxpool1(x)
x = self.conv4(x)
x = self.conv5(x)
x = self.conv6(x)
x = self.maxpool2(x)
x = self.inceptionA1(x)
x = self.inceptionA2(x)
x = self.inceptionA3(x)
x = self.inceptionB1(x)
x = self.inceptionB2(x)
x = self.inceptionB3(x)
x = self.inceptionB4(x)
x = self.inceptionB5(x)
x = self.maxpool3(x)
x = self.inceptionC1(x)
x = self.inceptionC2(x)
x = self.avgpool(x)
# N x 1024 x 1 x 1
x = torch.flatten(x, 1)
x = self.dropout(x)
x = self.fc(x)
return x
def _initialize_weights(self):
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
if m.bias is not None:
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
nn.init.normal_(m.weight, 0, 0.01)
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
# 第一种测试模型的各层维度的方式:
# input = torch.ones((1,3,299,299))
# print(input.shape)
# model = GoogLeNetV2(num_classes=2, init_weights=True)
# output = model.test(input) # 把forward改成test
# print(output.shape)
三、GoogLeNet-V4
1. 搭建神经网络结构
(1)定义基本的卷积:卷积+激活函数
class BasicConv2d(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, **kwargs):
super(BasicConv2d, self).__init__()
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, **kwargs)
self.relu = nn.ReLU6(inplace=True)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv(x)
x = self.relu(x)
return x
(2)定义带BN的卷积:卷积+BN+ReLu
class ConvBNReLU(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, **kwargs):
super(ConvBNReLU, self).__init__()
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, **kwargs)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
self.relu = nn.ReLU6(inplace=True)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv(x)
x = self.bn(x)
x = self.relu(x)
return x
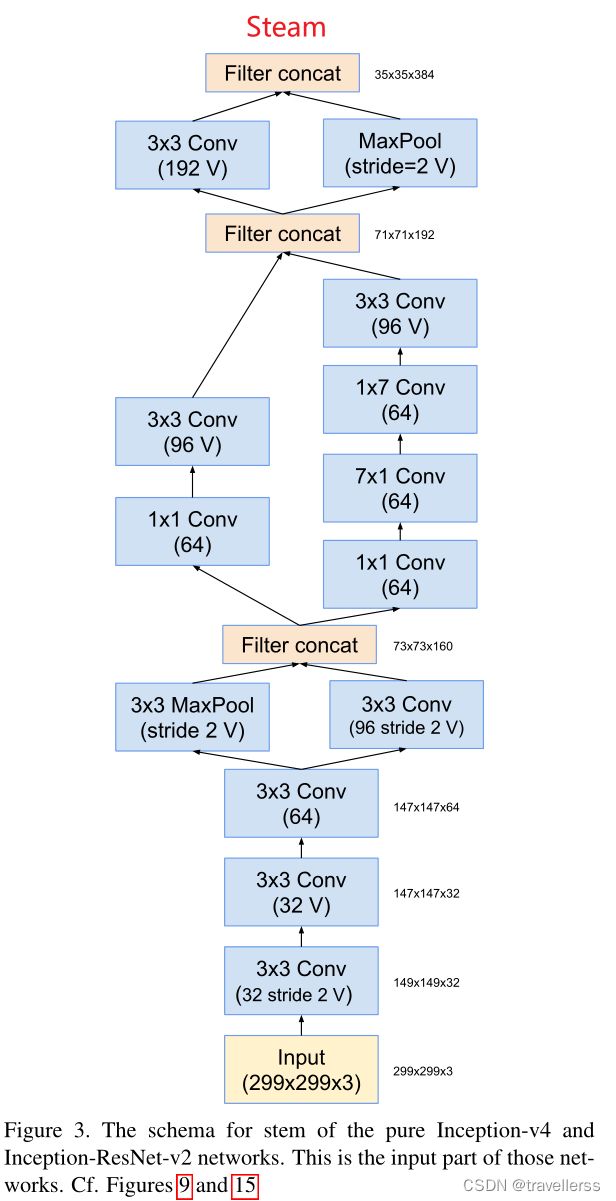
(3)Stem
class Stem(nn.Module):
"""
stem block for Inception-v4
"""
def __init__(self):
super(Stem, self).__init__()
# 连续3个3x3的卷积核
self.step1 = nn.Sequential(
# 299x299x3 -> 149x149x32
ConvBNReLU(in_channels=3, out_channels=32, kernel_size=3, stride=2),
# 149x149x32 -> 147x147x32
ConvBNReLU(in_channels=32, out_channels=32, kernel_size=3, stride=1),
# 147x147x32 -> 147x147x64
ConvBNReLU(in_channels=32, out_channels=64, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
)
# 分支1:147x147x64 -> 72x72x64
self.step2_pool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2)
# 分支2:147x147x64 -> 72x72x96
self.step2_conv = ConvBNReLU(in_channels=64, out_channels=96, kernel_size=3, stride=2)
# 分支1:1x1+3x3
self.step3_1 = nn.Sequential(
ConvBNReLU(in_channels=160, out_channels=64, kernel_size=1, stride=1),
ConvBNReLU(in_channels=64, out_channels=96, kernel_size=3, stride=1)
)
# 分支2:1x1+7x1+1x7+3x3
self.step3_2 = nn.Sequential(
ConvBNReLU(in_channels=160, out_channels=64, kernel_size=1, stride=1),
ConvBNReLU(in_channels=64, out_channels=64, kernel_size=[7,1], padding=[3,0]),
ConvBNReLU(in_channels=64, out_channels=64, kernel_size=[1,7], padding=[0,3]),
ConvBNReLU(in_channels=64, out_channels=96, kernel_size=3, stride=1)
)
# 分支1:池化
self.step4_pool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2)
# 分支2:3x3
self.step4_conv = ConvBNReLU(in_channels=192, out_channels=192, kernel_size=3, stride=2)
def forward(self, x):
out = self.step1(x)
tmp1 = self.step2_pool(out)
tmp2 = self.step2_conv(out)
out = torch.cat((tmp1, tmp2), 1)
tmp1 = self.step3_1(out)
tmp2 = self.step3_2(out)
out = torch.cat((tmp1, tmp2), 1)
tmp1 = self.step4_pool(out)
tmp2 = self.step4_conv(out)
outputs = [tmp1, tmp2]
return torch.cat(outputs, 1)
(4)Inception-A:
class InceptionV4_A(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels_1, out_channels_2, out_channels_3red, out_channels_3, out_channels_4red, out_channels_4):
"""
Args:
in_channels: 整个Inception的输入维度
out_channels_1: 分支1(1x1卷积核)的out_channels
out_channels_2: 分支2(1x1卷积核)的out_channels
out_channels_3red: 分支3(1x1卷积核)的out_channels
out_channels_3: 分支3(3x3卷积核)的out_channels
out_channels_4red: 分支4(1x1卷积核)的out_channels
out_channels_4: 分支4(3x3卷积核)的out_channels
"""
super(InceptionV4_A, self).__init__()
# 分支1:avg -> 1x1
self.branch1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
ConvBNReLU(in_channels, out_channels_1, kernel_size=1)
)
# 分支2:1x1
self.branch2 = nn.Sequential(
ConvBNReLU(in_channels, out_channels_2, kernel_size=1)
)
# 分支3:(1x1 -> 3x3)
self.branch3 = nn.Sequential(
ConvBNReLU(in_channels, out_channels_3red, kernel_size=1),
ConvBNReLU(out_channels_3red, out_channels_3, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)
)
# 分支4:(1x1 -> 3x3 -> 3x3)
self.branch4 = nn.Sequential(
ConvBNReLU(in_channels, out_channels_4red, kernel_size=1),
ConvBNReLU(out_channels_4red, out_channels_4, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
ConvBNReLU(out_channels_4, out_channels_4, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)
)
def forward(self, x):
branch1 = self.branch1(x)
branch2 = self.branch2(x)
branch3 = self.branch3(x)
branch4 = self.branch4(x)
outputs = [branch1, branch2, branch3, branch4]
return torch.cat(outputs, 1)
(5)Inception-B:
class InceptionV4_B(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels_1, out_channels_2,
out_channels_3_1x1, out_channels_3_1x7, out_channels_3,
out_channels_4_1x1, out_channels_4_1x7_1, out_channels_4_7x1_1,
out_channels_4_1x7_2, out_channels_4_7x1_2):
super(InceptionV4_B, self).__init__()
# 分支1:(AvgPool->1x1)
self.branch1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
ConvBNReLU(in_channels, out_channels_1, kernel_size=1)
)
# 分支2:(1x1)
self.branch2 = ConvBNReLU(in_channels, out_channels_2, kernel_size=1)
# 分支3:(1x1->1x7->7x1)
self.branch3 = nn.Sequential(
ConvBNReLU(in_channels, out_channels_3_1x1, kernel_size=1),
ConvBNReLU(out_channels_3_1x1, out_channels_3_1x7, kernel_size=[1,7], padding=[0,3]),
ConvBNReLU(out_channels_3_1x7, out_channels_3, kernel_size=[7,1], padding=[3,0])
)
# 分支4:(1x1->1x7->7x1->1x7->7x1)
self.branch4 = nn.Sequential(
ConvBNReLU(in_channels, out_channels_4_1x1, kernel_size=1),
ConvBNReLU(out_channels_4_1x1, out_channels_4_1x7_1, kernel_size=[1,7], padding=[0,3]),
ConvBNReLU(out_channels_4_1x7_1, out_channels_4_7x1_1, kernel_size=[7,1], padding=[3,0]),
ConvBNReLU(out_channels_4_7x1_1, out_channels_4_1x7_2, kernel_size=[1,7], padding=[0,3]),
ConvBNReLU(out_channels_4_1x7_2, out_channels_4_7x1_2, kernel_size=[7,1], padding=[3,0])
)
def forward(self, x):
branch1 = self.branch1(x)
branch2 = self.branch2(x)
branch3 = self.branch3(x)
branch4 = self.branch4(x)
outputs = [branch1, branch2, branch3, branch4]
return torch.cat(outputs, 1)
(6)Inception-C:
class InceptionV4_C(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels_1, out_channels_2,
out_channels_3red, out_channels_3,
out_channels_4_1x1, out_channels_4_1x3_1, out_channels_4_3x1_1,
out_channels_4_3x1_2, out_channels_4_1x3_2):
super(InceptionV4_C, self).__init__()
# 分支1:(AvgPool->1x1)
self.branch1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
ConvBNReLU(in_channels, out_channels_1, kernel_size=1)
)
# 分支2:(1x1)
self.branch2 = ConvBNReLU(in_channels, out_channels_2, kernel_size=1)
# 分支3:(1x1->两个分支:①1x3;②3x1)
self.branch3_conv1x1 = ConvBNReLU(in_channels, out_channels_3red, kernel_size=1)
self.branch3_conv1x3 = ConvBNReLU(out_channels_3red, out_channels_3, kernel_size=[1,3],padding=[0,1])
self.branch3_conv3x1 = ConvBNReLU(out_channels_3red, out_channels_3, kernel_size=[3,1],padding=[1,0])
# 分支4:(1x1->1x3->3x1->两个分支:①1x3;②3x1)
self.branch4_step1 = nn.Sequential(
ConvBNReLU(in_channels, out_channels_4_1x1, kernel_size=1),
ConvBNReLU(out_channels_4_1x1, out_channels_4_1x3_1, kernel_size=[1,3],padding=[0,1]),
ConvBNReLU(out_channels_4_1x3_1, out_channels_4_3x1_1, kernel_size=[3,1],padding=[1,0])
)
self.branch4_conv3x1 = ConvBNReLU(out_channels_4_3x1_1, out_channels_4_3x1_2, kernel_size=[3,1],padding=[1,0])
self.branch4_conv1x3 = ConvBNReLU(out_channels_4_3x1_1, out_channels_4_1x3_2, kernel_size=[1,3],padding=[0,1])
def forward(self, x):
# 分支1
branch1 = self.branch1(x)
# 分支2
branch2 = self.branch2(x)
# 分支3
branch3_tmp = self.branch3_conv1x1(x)
branch3 = torch.cat([self.branch3_conv1x3(branch3_tmp), self.branch3_conv3x1(branch3_tmp)], dim=1)
# 分支4
branch4_tmp = self.branch4_step1(x)
branch4 = torch.cat([self.branch4_conv3x1(branch4_tmp), self.branch4_conv1x3(branch4_tmp)], dim=1)
outputs = [branch1, branch2, branch3, branch4]
return torch.cat(outputs, 1)
(7)Reduction-A:
class Reduction_A(nn.Module):
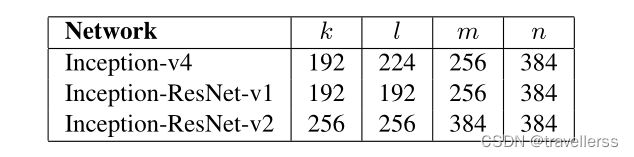
def __init__(self, in_channels, k, l, m, n):
super(Reduction_A, self).__init__()
# 分支1:MaxPool
self.branch1 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2)
# 分支2:(3x3)
self.branch2 = ConvBNReLU(in_channels, n, kernel_size=3, stride=2)
# 分支3:(1x1->3x3->3x3)
self.branch3 = nn.Sequential(
ConvBNReLU(in_channels, k, kernel_size=1),
ConvBNReLU(k, l, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
ConvBNReLU(l, m, kernel_size=3, stride=2)
)
def forward(self, x):
branch1 = self.branch1(x)
branch2 = self.branch2(x)
branch3 = self.branch3(x)
outputs = [branch1, branch2, branch3]
return torch.cat(outputs, 1)
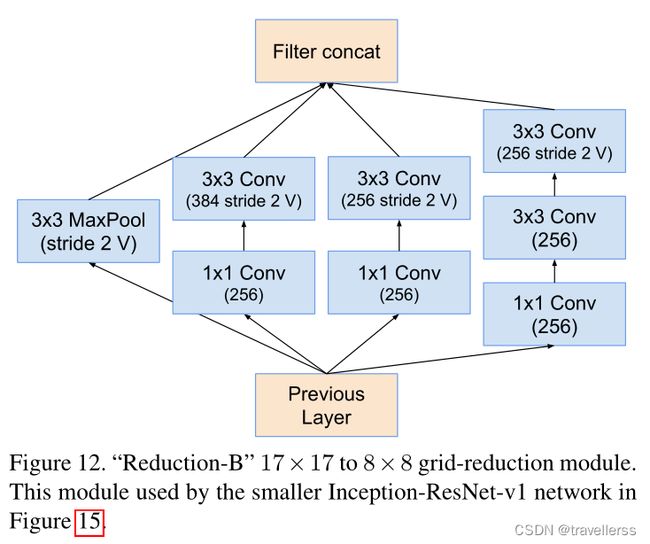
(8)Reduction-B:
class Reduction_B(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels_2_1x1, out_channels_2_3x3,
out_channels_3_1x1, out_channels_3_1x7, out_channels_3_7x1, out_channels_3_3x3):
super(Reduction_B, self).__init__()
# 分支1:MaxPool
self.branch1 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2)
# 分支2:(3x3)
self.branch2 = nn.Sequential(
ConvBNReLU(in_channels, out_channels_2_1x1, kernel_size=1),
ConvBNReLU(out_channels_2_1x1, out_channels_2_3x3, kernel_size=3, stride=2)
)
# 分支3:(1x1->1x7->7x1)
self.branch3 = nn.Sequential(
ConvBNReLU(in_channels, out_channels_3_1x1, kernel_size=1),
ConvBNReLU(out_channels_3_1x1, out_channels_3_1x7, kernel_size=[1,7], padding=[0,3]),
ConvBNReLU(out_channels_3_1x7, out_channels_3_7x1, kernel_size=[7,1], padding=[3,0]),
ConvBNReLU(out_channels_3_7x1, out_channels_3_3x3, kernel_size=3, stride=2)
)
def forward(self, x):
branch1 = self.branch1(x)
branch2 = self.branch2(x)
branch3 = self.branch3(x)
outputs = [branch1, branch2, branch3]
return torch.cat(outputs, 1)
(9)整体网络结构:
class GoogLeNetV4(nn.Module):
"""
implementation of Inception-v4
"""
def __init__(self, num_classes, init_weights=False):
super(GoogLeNetV4, self).__init__()
# 整体主干网络
self.stem = Stem()
self.inception_A = self.__make_inception_A()
self.Reduction_A = self.__make_reduction_A()
self.inception_B = self.__make_inception_B()
self.Reduction_B = self.__make_reduction_B()
self.inception_C = self.__make_inception_C()
# 输出部分:平均池化->全连接层
self.avgpool = nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=8, stride=1)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(0.2)
self.fc = nn.Linear(1536, num_classes)
if init_weights:
self._initialize_weights()
# 制造4层Inception-A
def __make_inception_A(self):
layers = []
for _ in range(4):
layers.append(InceptionV4_A(384, 96, 96, 64, 96, 64, 96)) # 384
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
# 制造1层Reduction-A
def __make_reduction_A(self):
return Reduction_A(384, 192, 224, 256, 384) # 1024
# 制造7层Inception-B
def __make_inception_B(self):
layers = []
for _ in range(7):
layers.append(InceptionV4_B(1024, 128, 384, 192, 224, 256,
192, 192, 224, 224, 256)) # 1024
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
# 制造1层Reduction-B
def __make_reduction_B(self):
return Reduction_B(1024, 192, 192, 256, 256, 320, 320) # 1536
# 制造3层Inception-C
def __make_inception_C(self):
layers = []
for _ in range(3):
layers.append(InceptionV4_C(1536, 256, 256, 384, 256, 384, 448, 512, 256, 256)) # 1536
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
def forward(self, x):
out = self.stem(x)
out = self.inception_A(out)
out = self.Reduction_A(out)
out = self.inception_B(out)
out = self.Reduction_B(out)
out = self.inception_C(out)
out = self.avgpool(out)
out = torch.flatten(out, 1)
out = self.dropout(out)
out = self.fc(out)
return out
def _initialize_weights(self):
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
if m.bias is not None:
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
nn.init.normal_(m.weight, 0, 0.01)
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
# # 第一种测试模型的各层维度的方式:
# input = torch.ones((1,3,299,299))
# print(input.shape)
# model = GoogLeNetV4(num_classes=2, init_weights=True)
# output = model.test(input) # 把forward改成test
# print(output.shape)
2. 将定义好的网络结构搭载到GPU/CPU,并定义优化器
#创建模型,部署gpu
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
model = GoogLeNetV4(num_classes=2, init_weights=True)
model.to(device)
# 第二种测试模型信息的方式
summary(model, (3, 299, 299))
#定义优化器
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.0001)
3. 绘图参数
# 训练次数
epoch = 10
# 绘图所用
plt_epoch = [] # 横坐标,训练次数
Train_Loss = [] # 训练损失
Train_Accuracy = [] # 训练精度
Test_Loss = [] # 测试损失
Test_Accuracy = [] # 测试精度
4. 训练函数
def train_runner(model, epoch):
#训练模型, 启用 BatchNormalization 和 Dropout, 将BatchNormalization和Dropout置为True
model.train()
total = 0 # 总样本数量
correct =0.0 # 每轮epoch分类正确样本数量
epoch_avg_loss = 0.0 # 每轮epoch的平均损失
#enumerate迭代已加载的数据集,同时获取数据和数据下标
for batch_idx, data in enumerate(trainloader, 0):
batch_avg_loss = 0.0 # 每个batch的平均损失
inputs, labels = data # 解包
inputs, labels = inputs.to(device), labels.to(device) # 把模型部署到device上
optimizer.zero_grad() # 梯度清零
outputs = model(inputs) # 保存训练结果
loss = criterion(outputs, labels) # 计算损失和
#dim=1表示返回每一行的最大值对应的列下标
predict = outputs.argmax(dim=1) #获取最大概率的预测结果
total += labels.size(0) # 总样本数
correct += (predict == labels).sum().item() # 统计正确分类样本个数
epoch_avg_loss += loss.item() # 把每轮epoch的损失累加
batch_avg_loss += loss.item() # 累加每100个batch的损失
loss.backward() # 反向传播
optimizer.step() # 更新参数
# 每100个batch进行一次loss输出
if batch_idx % 100 == 99:
print('[epoch:%d, batch_idx:%5d] batch_avg_loss: %.6f' % (epoch, batch_idx+1, batch_avg_loss/100))
batch_avg_loss = 0.0
# 这里train_batchsize是64,向上取整,所有小数都是向着数值更大的方向取整
batch_num = math.ceil(total/64)
# 每完成一次训练epoch,打印当前平均Loss和精度
epoch_avg_loss /= batch_num
print("Train Epoch{} \t epoch_avg_loss: {:.6f}, accuracy: {:.6f}%".format(epoch, epoch_avg_loss, 100*(correct/total)))
# 加入列表,以便于绘图
Train_Loss.append(epoch_avg_loss)
Train_Accuracy.append(correct/total)
5. 测试函数
def test_runner(model):
#模型验证, 必须要写, 否则只要有输入数据, 即使不训练, 它也会改变权值
#因为调用eval()将不启用 BatchNormalization 和 Dropout, BatchNormalization和Dropout置为False
model.eval()
#统计模型正确率, 设置初始值
correct = 0.0
test_loss = 0.0
total = 0
#torch.no_grad将不会计算梯度, 也不会进行反向传播
with torch.no_grad():
for data, label in testloader:
data, label = data.to(device), label.to(device)
output = model(data)
test_loss += criterion(output, label).item()
predict = output.argmax(dim=1)
#计算正确数量
total += label.size(0)
correct += (predict == label).sum().item()
# # 每完成一次训练epoch,打印当前平均Loss和精度
test_loss /= total
#计算损失值和精度
print("test_avarage_loss: {:.6f}, accuracy: {:.6f}%".format(test_loss, 100*(correct/total)))
# 加入列表,以便于绘图
Test_Loss.append(test_loss)
Test_Accuracy.append(correct/total)
6. 训练过程
if __name__ == '__main__':
print("start_time",time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S',time.localtime(time.time())))
for epoch in range(1, epoch+1):
plt_epoch.append(epoch)
train_runner(model, epoch)
test_runner(model)
print("end_time: ",time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S',time.localtime(time.time())),'\n')
print('Finished Training')
plt.subplot(2,2,1), plt.plot(plt_epoch, Train_Loss), plt.title('Train_Loss'), plt.grid()
plt.subplot(2,2,2), plt.plot(plt_epoch, Train_Accuracy), plt.title('Train_Accuracy'), plt.grid()
plt.subplot(2,2,3), plt.plot(plt_epoch, Test_Loss), plt.title('Test_Loss'), plt.grid()
plt.subplot(2,2,4), plt.plot(plt_epoch, Test_Accuracy), plt.title('Test_Accuracy'), plt.grid()
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
7. 保存模型并测试
print(model)
pathfile = './models/'
save_filename = 'GoogLeNetV4-catvsdog.pth'
model_path = os.path.join(pathfile, save_filename)
torch.save(model, model_path) #保存模型
if __name__ == '__main__':
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
pathfile = './models/'
save_filename = 'GoogLeNetV4-catvsdog.pth'
model_path = os.path.join(pathfile, save_filename)
model = torch.load(model_path) #加载模型
model = model.to(device)
model.eval() #把模型转为test模式
#读取要预测的图片
# 读取要预测的图片
img = Image.open("./pic/test_cat.jpg") # 读取图像
#img.show()
plt.imshow(img) # 显示图片
plt.axis('off') # 不显示坐标轴
plt.show()
# 导入图片,图片扩展后为[1,1,32,32]
trans = transforms.Compose(
[
transforms.Resize((299,299)),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))
])
img = trans(img)
img = img.to(device)
img = img.unsqueeze(0) #图片扩展多一维,因为输入到保存的模型中是4维的[batch_size,通道,长,宽],而普通图片只有三维,[通道,长,宽]
# 预测
classes = ('cat', 'dog')
output = model(img)
prob = F.softmax(output,dim=1) #prob是2个分类的概率
print("概率:",prob)
value, predicted = torch.max(output.data, 1)
predict = output.argmax(dim=1)
pred_class = classes[predicted.item()]
print("预测类别:",pred_class)
8. 下载在服务器上训练好的模型参数,在测试集上验证精度
if __name__ == '__main__':
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
pathfile = './models/'
save_filename = 'GoogLeNetV4-catvsdog.pth'
model_path = os.path.join(pathfile, save_filename)
model = torch.load(model_path) #加载模型
model = model.to(device)
#定义优化器
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
#模型验证, 必须要写, 否则只要有输入数据, 即使不训练, 它也会改变权值
#因为调用eval()将不启用 BatchNormalization 和 Dropout, BatchNormalization和Dropout置为False
model.eval()
#统计模型正确率, 设置初始值
correct = 0.0
test_loss = 0.0
total = 0
#torch.no_grad将不会计算梯度, 也不会进行反向传播
with torch.no_grad():
for data, label in testloader:
data, label = data.to(device), label.to(device)
output = model(data)
test_loss += criterion(output, label).item()
predict = output.argmax(dim=1)
#计算正确数量
total += label.size(0)
correct += (predict == label).sum().item()
# 每完成一次训练epoch,打印当前平均Loss和精度
test_loss /= total
#计算损失值和精度
print("test_avarage_loss: {:.6f}, accuracy: {:.6f}%".format(test_loss, 100*(correct/total)))
四、GoogLeNet-ResNet-V1
(1)定义基本的卷积:卷积+激活函数
class BasicConv2d(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, **kwargs):
super(BasicConv2d, self).__init__()
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, **kwargs)
self.relu = nn.ReLU6(inplace=True)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv(x)
x = self.relu(x)
return x
(2)定义带BN的卷积:卷积+BN+ReLu
class ConvBNReLU(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, **kwargs):
super(ConvBNReLU, self).__init__()
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, **kwargs)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
self.relu = nn.ReLU6(inplace=True)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv(x)
x = self.bn(x)
x = self.relu(x)
return x
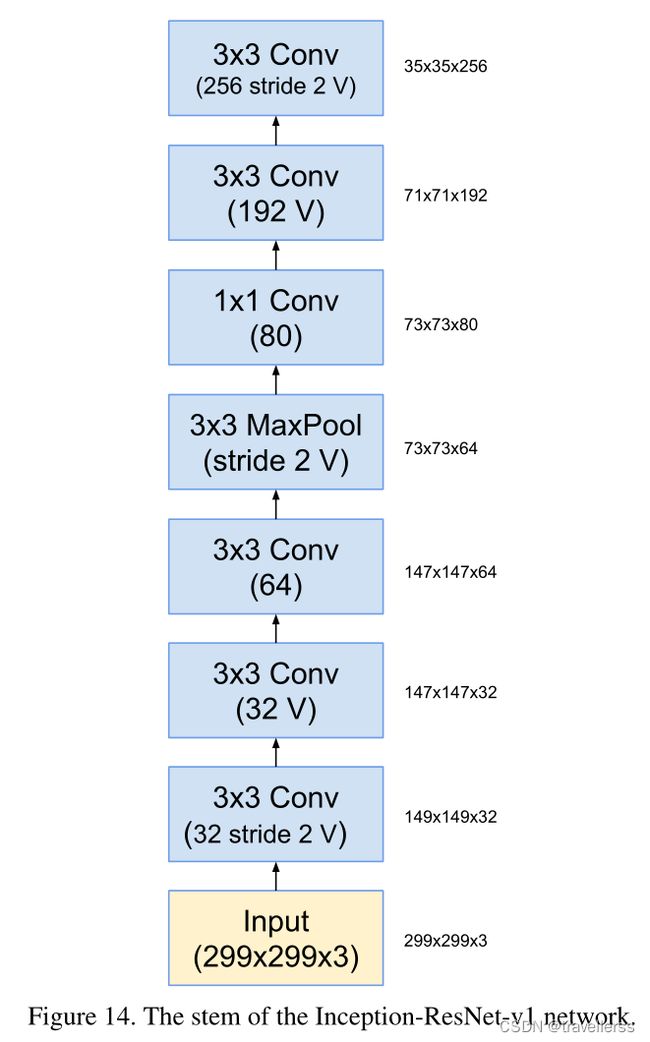
(3)Steam:
class Stem(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Stem, self).__init__()
self.stem = nn.Sequential(
ConvBNReLU(in_channels=3, out_channels=32, kernel_size=3, stride=2),
ConvBNReLU(in_channels=32, out_channels=32, kernel_size=3, stride=1),
ConvBNReLU(in_channels=32, out_channels=64, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2),
ConvBNReLU(in_channels=64, out_channels=80, kernel_size=1, stride=1),
ConvBNReLU(in_channels=80, out_channels=192, kernel_size=3, stride=1),
ConvBNReLU(in_channels=192, out_channels=256, kernel_size=3, stride=2),
)
def forward(self, x):
return self.stem(x)
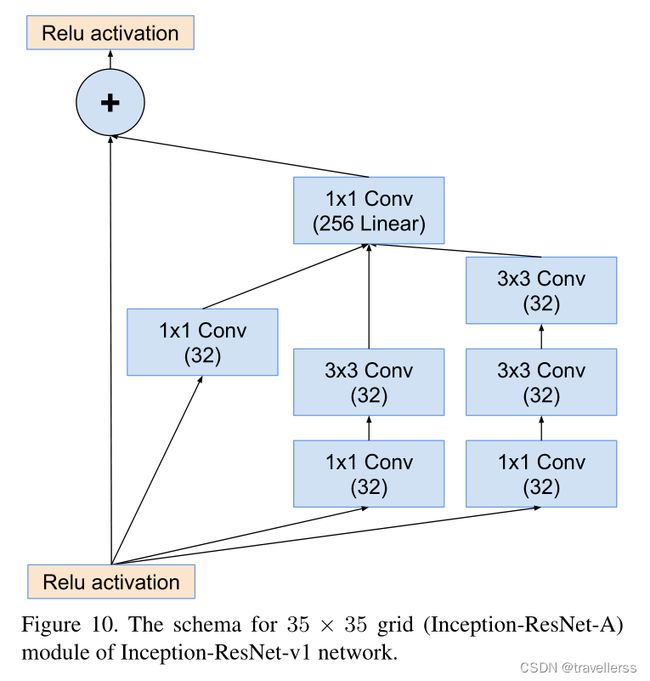
(4)Inception-A
class Inception_A(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, b1, b2_1x1, b2_3x3, b3_1x1, b3_3x3_1, b3_3x3_2, n1_linear):
super(Inception_A, self).__init__()
# 分支1:
self.branch1 = ConvBNReLU(in_channels, b1, kernel_size=1, stride=1)
# 分支2:1x1 -> 3x3
self.branch2 = nn.Sequential(
ConvBNReLU(in_channels, b2_1x1, kernel_size=1, stride=1),
ConvBNReLU(b2_1x1, b2_3x3, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)
)
# 分支3:1x1 -> 3x3 -> 3x3
self.branch3 = nn.Sequential(
ConvBNReLU(in_channels, b3_1x1, kernel_size=1, stride=1),
ConvBNReLU(b3_1x1, b3_3x3_1, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
ConvBNReLU(b3_3x3_1, b3_3x3_2, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)
)
# 1x1Conv
self.conv_linear = nn.Conv2d(b1+b2_3x3+b3_3x3_2, n1_linear, 1, 1, 0, bias=True)
"""
因为这里需要将原始输入通过直连边连接到输出部分,所以需要判断in_channels和n1_linear的关系
"""
# 如果in_channels==n1_linear,则不进行short_cut
self.short_cut = nn.Sequential()
# 如果in_channels!=n1_linear,则进行short_cut,把原始输入维度转为n1_linear
if in_channels != n1_linear:
self.short_cut = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, n1_linear, 1, 1, 0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(n1_linear)
)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
def forward(self, x):
out1 = self.branch1(x)
out2 = self.branch2(x)
out3 = self.branch3(x)
out = torch.cat((out1, out2, out3), 1)
out = self.conv_linear(out)
# 残差连接
out += self.short_cut(x)
out = self.relu(out)
return out
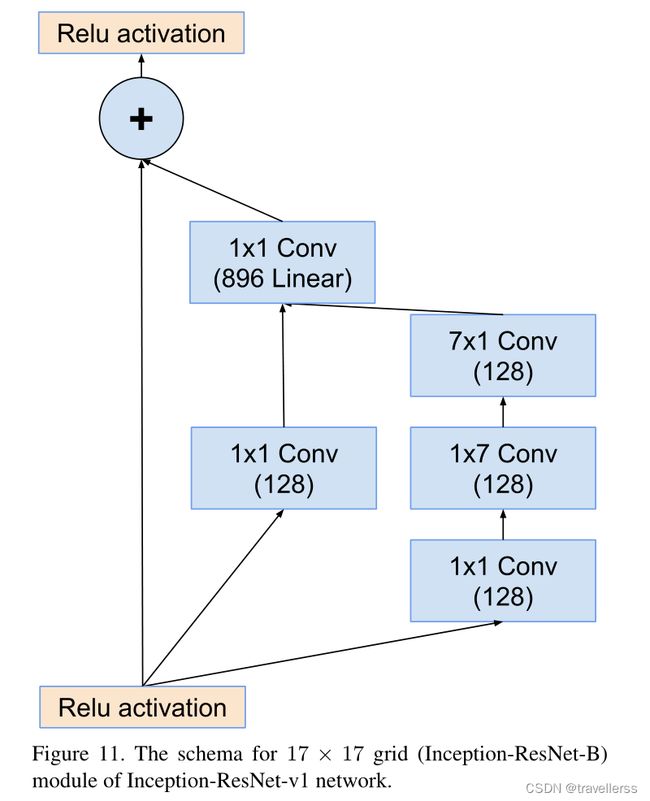
(5)Inception-B
class Inception_B(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, b1, b2_1x1, b2_1x7, b2_7x1, n1_linear):
super(Inception_B, self).__init__()
# 分支1:
self.branch1 = ConvBNReLU(in_channels, b1, kernel_size=1, stride=1)
# 分支2:
self.branch2 = nn.Sequential(
ConvBNReLU(in_channels, b2_1x1, kernel_size=1, stride=1),
ConvBNReLU(b2_1x1, b2_1x7, kernel_size=[1,7], padding=[0,3]),
ConvBNReLU(b2_1x7, b2_7x1, kernel_size=[7,1], padding=[3,0])
)
# 1x1Conv
self.conv_linear = nn.Conv2d(b1 + b2_7x1, n1_linear, 1, 1, 0, bias=False)
self.short_cut = nn.Sequential()
if in_channels != n1_linear:
self.short_cut = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, n1_linear, 1, 1, 0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(n1_linear)
)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
def forward(self, x):
out1 = self.branch1(x)
out2 = self.branch2(x)
out = torch.cat((out1, out2), 1)
out = self.conv_linear(out)
# 残差连接
out += self.short_cut(x)
out = self.relu(out)
return out
(6)Inception-C
class Inception_C(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, b1, b2_1x1, b2_1x3, b2_3x1, n1_linear):
super(Inception_C, self).__init__()
# 分支1:
self.branch1 = ConvBNReLU(in_channels, b1, kernel_size=1, stride=1)
# 分支2:
self.branch2 = nn.Sequential(
ConvBNReLU(in_channels, b2_1x1, kernel_size=1, stride=1),
ConvBNReLU(b2_1x1, b2_1x3, kernel_size=[1,3], padding=[0,1]),
ConvBNReLU(b2_1x3, b2_3x1, kernel_size=[3,1], padding=[1,0])
)
# 1x1Conv
self.conv_linear = nn.Conv2d(b1 + b2_3x1, n1_linear, 1, 1, 0, bias=False)
self.short_cut = nn.Sequential()
if in_channels != n1_linear:
self.short_cut = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, n1_linear, 1, 1, 0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(n1_linear)
)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
def forward(self, x):
out1 = self.branch1(x)
out2 = self.branch2(x)
out = torch.cat((out1, out2), 1)
out = self.conv_linear(out)
# 残差连接
out += self.short_cut(x)
out = self.relu(out)
return out
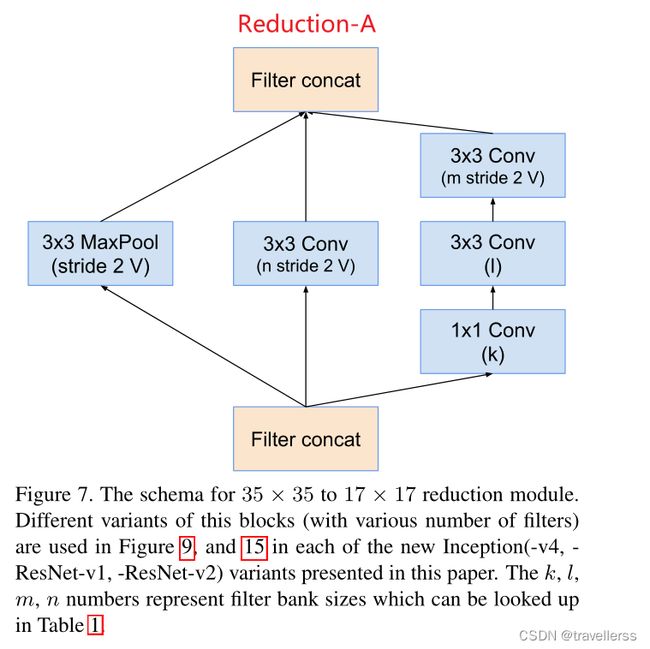
(7)Reduction-A:
class Reduction_A(nn.Module):
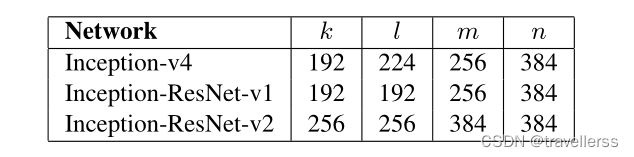
def __init__(self, in_channels, k, l, m, n):
super(Reduction_A, self).__init__()
# 分支1:MaxPool
self.branch1 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2)
# 分支2:(3x3)
self.branch2 = ConvBNReLU(in_channels, n, kernel_size=3, stride=2)
# 分支3:(1x1->3x3->3x3)
self.branch3 = nn.Sequential(
ConvBNReLU(in_channels, k, kernel_size=1),
ConvBNReLU(k, l, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
ConvBNReLU(l, m, kernel_size=3, stride=2)
)
def forward(self, x):
branch1 = self.branch1(x)
branch2 = self.branch2(x)
branch3 = self.branch3(x)
outputs = [branch1, branch2, branch3]
return torch.cat(outputs, 1)
(8)Reduction-B:
class Reduction_B(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, b2_1x1, b2_3x3, b3_1x1, b3_3x3, b4_1x1, b4_3x3_1, b4_3x3_2):
super(Reduction_B, self).__init__()
# 分支1:
self.branch1 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2)
# 分支2:
self.branch2 = nn.Sequential(
ConvBNReLU(in_channels, b2_1x1, kernel_size=1, stride=1),
ConvBNReLU(b2_1x1, b2_3x3, kernel_size=3, stride=2)
)
# 分支3:
self.branch3 = nn.Sequential(
ConvBNReLU(in_channels, b3_1x1, kernel_size=1, stride=1),
ConvBNReLU(b3_1x1, b3_3x3, kernel_size=3, stride=2)
)
# 分支4:
self.branch4 = nn.Sequential(
ConvBNReLU(in_channels, b4_1x1, kernel_size=1, stride=1),
ConvBNReLU(b4_1x1, b4_3x3_1, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
ConvBNReLU(b4_3x3_1, b4_3x3_2, kernel_size=3, stride=2),
)
def forward(self, x):
out1 = self.branch1(x)
out2 = self.branch2(x)
out3 = self.branch3(x)
out4 = self.branch4(x)
return torch.cat((out1, out2, out3, out4), 1)
(9)整体网络结构:
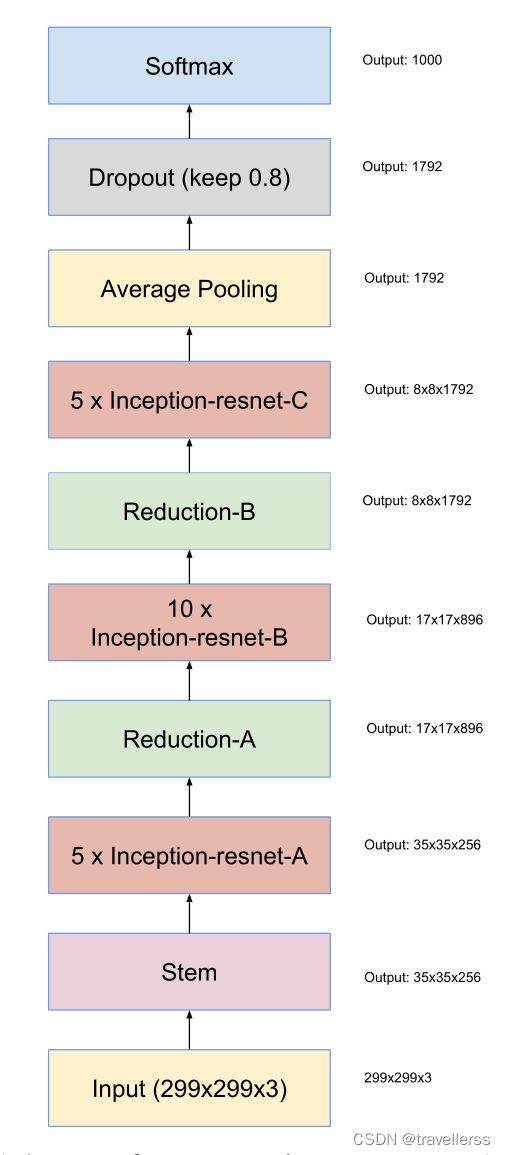
class GoogLeNet_ResNetV1(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes, init_weights=False):
super(GoogLeNet_ResNetV1, self).__init__()
# 整体主干网络
self.stem = Stem()
self.inception_A = self.__make_inception_A()
self.Reduction_A = self.__make_reduction_A()
self.inception_B = self.__make_inception_B()
self.Reduction_B = self.__make_reduction_B()
self.inception_C = self.__make_inception_C()
# 输出部分:平均池化->全连接层
self.avgpool = nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=8, stride=1)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(0.2)
self.fc = nn.Linear(1792, num_classes)
if init_weights:
self._initialize_weights()
# 制造5层Inception-A
def __make_inception_A(self):
layers = []
for _ in range(5):
layers.append(Inception_A(256, 32, 32, 32, 32, 32, 32, 256))
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
# 制造1层Reduction-A
def __make_reduction_A(self):
return Reduction_A(256, 192, 192, 256, 384)
# 制造10层Inception-B
def __make_inception_B(self):
layers = []
for _ in range(10):
layers.append(Inception_B(896, 128, 128, 128, 128, 896))
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
# 制造1层Reduction-B
def __make_reduction_B(self):
return Reduction_B(896, 256, 384, 256, 256, 256, 256, 256)
# 制造5层Inception-C
def __make_inception_C(self):
layers = []
for _ in range(5):
layers.append(Inception_C(1792, 192, 192, 192, 192, 1792))
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
def forward(self, x):
out = self.stem(x)
out = self.inception_A(out)
out = self.Reduction_A(out)
out = self.inception_B(out)
out = self.Reduction_B(out)
out = self.inception_C(out)
out = self.avgpool(out)
out = torch.flatten(out, 1)
out = self.dropout(out)
out = self.fc(out)
return out
def _initialize_weights(self):
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
if m.bias is not None:
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
nn.init.normal_(m.weight, 0, 0.01)
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
# # 第一种测试模型的各层维度的方式:
# input = torch.ones((1,3,299,299))
# print(input.shape)
# model = GoogLeNetV4(num_classes=2, init_weights=True)
# output = model.test(input) # 把forward改成test
# print(output.shape)
五、GoogLeNet-ResNet-V2
(1)定义基本的卷积:卷积+激活函数
class BasicConv2d(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, **kwargs):
super(BasicConv2d, self).__init__()
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, **kwargs)
self.relu = nn.ReLU6(inplace=True)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv(x)
x = self.relu(x)
return x
(2)定义带BN的卷积:卷积+BN+ReLu
class ConvBNReLU(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, **kwargs):
super(ConvBNReLU, self).__init__()
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, **kwargs)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
self.relu = nn.ReLU6(inplace=True)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv(x)
x = self.bn(x)
x = self.relu(x)
return x
(3)Stem
class Stem(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Stem, self).__init__()
# 连续3个3x3的卷积核
self.step1 = nn.Sequential(
# 299x299x3 -> 149x149x32
ConvBNReLU(in_channels=3, out_channels=32, kernel_size=3, stride=2),
# 149x149x32 -> 147x147x32
ConvBNReLU(in_channels=32, out_channels=32, kernel_size=3, stride=1),
# 147x147x32 -> 147x147x64
ConvBNReLU(in_channels=32, out_channels=64, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
)
# 分支1:147x147x64 -> 72x72x64
self.step2_pool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2)
# 分支2:147x147x64 -> 72x72x96
self.step2_conv = ConvBNReLU(in_channels=64, out_channels=96, kernel_size=3, stride=2)
# 分支1:1x1+3x3
self.step3_1 = nn.Sequential(
ConvBNReLU(in_channels=160, out_channels=64, kernel_size=1, stride=1),
ConvBNReLU(in_channels=64, out_channels=96, kernel_size=3, stride=1)
)
# 分支2:1x1+7x1+1x7+3x3
self.step3_2 = nn.Sequential(
ConvBNReLU(in_channels=160, out_channels=64, kernel_size=1, stride=1),
ConvBNReLU(in_channels=64, out_channels=64, kernel_size=[7,1], padding=[3,0]),
ConvBNReLU(in_channels=64, out_channels=64, kernel_size=[1,7], padding=[0,3]),
ConvBNReLU(in_channels=64, out_channels=96, kernel_size=3, stride=1)
)
# 分支1:池化
self.step4_pool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2)
# 分支2:3x3
self.step4_conv = ConvBNReLU(in_channels=192, out_channels=192, kernel_size=3, stride=2)
def forward(self, x):
out = self.step1(x)
tmp1 = self.step2_pool(out)
tmp2 = self.step2_conv(out)
out = torch.cat((tmp1, tmp2), 1)
tmp1 = self.step3_1(out)
tmp2 = self.step3_2(out)
out = torch.cat((tmp1, tmp2), 1)
tmp1 = self.step4_pool(out)
tmp2 = self.step4_conv(out)
outputs = [tmp1, tmp2]
return torch.cat(outputs, 1)
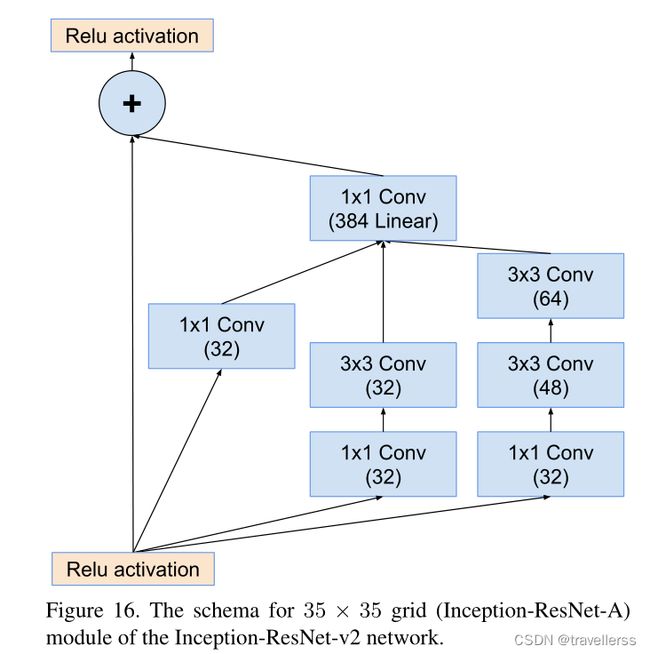
(4)Inception-A
class Inception_A(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, b1, b2_1x1, b2_3x3, b3_1x1, b3_3x3_1, b3_3x3_2, n1_linear):
super(Inception_A, self).__init__()
# 分支1:
self.branch1 = ConvBNReLU(in_channels, b1, kernel_size=1, stride=1)
# 分支2:1x1 -> 3x3
self.branch2 = nn.Sequential(
ConvBNReLU(in_channels, b2_1x1, kernel_size=1, stride=1),
ConvBNReLU(b2_1x1, b2_3x3, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)
)
# 分支3:1x1 -> 3x3 -> 3x3
self.branch3 = nn.Sequential(
ConvBNReLU(in_channels, b3_1x1, kernel_size=1, stride=1),
ConvBNReLU(b3_1x1, b3_3x3_1, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
ConvBNReLU(b3_3x3_1, b3_3x3_2, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)
)
# 1x1Conv
self.conv_linear = nn.Conv2d(b1+b2_3x3+b3_3x3_2, n1_linear, 1, 1, 0, bias=True)
"""
因为这里需要将原始输入通过直连边连接到输出部分,所以需要判断in_channels和n1_linear的关系
"""
# 如果in_channels==n1_linear,则不进行short_cut
self.short_cut = nn.Sequential()
# 如果in_channels!=n1_linear,则进行short_cut,把原始输入维度转为n1_linear
if in_channels != n1_linear:
self.short_cut = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, n1_linear, 1, 1, 0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(n1_linear)
)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
def forward(self, x):
out1 = self.branch1(x)
out2 = self.branch2(x)
out3 = self.branch3(x)
out = torch.cat((out1, out2, out3), 1)
out = self.conv_linear(out)
# 残差连接
out += self.short_cut(x)
out = self.relu(out)
return out
(5)Inception-B
class Inception_B(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, b1, b2_1x1, b2_1x7, b2_7x1, n1_linear):
super(Inception_B, self).__init__()
# 分支1:
self.branch1 = ConvBNReLU(in_channels, b1, kernel_size=1, stride=1)
# 分支2:
self.branch2 = nn.Sequential(
ConvBNReLU(in_channels, b2_1x1, kernel_size=1, stride=1),
ConvBNReLU(b2_1x1, b2_1x7, kernel_size=[1,7], padding=[0,3]),
ConvBNReLU(b2_1x7, b2_7x1, kernel_size=[7,1], padding=[3,0])
)
# 1x1Conv
self.conv_linear = nn.Conv2d(b1 + b2_7x1, n1_linear, 1, 1, 0, bias=False)
self.short_cut = nn.Sequential()
if in_channels != n1_linear:
self.short_cut = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, n1_linear, 1, 1, 0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(n1_linear)
)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
def forward(self, x):
out1 = self.branch1(x)
out2 = self.branch2(x)
out = torch.cat((out1, out2), 1)
out = self.conv_linear(out)
# 残差连接
out += self.short_cut(x)
out = self.relu(out)
return out
(6)Inception-C
class Inception_C(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, b1, b2_1x1, b2_1x3, b2_3x1, n1_linear):
super(Inception_C, self).__init__()
# 分支1:
self.branch1 = ConvBNReLU(in_channels, b1, kernel_size=1, stride=1)
# 分支2:
self.branch2 = nn.Sequential(
ConvBNReLU(in_channels, b2_1x1, kernel_size=1, stride=1),
ConvBNReLU(b2_1x1, b2_1x3, kernel_size=[1,3], padding=[0,1]),
ConvBNReLU(b2_1x3, b2_3x1, kernel_size=[3,1], padding=[1,0])
)
# 1x1Conv
self.conv_linear = nn.Conv2d(b1 + b2_3x1, n1_linear, 1, 1, 0, bias=False)
self.short_cut = nn.Sequential()
if in_channels != n1_linear:
self.short_cut = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, n1_linear, 1, 1, 0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(n1_linear)
)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
def forward(self, x):
out1 = self.branch1(x)
out2 = self.branch2(x)
out = torch.cat((out1, out2), 1)
out = self.conv_linear(out)
# 残差连接
out += self.short_cut(x)
out = self.relu(out)
return out
(7)Reduction-A:
class Reduction_A(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, k, l, m, n):
super(Reduction_A, self).__init__()
# 分支1:MaxPool
self.branch1 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2)
# 分支2:(3x3)
self.branch2 = ConvBNReLU(in_channels, n, kernel_size=3, stride=2)
# 分支3:(1x1->3x3->3x3)
self.branch3 = nn.Sequential(
ConvBNReLU(in_channels, k, kernel_size=1),
ConvBNReLU(k, l, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
ConvBNReLU(l, m, kernel_size=3, stride=2)
)
def forward(self, x):
branch1 = self.branch1(x)
branch2 = self.branch2(x)
branch3 = self.branch3(x)
outputs = [branch1, branch2, branch3]
return torch.cat(outputs, 1)
(8)Reduction-B:
class Reduction_B(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, b2_1x1, b2_3x3, b3_1x1, b3_3x3, b4_1x1, b4_3x3_1, b4_3x3_2):
super(Reduction_B, self).__init__()
# 分支1:
self.branch1 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2)
# 分支2:
self.branch2 = nn.Sequential(
ConvBNReLU(in_channels, b2_1x1, kernel_size=1, stride=1),
ConvBNReLU(b2_1x1, b2_3x3, kernel_size=3, stride=2)
)
# 分支3:
self.branch3 = nn.Sequential(
ConvBNReLU(in_channels, b3_1x1, kernel_size=1, stride=1),
ConvBNReLU(b3_1x1, b3_3x3, kernel_size=3, stride=2)
)
# 分支4:
self.branch4 = nn.Sequential(
ConvBNReLU(in_channels, b4_1x1, kernel_size=1, stride=1),
ConvBNReLU(b4_1x1, b4_3x3_1, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
ConvBNReLU(b4_3x3_1, b4_3x3_2, kernel_size=3, stride=2),
)
def forward(self, x):
out1 = self.branch1(x)
out2 = self.branch2(x)
out3 = self.branch3(x)
out4 = self.branch4(x)
return torch.cat((out1, out2, out3, out4), 1)
(9)整体网络结构:
class GoogLeNet_ResNetV2(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes, init_weights=False):
super(GoogLeNet_ResNetV2, self).__init__()
# 整体主干网络
self.stem = Stem()
self.inception_A = self.__make_inception_A()
self.Reduction_A = self.__make_reduction_A()
self.inception_B = self.__make_inception_B()
self.Reduction_B = self.__make_reduction_B()
self.inception_C = self.__make_inception_C()
# 输出部分:平均池化->全连接层
self.avgpool = nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=8, stride=1)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(0.2)
self.fc = nn.Linear(2144, num_classes)
if init_weights:
self._initialize_weights()
# 制造5层Inception-A
def __make_inception_A(self):
layers = []
for _ in range(5):
layers.append(Inception_A(384, 32, 32, 32, 32, 48, 64, 384))
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
# 制造1层Reduction-A
def __make_reduction_A(self):
return Reduction_A(384, 256, 256, 384, 384)
# 制造10层Inception-B
def __make_inception_B(self):
layers = []
for _ in range(10):
layers.append(Inception_B(1152, 192, 128, 160, 192, 1152))
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
# 制造1层Reduction-B
def __make_reduction_B(self):
return Reduction_B(1152, 256, 384, 256, 288, 256, 288, 320)
# 制造5层Inception-C
def __make_inception_C(self):
layers = []
for _ in range(5):
layers.append(Inception_C(2144, 192, 192, 224, 256, 2144))
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
def forward(self, x):
out = self.stem(x)
out = self.inception_A(out)
out = self.Reduction_A(out)
out = self.inception_B(out)
out = self.Reduction_B(out)
out = self.inception_C(out)
out = self.avgpool(out)
out = torch.flatten(out, 1)
out = self.dropout(out)
out = self.fc(out)
return out
def _initialize_weights(self):
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
if m.bias is not None:
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
nn.init.normal_(m.weight, 0, 0.01)
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)