Linux运维企业架构项目实战系列
Linux运维企业架构项目实战系列
目录
一、全网备份
(一)部署Rsync守护进程
1)服务端(backup)
2)客户端(web01/02/03 nfs01)
(二)编写脚本文件
1)客户端脚本编写
2)服务端
(三)配置邮件服务
1)服务端
(四)定时任务(实现自动完成全网数据备份)
1)服务端
2)客户端(web01/02/03 nfs01)
二、NFS存储共享服务
1)服务端
2)客户端(web01/02/03)
3)实现开机自动挂载
三、实时同步
(一)部署Rsync守护进程
1)服务端(backup)
2)客户端(nfs01)
(二)部署inotify监控服务
(三)部署sersync实时同步服务
四、web服务(LNMP架构)
(一)安装linux操作系统(略)
(二)安装配置Nginx服务
1)yum安装Nginx服务
2)配置Nginx服务
(三)安装配置PHP服务
(四)安装配置Mysql服务
(五)Nginx和PHP建立关系
(六)Nginx和Mysql建立关系
(七)部署搭建网站页面(代码上线)
1)安装wordpress服务
2)创建数据库和登录用户
五、Nginx负载均衡(反向代理)
(一)首先四台服务器预装Nginx服务(lb01 web01/02/03)
(二)web服务器编写测试文件(web01/02/03)
(三)配置负载均衡服务器
(四)测试
六、keepalived高可用
(一)部署keepalived高可用服务(lb01/02)
(二)keepalived脑裂问题(lb01/02)
1)脑裂问题产生的原因
2)如何解决脑裂问题?
(三)如何实现keepalived自动释放VIP地址资源(lb01/02)
(四)keepalived服务双主配置(lb0/02)
(五)keepalived服务安全访问配置(lb0/02)
七、ansible自动化管理服务
(一)部署ansible批量管理服务
(1)部署SSH基于密钥对的连接(m01)
(2)部署安装ansible服务
(二)ansible模块介绍
(1)command默认模块
(2)shell(万能模块)
(3)scripts模块(万能模块)
(4)copy文件类型模块
(5)file设置文件属性模块
(6)yum模块(批量安装和卸载软件包)
(7)service模块(管理服务的运行状态)
(8)cron模块(批量设置多个主机的定时任务信息)
(9)mount模块(批量进行挂载操作)
(10)user模块(批量创建用户并设置密码信息)
(三)剧本
(1)剧本的实现步骤
(2)一键化部署Rsync服务
(3) 一键化部署全网备份项目
(4) 一键化部署NFS服务
(5) 一键化部署实时同步服务
八、网站监控服务zabbix
(一)部署安装zabbix服务
(1)服务端(zabbix)
(2)客户端(其他服务器)
(二)实现zabbix自定义监控
(1)需求:监控Nginx服务是否启动
(2)复杂的自定义监控配置(多个服务状态)
(3)报警(邮件报警、微信报警、短信和电话)
总体架构介绍
| 序号 | 类型 | 名称 | 外网地址 | 内网地址 | 软件 |
| 01 | 防火墙服务器 | firewalld | 10.0.0.81 | 172.16.1.81 | firewalld |
| 02 | 负载均衡服务器 | lb01 | 10.0.0.5 | 172.16.1.5 | nginx keepalived |
| 03 | 负载均衡服务器 | lb02 | 10.0.0.6 | 172.16.1.6 | nginx keepalived |
| 04 | web服务器 | web01 | 10.0.0.7 | 172.16.1.7 | nginx |
| 05 | web服务器 | web02 | 10.0.0.8 | 172.16.1.8 | nginx |
| 06 | web服务器 | web03 | 10.0.0.9 | 172.16.1.9 | nginx |
| 07 | 数据库服务器 | db01 | 10.0.0.51 | 172.16.1.51 | mariadb mysql |
| 08 | 存储服务器 | nfs01 | 10.0.0.31 | 172.16.1.31 | nfs-utils rpcbind |
| 09 | 备份服务器 | backup | 10.0.0.41 | 172.16.1.41 | rsync |
| 10 | 批量管理服务器 | m01 | 10.0.0.61 | 172.16.1.61 | ansible |
| 11 | 跳板机服务器 | jumpserver | 10.0.0.71 | 172.16.1.71 | jumpserver |
| 12 | 监控服务器 | zabbix | 10.0.0.72 | 172.16.1.72 | zabbix |
| 13 | 缓存服务器 | redis |
一、全网备份
服务端:backup
客户端:web01 web02 web03 nfs01
要求:
每天晚上 00 点整在 Web 服务器上打包备份系统配置文件、网站程序目录及访问日志并通过 rsync 命令推送备份服务器 backup 上备份保留(备份思路可以是先在本地按日期打包,然后再推到备份服务器 backup 上) ,NFS 存储服务器同 Web 服务器,实际工作 中就是全部的服务器。
具体要求如下:
1)所有服务器的备份目录必须都为/backup。
2)要备份的系统配置文件包括但不限于:
a.定时任务服务的配置文件(/var/spool/cron/root)
b.开机自启动的配置文件(/etc/rc.local)
c.日常脚本的目录 (/server/scripts)。
d.防火墙 iptables 的配置文件(/etc/sysconfig/iptables)。
e.自己思考下还有什么需要备份呢?
3)Web 服务器站点目录(/var/html/www)。
4)Web 服务器 A 访问日志路径(/app/logs)
5)Web 服务器保留打包后的 7 天的备份数据即可(本地留存不能多于 7 天,因为太多硬盘会 满)
6)备份服务器上,保留每周一的所有数据副本,其它要保留 6 个月的数据副本。
7)备份服务器上要按照备份数据服务器的内网 IP 为目录保存备份,备份的文件按照时间名 字保存。
8)*需要确保备份的数据尽量完整正确,在备份服务器上对备份的数据进行检查,把备份的成功及失败结 果信息发给系统管理员邮箱中。
部署过程
(一)部署Rsync守护进程
1)服务端(backup)
第一步:下载安装Rsync
rpm -qa|grep rsync
yum install -y rsync
第二步:编写Rsync配置文件
[root@backup ~]# vim /etc/rsyncd.conf
##created by abin at 2020
###rsyncd.conf start##
uid = rsync
gid = rsync
port = 873
fake super = yes
use chroot = no
max connections =200
timeout = 300
pid file = /var/run/rsyncd.pid
lock file = /var/run/rsync.lock
log file = /var/log/rsyncd.log
ignore errors
read only = false
list = false
hosts allow = 172.16.1.0/24
hosts deny = 0.0.0.0/32
auth users = rsync_backup
secrets file = /etc/rsync.password
[backup]
comment = "backup dir by abin"
第三步:创建rsync服务的虚拟用户
useradd rsync -M -s /sbin/nologin
第四步:创建备份服务认证密码文件
echo "rsync_backup:123456" >/etc/rsync.password
chmod 600 /etc/rsync.password
第五步:创建备份目录并修改属主属组信息
mkdir /backup
chown rsync.rsync /backup/
第六步:启动备份服务
systemctl start rsyncd
systemctl enable rsyncd
systemctl status rsyncd
2)客户端(web01/02/03 nfs01)
第一步:创建密码认证文件
echo "123456" >/etc/rsync.password
chmod 600 /etc/rsync.password
第二步:进行交互式数据传输测试
rsync -avz /etc/hosts [email protected]::backup --password-file=/etc/rsync.password
(二)编写脚本文件
1)客户端脚本编写
web01/02/03服务器备份脚本:
mkdir -p /server/scripts
vim /server/scripts/backup.sh
#!/bin/bash
Backup_dir="/backup"
IP_info=$(hostname -i)
# create backup dir
mkdir -p $Backup_dir/$IP_info
# tar backup data
cd /
tar zchf /$Backup_dir/$IP_info/system_backup_$(date +%F_week%w -d -1day).tar.gz ./var/spool/cron/root ./etc/rc.local ./server/scripts ./etc/sysconfig/iptables
tar zchf /$Backup_dir/$IP_info/www_backup_$(date +%F_week%w).tar.gz ./var/html/www
tar zchf /$Backup_dir/$IP_info/www_log_backup_$(date +%F_week%w).tar.gz ./app/logs
# del 7 day ago data
find $Backup_dir -type f -mtime +7|xargs rm 2>/dev/null
# create finger file
find $Backup_dir/ -type f -mtime -1 ! -name "finger*"|xargs md5sum >/$Backup_dir/$IP_info/finger.txt
# backup push data info
rsync -az $Backup_dir/ [email protected]::backup --password-file=/etc/rsync.password
nfs01服务器备份脚本:
mkdir -p /server/scripts
vim /server/scripts/backup.sh
#!/bin/bash
Backup_dir="/backup"
IP_info=$(hostname -i)
# create backup dir
mkdir -p $Backup_dir/$IP_info
# tar backup data
cd /
tar zchf /$Backup_dir/$IP_info/system_backup_$(date +%F_week%w -d -1day).tar.gz ./var/spool/cron/root ./etc/rc.local ./server/scripts ./etc/sysconfig/iptables
# del 7 day ago data
find $Backup_dir -type f -mtime +7|xargs rm 2>/dev/null
# create finger file
find $Backup_dir/ -type f -mtime -1 ! -name "finger*"|xargs md5sum >/$Backup_dir/$IP_info/finger.txt
# backup push data info
rsync -az $Backup_dir/ [email protected]::backup --password-file=/etc/rsync.password2)服务端
mkdir -p /server/scripts
vim /server/scripts/backup_server.sh
#!/bin/bash
# del 180 day ago data
find /backup/ -type f -mtime +180 ! -name "*week1.tar.gz"|xargs rm 2>/dev/null
# check backup data
find /backup/ -type f -name "finger.txt"|xargs md5sum -c >/tmp/check.txt
# send check mail
mail -s "check backup info for $(date +%F)" [email protected] (三)配置邮件服务
1)服务端
第一步:浏览器登录163邮箱进行配置
打开163邮箱POP3/SMIP服务
复制授权密码
第二步:配置qq邮箱
打开qq邮箱POP3/SMIP服务
第三步:编写邮件服务配置文件(追加到最后面)
vim /etc/mail.rc
set [email protected] smtp=smtp.163.com
set [email protected] smtp-auth-password=授权密码(163邮箱) smtp-auth=login
重启邮箱服务
systemctl restart postfix.service
第四步:发送邮件测试
echo "邮件内容"|mail -s "邮件主题" [email protected]
mail -s "邮件测试" [email protected] (四)定时任务(实现自动完成全网数据备份)
1)服务端
[root@backup ~]# crontab -e
# check backup data
0 5 * * * /bin/sh /server/scripts/backup_server.sh &>/dev/null
ps:
crontab -l --查看已设定的定时任务2)客户端(web01/02/03 nfs01)
crontab -e
# backup data
0 0 * * * /bin/sh /server/scripts/backup.sh &>/dev/null
二、NFS存储共享服务
服务端:nfs01
客户端:web01/02/03
1)服务端
第一步:下载安装软件
rpm -qa|grep -E "nfs|rpc"
yum install -y nfs-utils rpcbind
第二步:编写nfs服务配置文件
vim /etc/exports
/data 172.16.1.0/24(rw,sync)
第三步:创建一个存储目录
mkdir /data
chown nfsnobody.nfsnobody /data
第四步:先启动rpc服务
systemctl start rpcbind.service
systemctl enable rpcbind.service
systemctl status rpcbind.service
再启动nfs服务
systemctl start nfs
systemctl enable nfs
systemctl status nfs
2)客户端(web01/02/03)
第一步:安装nfs服务
yum install -y nfs-utils
第二步:实现远程挂载共享目录
mount -t nfs 172.16.1.31:/data /mnt
ps:卸载设备
umount -lf /mnt
-l 不退出挂载点目录进行卸载
-f 强制进行卸载操作
3)实现开机自动挂载
方法一:利用rc.local开机自动加载脚本文件
echo "mount -t nfs 172.16.1.31:/data /mnt" >>/etc/rc.local
chmod a+x /etc/rc.d/rc.local
方法二:利用fstab配置文件
vim /etc/fstab
172.16.1.31:/data /mnt nfs defaults 0 0补充:
1.NFS配置参数权限
rw -- 存储目录是否有读写权限
ro -- 存储目录是否时只读权限
sync -- 同步方式存储数据 直接将数据保存到磁盘(数据存储安全)
async -- 异步方式存储数据 直接将数据保存到内存(提高数据存储效率)
no_root_squash -- 不要将root用户身份进行转换
root_squash -- 将root用户身份进行转换
all_squash -- 将所有用户身份都进行转换
no_all_squash -- 不要将普通用户身份进行转换
2.mount命令参数
rw --- 实现挂载后挂载点目录可读可写 (默认)
ro --- 实现挂载后挂载点目录可读可写
suid --- 在共享目录中可以让setuid权限位生效 (默认)
nosuid --- 在共享目录中可以让setuid权限位失效 提高共享目录的安全性
exec --- 共享目录中的执行文件可以直接执行
noexec --- 共享目录中的执行文件可以无法直接执行 提供共享目录的安全性
auto --- 可以实现自动挂载 mount -a 实现加载fstab文件自动挂载
noauto --- 不可以实现自动挂载
nouser --- 禁止普通用户可以卸载挂载点
user --- 允许普通用户可以卸载挂载点
3.NFS服务挂载不上排查方法:
服务端进行排查:
1. 检查nfs进程信息是否注册
rpcinfo -p localhost/172.16.1.31
问题原因:
服务启动顺序不对,没有启动nfs服务
2. 检查有没有可用存储目录
showmount -e 172.16.1.31
问题原因:
配置文件编写有问题,重启nfs服务
3. 在服务端进行挂载测试
是否能够在存储目录中创建或删除数据
客户端测试:
网络问题
ping 172.16.1.31
telnet 172.16.1.31 111
三、实时同步
服务端:backup
客户端:nfs01
(一)部署Rsync守护进程
1)服务端(backup)
第一步:下载安装Rsync
rpm -qa|grep rsync
yum install -y rsync
第二步:编写Rsync配置文件
[root@backup ~]# vim /etc/rsyncd.conf
##created bu abin at 2020
###rsyncd.conf start##
uid = rsync
gid = rsync
port = 873
fake super = yes
use chroot = no
max connections =200
timeout = 300
pid file = /var/run/rsyncd.pid
lock file = /var/run/rsync.lock
log file = /var/log/rsyncd.log
ignore errors
read only = false
list = false
hosts allow = 172.16.1.0/24
hosts deny = 0.0.0.0/32
auth users = rsync_backup
secrets file = /etc/rsync.password
[backup]
comment = "backup dir by abin"
第三步:创建rsync服务的虚拟用户
useradd rsync -M -s /sbin/nologin
第四步:创建备份服务认证密码文件
echo "rsync_backup:123456" >/etc/rsync.password
chmod 600 /etc/rsync.password
第五步:创建备份目录并修改属主属组信息
mkdir /backup
chown rsync.rsync /backup/
第六步:启动备份服务
systemctl start rsyncd
systemctl enable rsyncd
systemctl status rsyncd
2)客户端(nfs01)
第一步:创建密码认证文件
echo "123456" >/etc/rsync.password
chmod 600 /etc/rsync.password
第二步:进行交互式数据传输测试
rsync -avz /etc/hosts [email protected]::backup --password-file=/etc/rsync.password
(二)部署inotify监控服务
客户端:nfs01
第一步:安装inotify-tools服务
yum install -y inotify-tools
(三)部署sersync实时同步服务
客户端:nfs01
第一步:下载sersync软件上传至nfs服务器
https://github.com/wsgzao/sersync
第二步:解压sersync软件包
unzip sersync_installdir_64bit.zip
mv sersync_installdir_64bit/* /usr/local/
第三步:修改配置文件
[root@nfs01 /usr/local/sersync]# vim conf/confxml.xml
24
25
四、web服务(LNMP架构)
(一)安装linux操作系统(略)
(二)安装配置Nginx服务
1)yum安装Nginx服务
第一个历程: 更新nginx官方yum源
vim /etc/yum.repos.d/nginx.repo
[nginx-stable]
name=nginx stable repo
baseurl=http://nginx.org/packages/centos/$releasever/$basearch/
gpgcheck=1
enabled=1
gpgkey=https://nginx.org/keys/nginx_signing.key
第二个历程: yum安装nginx软件
yum install -y nginx
第三个历程: 启动nginx服务,检查服务是否安装正确
systemctl start nginx
systemctl enable nginx
测试访问nginx服务![]()
2)配置Nginx服务
vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf --- 主配置文件
第一个部分: 配置文件主区域配置
user www; --- 定义worker进程管理的用户
worker_processes 2; ---定义有几个worker进程 == CPU核数 / 核数的2倍
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log warn; --- 定义错误日志路径信息
pid /var/run/nginx.pid; --- 定义pid文件路径信息
第二个部分: 配置文件事件区域
events {
worker_connections 1024; --- 一个worker进程可以同时接收1024访问请求
}
第三个部分: 配置http区域
http {
include /etc/nginx/mime.types; --- 加载一个配置文件
default_type application/octet-stream; --- 指定默认识别文件类型
log_format oldboy '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
--- 定义日志的格式
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log oldboy;
--- 指定日志路径
sendfile on; ???
#tcp_nopush on; ???
keepalive_timeout 65; --- 超时时间
#gzip on;
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf; --- 加载一个配置文件
}
补充: nginx的进程
master process: 主进程 ---管理服务是否能够正常运行 boss
worker process: 工作进程 ---处理用户的访问请求 员工 (三)安装配置PHP服务
1.使用remi源安装php
yum remove -y epel-release.noarch --(如果没有这个包可以不用卸载)
yum install -y epel-release
yum install -y https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/remi/enterprise/remi-release-7.rpm
yum --enablerepo=remi-php71 install -y php php-cli php-common php-devel php-embedded php-gd php-mbstring php-pdo php-xml php-fpm php-mysqlnd php-opcache php-mcrypt php-pecl-memcached php-pecl-mongodb php-pecl-redis
2.编写配置文件(24/26行)
vim /etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf
user = www
group = www
PS:创建一个www用户
3.启动php服务
systemctl start php-fpm.service
systemctl enable php-fpm.service
systemctl status php-fpm.service(四)安装配置Mysql服务
安装数据库软件
[root@web01 ~]# yum install mariadb-server mariadb -y
启动数据库服务
[root@web01 ~]# systemctl start mariadb.service
[root@web01 ~]# systemctl enable mariadb.service
创建数据库的密码信息
[root@web01 ~]# mysqladmin -u root password '123456'
[root@web01 ~]# mysql -u root -p123456 --密码登录(五)Nginx和PHP建立关系
1.编写nginx文件
[root@web01 /etc/nginx/conf.d]# vim www.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.abins.cn;
location / {
root /html/www;
index index.php index.html;
}
location ~ \.php$ {
root /html/www;
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
include fastcgi_params;
}
}
[root@web01 /etc/nginx/conf.d]# systemctl restart nginx
2.编写动态资源文件
[root@web01 /html/www]# vim test_php.php
3.配置本地DNS解析
在C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts文件
后面追加
10.0.0.7 www.cxt.com
4.进行访问测试
www.cxt.com/test_php.php![]()
(六)Nginx和Mysql建立关系
1.编写php代码文件
[root@web02 /html/www]# vim test_mysql.php
2.进行访问测试![]()
(七)部署搭建网站页面(代码上线)
1)安装wordpress服务
第一个历程: 获取代码信息(git)---使用开源的网站代码
www网站页面: http://www.dedecms.com/
bbs网站页面: http://www.discuz.net/forum.php
blog网站页面: https://cn.wordpress.org/
wecenter网站页面: http://www.wecenter.com/?copyright
第二个历程: 将代码解压,将解压后信息放入到站点目录中
[root@web01 /html]# rz -E
rz waiting to receive.
[root@web01 /html]# ll
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 11199196 Apr 7 20:40 wordpress-5.2.1.tar.gz
[root@web02 /html]# tar xf wordpress-5.2.1.tar.gz
[root@web01 /html]# ll
drwxr-xr-x 5 nobody 65534 4096 May 22 2019 wordpress
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 11199196 Apr 7 20:40 wordpress-5.2.1.tar.gz
drwxr-xr-x 2 www www 48 May 24 15:17 www
[root@web01 /html]# mv wordpress/* www/
第三个历程: 修改站点目录权限
chown -R www.www www
第四个历程: 进行网站页面初始化操作
www.cxt.com/index.php![]()
2)创建数据库和登录用户
[root@web01 ~]# mysql -u root -p123456 --以root身份登录MySQL
MariaDB [(none)]> create database wordpress; --创建wordpress数据库
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.09 sec)
MariaDB [(none)]> show databases; --检查wordpress数据库是否创建成功
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| mysql |
| performance_schema |
| test |
| wordpress |
+--------------------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
MariaDB [(none)]> grant all on wordpress.* to 'wordpress'@'localhost' identified by '123456'; --创建wordpress用户,密码为123456
MariaDB [(none)]> select user,host from mysql.user; --查看数据库user表的用户信息和主机信息
+-----------+-----------+
| user | host |
+-----------+-----------+
| root | 127.0.0.1 |
| root | ::1 |
| | localhost |
| root | localhost |
| wordpress | localhost |
| | web02 |
| root | web02 |
+-----------+-----------+
7 rows in set (0.10 sec)
MariaDB [(none)]> flush privileges; --刷新数据库信息![]()
![]()
![]()
看到这个界面,那么恭喜你网站搭建成功啦!
五、Nginx负载均衡(反向代理)
服务端:lb01
客户端:web01/02/03
(一)首先四台服务器预装Nginx服务(lb01 web01/02/03)
vim /etc/yum.repos.d/nginx.repo ##更新nginx的官方yum源
[nginx-stable]
name=nginx stable repo
baseurl=http://nginx.org/packages/centos/$releasever/$basearch/
gpgcheck=1
enabled=1
gpgkey=https://nginx.org/keys/nginx_signing.key
yum install -y nginx ##安装nginx服务
systemctl start nginx ##启动nginx服务(二)web服务器编写测试文件(web01/02/03)
[root@web01 /html/www]# vim fzjh.html
Welcome to nginx!
Welcome to nginx! 10.0.0.7
(三)配置负载均衡服务器
[root@lb01 /etc/nginx]# vim nginx.conf
user www;
[root@lb01 /etc/nginx/conf.d]# vim www.conf
upstream cxt {
server 10.0.0.7:80;
server 10.0.0.8:80;
server 10.0.0.9:80;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.cxt.com;
location / {
proxy_pass http://cxt;
client_max_body_size 100m;
}
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name bbs.cxt.com;
location / {
proxy_pass http://cxt;
client_max_body_size 100m;
}
}(四)测试
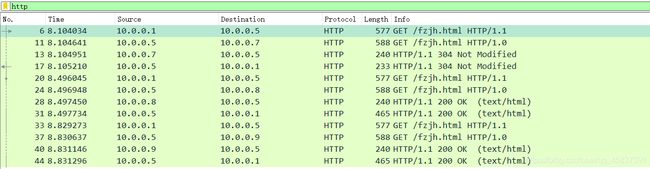
打开浏览器输入www.cxt.com/fzjh.html
不断刷新,10.0.0.7/10.0.0.8/10.0.0.9交替出现时说明负载均衡配置成功
下面时通过抓包工具抓取的http记录
六、keepalived高可用
(一)部署keepalived高可用服务(lb01/02)
第一个历程: 准备两台服务器并且均配置好负载均衡服务 (lb01 lb02)
第二个历程: 安装部署keepalived软件 (lb01 lb02)
yum install -y keepalived
第三个历程: 编写keepalived配置文件(lb01 lb02)
lb01配置信息: --此处配置文件同ansible配置文件一样都需要注意格式,否则不会被执行
[root@lb01 ~]# cat /etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf
! Configuration File for keepalived
global_defs {
router_id lb01
}
vrrp_instance yb {
state MASTER
interface eth0
virtual_router_id 51
priority 150
advert_int 1
authentication {
auth_type PASS
auth_pass 1111
}
virtual_ipaddress {
10.0.0.3/24
}
}
lb02配置信息: --此处配置文件同ansible配置文件一样都需要注意格式,否则不会被执行
! Configuration File for keepalived
global_defs {
router_id lb02
}
vrrp_instance yb {
state BACKUP
interface eth0
virtual_router_id 51
priority 100
advert_int 1
authentication {
auth_type PASS
auth_pass 1111
}
virtual_ipaddress {
10.0.0.3/24
}
}
第四个历程: 启动keepalived服务
systemctl start keepalived
systemctl enable keepalived
systemctl status keepalived
第五个历程: 修改域名和IP地址解析关系
windows修改hosts主机文件
10.0.0.3 www.cxt.com
第六个历程:测试
当lb01的keepalived服务停止运行时,lb02收不到来自lb01的组播信息会夺取vip地址信息10.0.0.3成为新的主,保证负载均衡正常运作。(二)keepalived脑裂问题(lb01/02)
1)脑裂问题产生的原因
出现原因:
高可用备服务器接收不到主服务器发送的组播包,备服务器上会自动生成VIP地址
物理原因:
高可用集群之间通讯线路出现问题
逻辑原因:
有安全策略阻止(防火墙等)
2)如何解决脑裂问题?
01. 进行监控,发出告警
备服务器出现VIP地址的原因:
a 主服务器出现故障
b 出现脑裂问题
监控脑裂的shell脚本:
[root@lb02 ~]# vim /server/scripts/naolie.sh
#!/bin/bash
ip a s eth0|grep "10.0.0.3" >/dev/null
if [ $? -eq 0 ]
then
echo "keepalived服务出现异常,请进行检查"|mail -s 异常告警-keepalived [email protected]
fi
加入定时任务每隔一分钟执行一次
corntab -e
补充:shell脚本进行比较判断
-eq 等于
-ne 不等于
-lt 小于
-gt 大于
-le 小于等于
-ge 大于等于
02. 直接关闭一台服务器的keepalived服务(三)如何实现keepalived自动释放VIP地址资源(lb01/02)
第一个历程: 编写监控nginx服务状态监控
vim /server/scripts/check_web.sh
#!/bin/bash
num=`ps -ef|grep -c [n]ginx`
if [ $num -lt 2 ]
then
systemctl stop keepalived
fi
ps:别忘了给脚本x权限
第二个历程: 测试监控脚本
[root@lb01 scripts]# cat /etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf
! Configuration File for keepalived
global_defs {
router_id lb01
}
vrrp_script check_web {
script "/server/scripts/check_web.sh"
interval 3
weight 2
}
vrrp_instance yb {
state MASTER
interface eth0
virtual_router_id 51
priority 150
advert_int 1
authentication {
auth_type PASS
auth_pass 1111
}
virtual_ipaddress {
10.0.0.3/24
}
track_script {
check_web
}
}
第三个历程: 测试
停掉nginx服务的同时keepailved服务也会自动停掉
这样vip地址资源会释放给备,备会成为新的主,保证用户可以正常访问
systemctl stop nginx
systemctl status keepalived (四)keepalived服务双主配置(lb0/02)
第一个历程: 编写lb01服务器keepalived配置文件
[root@lb01 ~]# cat /etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf
! Configuration File for keepalived
global_defs {
router_id lb01
}
vrrp_instance yb {
state MASTER
interface eth0
virtual_router_id 51
priority 150
advert_int 1
authentication {
auth_type PASS
auth_pass 1111
}
virtual_ipaddress {
10.0.0.3/24
}
}
vrrp_instance cxt {
state BACKUP
interface eth0
virtual_router_id 52
priority 100
advert_int 1
authentication {
auth_type PASS
auth_pass 1111
}
virtual_ipaddress {
10.0.0.4/24
}
}
第二个历程: 编写lb02服务器keepalived配置文件
[root@lb02 ~]# cat /etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf
! Configuration File for keepalived
global_defs {
router_id lb02
}
vrrp_instance yb {
state BACKUP
interface eth0
virtual_router_id 51
priority 100
advert_int 1
authentication {
auth_type PASS
auth_pass 1111
}
virtual_ipaddress {
10.0.0.3/24
}
}
vrrp_instance cxt {
state MASTER
interface eth0
virtual_router_id 52
priority 150
advert_int 1
authentication {
auth_type PASS
auth_pass 1111
}
virtual_ipaddress {
10.0.0.4/24
}
}
第三个历程: 进行抓包测试
进行抓包查看:
www.cxt.com/fzjh --- 10.0.0.3(10.0.0.5)
10.0.0.1 --- 10.0.0.3
10.0.0.5 --- 10.0.0.7
10.0.0.7 --- 10.0.0.5
10.0.0.3 --- 10.0.0.1
bbs.test.com/fzjh --- 10.0.0.4(10.0.0.6) --若访问bbs.cxt.com/fzjh.html出现404错误,可能是lb02的www.conf中没有配置bbs.cxt.com的负载均衡
10.0.0.1 --- 10.0.0.4
10.0.0.6 --- 10.0.0.7
10.0.0.7 --- 10.0.0.6
10.0.0.4 --- 10.0.0.1(五)keepalived服务安全访问配置(lb0/02)
通过设置监听地址限制用户访问通道:
外网接口只开通10.0.0.3/10.0.0.4
第一个历程: 修改内核文件
异常问题:
01. 如何设置监听网卡上没有的地址
解决: 需要修改内核信息
echo 'net.ipv4.ip_nonlocal_bind = 1' >>/etc/sysctl.conf
sysctl -p
第二个历程: 修改nginx负载均衡文件
lb01/lb02
vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/lb.conf
upstream cxt {
server 10.0.0.7:80;
server 10.0.0.8:80;
server 10.0.0.9:80;
}
server {
listen 10.0.0.3:80;
server_name www.cxt.com;
location / {
proxy_pass http://cxt;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $remote_addr;
proxy_next_upstream error timeout http_404 http_502 http_403;
}
}
server {
listen 10.0.0.4:80;
server_name bbs.cxt.com;
location / {
proxy_pass http://cxt;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $remote_addr;
}
}
第三个历程: 重启nginx负载均衡服务
systemctl restart nginx --涉及到ip地址的修改要用restart重启
七、ansible自动化管理服务
服务端:m01
客户端:其他服务器
PS:selinux需要关闭,不然ansible连接管理主机会报错
(一)部署ansible批量管理服务
(1)部署SSH基于密钥对的连接(m01)
第一步:管理端创建密钥对信息
[root@m01 ~]# ssh-keygen -t dsa --默认一直回车
第二步:管理端需要将公钥进行分发
[root@m01 /server/scripts]# yum install -y sshpass
[root@m01 /server/scripts]# vim fenfa_pub_key.sh --注意脚本x权限
#!/bin/bash
for ip in 7 31 41
do
echo "============ host 172.16.1.$ip pub-key start fenfa============="
sshpass -p123456 ssh-copy-id -i /root/.ssh/id_dsa.pub [email protected].$ip "-o StrictHostKeyChecking=no" &>/dev/null
echo "host 172.16.1.$ip fenfa success."
echo "============ host 172.16.1.$ip fenfa end============="
done
[root@m01 /server/scripts]# sh fenfa_pub_key.sh
============ host 172.16.1.5 pub-key start fenfa=============
host 172.16.1.5 fenfa success.
...
第三步:进行ssh远程连接测试
[root@m01 /server/scripts]# vim check_pub_key.sh --注意脚本x权限
#!/bin/bash
CMD=$1 #--传参(执行脚本的时候后面可以写一些命令,不用去调整脚本)
for ip in {5,6,7,8,9,31,51}
do
echo "==================== host 172.16.1.$ip check ==================== "
ssh 172.16.1.$ip $CMD
echo ""
done
[root@m01 /server/scripts]# sh check_pub_key.sh "hostname"
==================== host 172.16.1.5 check ====================
lb01
...(2)部署安装ansible服务
第一步:安装ansible软件
[root@m01 ~]# yum install -y ansible --- 需要依赖epel的yum源
第二步:编写主机清单文件
[root@m01 ~]# vim /etc/ansible/hosts
#定义可以管理的主机信息
172.16.1.5
172.16.1.6
172.16.1.7
172.16.1.8
172.16.1.9
172.16.1.31
172.16.1.51
第三步:测试是否可以管理多台主机
[root@m01 ~]# ansible all -a "hostname"
172.16.1.5 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
lb01
...
ps:补充
/etc/ansible/ansible.cfg --- ansible服务配置文件
/etc/ansible/hosts --- 主机清单文件 定义可以管理的主机信息
/etc/ansible/roles --- 角色目录
(二)ansible模块介绍
模块的应用语法格式:
ansible 主机名称/主机组名称/主机地址信息/all -m(指定应用的模块信息) 模块名称 -a(指定动作信息) "执行什么动作"
ansible软件输出颜色说明:
01. 绿色信息: 查看主机信息/对主机未做改动
02. 黄色信息: 对主机数据信息做了修改
03. 红色信息: 命令执行出错了
04. 粉色信息: 忠告信息
05. 蓝色信息: 显示ansible命令执行的过程
(1)command默认模块
command – Executes a command on a remote node
在一个远程主机上执行一个命令
简单用法:
[root@m01 ~]# ansible 172.16.1.7 -m command -a "hostname"
172.16.1.7 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
web01
扩展用法:
1)chdir Change into this directory before running the command.
在执行命令之前对目录进行切换
ansible 172.16.1.7 -m command -a "chdir=/tmp/ touch test.txt"
2)creates If it already exists, this step won't be run.
如果文件存在,不执行命令操作
ansible 172.16.1.7 -m command -a "creates=/tmp/ touch test.txt"
skipped, since /tmp/ exists --跳过,因为/tmp/中存在
3)removes If it already exists, this step will be run.
如果文件存在,继续执行
ansible 172.16.1.7 -m command -a "removes=/tmp/ touch test.txt"
4) free_form(required)
The command module takes a free form command to run.
There is no parameter actually named 'free form'. See the examples!
使用command模块的时候,-a参数后面必须写上一个合法linux命令信息
注意事项:
有些符号信息无法识别: "<", ">", "|", ";" and "&"(2)shell(万能模块)
shell – Execute commands in nodes
在节点上执行操作
简单用法:
和command默认模块用法一致
实践应用:利用shell模块远程执行脚本
第一步:在管理主机编写脚本
[root@m01 /server/scripts]# vim yum.sh
#!/bin/bash
##yum
yum install -y htop
第二步:将脚本发送到远程主机
[root@m01 /server/scripts]# scp -rp ./yum.sh 172.16.1.7:/server/scripts
yum.sh 100% 39 37.0KB/s 00:00
第三步:使用file模块为脚本增加可执行权限
[root@m01 ~]# ansible 172.16.1.7 -m file -a "dest=/server/scripts/yum.sh mode=777"
第四步:使用ansible命令执行脚本
[root@m01 ~]# ansible 172.16.1.7 -m shell -a "chdir=/server/scripts sh yum.sh"(3)scripts模块(万能模块)
PS:scripts模块参数功能和command模块类似
第一个步骤: 编写一个脚本
第二个步骤: 运行ansible命令执行脚本(4)copy文件类型模块
copy – Copies files to remote locations
将数据信息进行批量分发
基本用法:
ansible 172.16.1.7 -m copy -a "src=/etc/hosts dest=/etc/"
将管理主机/etc目录中的hosts文件分发到远程主机的/etc目录中
172.16.1.7 | CHANGED => { --- 对哪台主机进行操作
"changed": true, --- 是否对主机信息进行改变
"checksum": "6ed7f68a1d6b4b36c1418338b2001e421eeba270", --- 生成一个文件校验码==MD5数值
"dest": "/etc/hosts", --- 显示目标路径信息
"gid": 0, --- 显示复制后文件gid信息
"group": "root", --- 显示复制后文件属组信息
"md5sum": "7afd7b74854f0aaab646b3e932f427c0", --- 生成一个文件校验码==MD5数值
"mode": "0644", --- 显示复制后文件权限信息
"owner": "root", --- 显示复制后文件属主信息
"size": 401, --- 显示文件的大小信息
"src": "/root/.ansible/tmp/ansible-tmp-1557804498.23-26487341925325/source",
"state": "file", --- 显示文件的类型信息
"uid": 0 --- 显示复制后文件uid信息
}
扩展用法:
01. 在传输文件时修改文件的属主和属组信息
ansible 172.16.1.7 -m copy -a "src=/etc/ansible/file/rsync/rsync.password dest=/etc/ owner=rsync group=rsync"
02. 在传输文件时修改文件的权限信息
ansible 172.16.1.7 -m copy -a "src=/etc/ansible/file/rsync/rsync.password dest=/etc/ mode=1777"
03. 在传输数据文件信息时对远程主机源文件进行备份
ansible 172.16.1.7 -m copy -a "src=/etc/ansible/file/rsync/rsync.password dest=/etc/ backup=yes"
04. 创建一个文件并直接编辑文件的信息
ansible 172.16.1.7 -m copy -a "content='123456' dest=/etc/rsync.password"
content:文件内容
dest:远端文件路径
PS: ansible软件copy模块复制目录信息
ansible 172.16.1.7 -m copy -a "src=/tmp dest=/tmp"
src后面目录没有/: 将目录本身以及目录下面的内容都进行远程传输复制
ansible 172.16.1.7 -m copy -a "src=/tmp/ dest=/tmp"
src后面目录有/: 只将目录下面的内容都进行远程传输复制
(5)file设置文件属性模块
file – Sets attributes of files
设置文件属性信息
基本用法:
-dest 远端文件或目录路径
-owner 属主
-group 属组
-mode 权限
ansible 172.16.1.7 -m file -a "dest=/etc/hosts owner=www group=www mode=666"
扩展用法:
1. 可以利用模块创建数据信息 (文件 目录 链接文件)
state 参数
=absent --- 缺席/删除数据信息
=directory --- 创建一个目录信息
=file --- 检查创建的数据信息是否存在 绿色存在 红色不存在
=hard --- 创建一个硬链接文件
=link --- 创建一个软链接文件
=touch --- 创建一个文件信息
创建目录信息:
ansible 172.16.1.7 -m file -a "dest=/test/ state=directory"
ansible 172.16.1.7 -m file -a "dest=/test/test01/test02/ state=directory"
创建文件信息:
ansible 172.16.1.7 -m file -a "dest=/test/test.txt state=touch"
创建链接文件信息:
ansible 172.16.1.7 -m file -a "src=/test/test.txt dest=/test/test_hard.txt state=hard"
ansible 172.16.1.7 -m file -a "src=/test/test.txt dest=/test/test_link.txt state=link"
2. 可以利用模块删除数据信息
ansible 172.16.1.7 -m file -a "dest=/test/test.txt state=absent"
ansible 172.16.1.7 -m file -a "dest=/test/ state=absent"
补充:
recurse 递归
Recursively set the specified file attributes on directory contents.
递归地对目录内容设置指定的文件属性。
This applies only when state is set to directory.
recurse=yes/no
仅当状态设置为“目录”时才适用。
[root@m01 ~]# ansible 172.16.1.41 -m file -a "dest=/backup owner=rsync recurse=yes"(6)yum模块(批量安装和卸载软件包)
name --- 指定安装软件名称
state --- 指定是否安装软件
installed --- 安装软件
present
latest
absent --- 卸载软件
removed
ansible 172.16.1.7 -m yum -a "name=iotop state=installed" (7)service模块(管理服务的运行状态)
name: --- 指定管理的服务名称
state: --- 指定服务状态
started 启动
restarted 重启
stopped 停止
enabled=yes/no --- 指定服务是否开机自启动
ansible 172.16.1.31 -m service -a "name=nfs state=started enabled=yes"(8)cron模块(批量设置多个主机的定时任务信息)
crontab -e
* * * * * 定时任务动作
分 时 日 月 周
minute: # Minute when the job should run ( 0-59, *, */2, etc )
设置分钟信息
hour: # Hour when the job should run ( 0-23, *, */2, etc )
设置小时信息
day: # Day of the month the job should run ( 1-31, *, */2, etc )
设置日期信息
month: # Month of the year the job should run ( 1-12, *, */2, etc )
设置月份信息
weekday: # Day of the week that the job should run ( 0-6 for Sunday-Saturday, *, etc )
设置周信息
job 用于定义定时任务需要干的事情
基本用法:
ansible 172.16.1.31 -m cron -a "minute=0 hour=2 job='/usr/sbin/ntpdate ntp1.aliyun.com >/dev/null 2>&1'"
扩展用法:
01. 给定时任务设置注释信息
ansible 172.16.1.31 -m cron -a "name='time sync' minute=0 hour=2 job='/usr/sbin/ntpdate ntp1.aliyun.com >/dev/null 2>&1'"
02. 如何删除指定定时任务
ansible 172.16.1.31 -m cron -a "name='time sync01' state=absent"
PS: ansible可以删除的定时任务,只能是ansible设置好的定时任务
03. 如何批量注释定时任务
ansible 172.16.1.31 -m cron -a "name='time sync' job='/usr/sbin/ntpdate ntp1.aliyun.com >/dev/null 2>&1' disabled=yes"(9)mount模块(批量进行挂载操作)
mount: 批量进行挂载操作
src: 需要挂载的存储设备或文件信息
path: 指定目标挂载点目录
fstype: 指定挂载时的文件系统类型
state
present/mounted --- 进行挂载
present: 不会实现立即挂载,修改fstab文件,实现开机自动挂载
mounted: 会实现立即挂载, 并且会修改fstab文件,实现开机自动挂载 *****
absent/unmounted --- 进行卸载
absent: 会实现立即卸载, 并且会删除fstab文件信息,禁止开机自动挂载
unmounted: 会实现立即卸载, 但是不会会删除fstab文件信息 *****(10)user模块(批量创建用户并设置密码信息)
基本用法:
ansible 172.16.1.31 -m user -a "name=www"
扩展用法:
1) 指定用户uid信息
ansible 172.16.1.31 -m user -a "name=www uid=6666"
2) 指定用户组信息
ansible 172.16.1.31 -m user -a "name=www group=www"
3) 批量创建虚拟用户
ansible 172.16.1.31 -m user -a "name=rsync create_home=no shell=/sbin/nologin"
4) 给指定用户创建密码
PS: 利用ansible程序user模块设置用户密码信息,需要将密码明文信息转换为密文信息进行设置
生成密文密码信息方法:
方法一:
ansible all -i localhost, -m debug -a "msg={{ '123456' | password_hash('sha512', 'www') }}"
localhost | SUCCESS => {
"msg": "$6$oldboy$MVd3DevkLcimrBLdMICrBY8HF82Wtau5cI8D2w4Zs6P1cCfMTcnnyAmmJc7mQaE9zuHxk8JFTRgYMGv9uKW7j1"
}
方法二:(忽略)
mkpasswd --method=sha-512
方法三:
yum install -y python-pip
pip install passlib
python -c "from passlib.hash import sha512_crypt; import getpass; print(sha512_crypt.using(rounds=5000).hash(getpass.getpass()))"
Password:
$6$rJJeiIerQ8p2eR82$uE2701X7vY44voF4j4tIQuUawmTNHEZhs26nKOL0z39LWyvIvZrHPM52Ivu9FgExlTFgz1VTOCSG7KhxJ9Tqk.
ansible 172.16.1.31 -m user -a 'name=oldboy08 password=$6$oldboy$MVd3DevkLcimrBLdMICrBY8HF82Wtau5cI8D2w4Zs6P1cCfMTcnnyAmmJc7mQaE9zuHxk8JFTRgYMGv9uKW7j1'(三)剧本
(1)剧本的实现步骤
第一步:配置主机清单
如何配置主机清单
第一种方式: 分组配置主机信息
[web]
172.16.1.7
172.16.1.8
172.16.1.9
[data]
172.16.1.31
172.16.1.41
操作过程
[root@m01 ansible-playbook]# ansible data -a "hostname"
172.16.1.31 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
nfs01
172.16.1.41 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
backup
[root@m01 ansible-playbook]# ansible web -a "hostname"
172.16.1.7 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
web01
第二种方式: 主机名符号匹配配置
[web]
172.16.1.[7:9]
[web]
web[01:03]
第三种方式: 跟上非标准远程端口
[web]
web01:52113
172.16.1.7:52113
第四种方式: 主机使用特殊的变量
[web]
172.16.1.7 ansible_ssh_port=52113 ansible_ssh_user=root ansible_ssh_pass=123456
[web]
web01 ansible_ssh_host=172.16.1.7 ansible_ssh_port=52113 ansible_ssh_user=root ansible_ssh_pass=123456
第五种方式: 主机组名嵌入配置
[rsync:children] --- 嵌入子组信息
rsync_server
rsync_client
[rsync_server]
172.16.1.41
[rsync_client]
172.16.1.31
172.16.1.7
[root@m01 /etc/ansible]# ansible rsync -a "hostname"
172.16.1.7 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
web01.com
172.16.1.41 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
backup
172.16.1.31 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
nfs01
[web:vars] --- 嵌入式变量信息
ansible_ssh_host=172.16.1.7
ansible_ssh_port=52113
ansible_ssh_user=root
ansible_ssh_pass=123456
[web]
web01
第二步:编写剧本
剧本编写规范: pyyaml -- 三点要求
1. 合理的信息缩进 两个空格表示一个缩进关系
标题一
标题二
标题三
PS: 在ansible中一定不能用tab进行缩进
2. 冒号的使用方法
hosts: 172.16.1.41
tasks:
yum: name=xx
PS: 使用冒号时后面要有空格信息
以冒号结尾,冒号信息出现在注释说明中,后面不需要加上空格
3. 短横线应用 -(列表功能)
- 张三
男
- 打游戏
- 运动
- 李四
女
学习
湖南
- 王五
男
运动
深圳
PS: 使用短横线构成列表信息,短横线后面需要有空格
剧本编写常见错误:
01. 剧本语法规范是否符合(空格 冒号 短横线)
02. 剧本中模块使用是否正确
03. 剧本中一个name标识下面只能写一个模块任务信息
04. 剧本中尽量不要大量使用shell模块
第三步:执行剧本
如何执行剧本:
第一个步骤: 检查剧本的语法格式
ansible-playbook --syntax-check rsync_server.yaml
第二个步骤: 模拟执行剧本
ansible-playbook -C rsync_server.yaml
第三个步骤: 直接执行剧本
ansible-playbook rsync_server.yaml (2)一键化部署Rsync服务
1.命令实现
服务端的操作
第一个历程安装软件:
ansible 172.16.1.41 -m yum -a "name=rsync state=installed"
第二个历程编写文件:
ansible 172.16.1.41 -m copy -a "src=/etc/rsyncd.conf dest=/etc/"
第三个历程创建用户
ansible 172.16.1.41 -m user -a "name=rsync create_home=no shell=/sbin/nologin"
第四个历程创建目录
ansible 172.16.1.41 -m file -a "dest=/backup state=directory owner=rsync group=rsync"
第五个历程创建密码文件
ansible 172.16.1.41 -m copy -a "content='rsync_backup:123456' dest=/etc/rsync.password mode=600"
第六个历程启动服务
ansible 172.16.1.41 -m service -a "name=rsyncd state=started enabled=yes"
客户端的操作:
第一个历程: 创建密码文件
ansible 客户端地址 -m copy -a "content='rsync_backup:123456' dest=/etc/rsync.password mode=600"2.剧本实现
[root@m01 ansible-playbook]# vim rsync_server.yaml
- hosts: rsync_server
tasks:
- name: 01-install rsync
yum: name=rsync state=installed
- name: 02-push conf file
copy: src=/etc/ansible/server_file/rsync_server/rsyncd.conf dest=/etc/
- name: 03-create user
user: name=rsync create_home=no shell=/sbin/nologin
#shell: useradd rsync -M -s /sbin/nologin
- name: 04-create backup dir
file: path=/backup state=directory owner=rsync group=rsync
- name: 05-create password file
copy: content=rsync_backup:123456 dest=/etc/rsync.password mode=600
- name: 06-start rsync server
service: name=rsyncd state=started enabled=yes
- hosts: rsync_clients
tasks:
- name: 01-install rsync
yum: name=rsync state=installed
- name: 02-create password file
copy: content=123456 dest=/etc/rsync.password mode=600
- name: 03-create test file
file: dest=/tmp/test.txt state=touch
- name: 04-check test
shell: rsync -avz /tmp/test.txt [email protected]::backup --password-file=/etc/rsync.password(3) 一键化部署全网备份项目
(4) 一键化部署NFS服务
(5) 一键化部署实时同步服务
八、网站监控服务zabbix
服务端:zabbix
客户端:其他服务器
(一)部署安装zabbix服务
(1)服务端(zabbix)
第一步:配置zabbix仓库
[root@m01 ~]# rpm -ivh https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/zabbix/zabbix/4.0/rhel/7/x86_64/zabbix-release-4.0-1.el7.noarch.rpm
[root@m01 ~]# sed -i 's#repo.zabbix.com#mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/zabbix#g' /etc/yum.repos.d/zabbix.repo
第二步: 下载安装zabbix服务端相关软件
zabbix服务程序软件: zabbix-server-mysql
zabbix服务web软件: zabbix-web-mysql httpd php
数据库服务软件: mariadb-server
[root@m01 ~]# yum install -y zabbix-server-mysql zabbix-web-mysql httpd php mariadb-server
[root@m01 ~]# systemctl start mariadb.service && systemctl enable mariadb.service
第三步:软件配置
vim /etc/zabbix/zabbix_server.conf
126 DBPassword=zabbix
vim /etc/httpd/conf.d/zabbix.conf
21 php_value date.timezone Asia/Shanghai
第四步:编写配置数据库服务
systemctl start mariadb.service
systemctl status mariadb.service
mysql
create database zabbix character set utf8 collate utf8_bin; --创建zabbix数据库--zabbix
grant all privileges on zabbix.* to zabbix@localhost identified by 'zabbix'; --创建数据库管理用户
zcat /usr/share/doc/zabbix-server-mysql-4.0.21/create.sql.gz|mysql -uzabbix -pzabbix zabbix --在zabbix数据库中导入相应的表信息
chown -R apache /usr/share/zabbix/assets --必须有
第五个里程: 启动zabbix程序相关服务
数据库服务 zabbix服务 httpd服务
systemctl start zabbix-server.service httpd mariadb.service
systemctl enable zabbix-server.service httpd mariadb.service
说明: 至此zabbix-server命令行操作结束
LNMP: nginx php mysql
LAMP: apache(php模块) mysql
第六个里程: 登录zabbix服务端web界面, 进行初始化配置
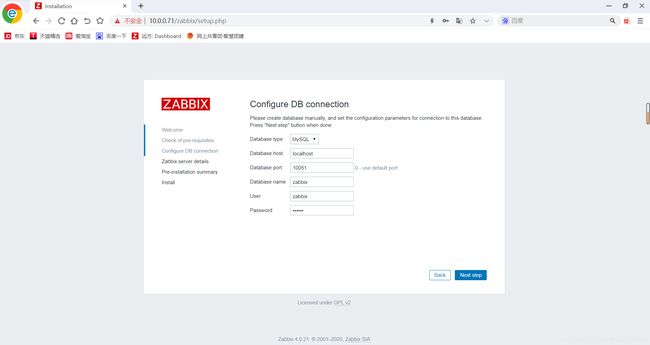
http://10.0.0.71/zabbix/setup.php
10051 zabbix-server 服务端端口号
10050 zabbix-agent 客户端端口号
/etc/zabbix/web/zabbix.conf.php -- 记录web页面初始化信息
第七个里程: 登录zabbix服务web页面
http://10.0.0.71/zabbix/
用户名Admin 密码zabbix(2)客户端(其他服务器)
第一个里程: 下载安装zabbix yum 源文件
LTS long time support
1) aliyun zabbix yum 源
2) 清华源
rpm -ivh https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/zabbix/zabbix/4.0/rhel/7/x86_64/zabbix-release-4.0-1.el7.noarch.rpm
第二个里程: 下载安装zabbix客户端软件
yum install -y zabbix-agent
或者
rpm -ivh https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/zabbix/zabbix/4.0/rhel/7/x86_64/zabbix-agent-4.0.0-2.el7.x86_64.rpm
第三个里程: 编写zabbix客户端配置文件
vim /etc/zabbix/zabbix_agentd.conf
98 Server=172.16.1.71
第四个里程: 启动zabbix-agent服务
[root@web01 ~]# systemctl start zabbix-agent
[root@web01 ~]# netstat -lntup|grep 10050
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:10050 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 4509/zabbix_agentd
tcp 0 0 :::10050 :::* LISTEN 4509/zabbix_agentd(二)实现zabbix自定义监控
(1)需求:监控Nginx服务是否启动
1) 在zabbix-agent进行配置文件编写
第一步: 编写自定义监控命令
ps -ef|grep -c [n]ginx
第二步: 编写zabbix-agent配置文件
第一种方法: 直接修改zabbix-agent配置文件参数
UserParameter=
第二种方法: 在/etc/zabbix/zabbix_agentd.d/目录中编写自定义监控文件
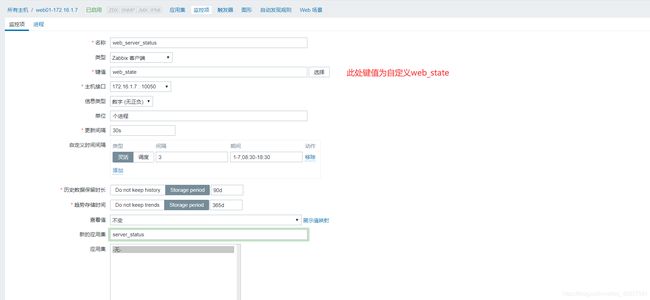
vim web_server.conf
UserParameter=键(变量名),值(变量信息)
UserParameter=web_state,ps -ef|grep -c [n]ginx
第三步: 重启zabbix-agent服务
systemctl restart zabbix-agent
2) 在zabbix-server命令行进行操作
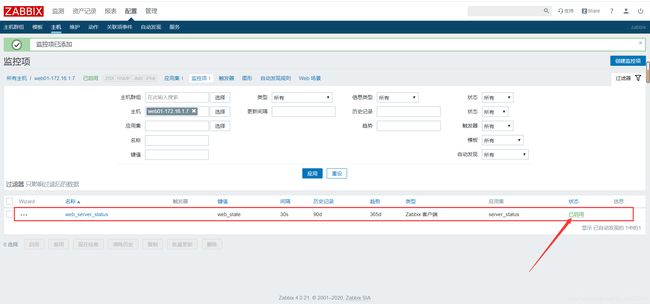
第一步: 检测自定义监控信息是否正确
yum install -y zabbix-get
zabbix_get -s 172.16.1.7 -k 'web_state'
ps:
-s 表示要监控的主机IP 与zabbix-agent配置文件里的信息一致
-k key即键信息
3) 在zabbix-server网站页面进行配置(如下图所示)
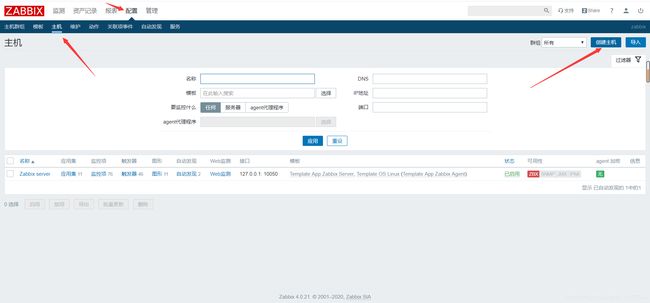
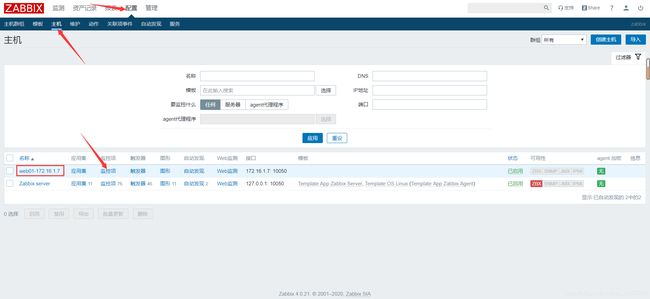
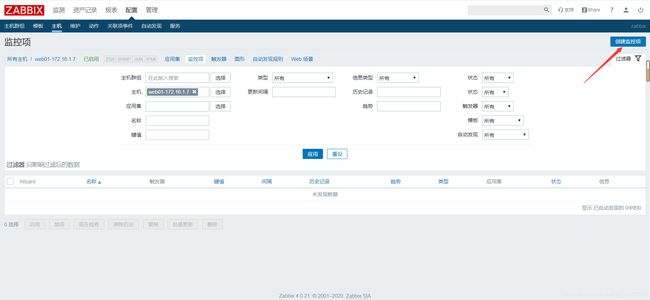
第一步: 进入到创建监控项页面:
配置---主机---选择相应主机的监控项
第二步: 监控项页面如何配置
名称 键值 更新间隔时间 应用集
第三步: 检查是否收集到监控信息
(2)复杂的自定义监控配置(多个服务状态)
1) 在zabbix-agent端编写配置文件
vim server_state.conf
UserParameter=server_state[*],netstat -lntup|grep -c $1
2) 在zabbix-server命令测试
zabbix_get -s 172.16.1.7 -k 'server_state[22]'
3) 修改配置页面
键值: server_state[22](3)报警(邮件报警、微信报警、短信和电话)
1.邮件信息报警
第一个历程: 创建触发器
配置---主机---选择相应监控主机触发器---创建触发器
设置好表达式
{web01:server_state[nginx].last()}<=2
{监控主机名称:键值名称.调用的表达式函数}<=2
第二个历程: 修改动作配置
配置---动作---将默认动作进行开启
第三个历程: 建立和163邮箱服务关系
管理---报警媒介类型---创建报警媒介
第四个历程: 定义接收报警的邮件地址
小人头--报警媒介--设置收件人信息
2.微信报警
第一个历程: 需要注册企业微信,并进行配置
我的企业:
01. 获取企业id: ww32d68104ab5f51b0
02. 获取企业二维码: 允许员工加入
管理工具:
01. 成员加入---进行审核通过
应用小程序:
01. 进行创建
02. 收集程序信息
AgentId: 1000006
Secret: RvQYpaCjWbYMCcwhnPqg1ZYcEGB9cOQCvvlkn-ft6j4
第二个历程: 编写脚本(python)
cat /etc/zabbix/zabbix-server.conf
AlertScriptsPath=/usr/lib/zabbix/alertscripts --- 放置告警脚本
执行脚本报错问题解决:
01. 问题: No module named requests
yum install -y python-pip
pip install requests
02. 问题: 脚本执行语法
第三个历程: 修改添加报警媒介---定义了发微信配置
第四个历程: 配置接收微信的人员
3.短信和电话:
利用第三方短信电话报警平台
01. 利用阿里大鱼(收费)
https://yq.aliyun.com/articles/658524?spm=a2c4e.11155472.0.0.d821153fAjrH3q --- 自行研究
02. 利用onealert发送告警
第一个历程: 配置报警平台
01. 配置--应用--选择zabbix报警
02. 配置--通知策略
03. 配置--分派策略