算法通关村第19关【白银】| 动态规划高频问题
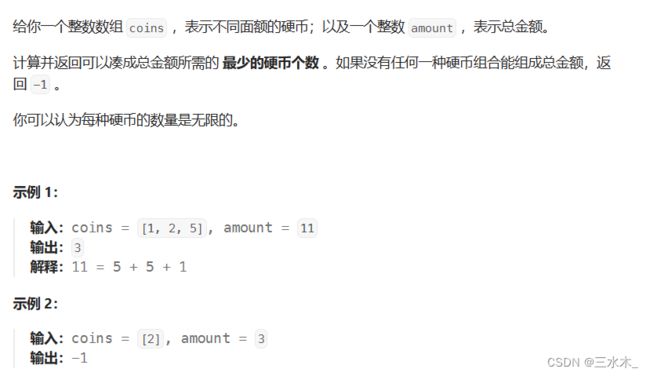
1.零钱兑换
思路:
确定dp:这里是最少硬币的个数,不是种类
确定递推公式:dp[j] = Math.min(dp[j],dp[j-coins[i]]+1),不要当前硬币dp[j]还是保持以前的组合方法,要当前硬币dp[j-coins[i]]+1
确定初始化:dp[0]=0,其他的都得初始化最大值
确定遍历顺序:组合排列都无所谓,保证完全背包从前往后即可
class Solution {
public int coinChange(int[] coins, int amount) {
int max = amount + 1;
int[] dp = new int[amount+1];
Arrays.fill(dp,max);
dp[0] = 0;
for(int i = 1;i= max?-1:dp[amount];
}
} 2.最长连续递增序列
思路:
dp:当前最长的递增子序列长度
递增的时候:dp[i] = dp[i-1]+1
class Solution {
public int findLengthOfLCIS(int[] nums) {
int[] dp = new int[nums.length];
int res = 1;
for(int i = 0;inums[i-1]){
dp[i] = dp[i-1] + 1;
}
res = res > dp[i] ? res : dp[i];
}
return res;
}
} 3.最长递增子序列
思路:
确定dp:包含当前数字的最长递增子序列长度
确定递推公式:dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i],dp[j]+1),
确定初始化:dp[i]=1,只包含当前元素长度为1
确定遍历顺序:后面的dp依赖前面的得出从前往后
class Solution {
public int lengthOfLIS(int[] nums) {
int[] dp =new int[nums.length];
Arrays.fill(dp,1);
int res = 0;
for(int i = 0;inums[j]){
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i],dp[j]+1);
}
}
res = Math.max(res,dp[i]);
}
return res;
}
} 4.完全平方数
思路:
确定dp:当前数字最少组成数量
确定递推公式:dp[i] = Math.min(dp[i],dp[i-j*j]+1);当前和取j*j之中的最小
确定初始化:dp[0]=0,dp为max
确定遍历顺序:后面的dp依赖前面的得出从前往后
class Solution {
public int numSquares(int n) {
int[] dp = new int[n+1];
Arrays.fill(dp,Integer.MAX_VALUE);
dp[0] = 0;
for(int i = 1;i<=n;i++){
for(int j = 1;j*j<=i;j++){
dp[i] = Math.min(dp[i],dp[i-j*j]+1);
}
}
return dp[n];
}
}5.跳跃游戏
思路:
确定dp:当前能跳的最远距离
确定递推公式:dp[i] = Math.max(dp[j],j+nums[j]);
确定初始化:dp[0]=nums[0],dp为0
确定遍历顺序:后面的dp依赖前面的得出从前往后
class Solution {
public boolean canJump(int[] nums) {
int len = nums.length;
if(len == 1){
return true;
}
int[] dp = new int[len];
Arrays.fill(dp,0);
dp[0] = nums[0];
for(int i = 0;i6.解码方法
思路:
确定dp:当前的解码方案数
确定递推公式:dp[i] = dp[i-1]+dp[i-2]
- 当 i-1 和 i 为0 或者 i 为0且 i-1 和 i 大于26:不符合条件,返回0
- 当i为0,则dp[i] = dp[i-2]
- 当i-1为0或者i-1不为0且i-1 和 i 大于26,则dp[i] = dp[i-1]
- 其他情况,dp[i] = dp[i-1] + dp[i-2]
确定初始化:dp[0]=0
确定遍历顺序:后面的dp依赖前面的得出从前往后
class Solution {
public int numDecodings(String s) {
int len = s.length();
if(s.charAt(0) == '0'){
return 0;
}
if(len == 1){
return 1;
}
int[] dp = new int[len];
char[] c = s.toCharArray();
dp[0] = 1;
if(isAble(c[0],c[1])&&c[1]!='0'){
dp[1] = 2;
}else{
dp[1] = 1;
}
if(c[1] == '0'&&!isAble(c[0],c[1])){
return 0;
}
for(int i = 2;i也可以判断不符合的条件,更加简洁
class Solution {
public int numDecodings(String s) {
int n = s.length();
int[] f = new int[n + 1];
f[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
if (s.charAt(i - 1) != '0') {
f[i] += f[i - 1];
}
if (i > 1 && s.charAt(i - 2) != '0' && ((s.charAt(i - 2) - '0') * 10 + (s.charAt(i - 1) - '0') <= 26)) {
f[i] += f[i - 2];
}
}
return f[n];
}
}
7.不同路径II
思路:
确定dp:能到达当前位置的路径数
确定递推公式: dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j] + dp[i][j-1];
确定初始化:第一行和第一列为1,注意碰到障碍物后面全是0
确定遍历顺序:后面的dp依赖前面的得出从前往后,从左往右
class Solution {
public int uniquePathsWithObstacles(int[][] obstacleGrid) {
int[][] dp = new int[obstacleGrid.length][obstacleGrid[0].length];
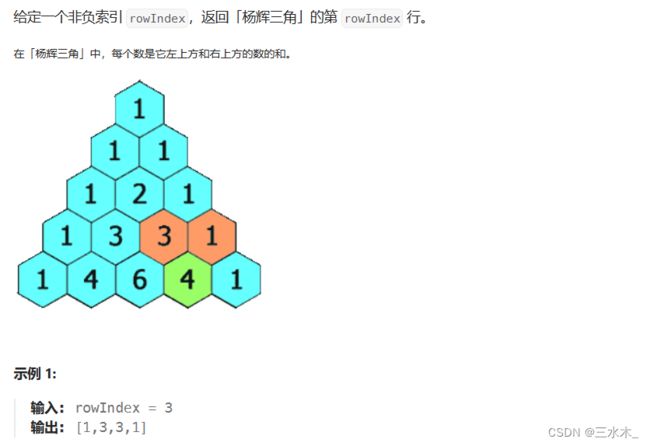
for(int i = 0;i8.滚动数组技巧
思路:
杨辉三角,除了0号位置和i==j的位置是1,其他都是左上角+右上角的值
一般解法:二维数组就是初始化一个dp[i][j],然后逐行遍历相加,输出指定行的值
现在要进行空间优化O(rowIndex)
如果我们使用一个一维数组dp[]:
从前往后遍历相加:121=>131=>1341 会发现原先的2被覆盖替换为了3,导致后面的数计算错误。这时我们可以使用第二个一维数组来帮助我们记录值
class Solution {
public List getRow(int rowIndex) {
List pre = new ArrayList();
for (int i = 0; i <= rowIndex; ++i) {
List cur = new ArrayList();
for (int j = 0; j <= i; ++j) {
if (j == 0 || j == i) {
cur.add(1);
} else {
cur.add(pre.get(j - 1) + pre.get(j));
}
}
pre = cur;
}
return pre;
}
}
从后往前遍历:121=>31=>331=>1331 会发现左上角和右上角的值并没被覆盖√
class Solution {
public List getRow(int rowIndex) {
List row = new ArrayList();
row.add(1);
for (int i = 1; i <= rowIndex; ++i) {
row.add(0);
for (int j = i; j > 0; --j) {
row.set(j, row.get(j) + row.get(j - 1));
}
}
return row;
}
}