牛客Leetcode高频题解
01 链表
| 编号 | 题目 | 思路 | 难度 | 频率 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BM1 | 反转链表 | 思路 | 简单 | 38.85% |
| BM2 | 链表内指定区间反转 | 思路 | 中等 | 27.57% |
| BM3 | 链表中的节点每k个一组翻转 | 思路 | 中等 | 36.39% |
| BM4 | 合并两个排序的链表 | 思路 | 简单 | 31.88% |
| BM5 | 合并k个已排序的链表 | 思路 | 较难 | 33.12% |
| BM6 | 判断链表中是否有环 | 思路 | 简单 | 36.46% |
| BM7 | 链表中环的入口结点 | 思路 | 中等 | 35.85% |
| BM8 | 链表中倒数最后k个结点 | 思路 | 简单 | 32.64% |
| BM9 | 删除链表的倒数第n个节点 | 思路 | 中等 | 36.01% |
| BM10 | 两个链表的第一个公共结点 | 思路 | 简单 | 37.17% |
| BM11 | 链表相加(二) | 思路 | 中等 | 33.91% |
| BM12 | 单链表的排序 | 思路 | 中等 | 45.40% |
| BM13 | 判断一个链表是否为回文结构 | 思路 | 简单 | 31.83% |
| BM14 | 链表的奇偶重排 | 思路 | 中等 | 43.05% |
| BM15 | 删除有序链表中重复的元素-I | 思路 | 简单 | 36.82% |
| BM16 | 删除有序链表中重复的元素-II | 思路 | 中等 | 32.01% |
02 二分查找/排序
| 编号 | 题目 | 思路 | 难度 | 频率 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BM17 | 二分查找-I | 思路 | 简单 | 29.19% |
| BM18 | 二维数组中的查找 | 思路 | 中等 | 26.24% |
| BM19 | 寻找峰值 | 思路 | 中等 | 27.01% |
| BM20 | 数组中的逆序对 | 思路 | 中等 | 17.02% |
| BM21 | 旋转数组的最小数字 | 思路 | 简单 | 33.39% |
| BM22 | 比较版本号 | 思路 | 中等 | 26.80% |
03 二叉树
| 编号 | 题目 | 思路 | 难度 | 频率 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BM23 | 二叉树的前序遍历 | 简单 | 51.63% | |
| BM24 | 二叉树的中序遍历 | 中等 | 54.38% | |
| BM25 | 二叉树的后序遍历 | 简单 | 64.33% | |
| BM26 | 求二叉树的层序遍历 | 思路 | 中等 | 45.52% |
| BM27 | 按之字形顺序打印二叉树 | 思路 | 中等 | 28.57% |
| BM28 | 二叉树的最大深度 | 思路 | 简单 | 60.03% |
| BM29 | 二叉树中和为某一值的路径(一) | 思路 | 简单 | 36.83% |
| BM30 | 二叉搜索树与双向链表 | 思路 | 中等 | 31.35% |
| BM31 | 对称的二叉树 | 思路 | 简单 | 32.52% |
| BM32 | 合并二叉树 | 思路 | 简单 | 68.61% |
| BM33 | 二叉树的镜像 | 思路 | 简单 | 65.30% |
| BM34 | 判断是不是二叉搜索树 | 思路 | 中等 | 27.23% |
| BM35 | 判断是不是完全二叉树 | 思路 | 中等 | 31.66% |
| BM36 | 判断是不是平衡二叉树 | 思路 | 简单 | 38.46% |
| BM37 | 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先 | 思路 | 简单 | 42.44% |
| BM38 | 在二叉树中找到两个节点的最近公共祖先 | 思路 | 中等 | 42.20% |
| BM39 | 序列化二叉树 | 思路 | 较难 | 24.74% |
| BM40 | 重建二叉树 | 思路 | 中等 | 27.60% |
| BM41 | 输出二叉树的右视图 | 思路 | 中等 | 53.88% |
04 堆/栈/队列
| 编号 | 题目 | 思路 | 难度 | 频率 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BM42 | 用两个栈实现队列 | 思路 | 简单 | 41.27% |
| BM43 | 包含min函数的栈 | 思路 | 简单 | 34.79% |
| BM44 | 有效括号序列 | 思路 | 简单 | 30.83% |
| BM45 | 滑动窗口的最大值 | 思路 | 较难 | 26.96% |
| BM46 | 最小的K个数 | 思路 | 中等 | 27.59% |
| BM47 | 寻找第K大 | 思路 | 中等 | 27.86% |
| BM48 | 数据流中的中位数 | 思路 | 中等 | 29.35% |
| BM49 | 表达式求值 | 思路 | 中等 | 38.99% |
05 哈希
| 编号 | 题目 | 思路 | 难度 | 频率 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BM50 | 两数之和 | 思路 | 简单 | 34.76% |
| BM51 | 数组中出现次数超过一半的数字 | 思路 | 简单 | 32.74% |
| BM52 | 数组中只出现一次的两个数字 | 思路 | 中等 | 52.17% |
| BM53 | 缺失的第一个正整数 | 思路 | 中等 | 33.63% |
| BM54 | 三数之和 | 思路 | 中等 | 22.65% |
06 递归/回溯
| 编号 | 题目 | 思路 | 难度 | 频率 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BM55 | 没有重复项数字的全排列 | 思路 | 中等 | 53.80% |
| BM56 | 有重复项数字的全排列 | 思路 | 中等 | 35.77% |
| BM57 | 岛屿数量 | 思路 | 中等 | 38.95% |
| BM58 | 字符串的排列 | 思路 | 中等 | 23.33% |
| BM59 | N皇后问题 | 思路 | 较难 | 41.68% |
| BM60 | 括号生成 | 思路 | 中等 | 51.69% |
| BM61 | 矩阵最长递增路径 | 思路 | 中等 | 32.31% |
07 动态规划
| 编号 | 题目 | 思路 | 难度 | 频率 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BM62 | 斐波那契数列 | 思路 | 入门 | 36.47% |
| BM63 | 跳台阶 | 思路 | 简单 | 40.26% |
| BM64 | 最小花费爬楼梯 | 思路 | 简单 | 41.86% |
| BM65 | 最长公共子序列(二) | 思路 | 中等 | 32.29% |
| BM66 | 最长公共子串 | 思路 | 中等 | 32.84% |
| BM67 | 不同路径的数目(一) | 思路 | 简单 | 44.18% |
| BM68 | 矩阵的最小路径和 | 思路 | 中等 | 48.13% |
| BM69 | 把数字翻译成字符串 | 思路 | 中等 | 17.15% |
| BM70 | 兑换零钱(一) | 思路 | 中等 | 34.76% |
| BM71 | 最长上升子序列(一) | 思路 | 中等 | 25.39% |
| BM72 | 连续子数组的最大和 | 思路 | 简单 | 39.42% |
| BM73 | 最长回文子串 | 思路 | 中等 | 36.05% |
| BM74 | 数字字符串转化成IP地址 | 思路 | 中等 | 34.49% |
| BM75 | 编辑距离(一) | 思路 | 较难 | 42.05% |
| BM76 | 正则表达式匹配 | 思路 | 较难 | 27.07% |
| BM77 | 最长的括号子串 | 思路 | 较难 | 24.68% |
| BM78 | 打家劫舍(一) | 思路 | 中等 | 36.16% |
| BM79 | 打家劫舍(二) | 思路 | 中等 | 37.77% |
| BM80 | 买卖股票的最好时机(一) | 思路 | 简单 | 51.93% |
| BM81 | 买卖股票的最好时机(二) | 思路 | 中等 | 61.25% |
| BM82 | 买卖股票的最好时机(三) | 思路 | 较难 | 42.26% |
08 字符串
| 编号 | 题目 | 思路 | 难度 | 频率 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BM83 | 字符串变形 | 思路 | 简单 | 22.33% |
| BM84 | 最长公共前缀 | 思路 | 简单 | 31.48% |
| BM85 | 验证IP地址 | 思路 | 中等 | 19.66% |
| BM86 | 大数加法 | 思路 | 中等 | 39.35% |
09 双指针
| 编号 | 题目 | 思路 | 难度 | 频率 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BM87 | 合并两个有序的数组 | 思路 | 简单 | 35.80% |
| BM88 | 判断是否为回文字符串 | 思路 | 入门 | 59.27% |
| BM89 | 合并区间 | 思路 | 中等 | 26.98% |
| BM90 | 最小覆盖子串 | 思路 | 较难 | 26.72% |
| BM91 | 反转字符串 | 思路 | 入门 | 65.44% |
| BM92 | 最长无重复子数组 | 思路 | 中等 | 30.55% |
| BM93 | 盛水最多的容器 | 思路 | 中等 | 39.59% |
| BM94 | 接雨水问题 | 思路 | 较难 | 39.94% |
010 贪心算法
| 编号 | 题目 | 思路 | 难度 | 频率 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BM95 | 分糖果问题 | 思路 | 较难 | 22.93% |
| BM96 | 主持人调度(二) | 思路 | 中等 | 22.87% |
11 模拟
| 编号 | 题目 | 思路 | 难度 | 频率 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BM97 | 旋转数组 | 思路 | 中等 | 42.30% |
| BM98 | 螺旋矩阵 | 思路 | 简单 | 27.46% |
| BM99 | 顺时针旋转矩阵 | 思路 | 中等 | 51.14% |
| BM100 | 设计LRU缓存结构 | 思路 | 较难 | 41.36% |
| BM101 | 设计LFU缓存结构 | 思路 | 较难 | 30.80% |
反转链表
(1)使用栈解法:import java.util.Stack;
public class Solution {
public ListNode ReverseList(ListNode head) {
Stack<ListNode> stack= new Stack<>();
//把链表节点全部摘掉放到栈中
while (head != null) {
stack.push(head);
head = head.next;
}
if (stack.isEmpty())
return null;
ListNode node = stack.pop();
ListNode dummy = node;
//栈中的结点全部出栈,然后重新连成一个新的链表
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
ListNode tempNode = stack.pop();
node.next = tempNode;
node = node.next;
}
//最后一个结点就是反转前的头结点,一定要让他的next
//等于空,否则会构成环
node.next = null;
return dummy;
}
}
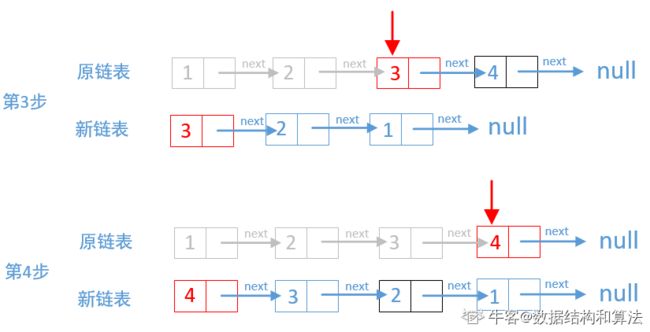
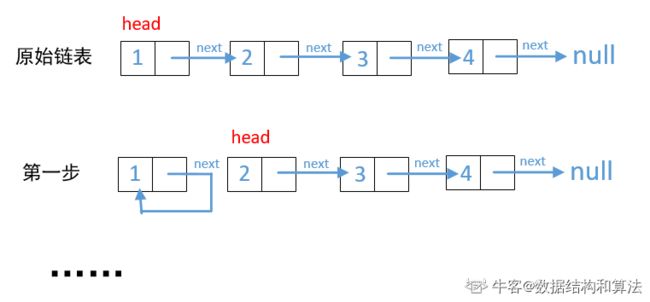
(2)双链表解法:
public ListNode ReverseList(ListNode head) {
//新链表
ListNode newHead = null;
while (head != null) {
//先保存访问的节点的下一个节点,保存起来
//留着下一步访问的
ListNode temp = head.next;
//每次访问的原链表节点都会成为新链表的头结点,
//其实就是把新链表挂到访问的原链表节点的
//后面就行了
head.next = newHead;
//更新新链表
newHead = head;
//重新赋值,继续访问
head = temp;
}
//返回新链表
return newHead;
}
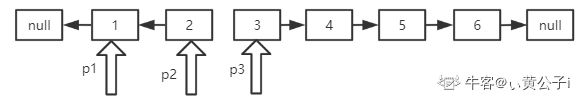
(3)双指针解法:
public class Solution {
public ListNode ReverseList(ListNode head) {
if(head == null){
return null;
}
ListNode p1 = null;
ListNode p2 = head;
ListNode p3 = head.next;
while(p2 != null){
p2.next = p1;
p1 = p2;
p2 = p3;
if(p3 != null){
p3 = p3.next;
}
}
return p1;
}
}
链表内指定区间反转
(1)递归解法:
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
ListNode temp = null;
public ListNode reverse(ListNode head, int n){
//只颠倒第一个节点,后续不管
if(n == 1){
temp = head.next;
return head;
}
//进入子问题
ListNode node = reverse(head.next, n - 1);
//反转
head.next.next = head;
//每个子问题反转后的尾拼接第n个位置后的节点
head.next = temp;
return node;
}
public ListNode reverseBetween (ListNode head, int m, int n) {
//从第一个节点开始
if(m == 1) return reverse(head, n);
//缩减子问题
ListNode node = reverseBetween(head.next, m - 1, n - 1);
//拼接已翻转
head.next = node;
return head;
}
}
(2)头插法迭代:
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public ListNode reverseBetween (ListNode head, int m, int n) {
//加个表头
ListNode res = new ListNode(-1);
res.next = head;
//前序节点
ListNode pre = res;
//当前节点
ListNode cur = head;
//找到m
for(int i = 1; i < m; i++){
pre = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
//从m反转到n
ListNode temp = null;
for(int i = m; i < n; i++){
temp = cur.next;
cur.next = temp.next;
temp.next = pre.next;
pre.next = temp;
}
//返回去掉表头
return res.next;
}
}
排序
(1)冒泡排序 (2)快速排序 ```java import java.util.*; public class Solution { /** * 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可 * 将给定数组排序 * @param arr int整型一维数组 待排序的数组 * @return int整型一维数组 */ public int[] MySort (int[] arr) { quickSort(arr , 0 , arr.length-1); return arr; } public void quickSort(int[] list, int left, int right) { if (left < right) { // 分割数组,找到分割点 int point = partition(list, left, right); // 递归调用,对左子数组进行快速排序 quickSort(list, left, point - 1); // 递归调用,对右子数组进行快速排序 quickSort(list, point + 1, right); } }/**
* 分割数组,找到分割点
*/
public int partition(int[] list, int left, int right) {
// 用数组的第一个元素作为基准数
int first = list[left];
while (left < right) {
while (left < right && list[right] >= first) {
right--;
}
// 交换
swap(list, left, right);
while (left < right && list[left] <= first) {
left++;
}
// 交换
swap(list, left, right);
}
// 返回分割点所在的位置
return left;
}
private void swap(int[] arr, int i, int j) {
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
}
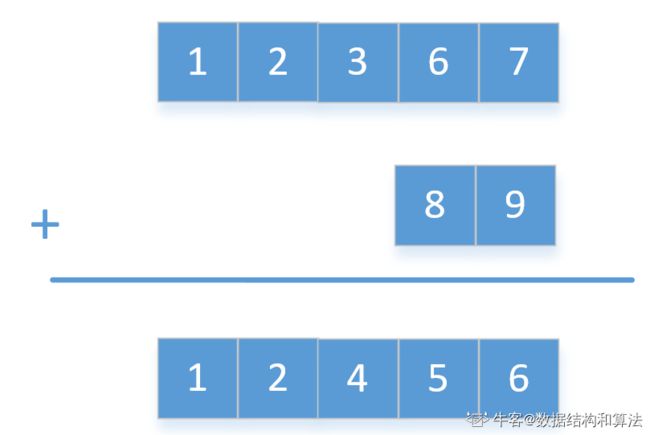
(3)归并排序MergeSort
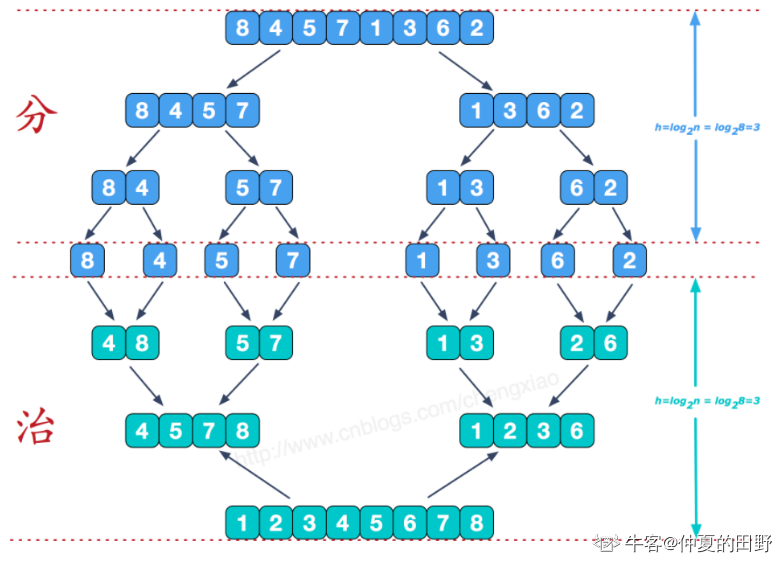
```java
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
/**
* 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
* 将给定数组排序
* @param arr int整型一维数组 待排序的数组
* @return int整型一维数组
*/
public int[] MySort (int[] arr) {
mergeSort(arr,0,arr.length-1);
return arr;
}
public void mergeSort(int[] arr,int l,int r){
if(l==r){
return;
}
int mid = l+((r-l)>>1); //中点位置,即(l+r)/2
mergeSort(arr,l,mid);
mergeSort(arr,mid+1,r);
merge(arr,l,mid,r);
}
public void merge(int[] arr,int l,int mid,int r){
int [] help= new int[r-l+1]; //辅助数组
int i=0;
int p1=l; //左半数组的下标
int p2=mid+1; //右半数组的下标
//判断是否越界
while(p1<=mid && p2<=r){
help[i++]=arr[p1](4)堆排序
public int[] MySort (int[] arr) {
heapSort(arr);
return arr;
}
public static void heapSort(int[] arr){
if(arr == null || arr.length<2){
return;
}
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
heapInsert(arr,i); //构造完全二叉树
}
int size = arr.length;
swap(arr,0,--size);
while(size>0){
heapify(arr,0,size);// 最后一个数与根交换
swap(arr,0,--size);
}
}
//判断该结点与父结点的大小,大结点一直往,建立大根堆
public static void heapInsert(int[] arr,int index){
while(arr[index]>arr[(index-1)/2]){
swap(arr,index,(index-1)/2);
index=(index-1)/2;
}
}
//一个值变小往下沉的过程
public static void heapify(int[] arr,int index,int size){
int left=index*2+1;
while(left<size){
int largest = left + 1 < size && arr[left+1] > arr[left] ? left+1 : left;
largest = arr[largest] > arr[index] ? largest :index;
if(largest==index){
break;
}
swap(arr,largest,index);
index=largest;
left=index*2 +1;
}
}
//交换函数
public static void swap(int[] arr, int i, int j){
int tmp;
tmp=arr[i];
arr[i]=arr[j];
arr[j]=tmp;
}
(5)优先队列
-
优先队列不再遵循先入先出的原则,而是分为两种情况:
-
最大优先队列,无论入队顺序,当前最大的元素优先出队;
-
最小优先队列,无论入队顺序,当前最小的元素优先出队;
-
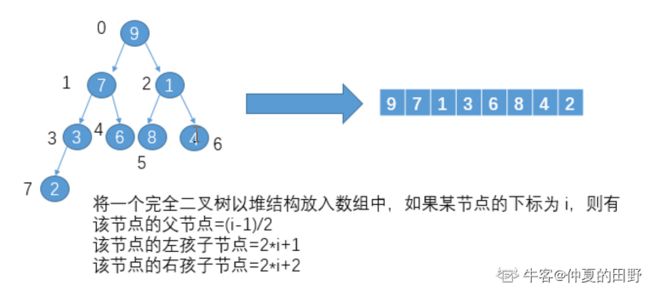
优先级队列,也叫二叉堆、堆(不要和内存中的堆区搞混了,一个是内存区域,一个是数据结构)。
堆的本质上是一种完全二叉树,分为: -
小根堆:树中每个非叶子结点都不大于其左右孩子结点的值,也就是根节点最小的堆,图a
-
大根堆:树中每个非叶子结点都不小于其左右孩子结点的值,也就是根节点最大的堆,图b
public int[] MySort (int[] arr) { PriorityQueue<Integer> queue=new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator<Integer>(){ public int compare(Integer a,Integer b){ return a.compareTo(b); } }); for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){ queue.offer(arr[i]); } int[] newarr=new int[arr.length]; for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){ newarr[i]=queue.poll(); } return newarr; }
设计LRU缓存结构
(1)解法1import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
private Map<Integer, Node> map = new HashMap<>();
private Node head = new Node(-1,-1);
private Node tail = new Node(-1,-1);
private int k;
public int[] LRU (int[][] operators, int k) {
this.k = k;
head.next = tail;
tail.prev = head;
int len = (int)Arrays.stream(operators).filter(x -> x[0] == 2).count();
int[] res = new int[len];
for(int i = 0, j = 0; i < operators.length; i++) {
if(operators[i][0] == 1) {
set(operators[i][1], operators[i][2]);
} else {
res[j++] = get(operators[i][1]);
}
}
return res;
}
private void set(int key, int val) {
if(get(key) > -1) {
map.get(k).val = val;
} else {
if(map.size() == k) {
int rk = tail.prev.key;
tail.prev.prev.next = tail;
tail.prev = tail.prev.prev;
map.remove(rk);
}
Node node = new Node(key, val);
map.put(key, node);
moveToHead(node);
}
}
private int get(int key) {
if(map.containsKey(key)) {
Node node = map.get(key);
node.prev.next = node.next;
node.next.prev = node.prev;
moveToHead(node);
return node.val;
}
return -1;
}
private void moveToHead(Node node) {
node.next = head.next;
head.next.prev = node;
head.next = node;
node.prev = head;
}
static class Node{
int key, val;
Node prev, next;
public Node(int key, int val) {
this.key = key;
this.val = val;
}
}
}
(2)解法2
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
/**
* lru design
* @param operators int整型二维数组 the ops
* @param k int整型 the k
* @return int整型一维数组
*/
public int[] LRU (int[][] operators, int k) {
// write code here
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
LRUCache lru = new LRUCache(k);
for(int[] opt:operators){
if(opt[0] == 1){
lru.put(opt[1],opt[2]);
}else{
list.add(lru.get(opt[1]));
}
}
int[] res = new int[list.size()];
int i = 0;
for(int val:list){
res[i] = list.get(i);
i++;
}
return res;
}
}
//设置LRU缓存结构
class LRUCache{
int cap;
LinkedHashMap<Integer, Integer> cache = new LinkedHashMap<>();
public LRUCache(int capactity){
this.cap = capactity;
}
// 将key变为最近使用
private void makeRecently(int key){
int val = cache.get(key);
//删除key,重新插入到队尾
cache.remove(key);
cache.put(key, val);
}
//获取值
public int get(int key){
if(!cache.containsKey(key)){
return -1;
}
//将这个key变为最近使用的
makeRecently(key);
return cache.get(key);
}
//存进值
public void put(int key,int val){
if(cache.containsKey(key)){
cache.put(key, val);
//设置为最近使用
makeRecently(key);
return;
}
//超出缓存的大小
if(cache.size() >= this.cap){
//拿到链表头部的key(其最久未使用的key)
int oldstKet = cache.keySet().iterator().next();
cache.remove(oldstKet);
}
//将新的key添加到链表尾部
cache.put(key,val);
}
}
实现二叉树先序-中序和后序遍历
(1)递归解法
public void preorder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> list) {
if (root != null) {
list.add(root.val);
preorder(root.left, list);
preorder(root.right, list);
}
}
public void inorder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> list) {
if (root != null) {
inorder(root.left, list);
list.add(root.val);
inorder(root.right, list);
}
}
public void postorder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> list) {
if (root != null) {
postorder(root.left, list);
postorder(root.right, list);
list.add(root.val);
}
}
(2)迭代解法
1) 前序遍历迭代
- 算法1
- 1.根节点入栈
- 2.当栈非空时,栈顶出栈,把出栈的节点值添加到 list 结尾,然后依次再入栈其右子节点和左子节点
- ps:因为前序遍历要左子节点在右子节点前面,所以先入栈右子节点,后入栈左子节点
- 算法2
- 1.辅助变量 curr 初始化为根节点
- 2.当 curr != null 时,就保存这个节点值到 list 中,然后将其入栈并置 curr 为它自己的左子节点
- 3.当 curr == null 时,说明已经遍历到二叉树的左下节点了,这时前序遍历应该遍历右子树了,首先 pop 出已经遍历保存过的父节点,然后置 curr 为 pop 出的父节点的右子节点
- 算法3
- 和算法2的区别:父节点遍历到之后直接保存下来不再入栈,随后入栈其右子节点,这样出栈的时候也不必再置为其右子节点
public void preorder(TreeNode root, ArrayList<Integer> list) {
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(root);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode curr = stack.pop();
list.add(curr.val);
if (curr.right != null) {
stack.push(curr.right);
}
if (curr.left != null) {
stack.push(curr.left);
}
}
}
public void preorder(TreeNode root, ArrayList<Integer> list) {
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode curr = root;
while (!stack.isEmpty() || curr != null) {
if (curr != null) {
list.add(curr.val);
stack.push(curr);
curr = curr.left;
} else {
curr = stack.pop();
curr = curr.right;
}
}
}
public void preorder(TreeNode root, ArrayList<Integer> list) {
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode curr = root;
while (!stack.isEmpty() || curr != null) {
if (curr != null) {
list.add(curr.val);
if (curr.right != null) {
stack.push(curr.right);
}
curr = curr.left;
} else {
curr = stack.pop();
}
}
}
2)中序遍历迭代
- 算法1
- 1.辅助变量 curr 初始化 root
- 3.当栈非空或 curr 非 null 时,循环
- 3.1 curr != null 时,说明还有左子节点存在,将 curr 入栈,并且将 curr 置为它自己的左子节点(和前序遍历的区别在于这里遍历到先不保存到 list 中,出栈的时候再将其保存到 list 中)
- 3.2 curr == null 时,说明到二叉树左下的节点了,这时栈顶的父节点出栈赋值给 curr ,并保存节点值到 list ,将 curr 置为栈顶节点的右子节点继续循环
- 算法2
- 算法1的另一种形式
public void inorder(TreeNode root, ArrayList<Integer> list) {
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode curr = root;
while (!stack.isEmpty() || curr != null) {
if (curr != null) {
stack.push(curr);
curr = curr.left;
} else {
curr = stack.pop();
list.add(curr.val);
curr = curr.right;
}
}
}
public void inorder(TreeNode root, ArrayList<Integer> list) {
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode curr = root;
while (!stack.isEmpty() || curr != null) {
while (curr != null) {
stack.push(curr);
curr = curr.left;
}
curr = stack.pop();
list.add(curr.val);
curr = curr.right;
}
}
3) 后序遍历迭代
- 三种算法分别对应前序遍历的反操作:
- 前序遍历从尾部添加元素,后序遍历从头部添加元素
- 前序遍历去左子树,后序遍历去右子树
public void postorder(TreeNode root, ArrayList<Integer> list) {
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(root);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode curr = stack.pop();
list.add(0, curr.val);
if(curr.left != null) {
stack.push(curr.left);
}
if(curr.right != null) {
stack.push(curr.right);
}
}
}
public void postorder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> list) {
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode curr = root;
while (!stack.isEmpty() || curr != null) {
if (curr != null) {
stack.push(curr);
list.add(0, curr.val);
curr = curr.right;
} else {
curr = stack.pop();
curr = curr.left;
}
}
}
public void postorder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> list) {
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode curr = root;
while (!stack.isEmpty() || curr != null) {
if (curr != null) {
list.add(0, curr.val);
if (curr.left != null) {
stack.push(curr.left);
}
curr = curr.right;
} else {
curr = stack.pop();
}
}
}
求二叉树的层序遍历
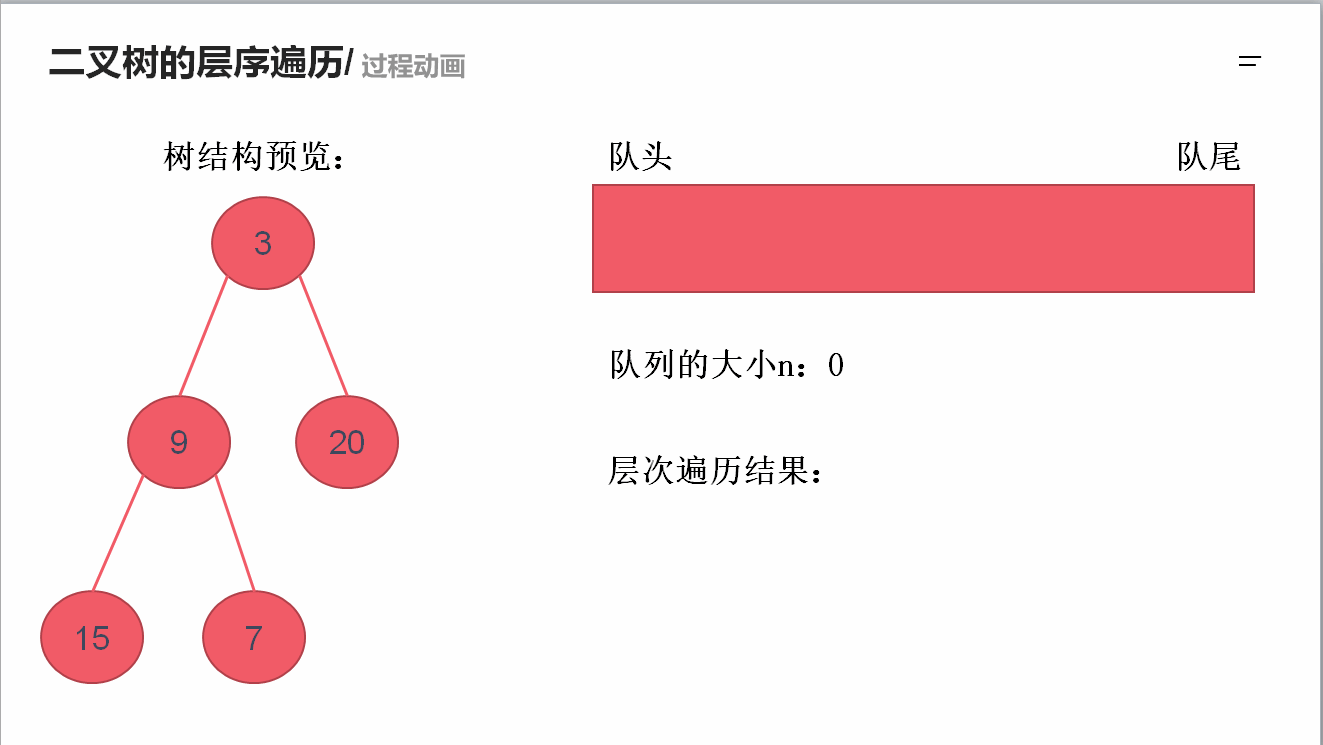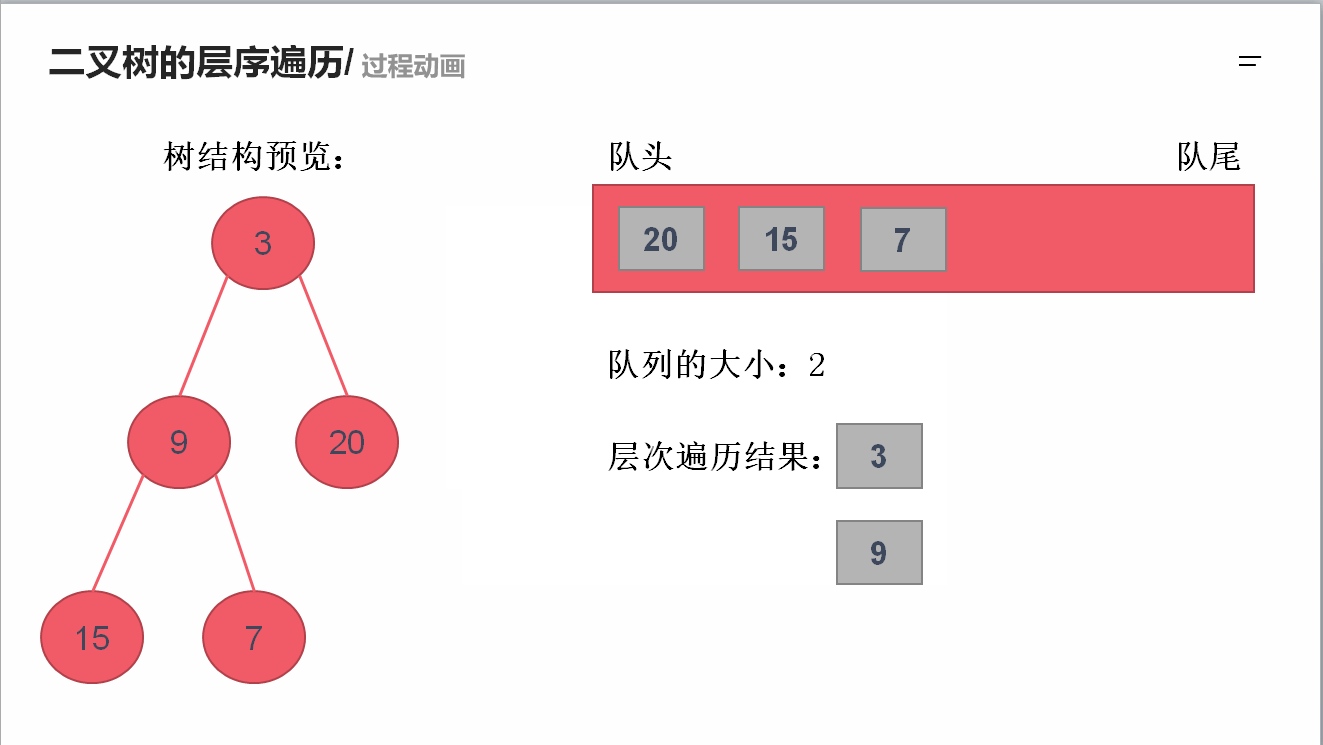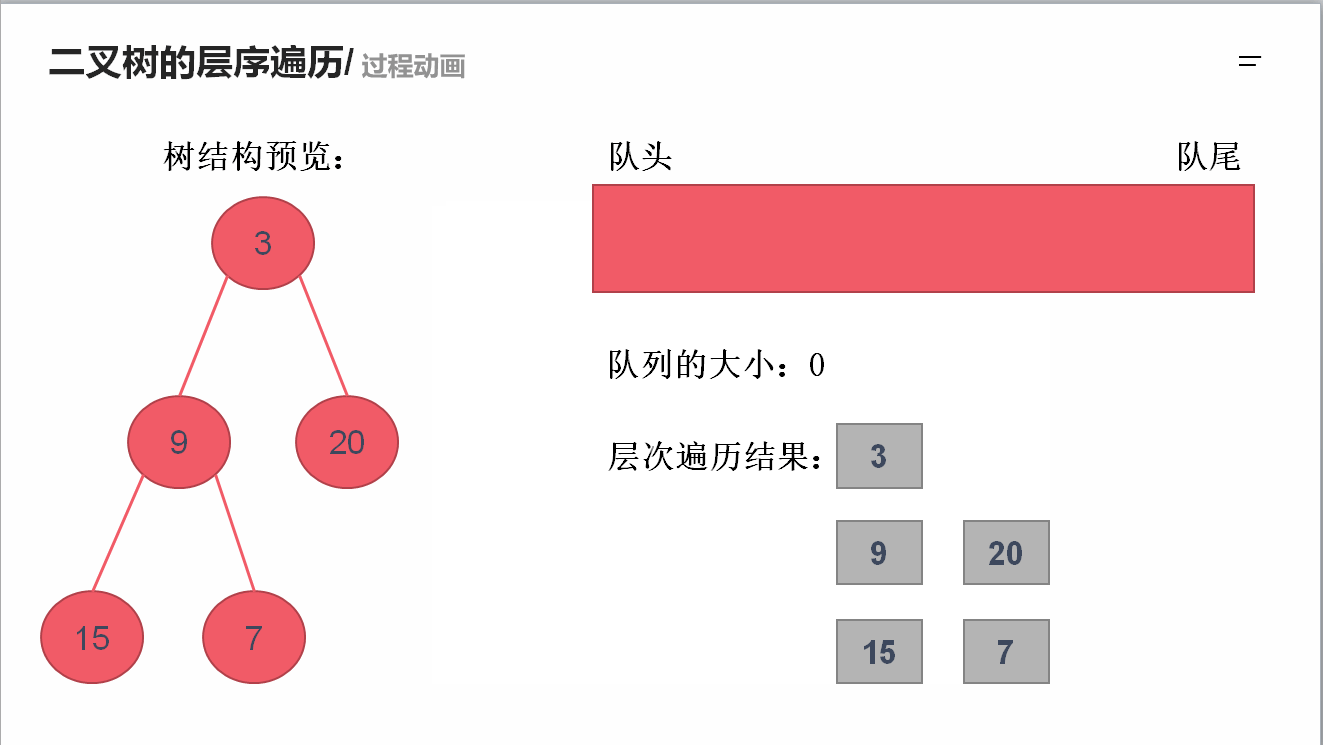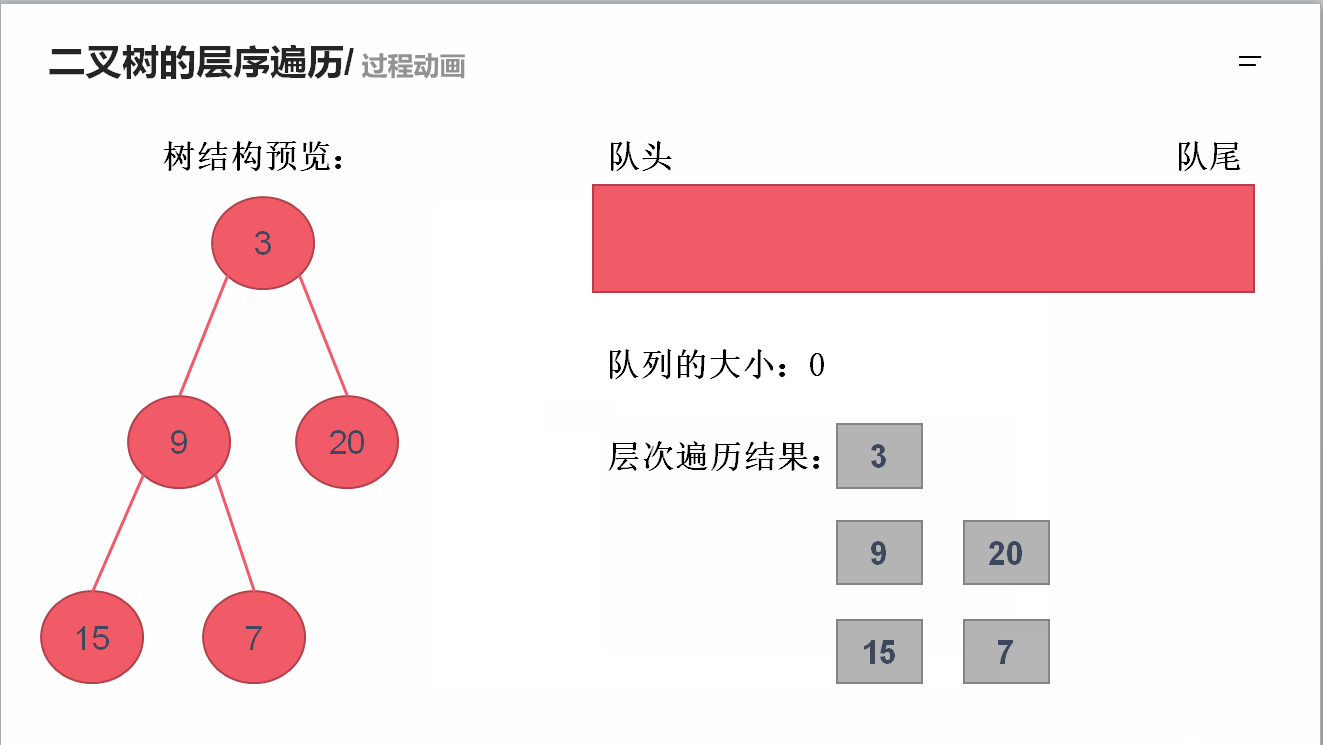需要借助队列的先进先出特性来实现
java Queue中 remove/poll, add/offer, element/peek区别
offer,add区别:
一些队列有大小限制,因此如果想在一个满的队列中加入一个新项,多出的项就会被拒绝。
这时新的 offer 方法就可以起作用了。它不是对调用 add() 方法抛出一个 unchecked 异常,而只是得到由 offer() 返回的 false。
poll,remove区别:
remove() 和 poll() 方法都是从队列中删除第一个元素。remove() 的行为与 Collection 接口的版本相似,
但是新的 poll() 方法在用空集合调用时不是抛出异常,只是返回 null。因此新的方法更适合容易出现异常条件的情况。
peek,element区别:
element() 和 peek() 用于在队列的头部查询元素。与 remove() 方法类似,在队列为空时, element() 抛出一个异常,而 peek() 返回 null
(1)队列解法:
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>();
if(root != null){
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int size = queue.size();
ArrayList<Integer> newLevel = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for(int i=0; i<size; i++){
TreeNode temp = queue.poll();
newLevel.add(temp.val);
if(temp.left != null)
queue.offer(temp.left);
if(temp.right != null)
queue.offer(temp.right);
}
result.add(newLevel);
}
}
return result;
}
}
(2)递归解法:
public class Solution {
private ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>();
public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> levelOrder (TreeNode root) {
order(root, 0);
return result;
}
private void order(TreeNode root, int level) {
if (root == null) return;
if (result.size() <= level) // 用level来判断
result.add(new ArrayList<Integer>());
result.get(level).add(root.val);
order(root.left, level+1);
order(root.right, level+1);
}
}
最小的K个数
对于n个整数中最小的K个数的查找,可以使用各种排序算法:冒泡/堆排/快排/希尔排序等等。将此n个整数从小到大排序之后,前k个数就是所求的结果。
但是当原数组中的数据顺序不可修改,并且n的值过于大的时候,各种排序算法要将n个数加载到内存中,即:如果是海量数据中查找出最小的k个数,那么这种办法是效率很低的。接下来介绍另外一种算法:
创建一个大小为k的数组,遍历n个整数,如果遍历到的数小于大小为k数组的最大值,则将此数与其最大值替换。
由于每次都要拿n个整数和数组中的最大值比较,所以选择大根堆这一数据结构(大家要分清楚大根堆这一数据结构和堆排序之间的区别:堆排序是在大根堆这一数据结构上进行排序的一种排序算法,一个是数据结构,一个是算法)
(1)解法一:普通排序
直接排序,然后去前k小数据。
-
快速排序
import java.util.*; public class Solution { public ArrayList<Integer> GetLeastNumbers_Solution(int[] input, int k) { ArrayList<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>(); if(input == null || input.length == 0 || k == 0) { return ans; } partition(0, input.length-1, input, k); for(int i = 0; i < k; i++) { ans.add(input[i]); } return ans; } public void partition(int left, int right, int[] nums, int k) { if(left >= right) { return; } int pivot = nums[left]; int i = left, j = right; while(i < j) { while(i < j && nums[j] > pivot) { j--; } if(i < j) { nums[i] = nums[j]; i++; } while(i < j && nums[i] < pivot) { i++; } if(i < j) { nums[j] = nums[i]; j--; } } nums[i] = pivot; if(i == k) { return; } else if(i > k) { partition(left, i-1, nums, k); } else { partition(i+1, right, nums, k); } } } -
归并排序
(2)解法二:堆排序
建立一个容量为k的大根堆的优先队列。遍历一遍元素,如果队列大小 (3)解法三:快排思想 对数组[l, r]一次快排partition过程可得到,[l, p), p, [p+1, r)三个区间,[l,p)为小于等于p的值 如果[l,p), p,也就是p+1个元素(因为下标从0开始),如果p+1 == k, 找到答案 如果p+1 < k, 说明答案在[p+1, r)区间内, 如果p+1 > k , 说明答案在[l, p)内 写法1: 写法2: (4)解法四:大顶堆 (2)小顶堆: (2)解法2: (3)解法3: (1)迭代: (2)递归: (1)解法1: (2)解法2: 对于本题,前提只有 一次 1阶或者2阶的跳法。 a.如果两种跳法,1阶或者2阶,那么假定第一次跳的是一阶,那么剩下的是n-1个台阶,跳法是f(n-1); b.假定第一次跳的是2阶,那么剩下的是n-2个台阶,跳法是f(n-2) c.由a\b假设可以得出总跳法为: f(n) = f(n-1) + f(n-2) d.然后通过实际的情况可以得出:只有一阶的时候 f(1) = 1 ,只有两阶的时候可以有 f(2) = 2 e.可以发现最终得出的是一个斐波那契数列: | 1, (n=1) f(n) = | 2, (n=2) | f(n-1)+f(n-2) ,(n>2,n为整数) (1)递归 (2)迭代解法1 (3)迭代解法2: 自底向上型循环求解,时间复杂度为 [外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-HGnndKNE-1629356069694)(https://www.nowcoder.com/equation?tex=O(n)]&preview=true) 自底向上求递推式的过程,该方法二原始的版本为: (1)动态规划 (2)迭代 (2)迭代法 (3)递归 1、找到待翻转的k个节点(注意:若剩余数量小于 k 的话,则不需要反转,因此直接返回待翻转部分的头结点即可)。 写法1: 写法2:使用栈翻转 (1)方法一:滑动窗口法 我们可以利用双指针模拟一个滑动窗口。初始化该窗口为(left, right]。所以left从-1开始。窗口不断往右扩大。因为我们要的是无重复子数组,因此,遇到有重复的数字,在窗口左侧进行缩小。 (2)方法二:双指针 + 回头遍历 定义双指针, right指针对数组进行遍历,left指针对arr[right]前的子数组进行遍历。当left小于0或者遇到重复数字时,终止left遍历。 (1)快慢指针解决 判断链表是否有环应该是老生常谈的一个话题了,最简单的一种方式就是快慢指针,慢指针针每次走一步,快指针每次走两步,如果相遇就说明有环,如果有一个为空说明没有环 写法2: (2)逐个删除 一个链表从头节点开始一个个删除,所谓删除就是让他的next指针指向他自己。如果没有环,从头结点一个个删除,最后肯定会删完。如果是环形的,那么有两种情况,一种是o型的,一种是6型的。 (2)归并排序 (3)双指针 (4) (1) 指针判断 思路:1.判断链表中有环 -> 2.得到环中节点的数目 -> 3.找到环中的入口节点 写法2: (2)使用集合 写法1: 写法2: (2)字符替换 (1)快慢双指针 (2) 先找长度再找最后k (1)先得到链表的长度,然后删除倒数第n个结点 (2)方法二:快慢指针 (2)从头部插入 (3) 使用栈来解决 (1)队列+List 写法2: (2)队列+栈 (1) 解法1 (2)解法2 (3)动态规划 思路:遍历两遍这两个链表,如果有重复的节点,那么一定能够使遍历的指针相等。 (1)遍历 (2)集合Set (1) 使用栈 (2)后半部分反转 递归: 迭代: 动态规划: (1)从左下角找 (2)从右上角找 (1)二分法 (2)遍历查找
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<Integer> GetLeastNumbers_Solution(int [] input, int k) {
if(input == null || input.length==0 || k>input.length) return new ArrayList();
ArrayList<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
heapSort(input);
for(int i=0;i<k;i++){
result.add(input[i]);
}
return result;
}
//堆排序
public void heapSort(int arr[]){
int temp;
for(int i = arr.length/2 -1;i>=0;i--){
adjustHeap(arr,i,arr.length);
}
for(int j=arr.length-1;j>0;j--){
temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[0];
arr[0] = temp;
//调整对堆结构
adjustHeap(arr,0,j);
}
}
//调整当前以 i 索引处为堆的结构
public void adjustHeap(int[] arr,int i,int length){
//首先将 当前堆顶元素 arr[i] 保存起来
int temp = arr[i];
//接下来的循环就是在当前整个堆中不断地循环,找到堆中的最大值
for(int k = i*2+1;k<length;k = k*2+1){
// k = i*2+1,就是当前堆的左子节点的索引,
// 那么 k+1,代表的就是右子节点的索引
// 在数组界限内 判断 当前堆顶节点的左右节点哪个大
if(k+1<length && arr[k]<arr[k+1]){
//如果左子节点小于右子节点,我们将k指向右子节点的索引
k += 1;
// 此时 k 指向的位置就是当前堆下 值最大的位置
}
//判断arr[k]和堆顶顶元素的关系
if(arr[k] > temp){
//我们将较大值 赋给堆顶
arr[i] = arr[k];
//接着再以k处为堆顶,继续向下循环遍历
i = k;
}else{
break;
}
}
//将最初保存的堆顶元素赋值给“最终替换了”它的那个元素的索引上
//相当于就是将堆顶元素向下沉,所能沉到的最低位置就是 当前的 i
arr[i] = temp;
}
}
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<Integer> GetLeastNumbers_Solution(int [] input, int k) {
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
if (input == null || input.length == 0 || k > input.length || k == 0)
return list;
int[] arr = new int[k + 1];//数组下标0的位置作为哨兵,不存储数据
//初始化数组
for (int i = 1; i < k + 1; i++)
arr[i] = input[i - 1];
buildMaxHeap(arr, k + 1);//构造大根堆
for (int i = k; i < input.length; i++) {
if (input[i] < arr[1]) {
arr[1] = input[i];
adjustDown(arr, 1, k + 1);//将改变了根节点的二叉树继续调整为大根堆
}
}
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
list.add(arr[i]);
}
return list;
}
/**
* @Author: ZwZ
* @Description: 构造大根堆
* @Param: [arr, length] length:数组长度 作为是否跳出循环的条件
*/
public void buildMaxHeap(int[] arr, int length) {
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0 || arr.length == 1)
return;
for (int i = (length - 1) / 2; i > 0; i--) {
adjustDown(arr, i, arr.length);
}
}
/**
* @Author: ZwZ
* @Description: 堆排序中对一个子二叉树进行堆排序
* @Param: [arr, k, length]
*/
public void adjustDown(int[] arr, int k, int length) {
arr[0] = arr[k];//哨兵
for (int i = 2 * k; i <= length; i *= 2) {
if (i < length - 1 && arr[i] < arr[i + 1])
i++;//取k较大的子结点的下标
if (i > length - 1 || arr[0] >= arr[i])
break;
else {
arr[k] = arr[i];
k = i; //向下筛选
}
}
arr[k] = arr[0];
}
}
[p+1,r)为大于等于p的值。
然后再判断p,利用二分法
public class Solution {
ArrayList<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
public ArrayList<Integer> GetLeastNumbers_Solution(int [] input, int k) {
if(k == 0 || k >input.length) {
return result;
}
quickSearch(input, 0, input.length - 1, k - 1);
return result;
}
void quickSearch(int[] nums, int left, int right, int k) {
int index = partition(nums, left, right);
if (index == k) {
for (int i = 0; i <=k; i++) {
result.add(nums[i]);
}
}else if (index > k) {
quickSearch(nums, left, index - 1, k);
} else {
quickSearch(nums, index + 1, right, k);
}
}
int partition(int[]nums, int left, int right) {
int value = nums[left];
int index = left;
for (int i = left; i <= right; i++) {
if (nums[i] < value) {
index++;
swap(nums, i, index);
}
}
swap(nums, index, left);
return index;
}
void swap(int[] nums, int left, int right) {
int temp = nums[left];
nums[left] = nums[right];
nums[right] = temp;
}
}
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<Integer> GetLeastNumbers_Solution(int[] input, int k) {
ArrayList<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
if(input == null || input.length == 0 || k == 0) {
return ans;
}
partition(0, input.length-1, input, k);
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
ans.add(input[i]);
}
return ans;
}
public void partition(int left, int right, int[] nums, int k) {
if(left >= right) {
return;
}
int pivot = nums[left];
int i = left, j = right;
while(i < j) {
while(i < j && nums[j] > pivot) {
j--;
}
if(i < j) {
nums[i] = nums[j];
i++;
}
while(i < j && nums[i] < pivot) {
i++;
}
if(i < j) {
nums[j] = nums[i];
j--;
}
}
nums[i] = pivot;
if(i == k) {
return;
} else if(i > k) {
partition(left, i-1, nums, k);
} else {
partition(i+1, right, nums, k);
}
}
}
![]()
输入n个整数,找出其中最小的K个数。例如输入4,5,1,6,2,7,3,8这8个数字,则最小的4个数字是1,2,3,4。
维护一个大小为 K 的最小堆过程如下:使用大顶堆。在添加一个元素之后,如果大顶堆的大小大于 K,
那么将大顶堆的堆顶元素去除,也就是将当前堆中值最大的元素去除,从而使得留在堆中的元素都比被去除的元素来得小。
应该使用大顶堆来维护最小堆,而不能直接创建一个小顶堆并设置一个大小,企图让小顶堆中的元素都是最小元素
Java 的 PriorityQueue 实现了堆的能力,PriorityQueue 默认是小顶堆,
可以在在初始化时使用 Lambda 表达式 (o1, o2) -> o2 - o1 来实现大顶堆。
public class GetLeastNumbers_Solution {
public ArrayList<Integer> GetLeastNumbers_Solution(int [] nums,int k){
if (k > nums.length || k <0)return new ArrayList<>();
PriorityQueue<Integer> maxHeap = new PriorityQueue<>(((o1, o2) -> o2-o1));
for (int i = 0; i <nums.length ; i++) {
maxHeap.add(nums[i]);
if (maxHeap.size() >k){
maxHeap.poll();
}
}
return new ArrayList<>(maxHeap);
}
}
寻找第K大
(1)快排:
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public int findKth(int[] a, int n, int K) {
// write code here
return findK(a, 0, n-1, K);
}
public static int partition(int[] arr, int left, int right) {
int pivot = arr[left];
while (left < right) {
while (left < right && arr[right] <= pivot) {
right--;
}
arr[left] = arr[right];
while (left < right && arr[left] >= pivot) {
left++;
}
arr[right] = arr[left];
}
arr[left] = pivot;
return left;
}
public static int findK(int[] arr, int left, int right, int k) {
if (left <= right) {
int pivot = partition(arr, left, right);
if (pivot == k - 1) {
return arr[pivot];
} else if (pivot < k - 1) {
return findK(arr, pivot + 1, right, k);
} else {
return findK(arr, left, pivot - 1, k);
}
}
return -1;
}
}
public class Solution {
public int findKth(int[] a, int n, int K) {
// write code here
PriorityQueue<Integer> queue = new PriorityQueue<>(K,new Comparator<Integer>(){
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1 , Integer o2){ //初始化一个小顶堆
return o1.compareTo(o2);
}
});
for (int ele : a){
if (queue.size() < K || ele > queue.peek())
queue.offer(ele);
while (queue.size() > K)
queue.poll();
}
return queue.peek();
}
}
两数之和
(1)解法1:
public class Solution {
/**
*
* @param numbers int整型一维数组
* @param target int整型
* @return int整型一维数组
*/
public int[] twoSum (int[] numbers, int target) {
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int cur = 0, tmp; cur < numbers.length; cur++){
tmp = numbers[cur];
if (map.containsKey(target - tmp)){
return new int[] {map.get(target - tmp) + 1, cur + 1};
}
map.put(tmp, cur);
}
throw new RuntimeException("results not exits");
}
}
public class Solution {
/**
*
* @param numbers int整型一维数组
* @param target int整型
* @return int整型一维数组
*/
public int[] twoSum (int[] numbers, int target) {
// write code here
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
int index1 = -1;
int index2 = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < numbers.length; i++) {
if (map.containsKey(target - numbers[i])) {
index1 = map.get(target - numbers[i]);
index2 = i + 1;
break;
} else {
map.put(numbers[i], i + 1);
}
}
return new int[]{index1, index2};
}
}
public class Solution {
/**
*
* @param numbers int整型一维数组
* @param target int整型
* @return int整型一维数组
*/
public int[] twoSum (int[] numbers, int target) {
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for(int i = 0; i < numbers.length; i ++){
map.put(numbers[i], i);
}
for(int i = 0; i < numbers.length; i ++){
int num = target - numbers[i];
Integer numIndex = map.get(num);
if(numIndex != null && numIndex != i ){
return new int[]{i+1, numIndex+1};
}
}
return new int[]{-1,-1};
}
}
合并两个排序的链表
public class Solution {
public ListNode Merge(ListNode list1,ListNode list2) {
ListNode head = new ListNode(Integer.MIN_VALUE);
ListNode cur = head;
while (list1!=null && list2!=null) {
if (list1.val <list2.val) {
cur.next = list1;
cur = cur.next;
list1 = list1.next;
} else {
cur.next = list2;
cur = cur.next;
list2 = list2.next;
}
}
if (list1 == null) {
cur.next = list2;
} else {
cur.next = list1;
}
return head.next;
}
}
/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode Merge(ListNode list1,ListNode list2) {
if(list1 == null) return list2;
if(list2 == null) return list1;
if(list1.val > list2.val){
list2.next = Merge(list1,list2.next);
return list2;
}else{
list1.next = Merge(list1.next,list2);
return list1;
}
}
}
合并k个已排序的链表
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Solution {
//两个链表合并函数
public ListNode Merge(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
//一个已经为空了,直接返回另一个
if(list1 == null)
return list2;
if(list2 == null)
return list1;
//加一个表头
ListNode head = new ListNode(0);
ListNode cur = head;
//两个链表都要不为空
while(list1 != null && list2 != null){
//取较小值的节点
if(list1.val <= list2.val){
cur.next = list1;
//只移动取值的指针
list1 = list1.next;
}else{
cur.next = list2;
//只移动取值的指针
list2 = list2.next;
}
//指针后移
cur = cur.next;
}
//哪个链表还有剩,直接连在后面
if(list1 != null)
cur.next = list1;
else
cur.next = list2;
//返回值去掉表头
return head.next;
}
//划分合并区间函数
ListNode divideMerge(ArrayList<ListNode> lists, int left, int right){
if(left > right) return null;
//中间一个的情况
if(left == right) return lists.get(left);
//从中间分成两段,再将合并好的两段合并
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
return Merge(divideMerge(lists, left, mid), divideMerge(lists, mid + 1, right));
}
public ListNode mergeKLists(ArrayList<ListNode> lists) {
//k个链表归并排序
return divideMerge(lists, 0, lists.size() - 1);
}
}
用两个栈实现队列
public class Solution {
Stack<Integer> stack1 = new Stack<Integer>();
Stack<Integer> stack2 = new Stack<Integer>();
public void push(int node) {
stack1.push(node);
}
public int pop() {
if(stack2.isEmpty()){
while(!stack1.isEmpty()){
stack2.push(stack1.pop());
}
}
return stack2.pop();
}
}
public class Solution {
Stack<Integer> stack1 = new Stack<Integer>();
Stack<Integer> stack2 = new Stack<Integer>();
public void push(int node) {
while(!stack2.isEmpty()) {
stack1.push(stack2.pop());
}
stack2.push(node);
while(!stack1.isEmpty()) {
stack2.push(stack1.pop());
}
}
public int pop() {
return stack2.pop();
}
}
跳台阶
public class Solution {
public int jumpFloor(int target) {
if (target <= 0) {return -1;}
if (target == 1) { return 1;}
if (target ==2) { return 2;}
return jumpFloor(target-1)+jumpFloor(target-2);
}
}
public class Solution {
public int jumpFloor(int target) {
// 状态转移方程 dp(n) = dp(n-1) + dp(n-2)
// 初始值dp(0) = 1 dp(1) = 1
// 验证 dp(2) = dp(1) + dp(0) = 2
if (target <= 1) return 1;
int[] dp = new int[target+1];
dp[0] = 1;
dp[1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= target; i++) {
dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + dp[i - 2];
}
return dp[target];
}
}
public class Solution {
public int JumpFloor(int target) {
// f[1] = 1, f[0] = 1 (f[0]是为了简便作答自己添加的)
int a = 1, b = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= target; i++) {
// 求f[i] = f[i - 1] + f[i - 2]
a = a + b; // 这里求得的 f[i] 可以用于下次循环求 f[i+1]
// f[i - 1] = f[i] - f[i - 2]
b = a - b; // 这里求得的 f[i-1] 可以用于下次循环求 f[i+1]
}
return a;
}
}
public class Solution {
public int JumpFloor(int target) {
if (target <= 1) {
return 1;
}
// a 表示第 f[i-2] 项,b 表示第 f[i-1] 项
int a = 1, b = 1, c = 0;
for (int i = 2; i <= target; i++) {
c = a + b; // f[i] = f[i - 1] + f[i - 2];
// 为下一次循环求 f[i + 1] 做准备
a = b; // f[i - 2] = f[i - 1]
b = c; // f[i - 1] = f[i]
}
return c;
}
}
子数组的最大累加和问题
public int maxsumofSubarray (int[] arr) {
//1.dp状态设置: dp[i]就是以nums[i]为结尾的的连续子数组的最大和
int[] dp = new int[arr.length];
//2.初态设置:dp[0]必须包含nums[0] 所以:
dp[0] = arr[0];
int max = dp[0];
//3.转移方程:
//因为nums[i]无论如何都要包括 那么可以选择的余地就是dp[i-1]了
//dp[i-1]<0 那么不如只选nums[i]了 dp[i-1]>0 那就nums[i]带上dp[i-1]
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
dp[i] = dp[i-1]>0?dp[i-1]+arr[i]:arr[i];
//由于无论如何都要包括nums[i] 那么如果最后的nums[len-1]<0
//那么此时dp[len-1]肯定不是最大连续和 需要max筛选
max = Math.max(max,dp[i]);
}
return max;
}
public int maxsumofSubarray (int[] arr) {
if(arr.length == 0) return 0;
int maxSum = 0;
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++){
sum = sum + arr[i] > 0 ? sum + arr[i] : 0;
maxSum = maxSum > sum ? maxSum : sum;
}
return maxSum;
}
链表中的节点每k个一组翻转
(1)链表头插法
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public ListNode reverseKGroup (ListNode head, int k) {
if(head==null||head.next==null||k==1) return head;
ListNode res = new ListNode(0);
res.next = head;
int length = 0;
ListNode pre = res,
cur = head,
temp = null;
while(head!=null){
length++;
head = head.next;
}
//分段使用头插法将链表反序
for(int i=0; i<length/k; i++){
//pre作为每一小段链表的头节点,负责衔接
for(int j=1; j<k; j++){
temp = cur.next;
cur.next = temp.next;
//相当于头插法,注意:
//temp.next = cur是错误的,temp需要连接的不是前一节点,而是子序列的头节点
temp.next = pre.next;
pre.next = temp;
}
//每个子序列反序完成后,pre,cur需要更新至下一子序列的头部
pre = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
return res.next;
}
}
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
if (head == null || head.next == null){
return head;
}
//定义一个假的节点。
ListNode dummy=new ListNode(0);
//假节点的next指向head。
// dummy->1->2->3->4->5
dummy.next=head;
//初始化pre和end都指向dummy。pre指每次要翻转的链表的头结点的上一个节点。
//end指每次要翻转的链表的尾节点
ListNode pre=dummy;
ListNode end=dummy;
while(end.next!=null){
//循环k次,找到需要翻转的链表的结尾,这里每次循环要判断end是否等于空
//因为如果为空,end.next会报空指针异常。
//dummy->1->2->3->4->5 若k为2,循环2次,end指向2
for(int i=0;i<k&&end != null;i++){
end=end.next;
}
//如果end==null,即需要翻转的链表的节点数小于k,不执行翻转。
if(end==null){
break;
}
//先记录下end.next,方便后面链接链表
ListNode next=end.next;
//然后断开链表
end.next=null;
//记录下要翻转链表的头节点
ListNode start=pre.next;
//翻转链表,pre.next指向翻转后的链表。1->2 变成2->1。
//dummy->2->1
pre.next=reverse(start);
//翻转后头节点变到最后。通过.next把断开的链表重新链接。
start.next=next;
//将pre换成下次要翻转的链表的头结点的上一个节点。即start
pre=start;
//翻转结束,将end置为下次要翻转的链表的头结点的上一个节点。
//即start
end=start;
}
return dummy.next;
}
//链表翻转
// 例子: head: 1->2->3->4
public ListNode reverse(ListNode head) {
//单链表为空或只有一个节点,直接返回原单链表
if (head == null || head.next == null){
return head;
}
//前一个节点指针
ListNode preNode = null;
//当前节点指针
ListNode curNode = head;
//下一个节点指针
ListNode nextNode = null;
while (curNode != null){
nextNode = curNode.next;
//nextNode 指向下一个节点,保存当前节点后面的链表。
curNode.next=preNode;
//将当前节点next域指向前一个节点 null<-1<-2<-3<-4
preNode = curNode;
//preNode 指针向后移动。preNode指向当前节点。
curNode = nextNode;
//curNode指针向后移动。下一个节点变成当前节点
}
return preNode;
}
2、对其进行翻转。并返回翻转后的头结点(注意:翻转为左闭又开区间,所以本作的尾结点其实就是下一作的头结点)。
3、对下一轮 k 个节点也进行翻转操作。
4、将上一轮翻转后的尾结点指向下一轮翻转后的头节点,即将每一轮翻转的k的节点连接起来。 public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode tail = head;
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
//剩余数量小于k的话,则不需要反转。
if (tail == null) {
return head;
}
tail = tail.next;
}
// 反转前 k 个元素
ListNode newHead = reverse(head, tail);
//下一轮的开始的地方就是tail
head.next = reverseKGroup(tail, k);
return newHead;
}
/*
左闭又开区间
*/
private ListNode reverse(ListNode head, ListNode tail) {
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode next = null;
while (head != tail) {
next = head.next;
head.next = pre;
pre = head;
head = next;
}
return pre;
}
public class Solution {
public ListNode reverseKGroup (ListNode head, int k) {
// write code here
//使用一个栈来反转每段链表
Stack<ListNode> stack = new Stack<ListNode>();
ListNode cur = head;
for(int i = 0;i<k;i++){
if(cur == null){
//如果这段链表长度不够k,则直接返回这个链表
return head;
}
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.next;
}
//根据栈中的节点构造链表,构造出来的是原来链表的反转
ListNode res = stack.pop();
ListNode temp = res;
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
temp.next = stack.pop();
temp = temp.next;
}
//反转后的链表的尾节点是递归返回的头节点
temp.next = reverseKGroup(cur,k);
return res;
}
}
最长无重复子数组
在每次滑动时,对窗口的大小进行比较,保留最大的长度。import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
/**
*
* @param arr int整型一维数组 the array
* @return int整型
*/
public int maxLength (int[] arr) {
// write code here
if(arr.length < 2){
return arr.length;
}
HashMap<Integer, Integer> windows = new HashMap<>();
int res = 0;
//用双指针来模拟一个滑动窗口
int left = -1;
//窗口向右滑动
for(int right = 0; right < arr.length; right++){
//遇到重复数字
if(windows.containsKey(arr[right])){
//因为有可能遇到的重复数字的位置 比 left还要前
//所以不能把left置于该位置前一位, 而是比较哪个最大,目的还是为了缩小窗口
//确保窗口内全是不重复的数字
left = Math.max(left, windows.get(arr[right]));
}
//每次更新窗口大小
res = Math.max(res, right-left);
//将数字位置更新到windows中
windows.put(arr[right], right);
}
return res;
}
}
定义res代表最长的长度,tmp代表当前字符拥有的子串长度。
每次更新tmp时,也得更新res。import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
/**
*
* @param arr int整型一维数组 the array
* @return int整型
*/
public int maxLength (int[] arr) {
// write code here
int res = 0, tmp = 0;
for(int right = 0; right < arr.length; right++){
int left = right -1;
//回头遍历
while(left >= 0 && arr[right] != arr[left]){
left --;
}
//若指针距离比上一个字符拥有的子串长度要大,就tmp+1 否则说明,遇到了重复数字,设置为新的指针距离,方便下一步res比较
tmp = tmp < right - left ? tmp + 1 : right - left;
//更新res指
res = Math.max(res, tmp);
}
return res;
}
}
判断链表中是否有环
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
if (head == null)
return false;
//快慢两个指针
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
//慢指针每次走一步
slow = slow.next;
//快指针每次走两步
fast = fast.next.next;
//如果相遇,说明有环,直接返回true
if (slow == fast)
return true;
}
//否则就是没环
return false;
}
/**
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
/**
判断链表是否有环,用快慢指针
*/
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast = head, slow = head;
while(slow != null && fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
// 判断是否重合
if(slow == fast) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
//如果head为空,或者他的next指向为空,直接返回false
if (head == null || head.next == null)
return false;
//如果出现head.next = head表示有环
if (head.next == head)
return true;
ListNode nextNode = head.next;
//当前节点的next指向他自己,相当于把它删除了
head.next = head;
//然后递归,查看下一个节点
return hasCycle(nextNode);
}
合并两个有序的数组
(1)插入排序
public class Solution {
public void merge(int A[], int m, int B[], int n) {
// 插入排序
int i=0;
int j=0;
while(i<m+n && j<n){
if(A[i]>B[j]){
// i以及i之后的往后移动
for(int cur=m+n-1;cur>i;cur--){
A[cur]=A[cur-1];
}
A[i]=B[j];
j++;
i++;
}else{i++;}
}
// 如果剩余的B大于A的最大值
for(int q=j;q<n;q++){
A[m+q]=B[q];
}
}
}
public class Solution {
public void merge(int A[], int m, int B[], int n) {
int[] result=new int[m+n];
int t=0;
int i=0,j=0;
while(i<m&&j<n){
if(A[i]<=B[j]){//两边有序数组相互比较得出小的元素依次存放
result[t++]=A[i++];
}else{
result[t++]=B[j++];
}
}
//将剩余元素依次存放在result数组中
while(i<m){//左边数组A如果还有剩余元素,全部存放在result数组中
result[t++]=A[i++];
}
while(j<n){//右边数组B如果还有剩余元素,全部存放在result数组中
result[t++]=B[j++];
}
for(int sum=0;sum<result.length;sum++){//最后通过遍历将result数组元素存放到A数组中
A[sum]=result[sum];
}
}
}
/***
*整体类比ArrayList中add操作的数组移动
*比较后用System.arraycopy()函数
****/
public class Solution {
public void merge(int A[], int m, int B[], int n) {
int a = 0;
int b = 0;
while(b < n){
if(a >= m || B[b] <= A[a]){
System.arraycopy(A , a, A, a+1, m-a);
m++;
A[a++] = B[b++];
}else{
a++;
}
}
}
}
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public void merge(int A[], int m, int B[], int n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
A[m + i] = B[i];
}
Arrays.sort(A);
}
}
链表中环的入口结点
/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode EntryNodeOfLoop(ListNode pHead)
{
if(pHead == null){
return null;
}
// 1.判断链表中有环
ListNode l=pHead,r=pHead;
boolean flag = false;
while(r != null && r.next!=null){
l=l.next;
r=r.next.next;
if(l==r){
flag=true;
break;
}
}
if(!flag){
return null;
}else{
// 2.得到环中节点的数目
int n=1;
r=r.next;
while(l!=r){
r=r.next;
n++;
}
// 3.找到环中的入口节点
l=r=pHead;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
r=r.next;
}
while(l!=r){
l=l.next;
r=r.next;
}
return l;
}
}
}
public class Solution {
public ListNode EntryNodeOfLoop(ListNode pHead) {
if(pHead == null || pHead.next == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode slow = pHead;
ListNode fast = pHead;
while(fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
if(slow == fast) {
ListNode p = pHead;
while(p != slow) {
p = p.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return p;
}
}
return null;
}
}
public ListNode EntryNodeOfLoop(ListNode pHead) {
//方法一:利用Map
Map<ListNode,Integer> map = new HashMap();
ListNode node = pHead;
while (node != null){
map.put(node,map.getOrDefault(node,0) + 1);
if (map.get(node) > 1) return node;
//或:if (map.get(node) == 2) return node; //一个意思
node = node.next;
}
return null;
}
public ListNode EntryNodeOfLoop(ListNode pHead) {
//方法二:利用Set
Set<ListNode> set = new HashSet();
while(pHead != null){
if(set.contains(pHead)) return pHead;
else set.add(pHead);
pHead = pHead.next;
}
return null;
}
括号序列
(1)压栈和取栈
'(','[','{' 这三个就压栈
')',']','}' 这三个就取栈,取栈时判断一下是不是对应的括号,如果是就取栈成功,不是就不能取。
这样最后看栈是不是为空,不为空就说明顺序不正确public boolean isValid (String s) {
//遇到括号匹配这样的题,首选使用栈来做
//每次遍历遇到'('、'['和'{'时,就将其对应的方括号')'、']'和'}'放入栈中
//然后遍历下一个,并与栈顶元素进行比较
//如果不同直接返回false;如果相同就将栈顶的反括号弹出,遍历结束都没有返回false就说明合法,返回true
Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<>();
char[] temp = s.toCharArray();
for (char c : temp){//遍历字符,如果遇到左括号,就把相应的右括号压入栈顶
if (c == '(') stack.push(')');
else if (c == '[') stack.push(']');
else if (c == '{') stack.push('}');
//else if (stack.isEmpty()) return false;//字符还没有遍历完就出现栈为空就返回false
//else if (stack.pop() != c) return false;//如果能到达这一步,就每次从栈顶pop出一个元素与当前元素c
//进行比较,如果不同就返回false
//也可以将上面两行代码合并:
else if (stack.isEmpty() || stack.pop() != c) return false;
}
return stack.isEmpty();//遍历结束如果栈为空就返回true,否则返回false
}
public boolean isValid (String s) {
boolean flag = true;
while(flag){
int len = s.length();
s=s.replace("()","");
s=s.replace("[]","");
s=s.replace("{}","");
if(len == s.length()){
flag=false;
}
}
return s.length() == 0;
}
链表中倒数最后k个结点
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public ListNode FindKthToTail (ListNode pHead, int k) {
int n = 0;
ListNode fast = pHead;
ListNode slow = pHead;
//快指针先行k步
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++){
if(fast != null)
fast = fast.next;
//达不到k步说明链表过短,没有倒数k
else
return slow = null;
}
//快慢指针同步,快指针先到底,慢指针指向倒数第k个
while(fast != null){
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
}
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public ListNode FindKthToTail (ListNode pHead, int k) {
int n = 0;
ListNode p = pHead;
//遍历链表,统计链表长度
while(p != null){
n++;
p = p.next;
}
//长度过小,返回空链表
if(n < k)
return null;
p = pHead;
//遍历n-k次
for(int i = 0; i < n - k; i++)
p = p.next;
return p;
}
}
删除链表的倒数第n个节点
public class Solution {
/**
*
* @param head ListNode类
* @param n int整型
* @return ListNode类
*/
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd (ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode cur = head;
if (head == null || head.next == null) return null;
List<ListNode> list = new ArrayList<>();
while (cur != null) {
list.add(cur);
cur = cur.next;
}
list.remove(list.size() - n);
ListNode resNode = list.get(0);
ListNode temp = resNode;
for (int i = 1; i < list.size(); i++) {
temp.next = list.get(i);
temp = temp.next;
}
temp.next = null;
return resNode;
}
}
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
// write code here
if (head == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode left = head;
ListNode right = head;
//right指针先走n步
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
right = right.next;
}
//此时right可能为null 把头节点删除
if (right == null) {
head = head.next;
return head;
}
//遍历,直至right.next为null,此时right就是链表的最后一个节点
while (right.next != null) {
left = left.next;
right = right.next;
}
//那么left.next就是需要删除的node
//target.next至少为right,所以不可能为null
//此时只需要把target节点删除即可
ListNode target = left.next;
left.next = target.next;
target.next = null;
return head;
}
大数加法
(1)从尾部插入
public String solve(String s, String t) {
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
int i = s.length() - 1, j = t.length() - 1, carry = 0;
while (i >= 0 || j >= 0 || carry != 0) {
int x = i < 0 ? 0 : s.charAt(i--) - '0';
int y = j < 0 ? 0 : t.charAt(j--) - '0';
int sum = x + y + carry;
stringBuilder.append(sum % 10);//添加到字符串尾部
carry = sum / 10;
}
return stringBuilder.reverse().toString();//对字符串反转
}
public String solve(String s, String t) {
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
int carry = 0, i = s.length() - 1, j = t.length() - 1;
while (i >= 0 || j >= 0 || carry != 0) {
int x = i < 0 ? 0 : s.charAt(i--) - '0';
int y = j < 0 ? 0 : t.charAt(j--) - '0';
int sum = x + y + carry;
stringBuilder.insert(0, sum % 10);//插入到s字符串的第一个位置
carry = sum / 10;
}
return stringBuilder.toString();
}
public String solve(String s, String t) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
int i = s.length() - 1, j = t.length() - 1, carry = 0;
while (i >= 0 || j >= 0 || carry != 0) {
carry += i >= 0 ? s.charAt(i--) - '0' : 0;
carry += j >= 0 ? t.charAt(j--) - '0' : 0;
stack.push(carry % 10);
carry = carry / 10;
}
while (!stack.isEmpty())
stringBuilder.append(stack.pop());
return stringBuilder.toString();
}
按之字形顺序打印二叉树
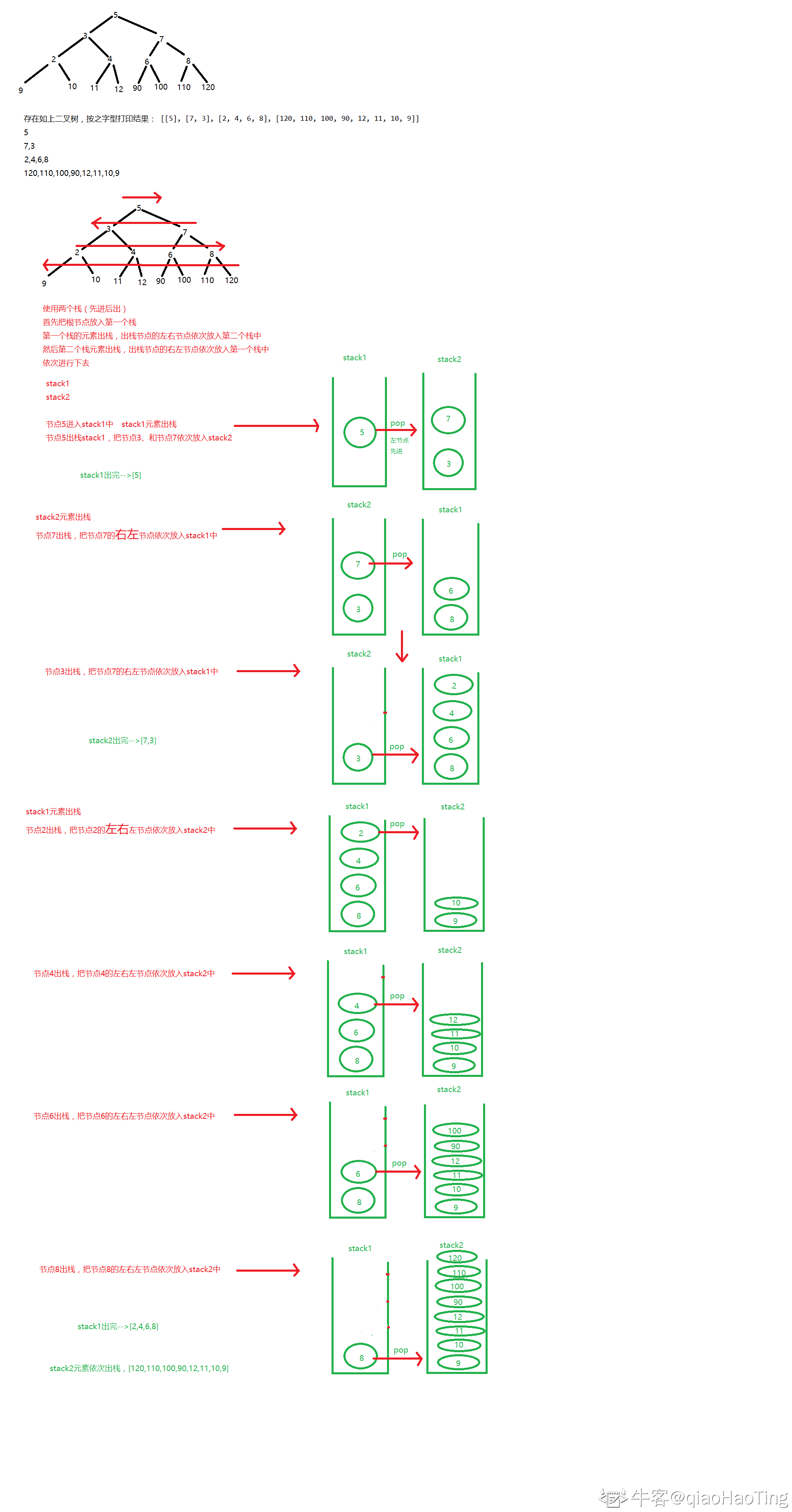
//解题思路:其实就是二叉树的层级遍历,不过是在遍历的时候,需要将偶数层的节点逆序。
//关键点:每次只处理上次在queue中剩余的节点,这是上一层的所有节点。
// 处理完后刚好将下一层的所有节点(包含null)又全部放了进去。
public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer> > Print(TreeNode pRoot) {
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer> > result=new ArrayList<>();
if(pRoot==null){
return result;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue=new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
queue.offer(pRoot);
boolean reverse=false;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int size=queue.size();
ArrayList<Integer> list=new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0;i<size;i++){
TreeNode node=queue.poll();
if(node==null){
continue;
}
if(!reverse){
list.add(node.val);
}else{
list.add(0,node.val);//每次加到0的位置,就自动逆序了
}
queue.offer(node.left);
queue.offer(node.right);
}
if(list.size()>0){
result.add(list);
}
reverse=!reverse;
}
return result;
}
public class Solution {//方法2和方法1相比,代码区别仅仅是把stack相关删去,然后换成ArrayList头插法
public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer> > Print(TreeNode pRoot) {
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>();
if(pRoot == null)return res;
ArrayList<TreeNode> queue = new ArrayList<TreeNode>();
queue.add(pRoot);
int layer = 1;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
int size = queue.size();
for(int i=0; i<=size-1; ++i){
TreeNode node = queue.get(0);
queue.remove(0);
if(layer % 2 == 1){
list.add(node.val);
}
else{
list.add(0,node.val);//头插法,逆序 //【代码简洁,但效率比Stack低】
}
if(node.left != null)queue.add(node.left);
if(node.right != null)queue.add(node.right);
}
res.add(list);
++layer;
}
return res;
}
}//时间、空间都是 O(N)
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer> > Print(TreeNode pRoot) {
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>();
if(pRoot == null)return res;
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<Integer>();//stack仅用于偶数层翻转val
ArrayList<TreeNode> queue = new ArrayList<TreeNode>();//queue是奇偶共用
queue.add(pRoot);
int layer = 1;//层数用layer (区别于深度depth = layer-1)
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();//新建行
int size = queue.size();//出本层前记录size,不然难以做到层数的切分 //提前写出来,因为size会变
for(int i=0; i<=size-1; ++i){
TreeNode node = queue.get(0);//一定要新建node副本,不然是引用会变
queue.remove(0);
if(layer % 2 == 1){
list.add(node.val);
} else{//偶数行,需要栈翻转
stack.push(node.val);
}
if(node.left != null)queue.add(node.left);
if(node.right != null)queue.add(node.right);
}
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
list.add(stack.pop());//偶数层一次性添加,奇数层一个个添加
}
res.add(list);
++layer;//本层结束,层数加一
}
return res;
}
}//时间、空间复杂度,都是树的规模 O(N)
最长公共子串
public String LCS (String str1, String str2) {
String result=new String();
for(int i=0;i<str1.length();i++){
int k=i;
int count=0;
for(int j=0; k<str1.length() && j<str2.length() ;j++){
if(str2.charAt(j)==str1.charAt(k)){
count++;
k++;
}else{
j=j-count;
k=i;
count=0;
}
if(count>result.length()){
result=str1.substring(i,k);
}
}
}
return result;
}
public String LCS (String str1, String str2) {
int start = 0;
int end = 1;
StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder();
while (end < str1.length()+1) {//注意是要加一,因substring函数是不包含上界
if (str2.contains(str1.substring(start, end))) {
if (s.length() < (end - start)) {
s.delete(0, s.length());
s.append(str1, start, end);
}
end++;
} else {
start++;
}
}
if (s.length() == 0) {
return "";
}
return s.toString();
}
public String LCS(String str1, String str2) {
int maxLenth = 0;//记录最长公共子串的长度
//记录最长公共子串最后一个元素在字符串str1中的位置
int maxLastIndex = 0;
int[] dp = new int[str2.length() + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < str1.length(); i++) {
//注意这里是倒序
for (int j = str2.length() - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
//递推公式,两个字符相等的情况
if (str1.charAt(i) == str2.charAt(j)) {
dp[j + 1] = dp[j] + 1;
//如果遇到了更长的子串,要更新,记录最长子串的长度,
//以及最长子串最后一个元素的位置
if (dp[j + 1] > maxLenth) {
maxLenth = dp[j + 1];
maxLastIndex = i;
}
} else {
//递推公式,两个字符不相等的情况
dp[j + 1] = 0;
}
}
}
//最字符串进行截取,substring(a,b)中a和b分别表示截取的开始和结束位置
return str1.substring(maxLastIndex - maxLenth + 1, maxLastIndex + 1);
}
两个链表的第一个公共结点
public ListNode FindFirstCommonNode(ListNode pHead1, ListNode pHead2) {
if(pHead1 == null || pHead2 == null)return null;
ListNode p1 = pHead1;
ListNode p2 = pHead2;
while(p1!=p2){
p1 = p1.next;
p2 = p2.next;
if(p1 != p2){
if(p1 == null)p1 = pHead2;
if(p2 == null)p2 = pHead1;
}
}
return p1;
}
public ListNode FindFirstCommonNode(ListNode pHead1, ListNode pHead2) {
HashSet<ListNode> set=new HashSet<>();
while(pHead1!=null){
set.add(pHead1);
pHead1=pHead1.next;
}
while(pHead2!=null){
if(set.contains(pHead2))
return pHead2;
pHead2=pHead2.next;
}
return null;
}
链表相加(二)
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
//反转链表
public ListNode ReverseList(ListNode pHead) {
if(pHead == null)
return null;
ListNode cur = pHead;
ListNode pre = null;
while(cur != null){
//断开链表,要记录后续一个
ListNode temp = cur.next;
//当前的next指向前一个
cur.next = pre;
//前一个更新为当前
pre = cur;
//当前更新为刚刚记录的后一个
cur = temp;
}
return pre;
}
public ListNode addInList (ListNode head1, ListNode head2) {
//任意一个链表为空,返回另一个
if(head1 == null)
return head2;
if(head2 == null)
return head1;
//反转两个链表
head1 = ReverseList(head1);
head2 = ReverseList(head2);
//添加表头
ListNode res = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode head = res;
//进位符号
int carry = 0;
//只要某个链表还有或者进位还有
while(head1 != null || head2 != null || carry != 0){
//链表不为空则取其值
int val1 = head1 == null ? 0 : head1.val;
int val2 = head2 == null ? 0 : head2.val;
//相加
int temp = val1 + val2 + carry;
//获取进位
carry = temp / 10;
temp %= 10;
//添加元素
head.next = new ListNode(temp);
head = head.next;
//移动下一个
if(head1 != null)
head1 = head1.next;
if(head2 != null)
head2 = head2.next;
}
//结果反转回来
return ReverseList(res.next);
}
}
单链表的排序
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
//合并两段有序链表
ListNode merge(ListNode pHead1, ListNode pHead2) {
//一个已经为空了,直接返回另一个
if(pHead1 == null)
return pHead2;
if(pHead2 == null)
return pHead1;
//加一个表头
ListNode head = new ListNode(0);
ListNode cur = head;
//两个链表都要不为空
while(pHead1 != null && pHead2 != null){
//取较小值的节点
if(pHead1.val <= pHead2.val){
cur.next = pHead1;
//只移动取值的指针
pHead1 = pHead1.next;
}else{
cur.next = pHead2;
//只移动取值的指针
pHead2 = pHead2.next;
}
//指针后移
cur = cur.next;
}
//哪个链表还有剩,直接连在后面
if(pHead1 != null)
cur.next = pHead1;
else
cur.next = pHead2;
//返回值去掉表头
return head.next;
}
public ListNode sortInList (ListNode head) {
//链表为空或者只有一个元素,直接就是有序的
if(head == null || head.next == null)
return head;
ListNode left = head;
ListNode mid = head.next;
ListNode right = head.next.next;
//右边的指针到达末尾时,中间的指针指向该段链表的中间
while(right != null && right.next != null){
left = left.next;
mid = mid.next;
right = right.next.next;
}
//左边指针指向左段的左右一个节点,从这里断开
left.next = null;
//分成两段排序,合并排好序的两段
return merge(sortInList(head), sortInList(mid));
}
}
判断一个链表是否为回文结构
public boolean isPail(ListNode head) {
ListNode temp = head;
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack();
//把链表节点的值存放到栈中
while (temp != null) {
stack.push(temp.val);
temp = temp.next;
}
//然后再出栈
while (head != null) {
if (head.val != stack.pop()) {
return false;
}
head = head.next;
}
return true;
}
public boolean isPail(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast = head, slow = head;
//通过快慢指针找到中点
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
//如果fast不为空,说明链表的长度是奇数个
if (fast != null) {
slow = slow.next;
}
//反转后半部分链表
slow = reverse(slow);
fast = head;
while (slow != null) {
//然后比较,判断节点值是否相等
if (fast.val != slow.val)
return false;
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return true;
}
//反转链表
public ListNode reverse(ListNode head) {
ListNode prev = null;
while (head != null) {
ListNode next = head.next;
head.next = prev;
prev = head;
head = next;
}
return prev;
}
链表的奇偶重排
public ListNode oddEvenList(ListNode head) {
//如果链表为空,不用重排
if(head == null)
return head;
//even开头指向第二个节点,可能为空
ListNode even = head.next;
//odd开头指向第一个节点
ListNode odd = head;
//指向even开头
ListNode evenhead = even;
while(even != null && even.next != null){
//odd连接even的后一个,即奇数位
odd.next = even.next;
//odd进入后一个奇数位
odd = odd.next;
//even连接后一个奇数的后一位,即偶数位
even.next = odd.next;
//even进入后一个偶数位
even = even.next;
}
//even整体接在odd后面
odd.next = evenhead;
return head;
}
删除有序链表中重复的元素-I
public ListNode deleteDuplicates (ListNode head) {
//空链表
if(head == null) return null;
//遍历指针
ListNode cur = head;
//指针当前和下一位不为空
while(cur != null && cur.next != null){
//如果当前与下一位相等则忽略下一位
if(cur.val == cur.next.val) {
cur.next = cur.next.next;
} else {
cur = cur.next;
}
}
return head;
}
删除有序链表中重复的元素-II
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
//空链表
if(head == null) return null;
ListNode res = new ListNode(0);
//在链表前加一个表头
res.next = head;
ListNode cur = res;
while(cur.next != null && cur.next.next != null){
//遇到相邻两个节点值相同
if(cur.next.val == cur.next.next.val){
int temp = cur.next.val;
//将所有相同的都跳过
while (cur.next != null && cur.next.val == temp)
cur.next = cur.next.next;
} else {
cur = cur.next;
}
}
//返回时去掉表头
return res.next;
}
连续子数组的最大和
public int FindGreatestSumOfSubArray(int[] array) {
int sum = 0;
int max = array[0];
for(int i=0;i<array.length;i++){
// 优化动态规划,确定sum的最大值
sum = Math.max(sum + array[i], array[i]);
// 每次比较,保存出现的最大值
max = Math.max(max, sum);
}
return max;
}
在二叉树中找到两个节点的最近公共祖先
public class Solution {
public int lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, int o1, int o2) {
return helper(root, o1, o2).val;
}
public TreeNode helper(TreeNode root, int o1, int o2) {
if (root == null || root.val == o1 || root.val == o2)
return root;
TreeNode left = helper(root.left, o1, o2);
TreeNode right = helper(root.right, o1, o2);
//如果left为空,说明这两个节点在root结点的右子树上,我们只需要返回右子树查找的结果即可
if (left == null) return right;
//同上
if (right == null) return left;
//如果left和right都不为空,说明这两个节点一个在root的左子树上一个在root的右子树上,
//我们只需要返回cur结点即可。
return root;
}
}
public int lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, int o1, int o2) {
//记录遍历到的每个节点的父节点。
Map<Integer, Integer> parent = new HashMap<>();
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
parent.put(root.val, Integer.MIN_VALUE);
queue.add(root);
//直到两个节点都找到为止。
while (!parent.containsKey(o1) || !parent.containsKey(o2)) {
//队列是一边进一边出,这里poll方法是出队,
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
if (node.left != null) {
//左子节点不为空,记录下他的父节点
parent.put(node.left.val, node.val);
//左子节点不为空,把它加入到队列中
queue.add(node.left);
}
//右节点同上
if (node.right != null) {
parent.put(node.right.val, node.val);
queue.add(node.right);
}
}
Set<Integer> ancestors = new HashSet<>();
//记录下o1和他的祖先节点,从o1节点开始一直到根节点。
while (parent.containsKey(o1)) {
ancestors.add(o1);
o1 = parent.get(o1);
}
//查看o1和他的祖先节点是否包含o2节点,如果不包含再看是否包含o2的父节点……
while (!ancestors.contains(o2))
o2 = parent.get(o2);
return o2;
}
最长回文子串
public class Solution {
public int getLongestPalindrome (String A) {
return getLongestPalindrome(A, A.length());
}
public int getLongestPalindrome(String A, int n) {
if (n < 2) return A.length();
int maxLen = 1; //maxLen表示最长回文串的长度
boolean[][] dp = new boolean[n][n];
for (int right = 1; right < n; right++) {
for (int left = 0; left <= right; left++) {
//如果两种字符不相同,肯定不能构成回文子串
if (A.charAt(left) != A.charAt(right))
continue;
//下面是s.charAt(left)和s.charAt(right)两个
//字符相同情况下的判断
//如果只有一个字符,肯定是回文子串
if (right == left) {
dp[left][right] = true;
} else if (right - left <= 2) {
//类似于"aa"和"aba",也是回文子串
dp[left][right] = true;
} else {
//类似于"a******a",要判断他是否是回文子串,只需要
//判断"******"是否是回文子串即可
dp[left][right] = dp[left + 1][right - 1];
}
//如果字符串从left到right是回文子串,只需要保存最长的即可
if (dp[left][right] && right - left + 1 > maxLen) {
maxLen = right - left + 1;
}
}
}
//最长的回文子串
return maxLen;
}
}
最长上升子序列(三)
public int[] LIS (int[] arr) {
int len = 1, n = arr.length;
if (n == 0) return new int[0];
int[] d = new int[n + 1];
int[] w = new int[n];
d[len] = arr[0];
w[0] = len;
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
if (arr[i] > d[len]) {
d[++len] = arr[i];
w[i] = len;
} else {
int l = 1, r = len, pos = 0;
while (l <= r) {
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if (d[mid] < arr[i]) {
pos = mid;
l = mid + 1;
} else {
r = mid - 1;
}
}
d[pos + 1] = arr[i];
w[i] = pos + 1;
}
}
int[] res = new int[len];
for (int i = n - 1, j = len; j > 0; --i) {
if (w[i] == j) {
res[--j] = arr[i];
}
}
return res;
}
接雨水问题
public long maxWater (int[] arr) {
//排除空数组
if(arr.length == 0) return 0;
long res = 0;
//左右双指针
int left = 0;
int right = arr.length - 1;
//中间区域的边界高度
int maxL = 0;
int maxR = 0;
//直到左右指针相遇
while(left < right){
//每次维护往中间的最大边界
maxL = Math.max(maxL, arr[left]);
maxR = Math.max(maxR, arr[right]);
//较短的边界确定该格子的水量
if(maxR > maxL)
res += maxL - arr[left++];
else
res += maxR - arr[right--];
}
return res;
}
买卖股票的最好时机(一)
public int maxProfit (int[] prices) {
int min = prices[0];
int max = 0;
for(int i=0;i<prices.length;i++){
min=Math.min(prices[i],min);
max=Math.max(max,prices[i]-min);
}
return max;
}
矩阵的最小路径和
public int minPathSum(int[][] matrix) {
int m = matrix.length, n = matrix[0].length;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (i == 0 && j == 0)
continue;
if (i == 0) {
//第一行只能从左边走过来
matrix[i][j] += matrix[i][j - 1];
} else if (j == 0) {
//第一列只能从上面走下来
matrix[i][j] += matrix[i - 1][j];
} else {
//递推公式,取从上面走下来和从左边走过来的最小值+当前坐标的值
matrix[i][j] += Math.min(matrix[i - 1][j], matrix[i][j - 1]);
}
}
}
return matrix[m - 1][n - 1];
}
public int minPathSum (int[][] matrix) {
int m = matrix.length;
int n = matrix[0].length;
int dp[][] = new int[m][n];
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
if(i==0&&j==0){
dp[0][0]=matrix[0][0];
}else if(i==0){
dp[i][j] = matrix[i][j] + dp[i][j-1];
}else if(j==0){
dp[i][j] = matrix[i][j] + dp[i-1][j];
}
else{
dp[i][j]= matrix[i][j] + Math.min(dp[i-1][j], dp[i][j-1]);
}
}
}
return dp[m-1][n-1];
}
最长公共子序列(二)
public String LCS (String s1, String s2) {
int n = s1.length();
int m = s2.length();
int [][]dp = new int[n + 1][m + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++) {
if (s1.charAt(i - 1) == s2.charAt(j - 1)) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
} else {
dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]);
}
}
}
if (dp[n][m] == 0) return "-1";
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
while (n > 0 && m > 0) {
if (s1.charAt(n - 1) == s2.charAt(m - 1)) {
sb.append(s1.charAt(n - 1));
n--;
m--;
} else {
if (dp[n - 1][m] > dp[n][m - 1]) {
n--;
} else {
m--;
}
}
}
return sb.reverse().toString();
}
二分查找-I
public int search (int[] nums, int target) {
int l = 0;
int r = nums.length - 1;
//从数组首尾开始,直到二者相遇
while(l <= r){
//每次检查中点的值
int m = (l + r) / 2;
if(nums[m] == target)
return m;
//进入左的区间
if(nums[m] > target)
r = m - 1;
//进入右区间
else
l = m + 1;
}
//未找到
return -1;
}
二维数组中的查找
public boolean Find(int target, int [][] array) {
int rows = array.length;
if(rows == 0){
return false;
}
int cols = array[0].length;
if(cols == 0){
return false;
}
// 左下
int row = rows-1;
int col = 0;
while(row>=0 && col<cols){
if(array[row][col] < target){
col++;
}else if(array[row][col] > target){
row--;
}else{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
public boolean Find(int target, int [][] array) {
int rows = array.length;
if(rows == 0){
return false;
}
int cols = array[0].length;
if(cols == 0){
return false;
}
// 右上
int row = 0; //注意
int col = cols-1; //注意
while(row<rows && col>=0){ //注意
if(array[row][col] < target){
row++; //注意
}else if(array[row][col] > target){
col--; //注意
}else{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
寻找峰值
public int findPeakElement (int[] nums) {
int left = 0;
int right = nums.length - 1;
//二分法
while(left < right){
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
//右边是往下,不一定有坡峰
if(nums[mid] > nums[mid + 1])
right = mid;
//右边是往上,一定能找到波峰
else
left = mid + 1;
}
return right;
}
数组中的逆序对
public class Solution {
public int mod = 1000000007;
public int mergeSort(int left, int right, int [] data, int [] temp){
//停止划分
if(left >= right)
return 0;
//取中间
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
//左右划分合并
int res = mergeSort(left, mid, data, temp) + mergeSort(mid + 1, right, data, temp);
//防止溢出
res %= mod;
int i = left, j = mid + 1;
for(int k = left; k <= right; k++)
temp[k] = data[k];
for(int k = left; k <= right; k++){
if(i == mid + 1)
data[k] = temp[j++];
else if(j == right + 1 || temp[i] <= temp[j])
data[k] = temp[i++];
//左边比右边大,答案增加
else{
data[k] = temp[j++];
// 统计逆序对
res += mid - i + 1;
}
}
return res % mod;
}
public int InversePairs(int [] array) {
int n = array.length;
int[] res = new int[n];
return mergeSort(0, n - 1, array, res);
}
}
旋转数组的最小数字
public int minNumberInRotateArray(int [] array) {
int left = 0;
int right = array.length - 1;
while(left < right){
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
//最小的数字在mid右边
if(array[mid] > array[right])
left = mid + 1;
//无法判断,一个一个试
else if(array[mid] == array[right])
right--;
//最小数字要么是mid要么在mid左边
else
right = mid;
}
return array[left];
}
public int minNumberInRotateArray(int [] array) {
//数组一定有元素
int res = array[0];
//遍历数组
for(int i = 1; i < array.length; i++) {
//每次维护最小值
res = Math.min(res, array[i]);
}
return res;
}
比较版本号
public int compare(String version1, String version2) {
String s1[] = version1.split("\\.");
String s2[] = version2.split("\\.");
int n1 = s1.length;
int n2 = s2.length;
int n = Math.max(n1, n2);
int k1[] = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < s1.length; i++) {
k1[i] = Integer.valueOf(s1[i]);
}
int k2[] = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < s2.length; i++) {
k2[i] = Integer.valueOf(s2[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (k1[i] > k2[i]) {
return 1;
} else if (k1[i] < k2[i]) {
return -1;
}
}
return 0;
}