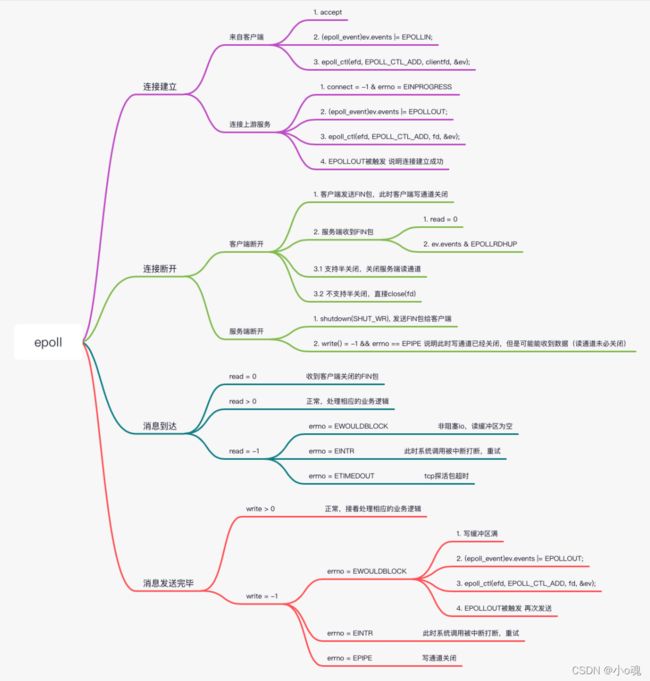
Linux网络编程-epoll
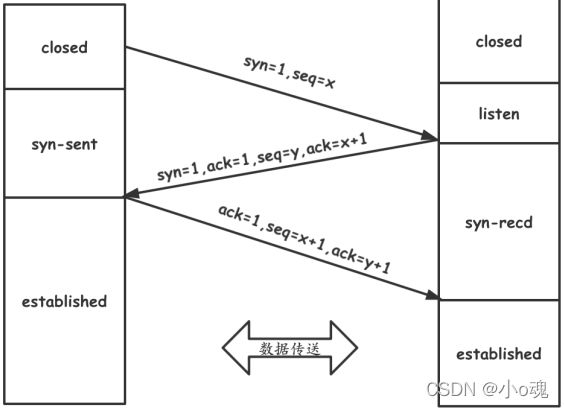
三次握手
四次挥手
主要函数
int epoll_create(int size);
int epoll_ctl(int epfd, int op, int fd, struct epoll_event* event);
int epoll_wait(int epfd, struct epoll_event* events, int maxevents, int timeout);int epoll_create(int size);
size参数告诉内核这个epoll对象会处理的事件⼤致数量,⽽不是能够处理的事件的最⼤数。
在现在linux版本中,这个size参数已经没有意义了;
返回: epoll对象句柄;之后针对该epoll的操作需要通过该句柄来标识该epoll对象;
int epoll_ctl(int epfd, int op, int fd, struct epoll_event* event);
epoll_ctl向epoll对象添加、修改或删除事件;
返回: 0表示成功, -1表示错误,根据errno错误码判断错误类型。
op类型:
| EPOLL_CTL_ADD EPOLL_CTL_MOD EPOLL_CTL_DEL event.events 取值: EPOLLIN |
添加新的事件到epoll中 修改epoll中的事件 删除epoll中的事件 |
| 表示该连接上有数据可读(tcp连接远端主动关闭连接,也是可读事 | |
| 件,因为需要处理发送来的FIN包; FIN包就是read 返回 0) | |
| EPOLLOUT | 表示该连接上可写发送(主动向上游服务器发起⾮阻塞tcp连接,连接 |
| 建⽴成功事件相当于可写事件) | |
| EPOLLRDHUP | 表示tcp连接的远端关闭或半关闭连接 |
| EPOLLPRI | 表示连接上有紧急数据需要读 |
| EPOLLERR | 表示连接发⽣错误 |
| EPOLLHUP | 表示连接被挂起 |
| EPOLLET | 将触发⽅式设置为边缘触发,系统默认为⽔平触发 |
| EPOLLONESHOT epoll_wait系统调⽤ |
表示该事件只处理⼀次,下次需要处理时需重新加⼊epoll |
int epoll_wait(int epfd, struct epoll_event* events, int maxevents, int timeout);
收集 epoll 监控的事件中已经发⽣的事件,如果 epoll 中没有任何⼀个事件发⽣,则最多等待
timeout 毫秒后返回。
返回:表示当前发⽣的事件个数
返回0表示本次没有事件发⽣;
返回-1表示出现错误,需要检查errno错误码判断错误类型。
注意:
events 这个数组必须在⽤户态分配内存,内核负责把就绪事件复制到该数组中;
maxevents 表示本次可以返回的最⼤事件数⽬,⼀般设置为 events 数组的⻓度;
timeout表示在没有检测到事件发⽣时最多等待的时间;如果设置为0,检测到rdllist为空⽴
刻返回;如果设置为-1,⼀直等待;
epoll(reactor) example
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
//#include
#include
#include
#define BUFFER_LENGTH 1024
// reactor main struct
// event-driven instead of manage socketfd
struct sockitem {
int sockfd;
int (*callback)(int fd, int events, void *arg);
char recvbuffer[BUFFER_LENGTH];
char sendbuffer[BUFFER_LENGTH];
int rlength;
int slength;
};
// similar mainloop/eventloop in libevent
struct reactor {
int epfd;
struct epoll_event events[512];
};
struct reactor *eventloop = NULL;
int recv_cb(int fd, int events, void *arg);
int send_cb(int fd, int events, void *arg) {
struct sockitem *si = (struct sockitem*)arg;
send(fd, si->sendbuffer, si->slength, 0); //
struct epoll_event ev;
ev.events = EPOLLIN | EPOLLET;
//ev.data.fd = clientfd;
si->sockfd = fd;
si->callback = recv_cb;
ev.data.ptr = si;
epoll_ctl(eventloop->epfd, EPOLL_CTL_MOD, fd, &ev);
}
int recv_cb(int fd, int events, void *arg) {
struct sockitem *si = (struct sockitem*)arg;
struct epoll_event ev;
int ret = recv(fd, si->recvbuffer, BUFFER_LENGTH, 0);
if (ret < 0) {
if (errno == EAGAIN || errno == EWOULDBLOCK) {
return -1;
} else {
// todo...
}
ev.events = EPOLLIN;
//ev.data.fd = fd;
epoll_ctl(eventloop->epfd, EPOLL_CTL_DEL, fd, &ev);
close(fd);
free(si);
} else if (ret == 0) {
printf("disconnect %d\n", fd);
ev.events = EPOLLIN;
epoll_ctl(eventloop->epfd, EPOLL_CTL_DEL, fd, &ev);
close(fd);
free(si);
} else {
printf("Recv: %s, %d Bytes\n", si->recvbuffer, ret);
si->rlength = ret;
memcpy(si->sendbuffer, si->recvbuffer, si->rlength);
si->slength = si->rlength;
struct epoll_event ev;
ev.events = EPOLLOUT | EPOLLET;
//ev.data.fd = clientfd;
si->sockfd = fd;
si->callback = send_cb;
ev.data.ptr = si;
epoll_ctl(eventloop->epfd, EPOLL_CTL_MOD, fd, &ev);
}
}
// lisent fd main function
int accept_cb(int fd, int events, void *arg) {
struct sockaddr_in client_addr;
memset(&client_addr, 0, sizeof(struct sockaddr_in));
socklen_t client_len = sizeof(client_addr);
int clientfd = accept(fd, (struct sockaddr*)&client_addr, &client_len);
if (clientfd <= 0) return -1;
char str[INET_ADDRSTRLEN] = {0};
printf("recv from %s at port %d\n", inet_ntop(AF_INET, &client_addr.sin_addr, str, sizeof(str)),
ntohs(client_addr.sin_port));
struct epoll_event ev;
ev.events = EPOLLIN | EPOLLET;
//ev.data.fd = clientfd;
struct sockitem *si = (struct sockitem*)malloc(sizeof(struct sockitem));
si->sockfd = clientfd;
si->callback = recv_cb;
ev.data.ptr = si;
epoll_ctl(eventloop->epfd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, clientfd, &ev);
return clientfd;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
if (argc < 2) {
return -1;
}
int port = atoi(argv[1]);
int sockfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
if (sockfd < 0) {
return -1;
}
struct sockaddr_in addr;
memset(&addr, 0, sizeof(struct sockaddr_in));
addr.sin_family = AF_INET;
addr.sin_port = htons(port);
addr.sin_addr.s_addr = INADDR_ANY;
if (bind(sockfd, (struct sockaddr*)&addr, sizeof(struct sockaddr_in)) < 0) {
return -2;
}
if (listen(sockfd, 5) < 0) {
return -3;
}
struct sockitem *si = (struct sockitem*)malloc(sizeof(struct sockitem));
si->sockfd = sockfd;
si->callback = accept_cb;
eventloop = (struct reactor*)malloc(sizeof(struct reactor));
eventloop->epfd = epoll_create(1);
struct epoll_event ev;
// dont set EPOLLIN and EPOLLOUT at same time
// it will return this fd always
// and it will be EPOLLLT if dont set epoll mode
// if you want set ET mode, just do 'EPOLLIN | EPOLLET'
ev.events = EPOLLIN;
ev.data.ptr = si;
epoll_ctl(eventloop->epfd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, sockfd, &ev);
while (1) {
int nready = epoll_wait(eventloop->epfd, eventloop->events, 512, -1);
if (nready < -1) {
break;
}
int i = 0;
for (i = 0;i < nready;i ++) {
if (eventloop->events[i].events & EPOLLIN) {
//printf("sockitem\n");
struct sockitem *si = (struct sockitem*)eventloop->events[i].data.ptr;
si->callback(si->sockfd, eventloop->events[i].events, si);
}
if (eventloop->events[i].events & EPOLLOUT) {
struct sockitem *si = (struct sockitem*)eventloop->events[i].data.ptr;
si->callback(si->sockfd, eventloop->events[i].events, si);
}
}
}
}
半关闭状态
tcp-keepalive

Redis源码:
// 开启tcp-keepalive
int val = 1;
if (setsockopt(fd, SOL_SOCKET, SO_KEEPALIVE, &val, sizeof(val)) == -1)
{
anetSetError(err, "setsockopt SO_KEEPALIVE: %s", strerror(errno));
return ANET_ERR;
}
// 设置
val = interval;
if (setsockopt(fd, IPPROTO_TCP, TCP_KEEPIDLE, &val, sizeof(val)) < 0) {
anetSetError(err, "setsockopt TCP_KEEPIDLE: %s\n", strerror(errno));
return ANET_ERR;
}
/* Send next probes after the specified interval. Note that we set the
* delay as interval / 3, as we send three probes before detecting
* an error (see the next setsockopt call). */
val = interval/3;
if (val == 0) val = 1;
if (setsockopt(fd, IPPROTO_TCP, TCP_KEEPINTVL, &val, sizeof(val)) < 0) {
anetSetError(err, "setsockopt TCP_KEEPINTVL: %s\n", strerror(errno));
return ANET_ERR;
}
/* Consider the socket in error state after three we send three ACK
* probes without getting a reply. */
val = 3;
if (setsockopt(fd, IPPROTO_TCP, TCP_KEEPCNT, &val, sizeof(val)) < 0) {
anetSetError(err, "setsockopt TCP_KEEPCNT: %s\n", strerror(errno));
return ANET_ERR;
}为什么应⽤层需要开启⼼跳检测?
因为传输层探活检测,⽆法判断进程阻塞或者死锁的情况;
⼼跳检测: 每隔10秒发送⼀次⼼跳包 3次没有收到 close
应用
1. 数据库间,主从复制,使⽤⼼跳检测;
2. 客户端与服务器,使⽤⼼跳检测;
3. 客户端->反向代理->上游服务器;反向代理与上游服务器使⽤探活检测;
4. 服务端->数据库,使⽤探活检测;对于数据库⽽⾔,服务端是否阻塞跟它⽆关;