Multi-Similarity Loss & Hard Triplet loss(附代码pytorch)
MS-Loss包含两部分,前一部分是Positive Part, 后一部分是Negative Part
参考
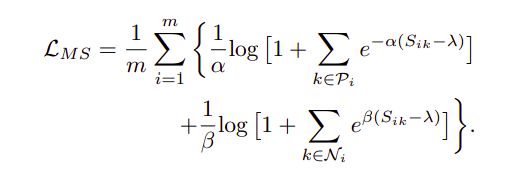
i) Positive Part(只考虑与Anchor同类样本间的关系,与anchor相似度越小,惩罚力度越大)
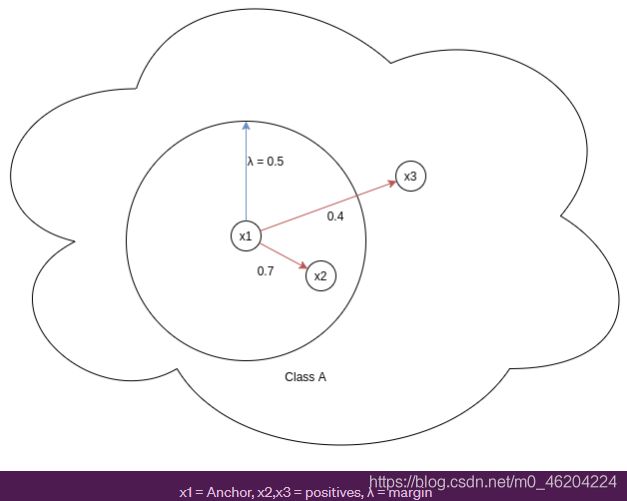
图中0.7,0.4表示余弦相似度,值越大,则表示两者的特征越相似
补充:余弦距离与欧式距离它们近似反比关系,因此图中,0.4的红线明明很长(欧式距离),但是值(余弦距离)很低。
x1 = Anchor, x2,x3 = positives,通过门限λ,将同类样本分成2parts,与x1相似程度越高的x2,(x1,x2)损失就越低,反之(x1,x3)的损失越高.
ii) Negative Part(只考虑与Anchor异类样本间的关系,与anchor相似度越大,惩罚力度越大)
下图对x2的惩罚力度大
![]()
![]()
Hard Triplet loss
MS考虑的是Anchor与所有正样本的余弦相似度,Anchor与所有异类样本的余弦相似度。
Triplet loss只使用了 hard negatives 和 hard positives 进行训练,并丢弃了所有其他对,仅选择携带最多信息的那些对使得算法计算速度更快。
Triplet loss考虑的是Anchor与最难的正样本间的欧式距离,所谓的最难的正样本,即在所有正样本中选择与Anchor的欧式距离最大的那个,去惩罚那个最不像anchor的正样本。
同时考虑了Anchor与最难的异类样本的欧式距离,所谓的最难的负样本,即在所有负样本中选择与Anchor的欧式距离最小的那个,去惩罚那个最像anchor的负样本。
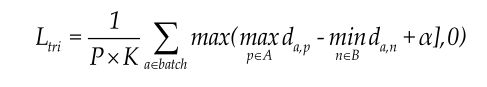
上式中a=Anchor p=Positive n=Negative
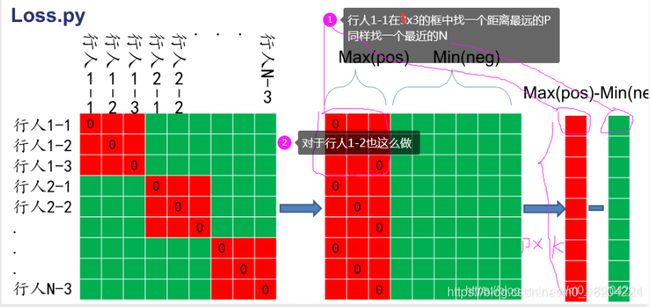
下图中,行人1-1所在的一行中,红色的表示正样本,绿色的表示负样本,那么行人1-1就要去惩罚Max(pos)和Min(negative)。
from __future__ import absolute_import
import sys
import torch
from torch import nn
DEVICE = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
class TripletLoss(nn.Module):
"""Triplet loss with hard positive/negative mining.
Reference:
Hermans et al. In Defense of the Triplet Loss for Person Re-Identification. arXiv:1703.07737.
Code imported from https://github.com/Cysu/open-reid/blob/master/reid/loss/triplet.py.
Args:
margin (float): margin for triplet.
"""
def __init__(self, margin=0.3):#三元组的阈值margin
super(TripletLoss, self).__init__()
self.margin = margin
self.ranking_loss = nn.MarginRankingLoss(margin=margin)#三元组损失函数
#ap an margin y:倍率 Relu(ap - anxy + margin)这个relu就起到和0比较的作用
def forward(self, inputs, targets):
"""
Args:
inputs: visualization_feature_map matrix with shape (batch_size, feat_dim)#32x2048
targets: ground truth labels with shape (num_classes)#tensor([32])[1,1,1,1,2,3,2,,,,2]32个数,一个数代表ID的真实标签
"""
n = inputs.size(0)#取出输入的batch
# Compute pairwise distance, replace by the official when merged
#计算距离矩阵,其实就是计算两个2048维之间的距离平方(a-b)**2=a^2+b^2-2ab
#[1,2,3]*[1,2,3]=[1,4,9].sum()=14 点乘
dist = torch.pow(inputs, 2).sum(dim=1, keepdim=True).expand(n, n)
dist = dist + dist.t()
dist.addmm_(1, -2, inputs, inputs.t())#生成距离矩阵32x32,.t()表示转置
dist = dist.clamp(min=1e-12).sqrt() # for numerical stability#clamp(min=1e-12)加这个防止矩阵中有0,对梯度下降不好
# For each anchor, find the hardest positive and negative
mask = targets.expand(n, n).eq(targets.expand(n, n).t())#利用target标签的expand,并eq,获得mask的范围,由0,1组成,,红色1表示是同一个人,绿色0表示不是同一个人
dist_ap, dist_an = [], []#用来存放ap,an
for i in range(n):#i表示行
# dist[i][mask[i]],,i=0时,取mask的第一行,取距离矩阵的第一行,然后得到tensor([1.0000e-06, 1.0000e-06, 1.0000e-06, 1.0000e-06])
dist_ap.append(dist[i][mask[i]].max().unsqueeze(0))#取某一行中,红色区域的最大值,mask前4个是1,与dist相乘
dist_an.append(dist[i][mask[i] == 0].min().unsqueeze(0))#取某一行,绿色区域的最小值,加一个.unsqueeze(0)将其变成带有维度的tensor
dist_ap = torch.cat(dist_ap)
dist_an = torch.cat(dist_an)
# Compute ranking hinge loss
y = torch.ones_like(dist_an)#y是个权重,长度像dist-an
loss = self.ranking_loss(dist_an, dist_ap, y) #ID损失:交叉商输入的是32xf f.shape=分类数,然后loss用于计算损失
#度量三元组:输入的是dist_an(从距离矩阵中,挑出一行(即一个ID)的最大距离),dist_ap
#ranking_loss输入 an ap margin y:倍率 loss: Relu(ap - anxy + margin)这个relu就起到和0比较的作用
# from IPython import embed
# embed()
return loss
class MultiSimilarityLoss(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, margin=0.7):
super(MultiSimilarityLoss, self).__init__()
self.thresh = 0.5
self.margin = margin
self.scale_pos = 2.0
self.scale_neg = 40.0
def forward(self, feats, labels):
assert feats.size(0) == labels.size(0), \
f"feats.size(0): {feats.size(0)} is not equal to labels.size(0): {labels.size(0)}"
batch_size = feats.size(0)
feats = nn.functional.normalize(feats, p=2, dim=1)
# Shape: batchsize * batch size
sim_mat = torch.matmul(feats, torch.t(feats))
epsilon = 1e-5
loss = list()
mask = labels.expand(batch_size, batch_size).eq(
labels.expand(batch_size, batch_size).t())
for i in range(batch_size):
pos_pair_ = sim_mat[i][mask[i]]
pos_pair_ = pos_pair_[pos_pair_ < 1 - epsilon]
neg_pair_ = sim_mat[i][mask[i] == 0]
neg_pair = neg_pair_[neg_pair_ + self.margin > min(pos_pair_)]
pos_pair = pos_pair_[pos_pair_ - self.margin < max(neg_pair_)]
if len(neg_pair) < 1 or len(pos_pair) < 1:
continue
# weighting step
pos_loss = 1.0 / self.scale_pos * torch.log(
1 + torch.sum(torch.exp(-self.scale_pos * (pos_pair - self.thresh))))
neg_loss = 1.0 / self.scale_neg * torch.log(
1 + torch.sum(torch.exp(self.scale_neg * (neg_pair - self.thresh))))
loss.append(pos_loss + neg_loss)
# pos_loss =
if len(loss) == 0:
return torch.zeros([], requires_grad=True, device=feats.device)
loss = sum(loss) / batch_size
return loss
if __name__ == '__main__':
#测试TripletLoss(nn.Module)
use_gpu = False
model = TripletLoss()
features = torch.rand(32, 2048)
label= torch.Tensor([1,1,1,1,2,2,2,2,3,3,3,3,4,4,4,4,5, 5, 5, 5, 6, 6, 6, 6, 7, 7, 7, 7, 8, 8, 8,8]).long()
loss = model(features, label)
print(loss)