Python Selenium.WebDriver 浏览器启动参数设置『Edge如何使用启动参数』
Python Selenium.WebDriver 浏览器启动参数设置『Edge如何使用启动参数』
文章目录
- Python Selenium.WebDriver 浏览器启动参数设置『Edge如何使用启动参数』
-
- 一、浏览器启动参数设置
- 二、WebDriver 实例化参数
- 三、浏览器启动参数大全
- 四、Edge浏览器使用启动参数与源码剖析
- 五、对启动参数选项进行封装
- 六、无头浏览器
- 七、自动化程序控制的提示「扩展」
- 参考资料
- 相关博客
一、浏览器启动参数设置
在创建 WebDriver 实例时,可以配置它的启动参数以进行一些初始设置,这些设置将会在 WebDriver 的整个生命周期内生效
对于不同类型的浏览器,WebDriver 传入的参数并不相同,但主要的几个参数是一样的
那么浏览器启动参数设置能做些什么呢,举两个例子:
- Selenium 默认在启动浏览器的时候,浏览器是以窗口化运行的,可对于页面点击或则进行动作链操作的时候,需要将浏览器最大化,在 Selenium 中有内置的方法
maximize_window()可以将浏览器最大化,但这是在启动浏览器之后将其的最大化行为,那么有没有方法能在启动浏览器时默认就是最大化呢,这时候 浏览器启动参数设置 就派上用场了,只需要在启动浏览器的时候传入参数值--start-maximized即可 - 在 Selenium 调用的浏览器不难发现会在浏览器上方带一个自动化提示条
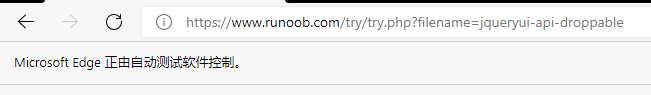
如果不想浏览器显示这行提示,只需要在 浏览器启动参数设置 传入参数值--disable-infobars即可(新版本已失效)
二、WebDriver 实例化参数
Selenium 支持的浏览器种类有很多,这里挑出 Chome「谷歌」浏览器 以及 Edge 浏览器 来讲
1)、Chome浏览器部分
webdriver.Chrome(executable_path=“chromedriver”, port=0, options=None, service_args=None, desired_capabilities=None, service_log_path=None, chrome_options=None, keep_alive=True)
参数如下:
-
executable_path:浏览器驱动程序路径,如果没有制定,则默认使用环境变量PATH中设置的路径
-
options:启动选项 (Options对象通常位于各浏览器的 WebDriver 模块下,列如:
from selenium.webdriver.浏览器名称.options import Options),建议优先使用options 参数来设置浏览器(options 基于 capabilities,在实例化某个浏览器的Options对象时会自动写入该浏览器预设的 capabilities) -
desired_capabilities:类似于 options 参数,主要在早期版本的 Selenium 中使用,现在推荐使用 options 参数,只有在实例化
RemoteWebDriver(远程运行系统不定或则浏览器不定) 时,才使用此参数 -
chrome_options:完全等同于 options 参数,此参数是早期版本 Selenium 使用的参数,现在的版本已不推荐使用
-
port:驱动程序启用的端口号,如果不填写,则自动使用任意闲置的端口号,默认参数为0
-
service_args:浏览器驱动程序的参数,根据所使用的浏览器驱动不同,参数也有可能不同。
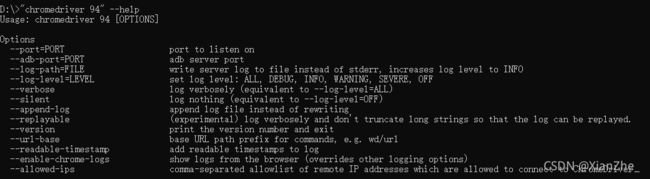
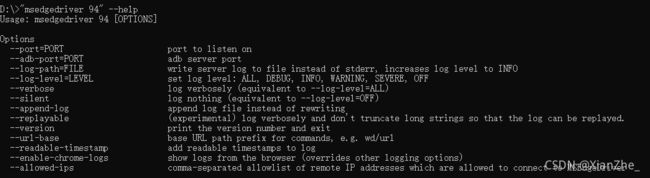
打开命令提示符窗口,在驱动程序所在路径下运行"驱动程序文件名" --help即可查看驱动程序所支持的参数,如下图在D盘根目录下有着名为 chromedriver 94 的驱动程序文件,查看其支持参数需要注意的是,驱动程序文件名最好加上双引号反正出错
-
service_log_path:驱动程序存放日志文件的位置
-
keep_alive:表示在与
ChromeDriver进行链接时,是否带上 HTTP 请求头Connection: keep-alive,既是否使用长链接,布尔类型参数,默认值为True
源码:
def __init__(self, executable_path="chromedriver", port=0,
options=None, service_args=None,
desired_capabilities=None, service_log_path=None,
chrome_options=None, keep_alive=True):
"""
Creates a new instance of the chrome driver.
Starts the service and then creates new instance of chrome driver.
:Args:
- executable_path - path to the executable. If the default is used it assumes the executable is in the $PATH
- port - port you would like the service to run, if left as 0, a free port will be found.
- options - this takes an instance of ChromeOptions
- service_args - List of args to pass to the driver service
- desired_capabilities - Dictionary object with non-browser specific
capabilities only, such as "proxy" or "loggingPref".
- service_log_path - Where to log information from the driver.
- chrome_options - Deprecated argument for options
- keep_alive - Whether to configure ChromeRemoteConnection to use HTTP keep-alive.
"""
演示代码:
实例化浏览器 WebDriver
chrome_path = r"chromedriver.exe" # 相对路径下
browser = webdriver.Chrome(executable_path=chrome_path)
传入 设置浏览器默认以最大化窗口运行 启动参数
edge_path = r"chromedriver.exe" # 相对路径下
options = Options()
options.add_argument("--start-maximized") # 添加最大化窗口运作参数
browser = webdriver.Chrome(executable_path=edge_path, options=options)
2)、Edge浏览器部分
webdriver.Edge(executable_path=‘MicrosoftWebDriver.exe’, capabilities=None, port=0, verbose=False, service_log_path=None, log_path=None, keep_alive=False)
参数如下:
- executable_path:浏览器驱动程序路径,如果没有制定,则默认使用环境变量PATH中设置的路径
- capabilities:非浏览器特定的字典对象,传入浏览器启动参数时需要使用到
- port:驱动程序启用的端口号,如果不填写,则自动使用任意闲置的端口号,默认参数为0
- verbose:是否在服务中设置详细日志记录
- service_log_path:驱动程序存放日志文件的位置
- log_path:不推荐使用的 service_log_path 参数
- keep_alive:表示在与
EdgeDriver进行链接时,是否带上 HTTP 请求头Connection: keep-alive,既是否使用长链接,布尔类型参数,默认值为True
def __init__(self, executable_path='MicrosoftWebDriver.exe',
capabilities=None, port=0, verbose=False, service_log_path=None,
log_path=None, keep_alive=False):
"""
Creates a new instance of the chrome driver.
Starts the service and then creates new instance of chrome driver.
:Args:
- executable_path - path to the executable. If the default is used it assumes the executable is in the $PATH
- capabilities - Dictionary object with non-browser specific
capabilities only, such as "proxy" or "loggingPref".
- port - port you would like the service to run, if left as 0, a free port will be found.
- verbose - whether to set verbose logging in the service
- service_log_path - Where to log information from the driver.
- log_path: Deprecated argument for service_log_path
- keep_alive - Whether to configure ChromeRemoteConnection to use HTTP keep-alive.
"""
演示代码:
实例化浏览器 WebDriver
edge_path = r"msedgedriver.exe" # 相对路径下
browser = webdriver.Edge(executable_path=edge_path)
传入 设置浏览器默认以最大化窗口运行 启动参数
edge_path = r"chromedriver.exe" # 相对路径下
options = {
"browserName": "MicrosoftEdge",
"version": "",
"platform": "WINDOWS",
"ms:edgeOptions": {
"extensions": [], "args": ["--start-maximized"] # 添加最大化窗口运作参数
}
}
browser = webdriver.Edge(executable_path=edge_path, capabilities=options)
三、浏览器启动参数大全
主要以 Chrome 为例,介绍各个启动参数的作用,在这里也推荐大家优先使用 Chrome 浏览器
| 序号 | 参数选项 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | --user-agent="客户端代理类型” |
设置请求头的 User-Agent,多用于响应式站点或根据 User-Agent 判断是否移动设备而返回不同网页的场景 |
| 2 | --window-size=宽度值,高度值 |
设置浏览器的默认窗口大小 |
| 3 | --headless |
无界面运行(无窗口),也叫无头浏览器,通常用于远程运行,在本地运行也可以通过该参数提升运行效率 |
| 4 | --disable-gpu |
禁用GPU加速 |
| 5 | --disable-gpu-program-cache |
禁用GPU程序缓存 |
| 6 | --start-maximized |
设置浏览器默认以最大化窗口运行 |
| 7 | --incognito |
设置浏览器以隐身模式(无痕模式运行) |
| 8 | --disable-javascript |
禁用Javascript代码运行 |
| 9 | --disable-infobars |
禁用浏览器正在被自动化程序控制的提示(新版本已失效) |
| 10 | --enable-automation |
通知用户他们的浏览器是由自动测试控制的 |
对于更多的浏览器启动参数,请参考这篇文章 Chrome浏览器启动参数大全
对于 Edge 浏览器由于使用的也是 Chromium 内核,对于 Chrome 的启动参数大部分是通用的,我自己比较习惯且常用的也是 Edge 浏览器,这也是我在文章中加入了对该浏览器的使用讲解的原因之一
四、Edge浏览器使用启动参数与源码剖析
对于Edge浏览器,在 二、WebDriver 实例化参数 中就能发现其实少了 options、desired_capabilities、chrome_options这三个参数,相反多出了一个capabilities,那么该如何使用浏览器启动参数呢?
(一)、先看看对于 Chrome 浏览器中的源码:
-
options、desired_capabilities、chrome_options这三个参数之间很容易让人疑惑,但查看下面的源码之后就能很快明白它们之间的关系if chrome_options: warnings.warn('use options instead of chrome_options', DeprecationWarning, stacklevel=2) options = chrome_options if options is None: # desired_capabilities stays as passed in if desired_capabilities is None: desired_capabilities = self.create_options().to_capabilities() else: if desired_capabilities is None: desired_capabilities = options.to_capabilities() else: desired_capabilities.update(options.to_capabilities())可以看到,
chrome_options在源码中有一句警告'use options instead of chrome_options',表示请使用options参数来代替chrome_options参数,最后实际上chrome_options赋值给了options,两者完全相同
然后是关于desired_capabilities的处理,在desired_capabilities为空时,会将options转换为desired_capabilities,已有desired_capabilities则合并options -
对于Chome浏览器的 Options 对象,我们主要看源码中这几个方法和属性
class Options(object): KEY = "goog:chromeOptions" def __init__(self): self._binary_location = '' self._arguments = [] self._extension_files = [] self._extensions = [] self._experimental_options = {} self._debugger_address = None self._caps = DesiredCapabilities.CHROME.copy() ...... @property def extensions(self): """ Returns a list of encoded extensions that will be loaded into chrome """ encoded_extensions = [] for ext in self._extension_files: file_ = open(ext, 'rb') # Should not use base64.encodestring() which inserts newlines every # 76 characters (per RFC 1521). Chromedriver has to remove those # unnecessary newlines before decoding, causing performance hit. encoded_extensions.append(base64.b64encode(file_.read()).decode('UTF-8')) file_.close() return encoded_extensions + self._extensions def add_extension(self, extension): """ Adds the path to the extension to a list that will be used to extract it to the ChromeDriver :Args: - extension: path to the \*.crx file """ if extension: extension_to_add = os.path.abspath(os.path.expanduser(extension)) if os.path.exists(extension_to_add): self._extension_files.append(extension_to_add) else: raise IOError("Path to the extension doesn't exist") else: raise ValueError("argument can not be null") ...... def to_capabilities(self): """ Creates a capabilities with all the options that have been set and returns a dictionary with everything """ caps = self._caps chrome_options = self.experimental_options.copy() chrome_options["extensions"] = self.extensions if self.binary_location: chrome_options["binary"] = self.binary_location chrome_options["args"] = self.arguments if self.debugger_address: chrome_options["debuggerAddress"] = self.debugger_address caps[self.KEY] = chrome_options return caps1)、添加浏览器参数要用到的方法是
to_capabilities,如果想要添加一个 设置浏览器默认以最大化窗口运行,写法是:options = Options() options.add_extension("--start-maximized")2)、
to_capabilities方法代码内部使用到了extensions方法,作用是将对象转化为webdriver实例化时能够识别的字典,格式如下所示:options = { "browserName": "MicrosoftEdge", "version": "", "platform": "WINDOWS", "ms:edgeOptions": { "extensions": [], "args": ["--start-maximized"] # 添加最大化窗口运作参数 } }
(二)、Edge浏览器使用启动参数:
为什么要来讲这个呢,我们先开看看 options 的源码,结合 二、WebDriver 实例化参数 中的 Edge浏览器部分
1)、Edge下 options 源码
class Options(object):
def __init__(self):
self._page_load_strategy = "normal"
self._caps = DesiredCapabilities.EDGE.copy()
@property
def page_load_strategy(self):
return self._page_load_strategy
@page_load_strategy.setter
def page_load_strategy(self, value):
if value not in ['normal', 'eager', 'none']:
raise ValueError("Page Load Strategy should be 'normal', 'eager' or 'none'.")
self._page_load_strategy = value
@property
def capabilities(self):
return self._caps
def set_capability(self, name, value):
"""Sets a capability."""
self._caps[name] = value
def to_capabilities(self):
"""
Creates a capabilities with all the options that have been set and
returns a dictionary with everything
"""
caps = self._caps
caps['pageLoadStrategy'] = self._page_load_strategy
return caps
可以看到在 Edge 下的 option 参数选项类并没有添加启动参数 add_extension 方法,且实例 Edge 驱动与实例 Chrome 驱动时所能传入的参数各不相同,如 options 参数
Edge 驱动实例是通过 capabilities 参数来传入启动参数,但传入的类型必须是格式能够被识别的字典类型,参考上述提到过的 chrome.option 下的 to_capabilities 方法
2)、手动添加启动参数
Edge 启动参数字典如下所示:
options = {
"browserName": "MicrosoftEdge",
"version": "",
"platform": "WINDOWS",
"ms:edgeOptions": {
"extensions": [], "args": []
}
}
浏览器启动参数写在 ms:edgeOptions -> args 的列表里,如添加一个最大化窗口运作参数,再将此字典传入 Edge 驱动实例化参数里:
edge_path = r"chromedriver.exe" # 相对路径下
options = {
"browserName": "MicrosoftEdge",
"version": "",
"platform": "WINDOWS",
"ms:edgeOptions": {
"extensions": [], "args": ["--start-maximized"] # 添加最大化窗口运作参数
}
}
browser = webdriver.Edge(executable_path=edge_path, capabilities=options)
3)、编写辅助函数
可以编写一个辅助函数来帮助我们传入启动参数
def get_options(params):
"""
Edge浏览器添加启动参数辅助函数
:param params: 启动参数,为字符串类型直接添加,为列表或元组类型添加多个
:return: 添加启动参数后的字典
"""
options = {
"browserName": "MicrosoftEdge",
"version": "",
"platform": "WINDOWS",
"ms:edgeOptions": {
"extensions": [], "args": []
}
}
if isinstance(params, str):
options["ms:edgeOptions"]["args"].append(params)
elif isinstance(params, (list, tuple)):
# 利用集合去重
params = list(set(params))
options["ms:edgeOptions"]["args"].extend(params)
return options
五、对启动参数选项进行封装
在上述内容中,我们得知了浏览器启动参数的原理后,我们就可以将 Chrome 和 Edge 参数选项类 Options 进行再一步的扩展和封装,通过这种形式就可以弥补某些浏览器启动参数类方法不全的问题,或编写提升效率的方法
-
Chrome 浏览器参数选项类
对于 Chrome 浏览器的
Options参数选项类来说,功能方法已经很全了,我们只需要继承这个类,并在此基础上增加一个同时添加多个浏览器参数的方法即可class ChromeOptions(Options): def add_argument(self, argument): """ 添加浏览器参数 :param argument: 启动参数 """ if argument: if self._is_infobars(argument): self._enable_infobars() self._arguments.append(argument) else: raise ValueError("argument参数不能为空") def add_arguments(self, arguments: list or tuple): """ 同时添加多个浏览器参数 :param arguments: 启动参数集 """ if arguments: if isinstance(arguments, str): self.add_argument(arguments) else: for arg in arguments: if self._is_infobars(arg): self._enable_infobars() self.add_argument(arg) else: raise ValueError("argument参数不能为空") @staticmethod def _is_infobars(string): return string == "--disable-infobars" def _enable_infobars(self): """ 启用'禁用浏览器正在被自动化程序控制的提示'启动参数 """ self._experimental_options["excludeSwitches"] = ["enable-automation"] -
Edge 浏览器参数选项类
对于 Edge 浏览器来说,其下的
Options参数选项类的方法就少的可怜,主要的add_argument方法并不存在,那咱直接编写一个属于我们自己的Options参数选项类,将几个主要的属性以及方法写上,添加自己自定义的方法即可from selenium.webdriver.common.desired_capabilities import DesiredCapabilities class EdgeOptions: KEY = "ms:edgeOptions" def __init__(self): self._arguments = [] self._experimental_options = {} self._caps = DesiredCapabilities.EDGE.copy() @property def arguments(self): return self._arguments @property def experimental_options(self): return self._experimental_options def add_argument(self, argument): """ 添加浏览器参数 :param argument: 启动参数 """ if argument: if self._is_infobars(argument): self._enable_infobars() else: self._arguments.append(argument) else: raise ValueError("argument参数不能为空") def add_arguments(self, arguments: list or tuple): """ 同时添加多个浏览器参数 :param arguments: 启动参数集 """ if arguments: if isinstance(arguments, str): self.add_argument(arguments) else: for arg in arguments: if self._is_infobars(arg): self._enable_infobars() else: self._arguments.append(arg) else: raise ValueError("argument参数不能为空") @staticmethod def _is_infobars(string): return string == "--disable-infobars" def _enable_infobars(self): """ 启用'禁用浏览器正在被自动化程序控制的提示'启动参数 """ self._experimental_options["excludeSwitches"] = ["enable-automation"] def to_capabilities(self): """ 使用已设置的所有选项创建功能 :return: 返回包含所有内容的字典 """ caps = self._caps edge_options = { "extensions": [], "args": self.arguments } edge_options.update(self.experimental_options) caps[self.KEY] = edge_options return caps
对于
_is_infobars、_enable_infobars方法的作用,这是一个扩展知识,用于启用 <禁用浏览器正在被自动化程序控制的提示> 启动参数。有兴趣的朋友可以去看看 七、自动化程序控制的提示「扩展」
六、无头浏览器
无头浏览器的应用比较重要,无头浏览器 又叫 无界面(无窗口)运行,即在运行程序的时候是不会弹出浏览器窗口,但程序依旧在运行,目前几个主流的浏览器都支持。
无头浏览器的好处:
- 这样可以大幅度提高效率,节约系统资源开销
- 减少运行误差,防止因误触浏览器窗口而导致的程序出错
- 可以用于远程运行
使用无头浏览器:
那么如何使用无头浏览器呢?其实很简单,只需要加上 --headless 启动参数即可,这里利用 五、对启动参数选项进行封装 中所封装的类添加启动参数
# Edge浏览器
options = EdgeOptions()
options.add_argument(r"--headless")
browser = Edge(executable_path=r"msedgedrive.exe", capabilities=options.to_capabilities())
# ----------------------------------------------------------------
# Chrome浏览器
options = ChromeOptions()
options.add_arguments(r"--headless")
browser = Chrome(executable_path=r"chromedriver.exe", options=options)
GPU加速:
通常来说,使用无头浏览器还会再加一个参数 --disable-gpu,此参数的作用是禁用 gpu 加速。这是配合无头浏览器经常用上的参数,在很多教程中都能见到其身影,可为什么要加上这个参数呢?
默认不加 --disable-gpu 启动参数情况下的占用情况,CPU和内存都是动态不确定的,把目光看向GPU,可以看到其实无头浏览器并没有成功使用到GPU来进行硬件加速
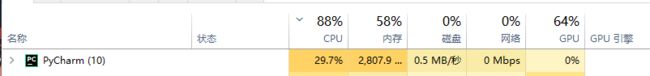
在加上 --disable-gpu 启动参数情况后,GPU 的使用率还是一样的
对比总结:
- 在对比运行了一段时间后,禁用 GPU 加速会比不禁用要更稳定一些,程序出错几率会小些,当然这也可能只是误差,大伙可以在自己的电脑上试一试
- GPU 加速可能会导致浏览器出现黑屏或则崩溃的情况
- 无头浏览器已经是无窗口运行,使用 GPU 加速的作用不大,还不如将其关闭提高稳定性
使用无头浏览器并关闭 GPU 加速
options = EdgeOptions()
options.add_arguments([r"--headless", r"--disable-gpu"])
browser = Edge(executable_path=r"msedgedrive.exe", capabilities=options.to_capabilities())
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Chrome浏览器
options = ChromeOptions()
options.add_arguments([r"--headless", r"--disable-gpu"])
browser = Chrome(executable_path=r"chromedriver.exe", options=options)
七、自动化程序控制的提示「扩展」
其实本文在 六、无头浏览器 就已经结束了,此部分是我在做测试时遇到的问题。将此作为一个扩展,在这里将解决方法分享给大家
对于不断更新版本的Chrome浏览器来说,可能会废除一些属性,也有可能睡更新一些属性
--disable-infobars 参数在高版本的浏览器中已经废除,它的作用就是禁用浏览器正在被自动化程序控制的提示,那么还有什么方法可以禁止该提示呢?

参考这篇文章 Chrome is being controlled by automated test software" notification,在此之中找到了方法,但在说明如何实现禁止提示以及原理讲解之前呢,需要先要了解此参数 --enable-automation,该参数作用为 通知用户他们的浏览器是由自动测试控制的,可以理解成 Selenium 在启动浏览器的时候自动将该参数传入。那么只需要排除这个参数就能够实现不出现提示
源码:
在看解决方法之前,咱先看看想要用到 add_experimental_option 方法的源码,位于 Options 参数选项类中。其实该方法也比较简单,就是给 to_capabilities 所输出的字典添加一个键值对
class Options(object):
KEY = "goog:chromeOptions"
def __init__(self):
self._binary_location = ''
self._arguments = []
self._extension_files = []
self._extensions = []
self._experimental_options = {}
self._debugger_address = None
self._caps = DesiredCapabilities.CHROME.copy()
......
@property
def experimental_options(self):
"""
Returns a dictionary of experimental options for chrome.
"""
return self._experimental_options
def add_experimental_option(self, name, value):
"""
Adds an experimental option which is passed to chrome.
Args:
name: The experimental option name.
value: The option value.
"""
self._experimental_options[name] = value
......
def to_capabilities(self):
"""
Creates a capabilities with all the options that have been set and
returns a dictionary with everything
"""
caps = self._caps
chrome_options = self.experimental_options.copy()
chrome_options["extensions"] = self.extensions
if self.binary_location:
chrome_options["binary"] = self.binary_location
chrome_options["args"] = self.arguments
if self.debugger_address:
chrome_options["debuggerAddress"] = self.debugger_address
caps[self.KEY] = chrome_options
return caps
解决方法:
目前的解决方法是通过一个名为 excludeSwitches 选项,然后排除 enable-automation 开关,代码很简单只需要三行即可
options = Options()
options.add_experimental_option("excludeSwitches", ["enable-automation"])
browser = webdriver.Chrome(executable_path="chromedriver.exe", options=options)
参考资料
- 书籍:
- 异步图书 《Selenium 自动化测试完全指南 基于Python》
这是一本2021年5月新出的书,各方面写的很全,对于学习爬虫或则自动化测试的同学一定不要错过
- 异步图书 《Selenium 自动化测试完全指南 基于Python》
- 博客文献:
- Chrome浏览器启动参数大全【1】
- Chrome浏览器启动参数大全【2】
- Chrome is being controlled by automated test software" notification
- 官方手册:
- Edge官方文档:使用 WebDriver 自动Microsoft Edge
- Selenium with Python中文翻译文档
- 浏览器驱动:
- edge 浏览器驱动
- chrome 浏览器驱动
相关博客
- 《Python Selenium.WebDriverWait 对Cookies的处理及用途『模拟登录』》
- 《Python Selenium.WebDriverWait 清除输入框再输入『详解』》