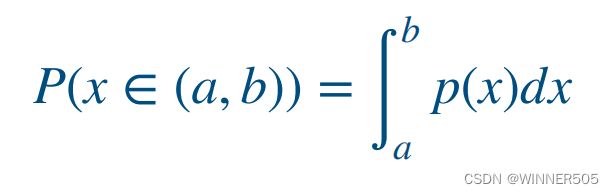【COMP329 LEC3】
LEC 3 Beliefs and Bayesian Filters
Part 1: Recap on Probability theory
1. Probabilistic Robotics
Explicit representation of uncertainty (using the calculus of probability theory)
Perception = state estimation
Interpreting what the robot senses about its environment
and coverting it into a probabilistic belief about the environment or itself
Action = utility optimisation
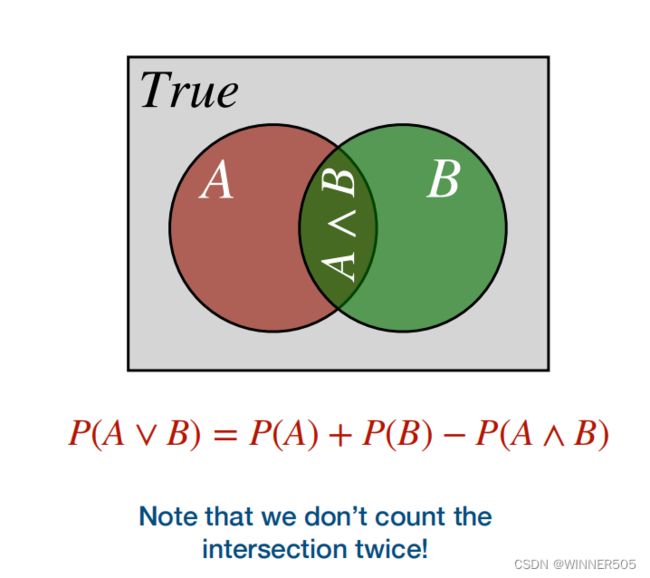
(a. P(A ∨ B) = P(A) + P(B) − P(A ∧ B)
可以转换为:
(b. P(A ∨ ¬A) = P(A) + P(¬A) − P(A ∧ ¬A)
(c. P(True) = P(A) + P(¬A) − P(False)
记住:A ∨ ¬A is True (tautology) ,and A ∧ ¬A is False (contradiction)
(d. 1 = P(A) + P(¬A) − 0 which is alse equal to P(A) = 1 - P(¬A)
因为P(True) = 1, P(false) = 0
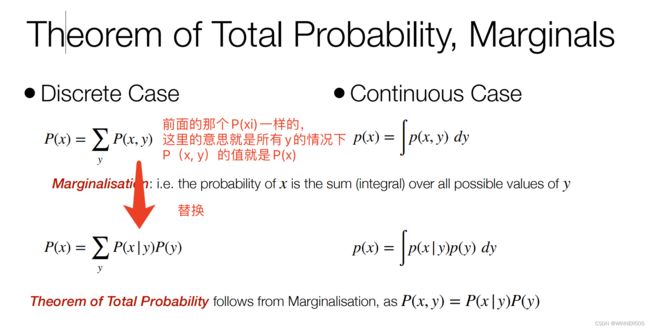
2. Probability mass function 概率质量函数
就是其中一种可能的概率就是P(Xi),然后P(X)的意思就是所有可能的概率,例如这里例子的P(Room)就是四个房间的分别的概率是0.7, 0.2, 0.0.8, 0.02, 但最后加起来的概率肯定是1
3. Probability density function 概率密度函数
X takes on values in the continuum
p(X = x) or p(x) is a probability density function
高中知识,值就是这条曲线和x = a和x = b还有x轴包围起来的面积
Within this module, we typically approximate the continuous case by using the discrete case
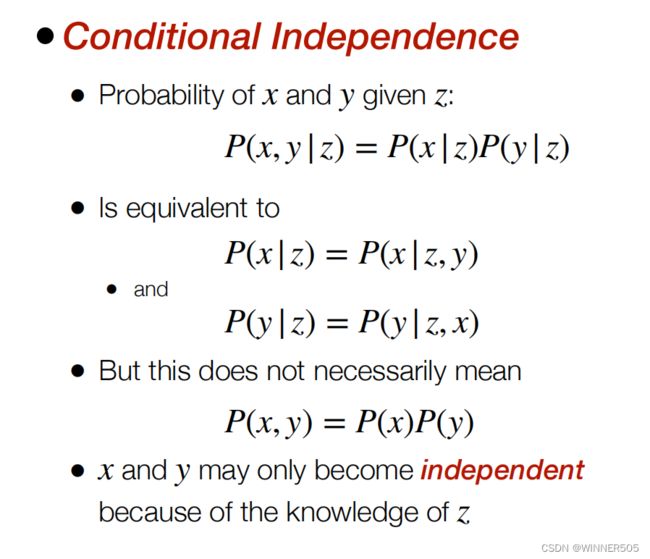
4. Joint and Conditional Probability
1. Joint probability
P( X = x and Y = y) = P(x, y)
and if x 和 y都是独立事件,那么P(x, y) = P(x)P(y)
2. Conditional probability
P(x | y) 意思是 在y的前提下,x发生的概率
P(x, y) = P(x | y)P(y)
那么根据上面的结论我们可以这样推导出来
如果x和y都是独立事件,那么P(x | y) = p(x, y) / p(y) = p(x)p(y) / p(y) = p(x) ,那么结论刚好就是正确的,因为是独立事件,所以x不受y影响,P(x | y) 就等于 p(x)
Part 2: Bayes Theorem, Normalisation and Background Knowledge
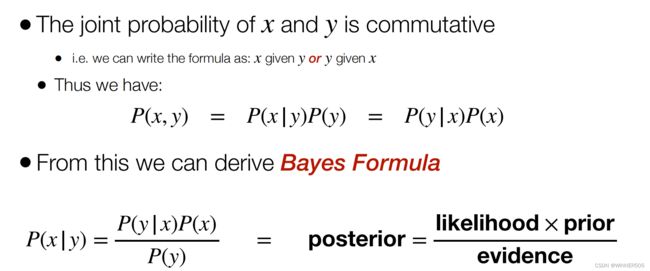
1. Bayes Formula:
The joint probability of x and y 是可以交换的
所以 p(x|y)p(y) = p(y|x) p(x)
所以p(x|y) = p(y|x)p(x) / p(y) = p(x|y)p(y) / p(y)
Normalisation 一下
就是引入了一个η概念,更好书写或者计算??
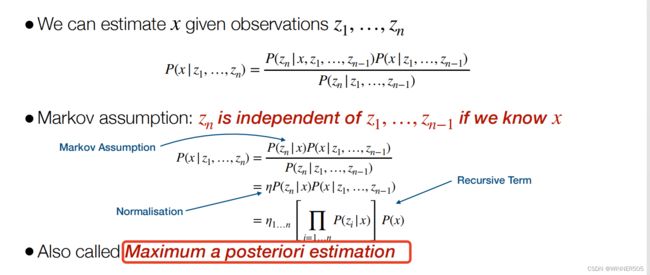
2. Bayes Formula 进阶版
这里的意思就是在同时发生y和z的前提下,发生x的概率
Part 3: State Estimation
第一个诊断性的是指:如果距离目标有多远,那么门是打开的概率是多少
第二个因果的是指:如果门是开着的话,那么传感器和目标的距离是z的概率是多少
增加了一个传感器的情况下
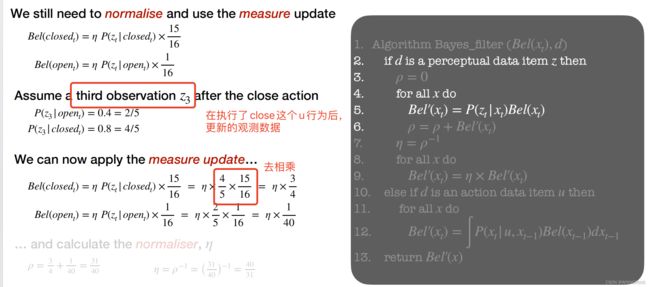
Part 4: Modelling actions and Bayesian Filters
Actions
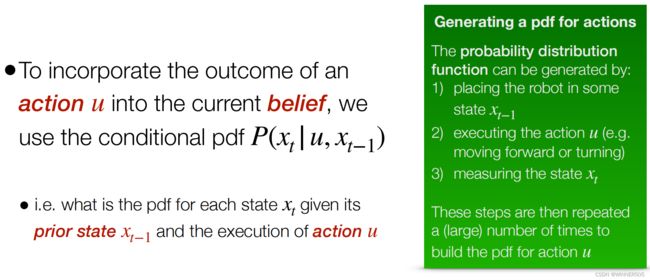
Modelling Actions
The probablility distribution function(pdf) can be generated by:
1. Xt-1 是当前状态
2. 进行u这个行为 例如:朝前行驶或者转弯
3. 计算最新的状态 Xt
重复进行这个过程,只是每次的行为u可能改变可能不变
这里的意思,就是在已知有两个传感器感知的情况下,再加上一个行为u之后,门的不同状态的概率