Mybatis源码(1) - SpringBoot整合Mybatis的核心原理
-
-
- 0. 前言:
- 1. 自动配置类MybatisAutoConfiguration:
-
- 1.1. SqlSessionFactory的生成:
- 1.2. Mapper的扫描和代理生成:
-
- 1.2.1. MapperScannerConfigurer
- 1.2.2. MapperFactoryBean
- 1.2.3. getMapper生成代理对象
- 1.2.4. 关于FactoryBean
- 1.3. MapperProxy#invoke
- 2. 小结:
-
0. 前言:
- SpringBoot整合Mybatis只需添加mybatis-spring-boot-starter的依赖(本文版本2.2.0,对应mybatis版本3.5.7),然后yml进行配置即可
- 本文对Mybatis一些底层原理进行探究,主要是一些自动配置以及Mapper代理对象的生成过程
spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/cloud?characterEncoding=utf8&autoReconnect=true&useUnicode=true&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC
username: root
password: 123456
mybatis:
# mybatis-config.xml 配置文件的路径 与 configuration 不可一起设置
#config-location: classpath:mapper/mybatis-config.xml
# sql映射文件的位置
mapper-locations: classpath:mapper/*.xml
# 开启驼峰命名转化
configuration:
map-underscore-to-camel-case: true
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
# 开启别名
type-aliases-package: com.example.demo.easy.domain
1. 自动配置类MybatisAutoConfiguration:
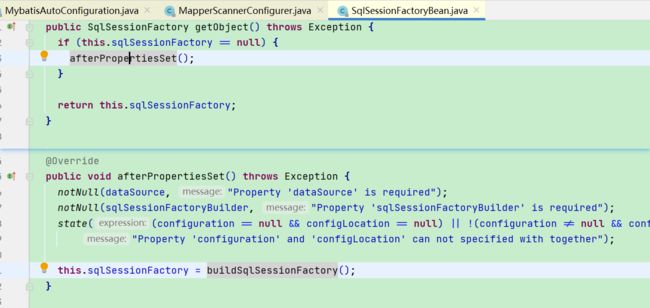
1.1. SqlSessionFactory的生成:
- 其中上述yml的mybatis配置项会被读取封装到properties里,通过SqlSessionFactoryBean来构建SqlSessionFactory
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory(DataSource dataSource) throws Exception {
SqlSessionFactoryBean factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
factory.setDataSource(dataSource);
factory.setVfs(SpringBootVFS.class);
if (StringUtils.hasText(this.properties.getConfigLocation())) {
factory.setConfigLocation(this.resourceLoader.getResource(this.properties.getConfigLocation()));
}
// ... ... 省略一些赋值,详细可看源码
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(this.properties.resolveMapperLocations())) {
factory.setMapperLocations(this.properties.resolveMapperLocations());
}
return factory.getObject();
}
org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean#buildSqlSessionFactory
- 过程中会将mybatis的配置被解析封装成Configuration对象(yml的配置项会被mybatis-config.xml的配置项覆盖)
- mapper.xml会被解析封装成MappedStatement对象(用于存储要映射的SQL语句的id、参数等信息)
- 最终会通过this.sqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build(targetConfiguration);去new一个DefaultSqlSessionFactory
protected SqlSessionFactory buildSqlSessionFactory() throws Exception {
final Configuration targetConfiguration;
XMLConfigBuilder xmlConfigBuilder = null;
if (this.configuration != null) {
... ...
} else if (this.configLocation != null) {
xmlConfigBuilder = new XMLConfigBuilder(this.configLocation.getInputStream(), null, this.configurationProperties);
targetConfiguration = xmlConfigBuilder.getConfiguration();
} else {
... ...
}
// ... ... yml的配置项赋值targetConfiguration
if (hasLength(this.typeAliasesPackage)) {
scanClasses(this.typeAliasesPackage, this.typeAliasesSuperType).stream()
.filter(clazz -> !clazz.isAnonymousClass()).filter(clazz -> !clazz.isInterface())
.filter(clazz -> !clazz.isMemberClass()).forEach(targetConfiguration.getTypeAliasRegistry()::registerAlias);
}
... ...
if (xmlConfigBuilder != null) {
try {
// 解析mybatis-config.xml配置项并会覆盖yml的配置
xmlConfigBuilder.parse();
LOGGER.debug(() -> "Parsed configuration file: '" + this.configLocation + "'");
} catch (Exception ex) {
throw new NestedIOException("Failed to parse config resource: " + this.configLocation, ex);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
... ...
if (this.mapperLocations != null) {
... ...
try {
// mapper.xml会被解析封装成MappedStatement对象(用于存储要映射的SQL语句的id、参数等信息)
XMLMapperBuilder xmlMapperBuilder = new XMLMapperBuilder(mapperLocation.getInputStream(),
targetConfiguration, mapperLocation.toString(), targetConfiguration.getSqlFragments());
xmlMapperBuilder.parse();
}
... ...
}
}
} else {
LOGGER.debug(() -> "Property 'mapperLocations' was not specified.");
}
// 创建DefaultSqlSessionFactory
return this.sqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build(targetConfiguration);
}
1.2. Mapper的扫描和代理生成:
- 如果没有使用@MapperScan和手动配置过MapperFactoryBean、MapperScannerConfigurer,默认会扫描启动类所在包路径
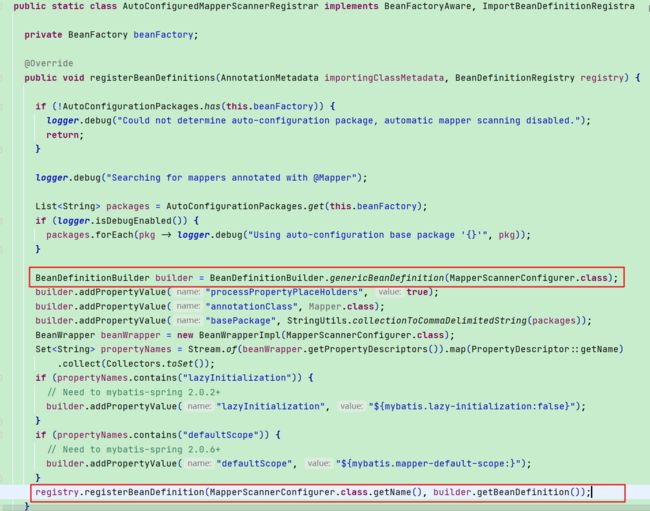
- MapperScannerRegistrarNotFoundConfiguration 这个bean还Import了
AutoConfiguredMapperScannerRegistrar- AutoConfiguredMapperScannerRegistrar实现了ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar扩展接口,容器启动时会执行registerBeanDefinitions方法
- 这个注册器中会定义
MapperScannerConfigurer的BeanDefinition,通过addPropertyValue来对内部属性赋值,然后进行注册
@org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration
@Import(AutoConfiguredMapperScannerRegistrar.class)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean({ MapperFactoryBean.class, MapperScannerConfigurer.class })
public static class MapperScannerRegistrarNotFoundConfiguration implements InitializingBean {
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
logger.debug(
"Not found configuration for registering mapper bean using @MapperScan, MapperFactoryBean and MapperScannerConfigurer.");
}
}
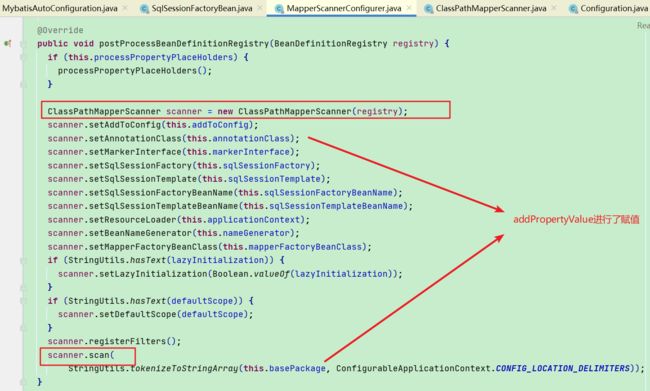
1.2.1. MapperScannerConfigurer
- 实现了BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor扩展接口,容器启动会执行postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法
- 引入类路径Mapper扫描器ClassPathMapperScanner,调用scan方法(最终调用doScan方法)进行Mapper接口扫描
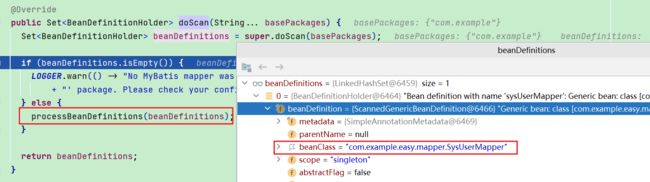
org.mybatis.spring.mapper.ClassPathMapperScanner#doScan
- ClassPathMapperScanner继承ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner,调用父类方法来扫描包路径下Mapper
- 父类的扫描器是Spring定义的,有其自身的扫描规则,最终会将Mapper接口扫描封装到BeanDefinition中
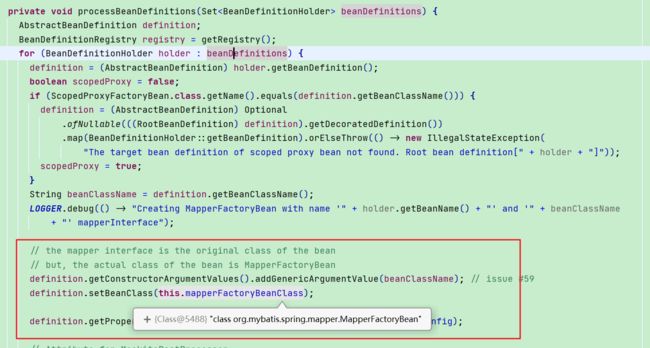
- 由于Mapper接口是没有实现类的,如果不做处理是无法生成Bean然后放入IOC容器使用的
- 所以要对BeanDefinition的beanClass做修改,修改成一个MapperFactoryBean,见processBeanDefinitions方法处理
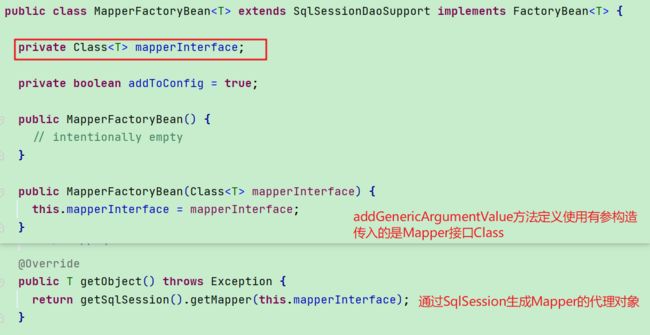
1.2.2. MapperFactoryBean
- 上文修改之后相当于beanDefinitionMap中(mapper,持有mapperClass的MapperFactoryBean的BeanDefinition)
- MapperFactoryBean实现了FactoryBean,在Bean生命周期管理时会调用getObject方法
- getObject方法中通过getMapper获取Mapper的代理对象
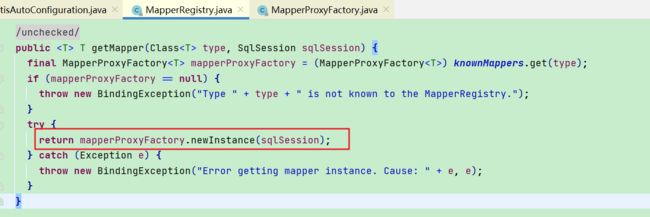
1.2.3. getMapper生成代理对象
- 最终通过MapperProxyFactory来创建Mapper的代理对象MapperProxy,可以看出采用的jdk动态代理
- 所以最终启动后IOC容器的Map储存(mapper,MapperProxy),通过DI进行注入MapperProxy使用
- MapperProxy是实现InvocationHandler的,最终调用时会触发代理对象的invoke方法
- 最终会通过SqlSessionFactor 创建的SqlSession去调用Executor执行器(入参:MappedStatement类型的参数),进行数据库操作
1.2.4. 关于FactoryBean
- 比如sysUserService中注入SysUserMapper
- 因为sysUserMapper的BeanDefinition是MapperFactoryBean,所以在sysUserService属性填充sysUserMapper时,会生成两个Bean
- 一个是MapperFactoryBean,一个是getObject方法中生成的代理对象MapperProxy,并将代理对象填充到sysUserMapper
@Service("sysUserService")
public class SysUserServiceImpl implements SysUserService {
@Resource
private SysUserMapper sysUserMapper;
@Override
public SysUser queryById(Long id) {
return sysUserMapper.queryById(id);
}
}
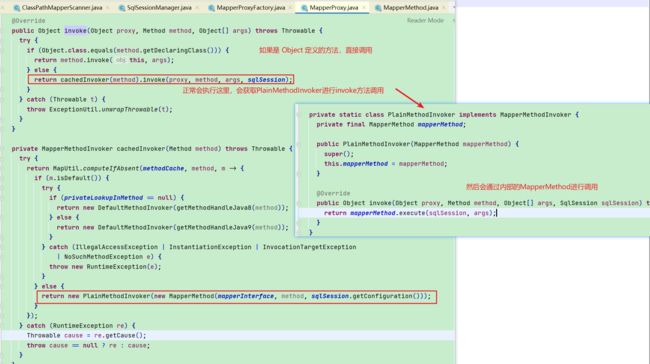
1.3. MapperProxy#invoke
- 当Mapper接口调用时,触发代理对象MapperProxy的invoke方法
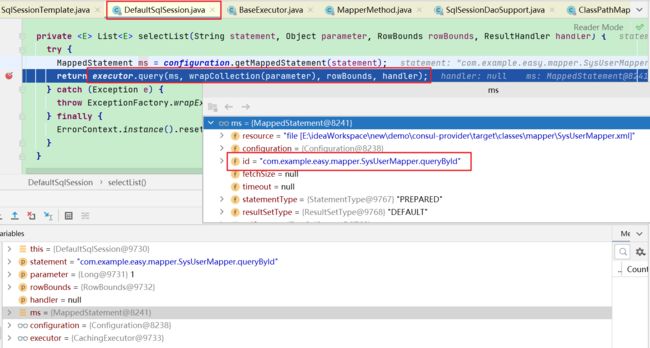
- 最终通过mapperMethod进行调用,根据对应的SqlCommand执行对应的分支代码,调用sqlSession的接口执行操作
- 自动配置时会解析Mapper.xml封装成的MappedStatement对象 ,其中SQL语句的标签,如
就会被解析封装成SqlCommandType - command.getType()就是上述的SqlCommandType
- command.getName()就是MappedStatement的id也就是namespace.id
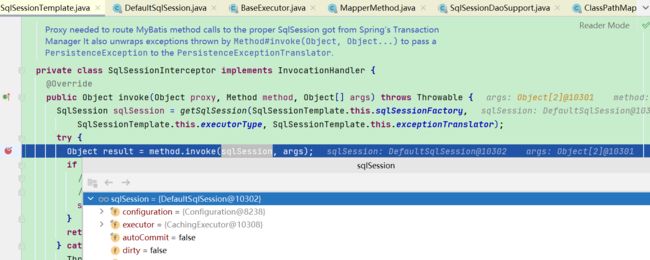
- 此时的SqlSession是SqlSessionTemplate,持有SqlSession的代理对象,调用时会触发InvocationHandler的invoke方法
- 会通过sqlSessionFactory去创建DefaultSqlSession,反射调用对应的方法
- 关于SqlSessionTemplate的介绍可查看SqlSessionTemplate的介绍及创建过程
- 然后调用执行器Executor进行JDBC操作数据库,调用过程后续再进行分析
2. 小结:
- 自动配置时,会将mybatis的配置被解析封装成Configuration对象
- mapper.xml也会被解析封装成MappedStatement对象(用于存储要映射的SQL语句的id、参数等信息)
- 然后通过this.sqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build(Configuration)去创建SqlSessionFactor
- 自动配置的过程中会通过ClassPathMapperScanner扫描器找到Mapper接口,封装成各自的BeanDefinition
- 然后循环遍历对Mapper的BeanDefinition修改beanClass为MapperFactoryBean
- MapperFactoryBean实现了FactoryBean,在Bean生命周期管理时会调用getObject方法,通过jdk动态代理生成代理对象MapperProxy
- Mapper接口请求的时候,执行MapperProxy代理类的invoke方法,执行的过程中通过SqlSessionFactory 创建的SqlSession去调用Executor执行器(入参:MappedStatement类型的参数),进行数据库操作