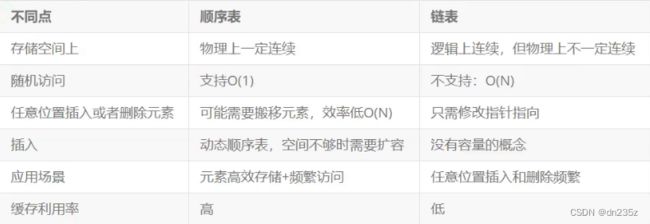
- 银行家算法
后会无期77
算法算法
文章目录银行家算法概述银行贷款案例A再次申请50万,能批准吗?B再次申请40万,能批准吗?或者C申请20万,能批准吗?安全序列和不安全序列多维度资源分配操作系统资源分配银行家算法总结数据结构银行家算法的步骤安全性算法步骤死锁的避免银行家算法概述银行家算法(Banker’sAlgorithm)是一个避免死锁(Deadlock)的著名算法,是由艾兹格·迪杰斯特拉在1965年为T.H.E系统设计的一种避
- Kyle的算法记录
Z2475269074
算法
本文将展示一个小白从0->1完成算法的全部历练已经心得PS:要求做到真正的自我思考而不是对着教程敲代码,并借用AI进行辅佐与思考LinkedListLinkedList里的add和remove,都是索引/索引+值进行操作//在链表头部插入元素0lst.addFirst(0);//在链表尾部插入元素6lst.addLast(6);队列QueueQueueq=newLinkedList();//向栈顶
- java面试题
墨京
java面试java开发语言
1.list和set的区别?list底层是数组,有序可重复,按对象进入顺序保存元素,可以有多个null元素,可以使用该iterator迭代器取出元素,也可以直接get(intindex)下标,取出元素。底层数据结构:动态数组(arraylist)或链表(Linkedlist)set底层是,无序不可重复,最多只能储存一个null元素,只能使用iterator接口取出所有元素,再逐一遍历各个元素。底层
- 深入理解Redis
深入理解Redis:高性能内存数据库的核心原理与应用实践1.引言在现代互联网应用中,高性能、低延迟的数据访问是至关重要的。传统的关系型数据库(如MySQL)虽然功能强大,但在高并发场景下往往成为性能瓶颈。Redis(RemoteDictionaryServer)应运而生,作为一个开源的内存键值数据库,它凭借极快的读写速度、丰富的数据结构和灵活的扩展能力,成为缓存、会话存储、消息队列等场景的首选解决
- 【学习】《算法图解》第八章学习笔记:平衡树
自学也学好编程
程序人生
前言在上一章中,我们学习了二叉搜索树(BST)的基本概念和操作。虽然BST在平均情况下提供了O(logn)的搜索、插入和删除效率,但在最坏情况下(如按顺序插入数据),它可能退化为链表,导致操作效率降为O(n)。为了解决这个问题,《算法图解》第八章介绍了平衡树的概念和几种主要的平衡树结构,这些结构能够在各种情况下保持较好的平衡性,确保操作的高效性。一、平衡树的基本概念(一)什么是平衡树平衡树是一种特
- 数据结构笔记3:双向链表
逑之
数据结构笔记链表c语言学习经验分享算法
目录双向链表的方法:双向链表的初始化方法我们可以对比双向链表和单链表方法在实现上的区别:双向链表的实现引进头结点的概念:双向链表的优势:1、尾插尾删2、指定位置的插入和删除双向链表:也叫做有头节点的双向循环链表双向链表的方法:typedefintLTDataType;typedefstructListNode{LTDataTypex;structListNode*next;structListNo
- 列表反转:reverse() 方法的深度剖析
测试者家园
测试开发和测试Python零基础学Python人工智能Python零基础学Python零基础职场和发展软件开发和测试智能化测试
数据结构的基本操作始终是打牢编程基础的关键。而在对列表(list)这一核心数据结构的操作中,反转(reversing)是一项既常用又容易被低估的重要操作。Python提供了原地反转的reverse()方法,与返回新序列的切片[::-1]或内置函数reversed()形成了鲜明对比。本文将全面剖析list.reverse()方法,从其语义、实现机制、适用场景,到其在测试、开发与自动化中的实际运用,力
- AcWing--数据结构1
谢耳朵(wer~wer~)
Acwing学习数据结构c++算法
用数组来模拟链表。这种实现链表的方式也叫静态链表。1.单链表写邻接表:存储图和树我们定义:e[N]用来表示某个点的值是多少;ne[N]用来表示某个点的next指针是多少e和ne是用下标关联起来的如:head->3->5->7->9->空(下标从0开始,3的下标是0,以此类推,空的下标为-1)那么e[0]=3,ne[0]=1;e[1]=5,ne[1]=2;...e[3]=9,ne[3]=-1//单
- HashMap
HansenPole825
哈希算法散列表算法
一、结构1.数组(桶数组)初始容量默认16。数组元素成为桶,每个桶存储链表或红黑树(jdk1.8及以后)。2.链表当不同key的哈希值映射到同一桶式,以链表形式存储。3.红黑树jdk1.8及以后引入红黑树:当链表长度大于等于8且桶数组长度大于等于64式,链表转化为红黑树,查询时间从O(n)降为O(logn)。树节点小于6时退化为链表二、关键机制1.哈希计算(jdk1.8)staticfinalin
- 红黑树与2-3树:插入、删除操作的时间复杂度与实现机制比较
一键难忘
红黑树数据结构
本文收录于专栏:算法之翼红黑树与2-3树:插入、删除操作的时间复杂度与实现机制比较红黑树(Red-BlackTree)和2-3树(2-3Tree)是两种广泛用于平衡二叉查找树的自平衡树结构。它们在插入、删除和查找操作中的性能都表现良好,并且可以确保树的高度是对数级别,从而保证了高效的操作时间。本文将对红黑树和2-3树进行深入的比较,并结合代码实例说明它们的实现和应用。1.数据结构简介1.1红黑树简
- deepseek:2025年Java面试必刷高频LeetCode题目
Alexon Xu
java面试leetcode
以下是2025年Java面试中高频LeetCode题目分类及对应链接,结合大厂实际考察频率整理:一、链表类反转链表(Easy)迭代法与递归实现双解,掌握三指针操作环形链表检测(Easy)快慢指针经典应用,延伸考察环入口点计算合并K个排序链表(Hard)优先队列解法时间复杂度O(NlogK)相交链表(Easy)双指针数学技巧:a+c+b=b+c+a删除链表的倒数第N个节点(Medium)快慢指针+虚
- linux驱动开发(20)-DMA(四)
yyc_audio
linux驱动开发驱动开发linux服务器
分散/聚集映射分散/聚集映射通过将虚拟地址上分散的DMA缓冲区通过一个类型为structscatterlist的数组或者链表组织起来,然后通过一次的DMA传输操作在主存RAM与设备之间传输数据,如图所示:图中显示了主存中三个分散的物理页面与设备之间进行的一次DMA传输时分散/聚集映射示意,其中单个物理页面与设备之间可以看做是一个单一的流式映射,每个这样的单一映射在内核中有数据结构structsca
- Go 中的 range 表达式详解:遍历数组、切片、字符串与 Map
Code季风
golang学习开发语言后端
在Go语言中,range是一个非常常用的结构,用于遍历集合类型的数据。它简洁、安全且易于使用,是Go开发者日常开发中最常使用的语法之一。本文将深入讲解Go的range表达式的使用方式、返回值含义以及常见错误,并通过多个示例帮助你更好地理解和应用range。一、什么是range?range是Go中用于迭代(遍历)集合类型的内置关键字,支持以下几种数据结构:数组(Array)切片(Slice)字符串(
- 数据结构与算法中单调栈的常见误区
数据结构与算法学习
服务器运维ai
数据结构与算法中单调栈的常见误区关键词:单调栈、数据结构、算法、误区、栈、时间复杂度、应用场景摘要:单调栈是一种特殊的数据结构,它在解决某些特定问题时非常高效。然而,许多初学者在使用单调栈时容易陷入一些常见的误区。本文将详细介绍单调栈的概念、原理和应用,重点分析使用单调栈时的常见误区,并通过实际代码示例展示如何正确使用单调栈解决问题。背景介绍目的和范围本文旨在帮助读者深入理解单调栈的概念和工作原理
- linux ARM64架构下进程切换核心代码分析
一、概述阶段核心代码/函数ARM64实现细节相关数据结构作用调度入口__schedule()调用context_switch()完成实际切换16structrq触发调度流程,选择下一个运行进程地址空间切换switch_mm_irqs_off()通过ttbr0_el1寄存器更新进程页表基址(PGD)3,处理ASID和TLB失效410structmm_struct(含pgd
- 【LangGraph】langgraph.store.base 模块:定义持久化键值存储的核心模块
彬彬侠
LangGraphLangGraphstorebase
有条理的详细介绍langgraph.store.base模块langgraph.store.base模块是LangGraph框架中用于定义持久化键值存储的核心模块,提供了标准化的接口和数据结构,以支持状态管理和长时记忆存储。它是LangGraph的重要组成部分,特别适合构建复杂、状态化的多代理应用。本文将从背景、功能、主要组件、使用方法、实际应用及注意事项等方面,详细介绍该模块,帮助开发者理解其设
- Python collections.abc模块介绍
qq_27390023
python开发语言
collections.abc是Python标准库中的一个模块,提供了一系列抽象基类(AbstractBaseClasses,ABCs),用于定义和检查容器类型(如序列、映射、集合等)的接口。这些抽象基类为常见的数据结构提供了统一的接口和行为规范,使得开发者可以更方便地实现和使用这些数据结构。1.collections.abc的作用collections.abc模块的主要作用是提供一组抽象基类,用
- 从Python到数据结构:为什么这是每个自学者必经的进阶之路
流水煮香茗
python数据结构mooc
当你熟练掌握Python语法后,下一步应该学什么?答案是数据结构。本文将深入分析为什么数据结构是编程进阶的关键,以及如何选择合适的学习资源。一、Python学会了,然后呢?如果你正在读这篇文章,很可能你已经:用Python写过小工具,能解决工作和生活中的一些小需求做过数据分析,会用pandas处理Excel表格但是,当你想要进一步提升时,却发现了一些困惑:困惑1:代码能跑,但总觉得"不够优雅"你的
- 【项目实战】Redis使用场景之基于Redis实现分布式限流
本本本添哥
002-进阶开发能力003-数据库redis分布式数据库
一、技术概览1.1定义分布式限流是指在分布式系统中限制请求的速率,以保护后端服务不被过多的请求压垮。它可以帮助我们控制系统的负载,保证服务的稳定性。Redis是一个高性能的键值存储系统,常用于缓存、消息队列和实时分析等场景。由于其支持丰富的数据结构和原子操作,非常适合用来实现分布式限流。专业术语:令牌桶算法(TokenBucket):一种流量整形算法,允许突发流量但不超过平均速度。漏桶算法(Lea
- 基于Anaconda环境开发IntelliJ IDEA实用JSON转Java实体插件
七夜zippoe
后端#Javajavajsonintellij-idea
在软件开发中,将JSON数据转换为Java实体类是常见需求。借助Anaconda环境强大的包管理能力与IntelliJIDEA的插件开发体系,我们可以打造一款高效实用的JSON转Java实体插件,显著提升开发效率。下面将从需求分析、技术选型、开发实现到优化部署,全方位阐述这款插件的开发过程。需求分析:明确痛点与功能方向在日常开发中,开发者经常需要根据JSON数据结构手动创建对应的Java实体类,这
- 整合性安全总结(ISS)早期规划
qq_34062333
临床试验NDA
1.ISS统一性建设工作启动1.1研究元数据标准化1.1.1不同类型研究元数据规范DBL研究锁定数据库后,需梳理元数据,确保信息完整准确,为后续分析奠定基础。OL研究进行中,实时更新元数据,反映研究进展,避免数据偏差影响结果。新启动研究,依据统一模板构建元数据,减少初期工作量,提高研究效率。1.1.2cADaM规范建立结合各类研究特点,制定跨研究核心分析数据集规范,提升数据整合性。规范涵盖数据结构
- 47、文件系统操作与管理
nnn11
C++编程精华:从基础到高级C++文件系统std::filesystem
文件系统操作与管理1.文件系统的概述文件系统是操作系统中用于组织、管理和存储文件的数据结构。在C++中,文件系统的操作主要依赖于标准库中的头文件,该库提供了丰富的API来处理文件和目录。通过std::filesystem命名空间,开发者可以轻松地进行文件路径解析、目录遍历、文件属性查询等操作,极大地提高了代码的可读性和可维护性。2.库简介C++17引入了库,使得文件系统操作更加简便和高效。std:
- 【学习】《算法图解》第七章学习笔记:树
程序员
前言在前面的章节中,我们学习了数组、链表、散列表等基本数据结构,以及一些基础算法。本章将介绍一种非常重要的数据结构——树(Tree),特别是二叉搜索树(BinarySearchTree)。树结构在计算机科学中应用广泛,从文件系统到数据库再到人工智能,都能看到树的身影。《算法图解》第七章深入浅出地介绍了树的基本概念、实现和应用,帮助读者理解这一关键数据结构。一、树的基本概念(一)什么是树树是一种分层
- 弹幕系统开发实战:QT框架与VS2015源码解析
Paula-柒月拾
本文还有配套的精品资源,点击获取简介:本源码项目融合了三个关键技术领域:弹幕系统设计、Qt框架开发和VisualStudio2015集成。它详细阐述了弹幕系统的核心功能实现,包括弹幕数据结构、渲染、碰撞检测和用户交互。同时,本项目介绍了如何利用Qt5的信号与槽机制、GUI组件和绘图系统来开发弹幕效果,并展示了如何在VisualStudio2015中进行项目管理、编辑、调试和构建。此项目提供了全面的
- Collection的子接口之【List】
丶小鱼丶
Java集合框架list数据结构
目录List自身提供了和index相关的方法List的特点List的常见实现类ArrayList底层数据结构是数组懒加载的体现最大容量为int类型的最大值扩容机制使用equals方法来判断是否包含某个元素随机增删元素效率较低,需要移动元素,时间复杂度为O(n)LinkedList底层数据结构是双向链表add(Ee)和remove()方法获取元素需要遍历节点,效率较低,时间复杂度为O(n)随机增删元
- python 内存空间管理、垃圾回收机制、对象的引用机制、引用计数法
贵哥的编程之路(热爱分享 为后来者)
开发语言python
一、对象与内存空间在Python中,一切皆对象。每当你创建一个变量、数据结构、函数、类实例等,Python都会在内存中为它分配空间。对象的内存空间由Python的内存管理器自动分配和回收,开发者无需手动管理。二、垃圾回收(GarbageCollection)垃圾回收指的是:当对象不再被使用时,Python会自动销毁该对象并释放其占用的内存空间。这样可以防止“内存泄漏”,让程序长期运行也不会因为无用
- 【学习】《算法图解》第七章学习笔记:树
自学也学好编程
程序人生
前言在前面的章节中,我们学习了数组、链表、散列表等基本数据结构,以及一些基础算法。本章将介绍一种非常重要的数据结构——树(Tree),特别是二叉搜索树(BinarySearchTree)。树结构在计算机科学中应用广泛,从文件系统到数据库再到人工智能,都能看到树的身影。《算法图解》第七章深入浅出地介绍了树的基本概念、实现和应用,帮助读者理解这一关键数据结构。一、树的基本概念(一)什么是树树是一种分层
- Python性能优化指南:让你的代码提速10倍的实用技巧
天天进步2015
pythonpython
Python以其简洁易用著称,但在性能方面常被诟病。其实,通过一些实用的优化技巧,你的Python代码性能完全可以提升数倍甚至十倍。本文将结合实际经验,系统介绍Python性能优化的常见思路与方法,并给出具体案例,助你写出高效的Python程序。1.算法与数据结构优化优先选择合适的数据结构:如查找用set/dict,顺序存储用list。避免不必要的嵌套循环,能用集合操作、字典映射解决的,绝不用暴力
- 虚幻引擎编程反射系统实现
污领巾
虚幻php游戏引擎
提示:文章写完后,目录可以自动生成,如何生成可参考右边的帮助文档文章目录前言1、反射的核心实现流程1.1宏定义标记1.2UnrealHeaderTool(UHT)处理1.3生成的代码结构1.4运行时反射数据注册2、反射系统的关键数据结构2.1UClass2.2UProperty及其派生类2.3UFunction3、反射的实际应用场景3.1蓝图与C++交互3.2序列化与反序列化3.3网络同步(Rep
- C# 索引器(Indexer)
C#索引器(Indexer)引言在C#编程语言中,索引器(Indexer)是一种特殊类型的属性,它允许我们通过索引来访问和设置对象的成员。索引器是动态数组和集合的基石,同时也可以用于创建自定义的数据结构,如字典等。本文将深入探讨C#索引器的概念、实现方式以及在实际开发中的应用。索引器的基本概念索引器是一种属性,它允许通过索引来访问和设置对象的成员。与普通的属性相比,索引器可以接受一个或多个参数,从
- HttpClient 4.3与4.3版本以下版本比较
spjich
javahttpclient
网上利用java发送http请求的代码很多,一搜一大把,有的利用的是java.net.*下的HttpURLConnection,有的用httpclient,而且发送的代码也分门别类。今天我们主要来说的是利用httpclient发送请求。
httpclient又可分为
httpclient3.x
httpclient4.x到httpclient4.3以下
httpclient4.3
- Essential Studio Enterprise Edition 2015 v1新功能体验
Axiba
.net
概述:Essential Studio已全线升级至2015 v1版本了!新版本为JavaScript和ASP.NET MVC添加了新的文件资源管理器控件,还有其他一些控件功能升级,精彩不容错过,让我们一起来看看吧!
syncfusion公司是世界领先的Windows开发组件提供商,该公司正式对外发布Essential Studio Enterprise Edition 2015 v1版本。新版本
- [宇宙与天文]微波背景辐射值与地球温度
comsci
背景
宇宙这个庞大,无边无际的空间是否存在某种确定的,变化的温度呢?
如果宇宙微波背景辐射值是表示宇宙空间温度的参数之一,那么测量这些数值,并观测周围的恒星能量输出值,我们是否获得地球的长期气候变化的情况呢?
&nbs
- lvs-server
男人50
server
#!/bin/bash
#
# LVS script for VS/DR
#
#./etc/rc.d/init.d/functions
#
VIP=10.10.6.252
RIP1=10.10.6.101
RIP2=10.10.6.13
PORT=80
case $1 in
start)
/sbin/ifconfig eth2:0 $VIP broadca
- java的WebCollector爬虫框架
oloz
爬虫
WebCollector主页:
https://github.com/CrawlScript/WebCollector
下载:webcollector-版本号-bin.zip将解压后文件夹中的所有jar包添加到工程既可。
接下来看demo
package org.spider.myspider;
import cn.edu.hfut.dmic.webcollector.cra
- jQuery append 与 after 的区别
小猪猪08
1、after函数
定义和用法:
after() 方法在被选元素后插入指定的内容。
语法:
$(selector).after(content)
实例:
<html>
<head>
<script type="text/javascript" src="/jquery/jquery.js"></scr
- mysql知识充电
香水浓
mysql
索引
索引是在存储引擎中实现的,因此每种存储引擎的索引都不一定完全相同,并且每种存储引擎也不一定支持所有索引类型。
根据存储引擎定义每个表的最大索引数和最大索引长度。所有存储引擎支持每个表至少16个索引,总索引长度至少为256字节。
大多数存储引擎有更高的限制。MYSQL中索引的存储类型有两种:BTREE和HASH,具体和表的存储引擎相关;
MYISAM和InnoDB存储引擎
- 我的架构经验系列文章索引
agevs
架构
下面是一些个人架构上的总结,本来想只在公司内部进行共享的,因此内容写的口语化一点,也没什么图示,所有内容没有查任何资料是脑子里面的东西吐出来的因此可能会不准确不全,希望抛砖引玉,大家互相讨论。
要注意,我这些文章是一个总体的架构经验不针对具体的语言和平台,因此也不一定是适用所有的语言和平台的。
(内容是前几天写的,现附上索引)
前端架构 http://www.
- Android so lib库远程http下载和动态注册
aijuans
andorid
一、背景
在开发Android应用程序的实现,有时候需要引入第三方so lib库,但第三方so库比较大,例如开源第三方播放组件ffmpeg库, 如果直接打包的apk包里面, 整个应用程序会大很多.经过查阅资料和实验,发现通过远程下载so文件,然后再动态注册so文件时可行的。主要需要解决下载so文件存放位置以及文件读写权限问题。
二、主要
- linux中svn配置出错 conf/svnserve.conf:12: Option expected 解决方法
baalwolf
option
在客户端访问subversion版本库时出现这个错误:
svnserve.conf:12: Option expected
为什么会出现这个错误呢,就是因为subversion读取配置文件svnserve.conf时,无法识别有前置空格的配置文件,如### This file controls the configuration of the svnserve daemon, if you##
- MongoDB的连接池和连接管理
BigCat2013
mongodb
在关系型数据库中,我们总是需要关闭使用的数据库连接,不然大量的创建连接会导致资源的浪费甚至于数据库宕机。这篇文章主要想解释一下mongoDB的连接池以及连接管理机制,如果正对此有疑惑的朋友可以看一下。
通常我们习惯于new 一个connection并且通常在finally语句中调用connection的close()方法将其关闭。正巧,mongoDB中当我们new一个Mongo的时候,会发现它也
- AngularJS使用Socket.IO
bijian1013
JavaScriptAngularJSSocket.IO
目前,web应用普遍被要求是实时web应用,即服务端的数据更新之后,应用能立即更新。以前使用的技术(例如polling)存在一些局限性,而且有时我们需要在客户端打开一个socket,然后进行通信。
Socket.IO(http://socket.io/)是一个非常优秀的库,它可以帮你实
- [Maven学习笔记四]Maven依赖特性
bit1129
maven
三个模块
为了说明问题,以用户登陆小web应用为例。通常一个web应用分为三个模块,模型和数据持久化层user-core, 业务逻辑层user-service以及web展现层user-web,
user-service依赖于user-core
user-web依赖于user-core和user-service
依赖作用范围
Maven的dependency定义
- 【Akka一】Akka入门
bit1129
akka
什么是Akka
Message-Driven Runtime is the Foundation to Reactive Applications
In Akka, your business logic is driven through message-based communication patterns that are independent of physical locatio
- zabbix_api之perl语言写法
ronin47
zabbix_api之perl
zabbix_api网上比较多的写法是python或curl。上次我用java--http://bossr.iteye.com/blog/2195679,这次用perl。for example: #!/usr/bin/perl
use 5.010 ;
use strict ;
use warnings ;
use JSON :: RPC :: Client ;
use
- 比优衣库跟牛掰的视频流出了,兄弟连Linux运维工程师课堂实录,更加刺激,更加实在!
brotherlamp
linux运维工程师linux运维工程师教程linux运维工程师视频linux运维工程师资料linux运维工程师自学
比优衣库跟牛掰的视频流出了,兄弟连Linux运维工程师课堂实录,更加刺激,更加实在!
-----------------------------------------------------
兄弟连Linux运维工程师课堂实录-计算机基础-1-课程体系介绍1
链接:http://pan.baidu.com/s/1i3GQtGL 密码:bl65
兄弟连Lin
- bitmap求哈密顿距离-给定N(1<=N<=100000)个五维的点A(x1,x2,x3,x4,x5),求两个点X(x1,x2,x3,x4,x5)和Y(
bylijinnan
java
import java.util.Random;
/**
* 题目:
* 给定N(1<=N<=100000)个五维的点A(x1,x2,x3,x4,x5),求两个点X(x1,x2,x3,x4,x5)和Y(y1,y2,y3,y4,y5),
* 使得他们的哈密顿距离(d=|x1-y1| + |x2-y2| + |x3-y3| + |x4-y4| + |x5-y5|)最大
- map的三种遍历方法
chicony
map
package com.test;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
public class TestMap {
public static v
- Linux安装mysql的一些坑
chenchao051
linux
1、mysql不建议在root用户下运行
2、出现服务启动不了,111错误,注意要用chown来赋予权限, 我在root用户下装的mysql,我就把usr/share/mysql/mysql.server复制到/etc/init.d/mysqld, (同时把my-huge.cnf复制/etc/my.cnf)
chown -R cc /etc/init.d/mysql
- Sublime Text 3 配置
daizj
配置Sublime Text
Sublime Text 3 配置解释(默认){// 设置主题文件“color_scheme”: “Packages/Color Scheme – Default/Monokai.tmTheme”,// 设置字体和大小“font_face”: “Consolas”,“font_size”: 12,// 字体选项:no_bold不显示粗体字,no_italic不显示斜体字,no_antialias和
- MySQL server has gone away 问题的解决方法
dcj3sjt126com
SQL Server
MySQL server has gone away 问题解决方法,需要的朋友可以参考下。
应用程序(比如PHP)长时间的执行批量的MYSQL语句。执行一个SQL,但SQL语句过大或者语句中含有BLOB或者longblob字段。比如,图片数据的处理。都容易引起MySQL server has gone away。 今天遇到类似的情景,MySQL只是冷冷的说:MySQL server h
- javascript/dom:固定居中效果
dcj3sjt126com
JavaScript
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml&
- 使用 Spring 2.5 注释驱动的 IoC 功能
e200702084
springbean配置管理IOCOffice
使用 Spring 2.5 注释驱动的 IoC 功能
developerWorks
文档选项
将打印机的版面设置成横向打印模式
打印本页
将此页作为电子邮件发送
将此页作为电子邮件发送
级别: 初级
陈 雄华 (
[email protected]), 技术总监, 宝宝淘网络科技有限公司
2008 年 2 月 28 日
&nb
- MongoDB常用操作命令
geeksun
mongodb
1. 基本操作
db.AddUser(username,password) 添加用户
db.auth(usrename,password) 设置数据库连接验证
db.cloneDataBase(fromhost)
- php写守护进程(Daemon)
hongtoushizi
PHP
转载自: http://blog.csdn.net/tengzhaorong/article/details/9764655
守护进程(Daemon)是运行在后台的一种特殊进程。它独立于控制终端并且周期性地执行某种任务或等待处理某些发生的事件。守护进程是一种很有用的进程。php也可以实现守护进程的功能。
1、基本概念
&nbs
- spring整合mybatis,关于注入Dao对象出错问题
jonsvien
DAOspringbeanmybatisprototype
今天在公司测试功能时发现一问题:
先进行代码说明:
1,controller配置了Scope="prototype"(表明每一次请求都是原子型)
@resource/@autowired service对象都可以(两种注解都可以)。
2,service 配置了Scope="prototype"(表明每一次请求都是原子型)
- 对象关系行为模式之标识映射
home198979
PHP架构企业应用对象关系标识映射
HELLO!架构
一、概念
identity Map:通过在映射中保存每个已经加载的对象,确保每个对象只加载一次,当要访问对象的时候,通过映射来查找它们。其实在数据源架构模式之数据映射器代码中有提及到标识映射,Mapper类的getFromMap方法就是实现标识映射的实现。
二、为什么要使用标识映射?
在数据源架构模式之数据映射器中
//c
- Linux下hosts文件详解
pda158
linux
1、主机名: 无论在局域网还是INTERNET上,每台主机都有一个IP地址,是为了区分此台主机和彼台主机,也就是说IP地址就是主机的门牌号。 公网:IP地址不方便记忆,所以又有了域名。域名只是在公网(INtERNET)中存在,每个域名都对应一个IP地址,但一个IP地址可有对应多个域名。 局域网:每台机器都有一个主机名,用于主机与主机之间的便于区分,就可以为每台机器设置主机
- nginx配置文件粗解
spjich
javanginx
#运行用户#user nobody;#启动进程,通常设置成和cpu的数量相等worker_processes 2;#全局错误日志及PID文件#error_log logs/error.log;#error_log logs/error.log notice;#error_log logs/error.log inf
- 数学函数
w54653520
java
public
class
S {
// 传入两个整数,进行比较,返回两个数中的最大值的方法。
public
int
get(
int
num1,
int
nu