C++ 文件流详解
前言:
我们刚开始学习C 时,都是使用iostream里面的cin和cout进行控制台的输入和输出,现在我们学习如何从文件读取流和向文件写入流。
IO: 向设备输入数据和输出数据
设备:
- 文件
- 控制台
- 特定的数据类型(stringstream)
c 中,必须通过特定的已经定义好的类, 来处理IO(输入输出)

欲要使用文件流,这就需要用到 C 中的标准库 #include < fstream >,它定义了三个数据类型:
ofstream:该数据类型表示输出文件流,用于创建文件并向文件写入信息。
ifstream:该数据类型表示输入文件流,用于从文件读取信息。
fstream:该数据类型表示输入和输出文件流,且同时具有 ofstream 和 ifstream 两种功能,这意味着它可以创建文件,向文件写入信息,从文件读取信息。
定义文件流
想要使用文件流对文件进行操作,修必须要先定义它。
定义时须包含头文件#include< fstream >
三种定义方法:
#include 打开文件
在从文件读取信息或者向文件写入信息之前,必须先打开文件。ofstream 和fstream 对象都可以用来打开文件进行写操作,如果只需要打开文件进行读操作,则使用 ifstream 和 fstream对象。
打开文件的方法:
使用open()函数进行文件的打开
#include < fstream >
void open( const char *filename );
例1:ofstream打开文件的方式(写数据进文件中)
ofstream outFile;
outFile.open("demo.txt"); // 默认方式打开文件
例2:ifstream打开文件的方式(读取文件中的数据)
ifstream inFile;
inFile.open("demo.txt"); // 默认当方式打开文件
例3: fstream打开文件的方式(读写文件中的数据)
fstream stream
stream.open("demo.txt"); // 默认方式打开文件
文件的打开方式
| 模式标志 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| ios::in | 读方式打开文件 |
| ios::out | 写方式打开文件 |
| ios::trunc | 如果此文件已经存在, 就会打开文件之前把文件长度截断为0 |
| ios::app | 尾部最加方式(在尾部写入) |
| ios::ate | 文件打开后, 定位到文件尾 |
| ios::binary | 二进制方式(默认是文本方式) |
以上打开方式, 可以使用位操作 | 组合起来
例:
如果你只是想对文件进行写入操作,当文件已经存在时,你希望对该文件进行截断操作,那么就可这样组合:
fstream stream;
stream.open("demo.txt", ios::out | ios::trunc);
如果你只是想对文件进行读取操作,而且想在文件尾部读取,那么就可以这样组合:
fstrem inFile;
inFile.open("demo.txt", ios::in | ios::ate);
判断文件是否打开成功
使用is_open()函数进行文件的判断
当成功打开文件返回真(true),失败返回假(false)
例:
fstream stream;
stream.open("demo.txt");
// 判断文件是否打开成功
if (!stream.is_open()) {
cout << "文件打开失败!" << endl;
system("pause");
exit(-1);
}
关闭文件
使用close()函数进行关闭文件
函数的作用是:关闭相关的文件流。
例:
// 定义文件流
fstream stream;
// 打开文件
stream.open("demo.txt");
// 关闭文件
stream.close();
///
我们要养成好习惯,打开文件后,一定义要关闭文件再结束程序。
写文件
在C 中,写文件除了要用到ofstream 或者 fstream 外,我们还需要用到一个流插入运算符(<<)。
例:
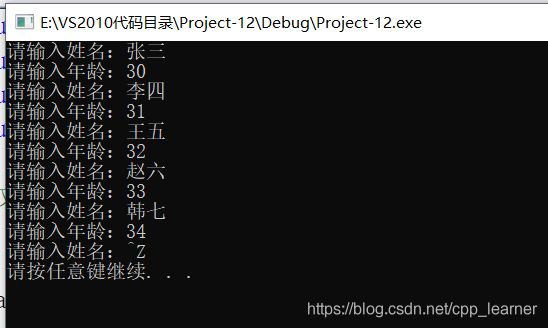
需求:
让用户来输入姓名和年龄,并保存到文件中。
直到用户输入ctrl z
/*
需求:
让用户来输入姓名和年龄,并保存到文件中。
直到用户输入ctrl z
*/
#include 读文件
在C 中,读文件除了要用到ifstream 或者 fstream 外,我们还需要用到一个流插入运算符(>>)。
例:
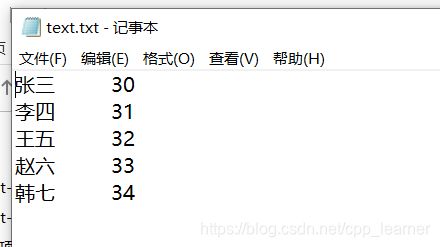
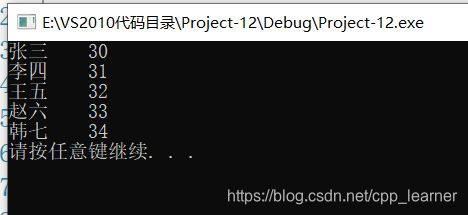
需求:
在上一个写入文件的例子中,把它写入的text.txt文件中的所有内容都读取出来,并打印出来。
#include 读取文件中的一行数据
使用getline()可以读取文件中的一行数据
例:
stream inFile;
string line;
inFile("text.txt");
// 从文件中读取一行数据,并将读取到的数据写入字符串变量line中
getline(inFile, line);
总结:
好了,这就是文件的基本用法,C 文件并不难,只要理解好,读取文件要用到搞混文件流,写入文件要用到哪个文件流;需要用到什么方式打开文件等等。不要搞混。