【深蓝学院】手写VIO第7章--VINS初始化和VIO系统--作业
0. 内容
1. T1
1. 下载EuRoc数据集(optional)
因为作业主要使用Ch2生成的数据,所以这一步也是可选的,但是为了整个系统的bring up,可以先用EuRoc数据集跑起来。
下载EuRoc数据集,SLAM相关数据集链接
2. 更换ceres版本(optional)
代码编译不过,发现是安装了最新的ceres 2.2,导致代码库里面有些东西被替换掉了,找不到,所以卸载掉2.2,安装2.1
卸载并安装新版本的ceres
3. 双版本OpenCV共存,切换(optional)
由于之前安装了OpenCV的4.6.0,导致编译不过,但是又不想卸载较新的版本,所以找了下使两个OpenCV版本共存的方法,参考博客,看了VINS-MONO使用的是3.3.1版本,就另外安装了这个版本,最后效果如下:
只需要在find_package前更改OpenCV_DIR即可找到另一个版本的OpenCV。

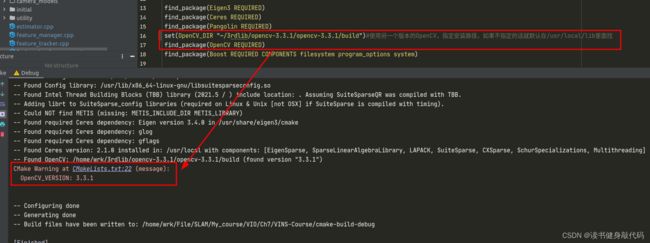
切换完之后就编译过了。
4. 解答
4.1 问题分析与解答
本章代码主要有三个线程:
- IMU线程 从Euroc数据集的IMU文件读取IMU数据
- Tracking线程 从Euroc数据集的Image文件读取Image数据, 并做光流跟踪等特征处理操作
- Estimator线程 后端处理, 根据前端提供的IMU数据和特征数据, 做预积分和相关后端优化
4.1.1 pub_imu
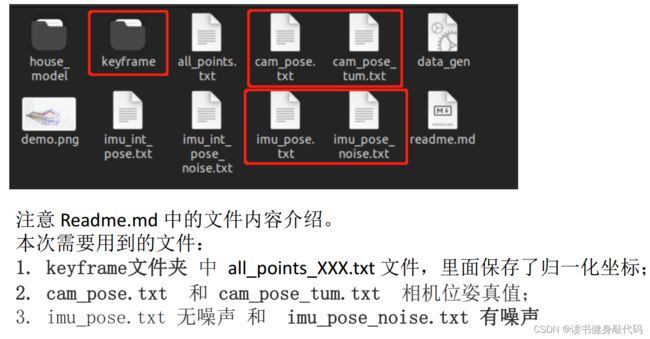
要清楚Ch2中生成的数据的header都是什么,cam_pose.txt和imu_pose.txt都分别是:
time_stamp, w, x, y, z, tx, ty, tz, gyro_x, gyro_y, gyro_z, acc_x, acc_y, acc_z
all_points_xxx.txt共7维数据:
x,y,z,1,u,v
x,y,z是landmark在camera系下的3D坐标,1代表是齐次的,u,v是归一化平面上的坐标(注意不要被u,v的名字混淆,归一化平面还是在camera系下,只是深度变成了1,还不是在像素平面下,等会儿还要用内参转换到像素平面上)
IMU数据我们只需要time_stamp和6维IMU数据, 而与imu posetime和w, x, y, z, tx, ty, tz我们都不需要,在读取时直接刷掉即可。
//将IMU数据传入VINS系统
void PubImuData()
{
string sImu_data_file = sConfig_path + "imu_pose.txt";//数据中的RSS不知道是什么,但是应该是6轴IMU数据
cout << "1 PubImuData start sImu_data_filea: " << sImu_data_file << endl;
ifstream fsImu;
fsImu.open(sImu_data_file.c_str());
if (!fsImu.is_open())
{
cerr << "Failed to open imu file! " << sImu_data_file << endl;
return;
}
std::string sImu_line;
double dStampNSec = 0.0;
Vector3d vAcc;
Vector3d vGyr;
while (std::getline(fsImu, sImu_line) && !sImu_line.empty()) // read imu data
{
std::istringstream ssImuData(sImu_line);
double tmp_data;//imu的pose不需要,所以不进行读取
ssImuData >> dStampNSec >> tmp_data >> tmp_data >> tmp_data >> tmp_data >> tmp_data >> tmp_data >> tmp_data
>> vGyr.x() >> vGyr.y() >> vGyr.z() >> vAcc.x() >> vAcc.y() >> vAcc.z();//读取时间戳,角速度,加速度
pSystem->PubImuData(dStampNSec, vGyr, vAcc);//这里读出来的时间直接就是s,不用再转
usleep(5000*nDelayTimes);
}
fsImu.close();
printf("imu pub finish!!!\n");
}
4.1.1 pub_img
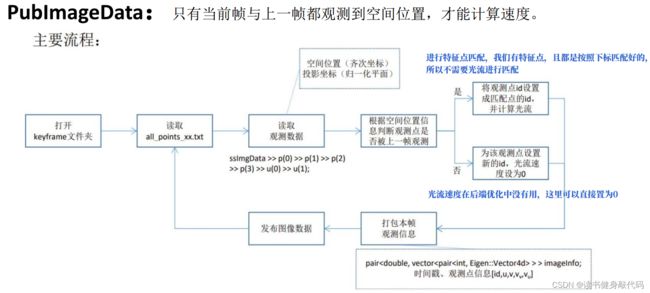
关于pub_img,由于我们直接有了匹配好的feature points,所有关于前端特征处理的都不用做(特征提取,LK光流匹配,去畸变等,也不用算光流的速度(虽然我算了一下)),我们需要做的核心的事情就是把这些feature喂给我们的特征点buffer(即代码中的feature_points)
代码如下:
run_euroc.cpp关于img的部分
//将视觉特征传入VINS系统
void PubImageData()
{
string sImage_file = sConfig_path + "cam_pose.txt";
printf("start pub img msg...\n");
printf("sImage_file: %s\n", sImage_file.c_str());
cout << "1 PubImageData start sImage_file: " << sImage_file << endl;
ifstream fsImage;
fsImage.open(sImage_file.c_str());
if (!fsImage.is_open()) {
cerr << "Failed to open image file! " << sImage_file << endl;
return;
}
std::string sImage_line;
double dStampNSec;
string sImgFileName;
vector<Matrix<double,6,1>> xyz_uv_sum;
int point_num = 0;
// cv::namedWindow("SOURCE IMAGE", CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
while (std::getline(fsImage, sImage_line) && !sImage_line.empty())
{
std::istringstream ssImgData(sImage_line);
ssImgData >> dStampNSec;//读取camera时间戳
Matrix<double,6,1> xyz_uv;
string KF_PointsFile = sConfig_path + "keyframe/all_points_" + to_string(point_num++) + ".txt";//读all_points_xx.txt
ifstream fin(KF_PointsFile);
if(!fin) {
printf("[ERROR] KF file: %s do not exist", KF_PointsFile.c_str());
}
printf("KF_PointsFile: %s\n", KF_PointsFile.c_str());
while(!fin.eof()) {
fin >> xyz_uv(0) >> xyz_uv(1) >> xyz_uv(2) >> xyz_uv(3) >> xyz_uv(4) >> xyz_uv(5);
xyz_uv_sum.push_back(xyz_uv);
}
pSystem->PubImageData(dStampNSec, xyz_uv_sum);//
xyz_uv_sum.clear();
// cv::imshow("SOURCE IMAGE", img);
// cv::waitKey(0);
usleep(50000*nDelayTimes);
}
fsImage.close();
printf("pub img finish, point_num: %d\n", point_num);
}
system.cpp
void System::PubImageData(double dStampSec, vector<Matrix<double,6,1>> &img)
{
PUB_THIS_FRAME = true;//直接pub
if (PUB_THIS_FRAME)
{
pub_count++;
printf("pub count: %d\n", pub_count);
shared_ptr<IMG_MSG> feature_points(new IMG_MSG());
feature_points->header = dStampSec;
vector<set<int>> hash_ids(NUM_OF_CAM);
for (int i = 0; i < NUM_OF_CAM; i++)
{
vector<cv::Point2f> tmp_pts;
printf("img.size: %d\n", img.size());
for (unsigned int j = 0; j < img.size(); j++)
{
int p_id = j;
hash_ids[i].insert(p_id);
double x = img[j][4];
double y = img[j][5];
double z = 1;
double u = 460 * x + 255; //u=fx * x / z + cx 使用内参将归一化坐标转换到像素平面下
double v = 460 * y + 255; //u=fx * x / z + cx
feature_points->points.emplace_back(x, y, z);
feature_points->id_of_point.push_back(p_id * NUM_OF_CAM + i);
feature_points->u_of_point.push_back(u);//仿真数据直接用xy代替像素坐标
feature_points->v_of_point.push_back(v);
tmp_pts.emplace_back(u, v);
if(prev_pts_.empty()) {
feature_points->velocity_x_of_point.push_back(0); //第一帧速度设为0
feature_points->velocity_y_of_point.push_back(0);
printf("prev_pts_ is empty set cur volecity to zero, cur_(u,v)=(%f, %f)\n", u, v);
} else {
//由于feature points都是一一对应的,所以直接取对应index的坐标相减然后处以时间即可得速度
double v_x = (u - prev_pts_[j].x) / 0.0333333;
double v_y = (v - prev_pts_[j].y) / 0.0333333;
feature_points->velocity_x_of_point.push_back(v_x);
feature_points->velocity_y_of_point.push_back(v_y);
printf("prev_(u,v)=(%f, %f), cur_(u,v)=(%f, %f), v_x: %f, v_y: %f\n",
prev_pts_[j].x, prev_pts_[j].y, u, v, v_x, v_y);
}
}
prev_pts_.clear();
prev_pts_ = tmp_pts;
tmp_pts.clear();
//}
// skip the first image; since no optical speed on frist image
if (!init_pub)
{
cout << "4 PubImage init_pub skip the first image!" << endl;
init_pub = 1;
}
else
{
m_buf.lock();
feature_buf.push(feature_points);
// cout << "5 PubImage t : " << fixed << feature_points->header
// << " feature_buf size: " << feature_buf.size() << endl;
m_buf.unlock();
con.notify_one();
}
}
}
}
总是会需要debug的,clion传参:
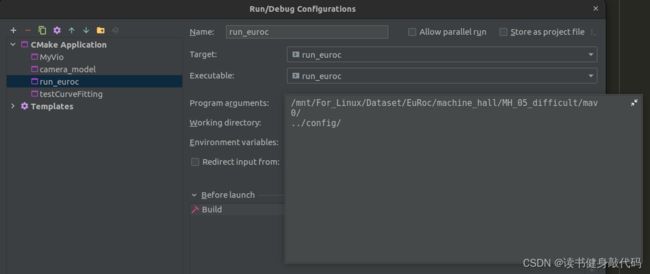
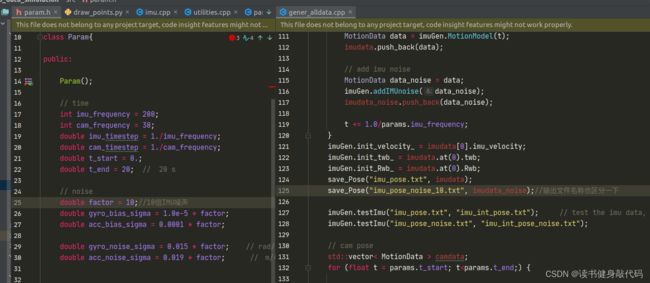
关于噪声的操作,我看很多博客都没有明说,不同噪声需要配置Ch2的参数先生成带有noise的文件imu_pose_noise.txt,然后将参数配置给VINS系统(比如乘了10倍就在VINS配置中也乘10),跑出来即可。
ch2生成noise数据配置:
VINS imu noise配置,这里我使用了离散的噪声(连续噪声就不用下面最后4行即可):
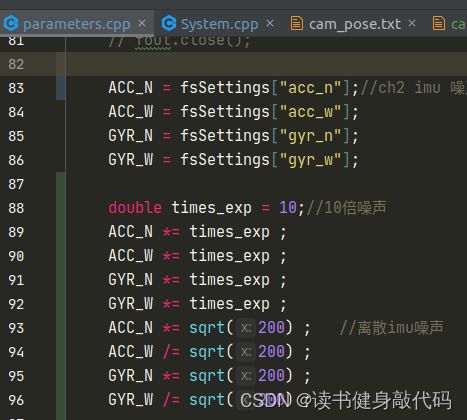
4.1.2 踩过的坑(optional)
分别在noise为0, 1,10, 30, 45, 60倍时进行了实验,需要说明一下,因为没有fix第一帧,所以会使得整体的pose在GT的world系下有漂移,我当时使用Ch2的可视化工具可视化出来output和GT发现差了个T,但是把T算出来感觉也不是固定的(事实证明T确实是固定的,但是不知道怎么align起来的,这部分evo直接给出了T),当时对着python脚本可视化出来的结果发愁了好一会儿,后来发现他们的作业都是使用evo可视化的(evo下文会讲)
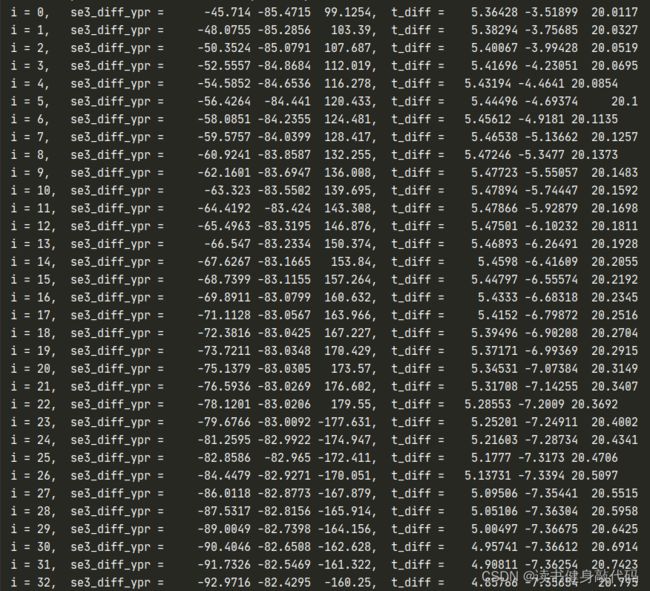
当时计算T的代码
void cal_diff() {
Quaterniond q;
Eigen::Matrix<double, 3, 1> tmp_mat;
double tmp_var;
vector<Sophus::SE3d> vec_T_gt;
std::string cam_pose_tum = "../config/cam_pose_tum_delete_first11rows.txt";
ifstream fin(cam_pose_tum);
if(!fin) {
printf("[ERROR] cam_pose_tum file: %s do not exist\n", cam_pose_tum.c_str());
}
printf("cam_pose_tum file: %s\n", cam_pose_tum.c_str());
while(!fin.eof()) {
fin >> tmp_var >>tmp_mat(0) >> tmp_mat(1) >> tmp_mat(2)
>> q.x() >> q.y() >> q.z() >> q.w();
vec_T_gt.emplace_back(Sophus::SE3d{q, tmp_mat});
}
vector<Sophus::SE3d> vec_T_vins;
std::string vins_cam_pose_tum = "../bin/VINS_pose_output_asTUM2.txt";
ifstream fin_vins(vins_cam_pose_tum);
if(!fin_vins) {
printf("[ERROR] vins_cam_pose_tum file: %s do not exist\n", vins_cam_pose_tum.c_str());
}
printf("vins_cam_pose_tum file: %s\n", vins_cam_pose_tum.c_str());
while(!fin_vins.eof()) {
fin_vins >> tmp_var >> q.x() >> q.y() >> q.z() >> q.w() >>
tmp_mat(0) >> tmp_mat(1) >> tmp_mat(2);
vec_T_vins.emplace_back(Sophus::SE3d{q, tmp_mat});
}
int index_min = min(vec_T_gt.size(), vec_T_vins.size());
for(int i = 0; i < index_min; ++i) {
//Tw_gt^(-1) * Tw_vins = Tgt_vins
Sophus::SE3d se3_diff = vec_T_gt[i].inverse() * vec_T_vins[i];
cout << "i = " << i << ",\t se3_diff_ypr = \t" << Utility::R2ypr(se3_diff.rotationMatrix()).transpose()
<< ",\t t_diff = \t" << se3_diff.translation().transpose() << endl;
}
}
evo计算出来的align的T

后来想了一下,我的计算方法中VINS和GT的world可能不是一个world,所以我那样算可能是有问题的。
这个Umeyama方法和evo后面有时间看一下,挖个坑。
4.2 实验结果和分析
4.2.1 整体实验结果
noise在60倍时,噪声过大,看LM迭代一直没有停止,说明一直没有达到停止条件,优化失败,没有比较的意义了,此时轨迹也无参考意义:

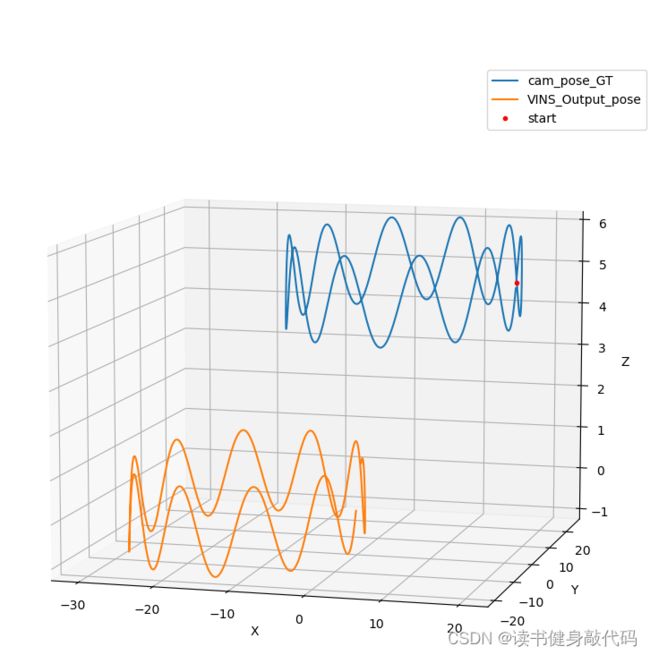
4.2.2 可视化对比
使用evo绘制出优化出的pose和GT的曲线,
evo安装:https://github.com/MichaelGrupp/evo
绘制指令:
tum cam_pose_tum.txt VINS_pose_output_asTUM2_noise_free_distcrete.txt -va --plot --plot_mode xyz
其中cam_pose_tum.txt是GT,VINS_pose_output_asTUM2_noise_free_distcrete.txt是VINS的输出,GT在图中以虚线表示。
将noise_free,noise * 1 , noise * 45进行联合对比,发现noise越大,误差越大:
4.3 结论
从上述实验中可以看出,随着imu数据noise的增大,VINS-MONO优化的误差也在增加,当误差大到一定程度时,数据就不能再使用了,需要重新采集数据。
本章作业代码重要性还是很高的,需要多花些时间看透整个代码的框架,包括系统初始化,变量管理,前端特征处理,后端求解(前几章主要工作),以及一些trick(如使用了VINS-MONO中的marg策略),如果要fix第一帧应该怎么做等等。