【c++】运算符重载实例
重载自增自减运算符
Intger num(2);
num++;
++num;
对自增运算符的重载要区分前置和后置。在重载之前需要思考一个问题,num++是返回一个临时变量还是num对象的本体。
为了解决这个问题可以考虑实现一个Inc_()函数和_Inc()函数分别模仿后置++和前置++的行为
Integer Inc_(){
int t=this->_num;
this->_num+=1;
return Integer(t);
}
Integer& _Inc(){
this->_num++;
return *this;
}
分别调用这两个函数
Integer num(3);
auto t=num.Inc_();
std::cout<<t.getValue();
Integer num(3);
auto t=num._Inc();
std::cout<<t.getValue();
通过这个例子不难看出后置++返回的是临时对象,前置++返回的是本体。
接下来就开始重载前置++和后置++
Integer operator++(){//后置++
int t=this->_num;
this->_num+=1;
return Integer(t);
}
Integer& operator++(){//前置++
this->_num++;
return *this;
}
但是如果这样写就会报错,因为函数重载是通过参数列表进行区分的,而不是通过返回值类型进行区分。
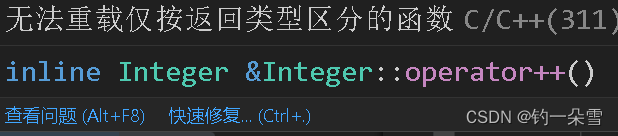
通常对于后置++要使用站位参数
Integer operator++(int){//后置++
int t=this->_num;
this->_num+=1;
return Integer(t);
}
重载逻辑运算符和单目运算符
逻辑与
bool operator&&(const Integer&right)const
{
return this->_num&&right._num;
}
std::cout<<std::boolalpha<<(Integer(0)&&Integer(1));
单目负
Integer operator -(){
return Integer(-this->_num);
}
括号运算符
()函数调用运算符
重载了这运算符,对象就有了函数的行为(仿函数)
class Program
{
public:
void operator()(){//第一个括号是运算符
std::cout<<"hello world";
}
};
Program p;
p();//调用括号运算符
重载括号运算符是可以有参数的
class Program
{
public:
void operator()(int i){//第一个括号是运算符
std::cout<<"i="<<i<<"hello world";
}
};
- 函数调用运算符只能用非静态成员函数重载
- 函数调用运算符可以有任意个参数,但不能有默认参数
[]下标访问运算符
class String
{
private:
int size;
char*str;
public:
String(const char*str)
{
size=strlen(str);
this->str=new char[size+1]{0};
strcpy(this->str,str);
}
int Size(){return size;}
};
int main()
{
String str="hello world";
return 0;
}
假设现在要有这样的一个操作
//循环遍历str内部的字符串
for(int i=0;i<str.Size();i++)
{
//to do
}
这个时候如何重载了下标访问运算符就可以通过str[i]遍历内部的字符串,这样操作是不是就相当方便了
char& operator[](int i){
return str[i];
}
说明
- []是一个二元运算符,具有数组名和下标两个参数,数组名由编译器通过this指针隐式传递,因此参数表中只需要提供一个参数。
- []可以同时出现在赋值运算符左边和右边,所以重载是常常返回引用,因为返回引用的函数可以出现在=的左边调用。
- 只能用非静态成员函数重载
和指针有关的运算符
int main()
{
int*a=new int[5];
return 0;
}
上面的这个程序进行new操作后没有delete会造成内存泄漏,但如果就是忘掉了delete呢?这个可以通过自己实现一个类来解决这个问题。
class Auto_Ptr
{
public:
Auto_Ptr(int*ptr):m_ptr(ptr){}
~Auto_Ptr(){delete m_ptr;}
private:
int*m_ptr;
};
int*a=new int[5];
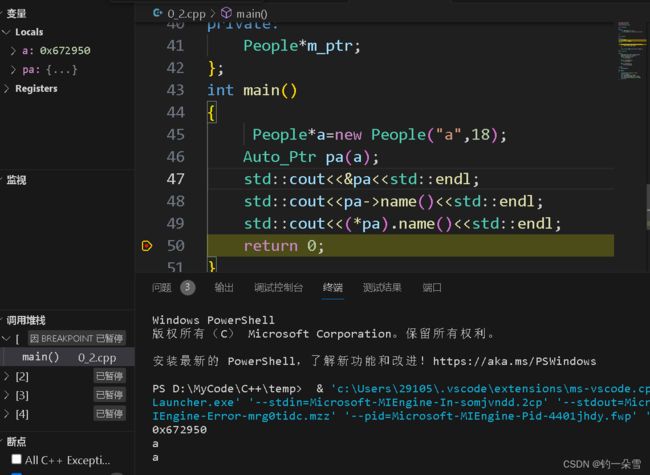
Auto_Ptr pa(a);
Auto_Ptr这个类帮我们完成了delete操作,这样就不用担心new了之后忘记delete了。
那么如何让Auto_Ptr则个类更像指针,那么就要重载一些运算符
class People
{
private:
int age_;
std::string name_;
public:
People(const std::string name,int age)
:name_(name),age_(age)
{}
std::string name()const{return name_;}
};
class Auto_Ptr
{
public:
Auto_Ptr(People*ptr):m_ptr(ptr){}
~Auto_Ptr(){delete m_ptr;}
People *operator->(){
return m_ptr;
}
People *operator&(){
return m_ptr;
}
People operator*(){
return m_ptr[0];
}
private:
People*m_ptr;
};
总结
- 目的:为已有的运算符赋予新的含义,以方便我们使用。
- 实质:函数重载的一种形式,或者说是一种特殊的函数。
- 规则:
- 只能重载C++中已经定义好的运算符。
- 不能创建新的运算符。
- 运算符重载后,其优先级、结合性等保持不变。
- 不能改变运算符的语法结构。
- 重载运算符的函数原型:返回类型 operator 运算符 (参数列表)。
- 重载运算符的参数:可以有一个或多个参数。当运算符有多个参数时,参数之间用逗号隔开。
- 重载运算符的返回类型:可以是任何数据类型,包括基本数据类型和自定义类型。
- 运算符重载的方法:
- 前缀形式:例如,重载++运算符时,函数名为 operator++()。
- 后缀形式:例如,重载++运算符时,函数名为 operator++(int)。注意,这里的int是虚拟参数,并不代表真实的类型。
注意事项:
- 重载的运算符必须与用户使用的输入匹配。如果用户使用了不同的输入,则不会调用该重载的运算符。
- 应该小心使用复杂的运算符重载,因为这可能导致程序的可读性和可维护性下降。如果发现自己在重载运算符时使用了过多的参数或者做出了过于复杂的操作,那么可能需要重新考虑一下设计。
- 在重载运算符时,需要确保不会破坏原有运算符的语义和语法规则。例如,你不能改变运算符的优先级或结合性。
在重载运算符时,需要确保重载后的运算符能够与使用它的代码和谐共存。例如,你不能让重载后的运算符破坏了原有代码的结构或者逻辑。
总的来说,虽然运算符重载提供了很大的灵活性,但是需要谨慎使用,以避免引入不必要的复杂性。在重载运算符时,应该尽量保持原有的语义和语法规则,以确保代码的可读性和可维护性。