全面的 iPerf3 Android平台移植编译、运行过程记录
1. iPerf 简介
iPerf 是什么?无需我多言,官网这条醒目的宣传语,已表达的很简洁、准确,甚至透露着一丝霸气:
iPerf——支持TCP、UDP和SCTP的终极测速工具!
iPerf 官方支持的平台非常全面,包括:Windows、Android、iOS、macOS 和 Linux 的多个发行版本。但遗憾的是,Android 版本提供的是两个开发好的、包含 iPerf 工具的Android应用,可以在谷歌应用商店下载。不像其他平台,提供了单独的 iPerf 可执行程序。
我结合自己的需求,获取源码,用 NDK 交叉编译一个可以在 Android 平台运行的 iPerf 工具。期间确实也遇到了不少的问题,Google 了无数次,也参考了很多其他博客,我将用这篇博客整理记录整个实践过程,方便自己查看,也希望帮助后续探索的朋友避一些坑。
作为学习记录,我这里记录了3种编译方式:传统交叉编译,以及更符合 Android 平台的 ndk-build 和 CMake 编译。实际应用中选择一种合适方式就好。
iPerf 有 iPerf2 和 iPerf3 两个版本,两者区别可以参考官网或其他资料,本博客记录的是移植运行 iPerf3 v3.1.3 的过程。源码下载地址:iPerf - Download iPerf3 and original iPerf pre-compiled binaries。
2. 移植环境
- 移植时间:2020年11月
- iPerf3:iperf-3.1.3-source.tar.gz
- 开发编译平台:macOS 10.14.6
- NDK 版本:ndk-r17c (17.2.4988734),通过 Android Studio 内的 SDK Manager 安装。
3. 传统交叉编译
编译阶段主要包括下面4个步骤:
- 下载源码压缩包,解压后进入源码根目录。
- 配置交叉编译工具链;
- ./configure --prefix=absolutepath/to/install_dir
- make && make install
3.1 本机平台编译测试
在 macOS 或 Linux 平台下,如果执行上面那样写的第1、3、4步,不配置任何额外的参数,编译完成后,在 --prefix 指定的路径 bin 目录下,就已经生成了可以在本机上直接运行的可执行程序,非常简单,有兴趣的读者可以试试。
3.1.1 macOS 可能遇到的问题
- make 过程报错:clang: error: the clang compiler does not support -pg option on versions of OS X 10.9 and later。
解决方法:查看一下 iperf-3.1.3/src 里面的 Makefile 和 Makefile.am 我们可以发现,编译器的 -pg 选项主要是编译 iperf_profile 用到的。至于 iperf_profile 是个啥,给个参考:iPerf Issues #335: What's difference between iperf3_profile and iperf3?。按里面的回答就是,这个东西连很多 iPerf 项目的成员自己都没用过,通常我们也用不上,那我们就可以去掉这个选项。具体操作方式有两种:
- 方式一:直接修改 iperf-3.1.3/src/Makefile,找到 iperf3_profile_CFLAGS 和 iperf3_profile_LDFLAGS 赋值的地方(第613行左右),去掉 -pg 参数,然后直接重新执行 make 命令。
# To fix: "clang: error: the clang compiler does not support -pg option on versions of OS X 10.9 and later" compile error on macOS.
#iperf3_profile_CFLAGS = -pg -g
iperf3_profile_CFLAGS = -g
iperf3_profile_LDADD = libiperf.la
# To fix: "clang: error: the clang compiler does not support -pg option on versions of OS X 10.9 and later" compile error on macOS.
#iperf3_profile_LDFLAGS = -pg -g
iperf3_profile_LDFLAGS = -g- 方式二:修改 iperf-3.1.3/src/Makefile.in 文件,找到 iperf3_profile_CFLAGS 和 iperf3_profile_LDFLAGS 赋值的地方(第613行左右),去掉 -pg参数,然后执行 ./configure 重新生成 的Makefile,再 make。
3.2 配置交叉编译工具链
根据 NDK 指南,使用 NDK 编译代码有三种方式:ndk-build、CMake、独立工具链。独立工具链方式虽然被标记为已废弃,但非常适合用于编译包含 configure 脚本的开源项目,iPerf3 就非常符合这种情况,所以我这里选择用独立工具链的方式。这一步可以参考 NDK 指南独立工具链的创建工具链章节。为了使用方便,我指定了在 iPerf 源码根目录的 ndk-standalone 目录中存放独立工具链,这个名字和路径可以根据自己需要更改。
cd iperf-3.1.3
$NDK/build/tools/make_standalone_toolchain.py \
--arch arm \
--api 21 \
--install-dir /Users/shenyong/iperf-3.1.3/ndk-standalone \
--force然后我们在终端中,把独立工具链的下的 bin 目录临时添加到 PATH 环境变量中。
export PATH=/Users/shenyong/iperf-3.1.3/ndk-standalone/bin:$PATH此时当我们在终端输入 arm,再按 Tab 键进行命令补全时,命令会自动补全为:arm-linux-androideabi-,再次双击 Tab,就会看到很多以 arm-linux-androideabi- 为前缀的交叉编译工具命令。可以用 which 验证,这些命令正是位于我们创建的独立工具链目录中:
$ arm-linux-androideabi-
arm-linux-androideabi-addr2line arm-linux-androideabi-clang++ arm-linux-androideabi-gcc-4.9 arm-linux-androideabi-gcov-tool arm-linux-androideabi-objcopy arm-linux-androideabi-strip
arm-linux-androideabi-ar arm-linux-androideabi-cpp arm-linux-androideabi-gcc-4.9.x arm-linux-androideabi-gprof arm-linux-androideabi-objdump
arm-linux-androideabi-as arm-linux-androideabi-dwp arm-linux-androideabi-gcc-ar arm-linux-androideabi-ld arm-linux-androideabi-ranlib
arm-linux-androideabi-c++ arm-linux-androideabi-elfedit arm-linux-androideabi-gcc-nm arm-linux-androideabi-ld.bfd arm-linux-androideabi-readelf
arm-linux-androideabi-c++filt arm-linux-androideabi-g++ arm-linux-androideabi-gcc-ranlib arm-linux-androideabi-ld.gold arm-linux-androideabi-size
arm-linux-androideabi-clang arm-linux-androideabi-gcc arm-linux-androideabi-gcov arm-linux-androideabi-nm arm-linux-androideabi-strings
$ which arm-linux-androideabi-gcc
/Users/shenyong/iperf-3.1.3/ndk-standalone/bin/arm-linux-androideabi-gcc一定注意:这是一种临时添加方法,只在当前执行命令的终端窗口有效,在其他已有终端和新打开的终端是不生效的!做这一步是为了方便后面配置和编译执行,可以精简一些参数项;同时不用添加到 .bashrc 中使其一直生效以至于影响电脑上的其他开发配置。是否需要配置为使其始终生效,可根据个人情况自行评估。
3.3 执行 ./configure
一开始其实我也不知道要怎么配置参数,所以参考了这篇 Medium 博客:How to compile iperf3 for Android(需要梯子),原文作者的参数项如下:
./configure \
--host=arm-linux-androideabi \
--prefix=/Users/shenyong/iperf-3.1.3/out_install \
-C \
CC=arm-linux-androideabi-gcc \
CFLAGS=-static \
CXX=arm-linux-androideabi-g++ \
CXXFLAGS=-static \
AR=arm-linux-androideabi-ar \
RANLIB=arm-linux-androideabi-ranlib参数解释:
- --host:交叉编译时的目标平台工具链前缀;
- --prefix:编译完成后,make install 的安装目录,如未指定,默认是 /usr/local。这个路径必须是绝对路径,否则configure脚本执行会报错提示。
- -C:表示 configure 会启用缓存,保存在 config.cache 文件中。可以用 ./configure -h 查看帮助信息
- CXX、CXXFLAGS、CC、CFLAGS、AR、RANLIB:这几个是交叉编译需要配置的变量,用于指定编译器等。在独立工具链 bin 目录中包含 gcc 和 clang 两种编译器,可以按需选择。由于从 ndk-r13开始,NDK 默认使用 clang 编译,所以如果我们想要用 gcc 编译,就必须手动指定 CC、CXX、AR、RANLIB 等工具,在以后的 NDK 更新版本中,gcc 工具链可能会被移除。
因为我前面在 PATH 环境变量中添加了工具链编译器的路径,所以可以不用像参考博客那样写很长一串 gcc、g++ 等的绝对路径,这样看起来更简洁清晰一些。经过我的测试,原博客的这个配置方案,虽然执行 ./configure 不会有问题,但是在 make 阶段会遇到下面记录的其他问题,当时我在这一块也爬了好久的坑~
我使用的一种经测试能顺利完成编译的配置如下:
./configure \
--host=arm-linux-androideabi \
--prefix=/Users/shenyong/iperf-3.1.3/out_install \
CC=arm-linux-androideabi-gcc \
CFLAGS="-D__ANDROID_API__=14 -pie -fPIE -static -s" \
CXX=arm-linux-androideabi-g++ \
CXXFLAGS="-D__ANDROID_API__=14 -pie -fPIE -static -s" \
AR=arm-linux-androideabi-ar \
RANLIB=arm-linux-androideabi-ranlib参数解释:
- -D__ANDROID_API__=14 -pie -fPIE:这几个都是为了解决对应的编译问题添加的,后面说到对应问题时有解释;
- -static:静态链接,最终生成的 iperf3 可执行文件是包含了 iperf 库的,strip 后文件大小140多KB,只需要一个文件就可以运行。若不使用 -static 则默认是动态链接,生成的 iperf3 可执行文件只有5KB,不包含 iperf 库,同时 lib 目录下会额外生成 libiperf.so。更多静态链接和动态链接的区别读者可自行查资料。为了方便拷贝到 Android 设备运行,推荐使用静态链接。
- -s:去掉编译产物中不影响执行的信息,如调试信息,符号表等,可以减小库文件/程序的文件大小。使用和不使用 -s 选项的差别,可以通过 file 命令对比,使用了 -s,file 查看编译输出的可执行程序或库文件的属性,会有 stripped 标识,未使用 -s 则是 not stripped 标识;并且对比两种情况的编译结果,会发现使用 -s 的输出文件,大小要小得多。
3.4 make 编译
./configure 正确执行后,就可以执行 make 进行编译了。
3.4.1 make 可能遇到的问题
1. 编译报错:iperf_api.c:function usage: error: undefined reference to 'stderr'
这个问题说起来就比较具体了,和 NDK 的一些历史问题及版本迭代有关,想要了解更详细的情况可以参阅 ndk issues #272 和我的另一篇翻译博客:NDK 中的 Unified Headers。我的解决方法参考了 ndk issues #272 下面的讨论,核心的一点就是在 CFLAGS 和 CXXFLAGS 中添加 一个 -D__ANDROID_API__=14 参数。
解决方法:./configure 阶段配置如下编译参数:
CFLAGS="-D__ANDROID_API__=14 -pie -fPIE -static -s" \
LDFLAGS=-D__ANDROID_API__=14 \
CXXFLAGS="-D__ANDROID_API__=14 -pie -fPIE -static -s"2. 编译报错:error: undefined reference to '__gnu_mcount_nc'
这个通常也是因为 iperf_profile 的 -pg 编译参数导致的,解决方法参考上面的本机平台编译测试一节,在 iperf-3.1.3/src/Makefile 或 iperf-3.1.3/src/Makefile.in 中找到 iperf3_profile_CFLAGS 和 iperf3_profile_LDFLAGS 赋值的地方(第613行左右),去掉 -pg 参数,重新编译即可。如果读者参考博客前面的章节做了本机平台编译测试并解决了相关问题,编译阶段应该是不会再出现这个问题。
3.5 make install 安装
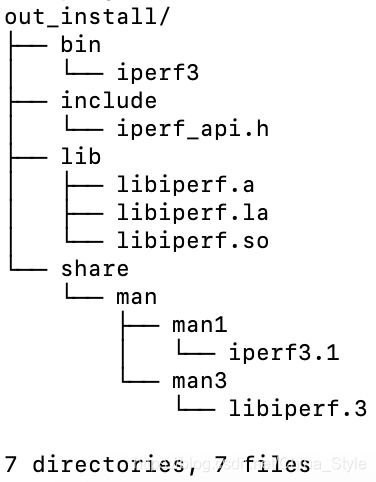
make 顺利完成后,就可以执行 make install,这两步也可以合并在一起执行:make && make install,这个看个人习惯。make install 完成后,会在 configure 阶段 --prefix 指定的目录下生成编译结果,其目录结构如下:
通过 file 命令可以查看到,bin/iperf3 和 lib/libiperf3.so,是 arm 平台的可执行文件和共享库:
$ file out_install/bin/iperf3
out_install/bin/iperf3: ELF 32-bit LSB executable, ARM, EABI5 version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /system/, with debug_info, not stripped
$ file out_install/lib/libiperf.so
out_install/lib/libiperf.so: ELF 32-bit LSB pie executable ARM, EABI5 version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /system/, with debug_info, not stripped4. 用 ndk-build 方式编译
上面的 ./configure -> make -> make install,这是典型的开源库编译方式,比较通用,虽然也适用于Android平台,但是配置工具链和 configure 略显繁琐。对于Android平台,我们可以使用Android开发者更熟悉的姿势,即 Android Studio + ndk-build/cmake 的方式,用这种方式充分利用了Android Studio的各种特性,如源码调用跳转等,更方便我们阅读 iPerf3 的源码。
我们可以直接将 iperf3 源码解压到 Android Studio 工程中,接下来的事就都可以在我们熟悉的IDE中进行了。类似这样:
4.1 生成必要的头文件
iPerf 源码中 iperf_config.h 和 version.h 两个头文件是由 configure 脚本生成的,所以我们还是要和上面一样在源码根目录执行 ./configure,不过这里可以不用加参数了,因为我们只是用它生成必要的头文件,不会再用它生成的 Makefile 进行编译。
$ ./configure 4.2 配置 ndk-build 编译脚本
在 jni 目录 下添加 Android.mk 和 Application.mk 文件,内容如下:
Android.mk:
LOCAL_PATH := $(call my-dir)
include $(CLEAR_VARS)
LOCAL_MODULE := iperf3
LOCAL_SRC_FILES := iperf-3.1.3/src/cjson.c \
iperf-3.1.3/src/iperf_api.c \
iperf-3.1.3/src/iperf_client_api.c \
iperf-3.1.3/src/iperf_error.c \
iperf-3.1.3/src/iperf_locale.c \
iperf-3.1.3/src/iperf_sctp.c \
iperf-3.1.3/src/iperf_server_api.c \
iperf-3.1.3/src/iperf_tcp.c \
iperf-3.1.3/src/iperf_udp.c \
iperf-3.1.3/src/iperf_util.c \
iperf-3.1.3/src/main.c \
iperf-3.1.3/src/net.c \
iperf-3.1.3/src/tcp_info.c \
iperf-3.1.3/src/tcp_window_size.c \
iperf-3.1.3/src/timer.c \
iperf-3.1.3/src/units.c
# 这3个 t_ 开头的文件是测试用的,不用包含,否则会有多个main方法入口
# iperf-3.1.3/src/test/t_timer.c \
# iperf-3.1.3/src/test/t_units.c \
# iperf-3.1.3/src/test/t_uuid.c
LOCAL_CFLAGS += -pie -fPIE -fPIC -s
LOCAL_C_INCLUDES += $(LOCAL_PATH)/iperf-3.1.3/src
include $(BUILD_EXECUTABLE)重要参数解释:
- LOCAL_SRC_FILES:规则很简单,加上源码目录中除了 t_ 开始的3个测试文件的其他所有 .c 文件;
- LOCAL_CFLAGS:为了编译出合适的 iperf3 可执行文件必要的参数,本文前面或后续章节有解释;
- LOCAL_C_INCLUDES:指定头文件搜索目录包含iperf源码目录。
Application.mk:
APP_PLATFORM := android-21
APP_ABI := armeabi-v7a x864.3 ndk-build
在 jni 目录打开一个终端,执行:ndk-build,编译完成后 iperf3 可执行文件会输出到和 jni 同级的 libs 目录下:
5. 用 CMake 编译
参考文档:NDK 入门指南 - CMAKE
用 CMake 编译的流程如下:
- 先执行 cmake,根据 CMakeLists.txt 生成 Makefile 文件;
- 然后执行 make 进行编译。
这里我和上面用 ndk-build 编译一样,所有操作都是在 Android Studio 工程的 jni 目录下进行。
5.1 添加 CMakeLists.txt 配置文件
在 Android Studio 工程的 jni 目录中添加 CMakeLists.txt 文件,内容如下:
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.4.1)
#file(GLOB variable [RELATIVE path] [globbing expressions]...)
#GLOB选项将会为所有匹配查询表达式的文件生成一个文件list,并将该list存储进变量variable里
file(GLOB IPERF3_C_SOURCES
iperf-3.1.3/src/cjson.c
iperf-3.1.3/src/iperf_api.c
iperf-3.1.3/src/iperf_client_api.c
iperf-3.1.3/src/iperf_error.c
iperf-3.1.3/src/iperf_locale.c
iperf-3.1.3/src/iperf_sctp.c
iperf-3.1.3/src/iperf_server_api.c
iperf-3.1.3/src/iperf_tcp.c
iperf-3.1.3/src/iperf_udp.c
iperf-3.1.3/src/iperf_util.c
iperf-3.1.3/src/main.c
iperf-3.1.3/src/net.c
iperf-3.1.3/src/tcp_info.c
iperf-3.1.3/src/tcp_window_size.c
iperf-3.1.3/src/timer.c
iperf-3.1.3/src/units.c)
include_directories(iperf-3.1.3/src)
SET(CMAKE_SYSTEM_NAME Android)
# API level
set(CMAKE_SYSTEM_VERSION 21)
set(CMAKE_C_FLAGS_RELEASE "-pie -fPIE -fPIC -s")
SET(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE "Release")
add_executable(iperf3 ${IPERF3_C_SOURCES})5.2 执行 cmake
NDK 通过工具链文件支持 CMake。工具链文件是用于自定义交叉编译工具链行为的 CMake 文件。用于 NDK 的工具链文件位于 NDK 中的
内。/build/cmake/android.toolchain.cmake
由于 cmake 会生成较多编译配置文件,可以用单独的目录保存编译配置和输出:
mkdir cmake_build
cd cmake_build
cmake -DCMAKE_TOOLCHAIN_FILE=$NDK/build/cmake/android.toolchain.cmake -DANDROID_ABI="arm64-v8a" ..cmake 命令需要指定包含 CMakeLists.txt 文件的目录,我这里是上一级目录,所以是 ..。同时,cmake 不支持一次指定多个 ABI,如需以多个 Android ABI 为目标,必须为每个 ABI 构建一次。
更多用法参考:NDK 指南 - cmake 命令行
5.3 执行 make
经过上面的 cmake,此时 cmake_build 目录中已经生成了 Makefile 和其他一些编译配置文件。此时只需要执行 make,编译完成后就会在当前目录下生成 iperf3 可执行文件:
编译阶段到这里也就圆满结束了~
6. 运行阶段
用 adb 将编译好的 iperf3 可执行文件 push 到手机上有执行权限的目录(如:/data/local/tmp/)即可运行。但你以为就万事大吉了吗? too naive。当你照做的时候,可能新的问题就来了。
6.1 运行可能遇到的问题
- 运行报错1:"./iperf3": error: Android 5.0 and later only support position-independent executables (-fPIE)。
$ adb push iperf3 /data/local/tmp/
iperf3: 1 file pushed, 0 skipped. 252.3 MB/s (216076 bytes in 0.001s)
$ adb shell
HWMHA:/ $ cd /data/local/tmp
HWMHA:/data/local/tmp $ ls -l iperf3
-rwxrwxrwx 1 shell shell 216076 2020-11-14 11:16 iperf3
HWMHA:/data/local/tmp $ ./iperf3 -version
"./iperf3": error: Android 5.0 and later only support position-independent executables (-fPIE).解决方法:这是 Android 5.0 中的一个系统安全特性导致的,参考:Android 5.0 中的安全增强功能。其实报错内容中就有处理提示,解决方法就是编译阶段在 configure 时在编译器标识中添加 -pie -fPIE 这两个选项:
CFLAGS="-D__ANDROID_API__=14 -pie -fPIE -static -s" \
CXXFLAGS="-D__ANDROID_API__=14 -pie -fPIE -static -s"好了,重新编译,push 到 Android 设备的 /data/local/tmp 下运行:
1|HWMHA:/data/local/tmp $ ./iperf3 -version
iperf 3.1.3
Linux localhost 4.9.148 #1 SMP PREEMPT Fri May 22 19:13:52 CST 2020 armv8l
Optional features available: CPU affinity setting, IPv6 flow label, TCP congestion algorithm setting, sendfile / zerocopy, socket pacing可以打印版本信息了,至少可以运行了嘛,离成功又近了一步。用 iPerf 官网提供的 Public iPerf3 servers 来测试一下,这时候我们又会遇到新问题:
- 运行报错2:iperf3: error - unable to create a new stream: No such file or directory。
- 关联问题:iperf3: error - unable to create a new stream: Permission denied。
HWMHA:/data/local/tmp $ ./iperf3 -c bouygues.iperf.fr -p 9200
Connecting to host bouygues.iperf.fr, port 9200
iperf3: error - unable to create a new stream: No such file or directory解决方法:这个问题和 iperf issue #374 类似,都是因为 iperf 源码 src/iperf_api.c 中创建临时文件使用了一个 /tmp/iperf3.XXXXXX 的绝对路径。/tmp/ 这个路径在 macOS 和 Linux 中都是存在的,所以不会有问题;但在一般的 Android 系统中是不存在的(一些定制系统除外),所以就会无法创建需要的文件。知道原因后,我们就可以修改一下源码的 iperf_api.c 文件,在 iperf_new_stream 方法中,将临时文件的路径改成一个 Android系统上稳妥存在且有操作权限的路径,比如:/data/local/tmp。
struct iperf_stream *
iperf_new_stream(struct iperf_test *test, int s)
{
int i;
struct iperf_stream *sp;
char template[1024];
if (test->tmp_template) {
snprintf(template, sizeof(template) / sizeof(char), "%s", test->tmp_template);
} else {
// To fix: "error - unable to create a new stream: No such file or directory" runtime error on Android.
// char buf[] = "/tmp/iperf3.XXXXXX";
char buf[] = "/data/local/tmp/iperf3.XXXXXX";
snprintf(template, sizeof(template) / sizeof(char), "%s", buf);
}
// 省略其他代码...
}但注意! /data/local/tmp 这个路径只有在使用 adb shell 时有效,可以用作修改验证。如果是把 iperf3 可执行文件打包进 APK 然后运行时调用,那么将会遇到 Permission denied 的问题,因为一个普通的 Android 应用进程还是没有权限访问 /data/local/tmp 这个目录的。这种情况就需要将路径修改为 /data/data/your_package_name/xxx,将 iperf3 可执行文件拷贝到 Android 内部存储包名下,并添加可执行权限再调用,iperf3 才有完全的执行权限。
// To fix: "error - unable to create a new stream: Permission denied" runtime error on Android.
// char buf[] = "/tmp/iperf3.XXXXXX";
char buf[] = "/data/data/YOUR_PACKAGE_NAME/files/iperf3.XXXXXX";如果反编译 iPerf 官网提供 的 he.net Network Tools 这个安卓应用的 APK,可以知道它的包名为:net.he.networktools。查看它 assets 里包含的 iperf 可执行文件的信息,我们会发现这个应用也是用的使用包名内路径的方法:
$ strings iperf3-pie | grep iperf3.XXXXXX
/data/data/net.he.networktools/cache/iperf3.XXXXXX- 运行问题3:执行 iperf3 时,不像执行 ping 命令一样,能逐步获得输出,而是执行完成后才全部返回。
解决方法:在源码的 iperf_api.c 文件 iprintf 方法中添加iflush() 方法调用:
int iprintf(struct iperf_test *test, const char* format, ...)
{
va_list argp;
int r = -1;
if (test->role == 'c') {
if (test->title)
fprintf(test->outfile, "%s: ", test->title);
va_start(argp, format);
r = vfprintf(test->outfile, format, argp);
va_end(argp);
/******** fix for Android start ********/
iflush(test);
/******** fix for Android end ********/
}
// 省略...
}7. Demo:通过可执行文件和 jni 调用方式使用 iperf3
对于 Android 平台在运行时调用 iperf3 可执行文件和用 jni 调用两种方式,我写了一个demo供大家参考,GitHub 地址:https://github.com/AndrewShen812/iPerfDemo-runtime。