WebRTC源码分析——Call模块
目录
- 1. 引言
- 2. Call对象的创建
-
- 2.1 创建CallFactory对象
- 2.2 创建Call对象
-
- 2.2.1 PeerConnection.CreateCall_w
- 2.2.2 CallFactory.CreateCall
- 2.2.3 Call::Create
- 3 Call功能详述
- 4 总结
1. 引言
Call模块是WebRTC会话中不可缺少的一个模块,一个Call对象可以包含多个发送/接收流,且这些流对应同一个远端端点,并共享码率估计。
Call在创建PeerConnection对象的过程中被创建出来,并成为PeerConnection成员。PeerConnection利用Call的能力对应用层提供了如下的功能:
- 发送码率设置(包含最大码率、最小码率、初始码率,初始码率作为编码器的初始参数以及带宽估计的先验值);
- 提供获取传输统计数据途径(包含估算的可用发送带宽、估算的可用接收带宽、平滑发送引入的延迟、RTT估计值、累计的最大填充bit);
- 提供获取所有发送的数据包回调;
- 另外其还持有PacketReceiver对象,因此,所有接收到RTP/RTCP数据包,也将经过Call。
Call对WebRTC内部还提供了其他重要的功能:
- 创建/销毁 AudioReceiveStream、AudioSendStream;
- 创建/销毁 VideoSendStream、VideoReceiveStream;
- 创建带有前向纠错Fec功能的FlexfecReceiveStream;
Call模块的源码分布:
2. Call对象的创建
CallFactory是Call对象的工厂类,负责Call对象的创建,想要知道Call如何被创建出来的,追根究底先要了解CallFactory对象是何时何地被创建出来的。大致的创建过程如下
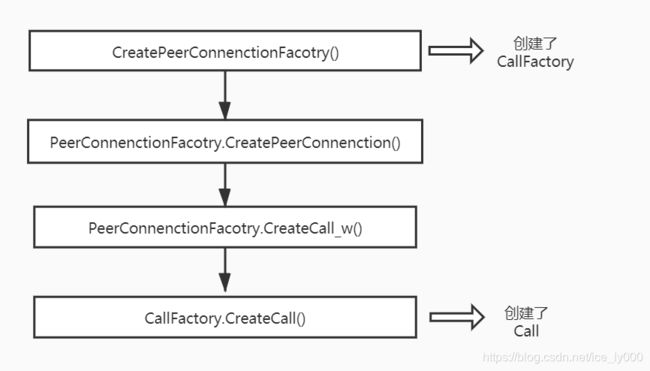
2.1 创建CallFactory对象
CallFactory对象是call层的实体对象,在api层对应的接口是CallFactoryInterface,提供的唯一方法就是创建Call对象。
class CallFactoryInterface {
public:
virtual ~CallFactoryInterface() {}
virtual Call* CreateCall(const CallConfig& config) = 0;
};
CallFactory是在应用层创建PeerConnectionFactory对象时被创建的,源码如下:
rtc::scoped_refptr<PeerConnectionFactoryInterface> CreatePeerConnectionFactory() {
...
dependencies.call_factory = CreateCallFactory();
...
}
std::unique_ptr<CallFactoryInterface> CreateCallFactory() {
return std::unique_ptr<CallFactoryInterface>(new CallFactory());
}
2.2 创建Call对象
正如前文所述,在创建PeerConnection的过程中,在PeerConnection.CreateCall_w方法中,Call对象被CallFactory工厂创建。
PS: 注意webrtc::Call只是一个纯虚的接口类,并非实体类。
2.2.1 PeerConnection.CreateCall_w
PeerConnection.CreateCall_w方法主要做了3件事:
- 断言,使得创建Call的动作必须在worker线程上执行;
- 收集CallConfig结构体的数据,以备真正创建Call对象时使用;通过这个结构体的数据,我们大致可以猜测Call会具备什么能力,这些能力正是CallConfig引入的这些模块所带来的;
- 调用CallFactory.CreateCall真正地创建Call对象。
源码及分析如下:
std::unique_ptr<Call> PeerConnectionFactory::CreateCall_w(
RtcEventLog* event_log) {
// 1. 确保Call在worker线程上被创建
RTC_DCHECK_RUN_ON(worker_thread_);
// 2. 创建CallConfig结构体,并填充该结构体对象,该结构体包含了Call需要用到的其他模块和参数
// 2.1 填充RtcEventLog
webrtc::Call::Config call_config(event_log);
// 2.2 填充AudioState:从通道的音频引擎中获取音频状态对象,该对象提供了如下功能:
// AudioState->audio_processing() 获取音频处理器,用以处理3A问题
// AudioState->audio_transport() 获取音频传输
// AudioState->SetPlayout() 控制音频播放
// AudioState->SetRecording() 控制音频采集
// 从上可知,Call对象也将通过AudioState获得音频处理和控制相关的能力
if (!channel_manager_->media_engine() || !call_factory_) {
return nullptr;
}
call_config.audio_state =
channel_manager_->media_engine()->voice().GetAudioState();
// 2.3 填充BitrateConstraints,为发送端码率参数
// 最小码率默认30kbps,最大码率默认2000kbps;
// 起始码率默认300kbps,该值既作为编码器的初始参数,又作为带宽估计的先验值。
FieldTrialParameter<DataRate> min_bandwidth("min", DataRate::kbps(30));
FieldTrialParameter<DataRate> start_bandwidth("start", DataRate::kbps(300));
FieldTrialParameter<DataRate> max_bandwidth("max", DataRate::kbps(2000));
ParseFieldTrial({&min_bandwidth, &start_bandwidth, &max_bandwidth},
trials_->Lookup("WebRTC-PcFactoryDefaultBitrates"));
call_config.bitrate_config.min_bitrate_bps =
rtc::saturated_cast<int>(min_bandwidth->bps());
call_config.bitrate_config.start_bitrate_bps =
rtc::saturated_cast<int>(start_bandwidth->bps());
call_config.bitrate_config.max_bitrate_bps =
rtc::saturated_cast<int>(max_bandwidth->bps());
// 2.4 填充FecControllerFactoryInterface,通过该对象,Call是可以实施Fec功能的
call_config.fec_controller_factory = fec_controller_factory_.get();
// 2.5 填充TaskQueueFactory
call_config.task_queue_factory = task_queue_factory_.get();
// 2.6 填充网络状态预测工厂NetworkStatePredictorFactory
call_config.network_state_predictor_factory =
network_state_predictor_factory_.get();
// 2.7 填充NetEqFactory,通过该对象对音频的网络传输NetEq处理
call_config.neteq_factory = neteq_factory_.get();
// 2.8 填空网络控制器工厂NetworkControllerFactory,是否使用外部提供的拥塞控制算法
if (IsTrialEnabled("WebRTC-Bwe-InjectedCongestionController")) {
RTC_LOG(LS_INFO) << "Using injected network controller factory";
call_config.network_controller_factory =
injected_network_controller_factory_.get();
} else {
RTC_LOG(LS_INFO) << "Using default network controller factory";
}
// 2.9 填充WebRtcKeyValueConfig,配置的Key-value对
call_config.trials = trials_.get();
// 3 创建Call对象
return std::unique_ptr<Call>(call_factory_->CreateCall(call_config));
}
2.2.2 CallFactory.CreateCall
CallFactory.CreateCall方法大致做了三件事:
- ParseDegradationConfig() 方法检索实验特性中是否存在发送/接收网络配置相关参数
- 若存在网络相关参数配置,则创建DegradedCall对象。
- 若不存在网络相关参数配置,则直接使用Call::Create() 创建Call对象。
源码及分析如下:
Call* CallFactory::CreateCall(const Call::Config& config) {
// 1. 应用层开启一些实验特性是通过提供字符串类型的配置来实现的,WebRTC内部能从这些字符串类型的配置
// 中检索出相关信息,比如ParseDegradationConfig方法就可以从字符串配置中检索出是否有发送/接收相
// 关的网络配置参数,同时根据这些参数来构建发送和接收的BuiltInNetworkBehaviorConfig配置对象。
absl::optional<webrtc::BuiltInNetworkBehaviorConfig> send_degradation_config =
ParseDegradationConfig(true);
absl::optional<webrtc::BuiltInNetworkBehaviorConfig>
receive_degradation_config = ParseDegradationConfig(false);
// 2. 若应用层开启了网络相关实验参数,则发送或接收BuiltInNetworkBehaviorConfig不为空
// 此时,创建并返回DegradedCall。
// DegradedCall对象继承于webrtc::Call,并且其构造中再传入一个webrtc::Call,外加
// 发送/接收的BuiltInNetworkBehaviorConfig对象。可以猜知DegradedCall对象一些功
// 能直接使用封装进来的webrtc::Call来提供;另外一些功能,会根据是否存在发送/接收
// BuiltInNetworkBehaviorConfig改变原始的webrtc::Call的行为。具体如何见后文拆解。
if (send_degradation_config || receive_degradation_config) {
return new DegradedCall(std::unique_ptr<Call>(Call::Create(config)),
send_degradation_config, receive_degradation_config,
config.task_queue_factory);
}
// 3. 调用Call::Create来创建真正的Call对象
return Call::Create(config);
}
2.2.3 Call::Create
Call* Call::Create(const Call::Config& config) {
return Create(config, Clock::GetRealTimeClock(),
ProcessThread::Create("ModuleProcessThread"),
ProcessThread::Create("PacerThread"));
}
Call* Call::Create(const Call::Config& config,
Clock* clock,
std::unique_ptr<ProcessThread> call_thread,
std::unique_ptr<ProcessThread> pacer_thread) {
RTC_DCHECK(config.task_queue_factory);
return new internal::Call(
clock, config,
std::make_unique<RtpTransportControllerSend>(
clock, config.event_log, config.network_state_predictor_factory,
config.network_controller_factory, config.bitrate_config,
std::move(pacer_thread), config.task_queue_factory, config.trials),
std::move(call_thread), config.task_queue_factory);
}
从上述源码中可知,最终创建的Call对象是webrtc::internal::Call。webrtc::internal::Call类的声明以及实现都位于call/call.cc源文件中。
3 Call功能详述
留待以后
4 总结
留待以后