拦截器ConnectInterceptor
ConnectInterceptor拦截器
ConnectInterceptor拦截器的主要功能是复用连接池里面的连接,创建新的连接,并把读写数据流的对象交由下一个拦截器处理。
可以看到OkHttp很多功能类比方代理管理、cookie管理等都是通过构造方式设置进来的,它们的实现方式交由开发者自定义,这样做既能满足高度的自定义性又能使每个类功能职责明确,提供良好的维护性。
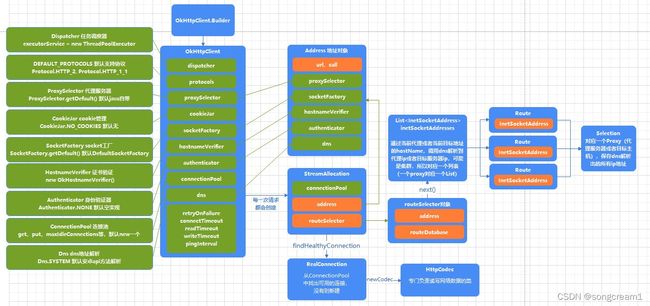
StreamAllocation
streamAllocation对象承担了连接的大部分工作,它内部持有connectionPool连接池对象、address地址对象、routeSelector代理管理对象。
值得注意的是,每一次新的网络请求,都会创建一个新的streamAllocation对象,并且通过streamAllocation从连接池中找到可以复用的相同地址的连接,当找不到时则会新建连接,而每个连接connection都会有个成员变量allocations列表,当streamAllocation和某个连接匹配时,streamAllocation就会被放入到这个连接的allocations列表中,并且每个连接connection都会控制streamAllocation数量,也即每个连接被请求复用的数量。
Address
address对象主要存储当前请求的地址、域名信息。
RealConnection
realConnection对象由streamAllocation.findHealthyConnection返回,连接池connectionPool中存放的就是这个东西,连接本身。
RouteSelector
routeSelector对象负责代理管理,它会通过配置的代理服务器,调用dns解析出代理服务器(没有时则为目标主机)的所有IP地址,当前请求无法请求到时,routeSelector会切换到下一个代理ip地址,去访问目标地址。
下面我们看下它的代码:
@Override public Response intercept(Chain chain) throws IOException {
RealInterceptorChain realChain = (RealInterceptorChain) chain;
Request request = realChain.request();
//协调代理、请求信息、连接池,找到或创建合适的连接对象
StreamAllocation streamAllocation = realChain.streamAllocation();
boolean doExtensiveHealthChecks = !request.method().equals("GET");
//主要方法,寻找连接池里可用的连接,没有则创建连接,并返回数据流读写对象
HttpCodec httpCodec = streamAllocation.newStream(client, chain, doExtensiveHealthChecks);
RealConnection connection = streamAllocation.connection();
return realChain.proceed(request, streamAllocation, httpCodec, connection);
}
我们具体看看streamAllocation.newStream方法
public HttpCodec newStream(
OkHttpClient client, Interceptor.Chain chain, boolean doExtensiveHealthChecks) {
//读取配置信息
int connectTimeout = chain.connectTimeoutMillis();
int readTimeout = chain.readTimeoutMillis();
int writeTimeout = chain.writeTimeoutMillis();
int pingIntervalMillis = client.pingIntervalMillis();
boolean connectionRetryEnabled = client.retryOnConnectionFailure();
try {
//寻找可用连接,没有则新建连接
RealConnection resultConnection = findHealthyConnection(connectTimeout, readTimeout,
writeTimeout, pingIntervalMillis, connectionRetryEnabled, doExtensiveHealthChecks);
//返回数据流读写对象
HttpCodec resultCodec = resultConnection.newCodec(client, chain, this);
synchronized (connectionPool) {
codec = resultCodec;
return resultCodec;
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RouteException(e);
}
}
主要逻辑集中在streamAllocation.findHealthyConnection方法
private RealConnection findHealthyConnection(int connectTimeout, int readTimeout,
int writeTimeout, int pingIntervalMillis, boolean connectionRetryEnabled,
boolean doExtensiveHealthChecks) throws IOException {
//while循环内不停的查找可用连接:todo具体逻辑,找不到怎么办
while (true) {
RealConnection candidate = findConnection(connectTimeout, readTimeout, writeTimeout,
pingIntervalMillis, connectionRetryEnabled);
// If this is a brand new connection, we can skip the extensive health checks.
synchronized (connectionPool) {
if (candidate.successCount == 0 && !candidate.isMultiplexed()) {
return candidate;
}
}
//当前连接不可用,则关闭,continue继续寻找
if (!candidate.isHealthy(doExtensiveHealthChecks)) {
noNewStreams();
continue;
}
return candidate;
}
}
再看findConnection方法
private RealConnection findConnection(int connectTimeout, int readTimeout, int writeTimeout,
int pingIntervalMillis, boolean connectionRetryEnabled) throws IOException {
boolean foundPooledConnection = false;
RealConnection result = null;
Route selectedRoute = null;
Connection releasedConnection;
Socket toClose;
synchronized (connectionPool) {
if (released) throw new IllegalStateException("released");
if (codec != null) throw new IllegalStateException("codec != null");
if (canceled) throw new IOException("Canceled");
releasedConnection = this.connection;
//这里面会去检测connection是否释放了,如果释放了会把this.connection置为null
toClose = releaseIfNoNewStreams();
//this.connection没有被释放,则result赋值为connection
if (this.connection != null) {
result = this.connection;
releasedConnection = null;
}
if (!reportedAcquired) {
releasedConnection = null;
}
//当前连接为空(streamAllocation刚新建)或者不可用
if (result == null) {
//从连接池中找到可用的连接(地址、域名相同,connection的streamAllocation对象没有超过规定数量等),找到后,会把当前的streamAllocation添加到
//connection的allocations列表中,由于每次请求都会新建一个streamAllocation,所以每个connection都管理着多个请求,请求复用连接
Internal.instance.get(connectionPool, address, this, null);
if (connection != null) {
foundPooledConnection = true;
result = connection;
} else {
selectedRoute = route;
}
}
}
closeQuietly(toClose);
if (releasedConnection != null) {
eventListener.connectionReleased(call, releasedConnection);
}
if (foundPooledConnection) {
eventListener.connectionAcquired(call, result);
}
if (result != null) {
//从连接池中找到了可用连接
//route包含了代理的ip地址或者目标服务器ip地址,将这些信息给到streamAllocation的route对象
route = connection.route();
return result;
}
//以下是在连接池中没有找到可用连接的情况
boolean newRouteSelection = false;
//通过routeSelector查询dns服务器,解析出目标主机的ip地址,或者代理服务器的ip地址
if (selectedRoute == null && (routeSelection == null || !routeSelection.hasNext())) {
newRouteSelection = true;
//routeSelection存储下一个代理服务器可用的所有ip地址,没有配置代理服务器则存储的目标主机的可用的所有ip地址
//routeSelector初始化时就初始化好了一个proxies列表,这个列表存储了代理服务器的列表,每一次next都切换到下一台
//代理服务器(没有配置代理时则为目标主机),并且解析出当前服务器的所有可用ip,包装到routeSelection中
routeSelection = routeSelector.next();
}
synchronized (connectionPool) {
if (canceled) throw new IOException("Canceled");
if (newRouteSelection) {
//使用新的代理地址去查找可用连接
List<Route> routes = routeSelection.getAll();
//每一个route就是代理服务器或者目标主机的一个可访问ip地址
for (int i = 0, size = routes.size(); i < size; i++) {
Route route = routes.get(i);
//再次从连接池中查找可复用连接,这次相比上次传入了route路由信息
Internal.instance.get(connectionPool, address, this, route);
if (connection != null) {
foundPooledConnection = true;
result = connection;
this.route = route;
break;
}
}
}
//还是没有找到可用连接
if (!foundPooledConnection) {
if (selectedRoute == null) {
//随意使用一个可用的ip
selectedRoute = routeSelection.next();
}
route = selectedRoute;
refusedStreamCount = 0;
//创建新的连接
result = new RealConnection(connectionPool, selectedRoute);
acquire(result, false);
}
}
//找到了连接,则返回,这个写在 if(!foundPooledConnection){} 之前会好理解些
if (foundPooledConnection) {
eventListener.connectionAcquired(call, result);
return result;
}
//tcp连接,最终还是调用socket.connect安卓的api去做连接
result.connect(connectTimeout, readTimeout, writeTimeout, pingIntervalMillis,
connectionRetryEnabled, call, eventListener);
routeDatabase().connected(result.route());
Socket socket = null;
synchronized (connectionPool) {
reportedAcquired = true;
//将连接放入连接池中,并触发连接池的清理runnable
Internal.instance.put(connectionPool, result);
// If another multiplexed connection to the same address was created concurrently, then
// release this connection and acquire that one.
if (result.isMultiplexed()) {
socket = Internal.instance.deduplicate(connectionPool, address, this);
result = connection;
}
}
closeQuietly(socket);
eventListener.connectionAcquired(call, result);
return result;
}