Java设计模式大揭秘,细致剖析5种经典模式
public class SingletonClass {
private static SingletonClass instance;
private SingletonClass() {
// 私有构造函数,防止外部实例化
}
public static SingletonClass getInstance() {
if (instance == null) {
instance = new SingletonClass();
}
return instance;
}
}
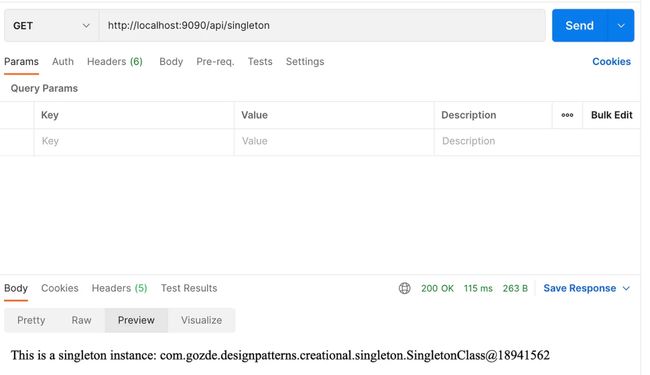
如下所示,当我们发送Postman请求时,控制器类和结果将是同一个实例:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class SingletonController {
private SingletonClass singletonClass;
public SingletonController(SingletonClass singletonClass) {
this.singletonClass = singletonClass;
}
@GetMapping("/singleton")
public String getSingleton() {
return "This is a singleton instance: " + singletonClass.toString();
}
}
当您想要确保类仅存在一个实例时(例如,由程序的不同部分共享的单个数据库对象),您应该使用单例设计模式。
2 工厂
工厂方法是一种创建型设计模式,它提供了一种在创建过程中无需指定其具体类即可创建产品对象的解决方案。
以下是Java代码示例,
PaymentProcessor是定义处理付款的合同的接口。
public interface PaymentProcessor {
void processPayment();
}
CreditCardPaymentProcessor和PaypalPaymentProcessor是实现PaymentProcessor接口的具体类。这些类为CreditCard和PayPal付款特定的processPayment()方法提供了实现。
@Service
public class CreditCardPaymentProcessor implements PaymentProcessor {
@Override
public void processPayment() {
// 信用卡支付交易
}
}
@Service
public class PaypalPaymentProcessor implements PaymentProcessor {
@Override
public void processPayment() {
// PayPal支付交易
}
}
PaymentProcessorFactory是实现工厂设计模式的工厂类。该类负责根据给定的付款方式创建不同PaymentProcessor实现的实例。
@Component
public class PaymentProcessorFactory {
private final CreditCardPaymentProcessor creditCardPaymentProcessor;
private final PaypalPaymentProcessor paypalPaymentProcessor;
public PaymentProcessorFactory(CreditCardPaymentProcessor creditCardPaymentProcessor,
PaypalPaymentProcessor paypalPaymentProcessor) {
this.creditCardPaymentProcessor = creditCardPaymentProcessor;
this.paypalPaymentProcessor = paypalPaymentProcessor;
}
public PaymentProcessor createPaymentProcessor(String paymentMethod) {
if (paymentMethod.equalsIgnoreCase("creditcard")) {
return creditCardPaymentProcessor;
} else if (paymentMethod.equalsIgnoreCase("paypal")) {
return paypalPaymentProcessor;
}
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid payment method: " + paymentMethod);
}
}
入口点处理对/processPayment/{paymentMethod}的请求,并使用PaymentProcessorFactory根据提供的paymentMethod创建适当的付款处理器。这简化了代码并使添加新付款处理器变得容易。
工厂方法是一种用于节省系统资源的设计模式,它通过重复使用现有对象而不是重复构建它们来实现这一目的。
3 抽象工厂
抽象工厂是一种创建型设计模式,它允许您生成相关对象系列,无需指定其具体类。
以下是Java代码示例,
//工厂类
public interface ProductFactory {
Product createProduct();
}
public class ProductAFactory implements ProductFactory{
@Override
public Product createProduct() {
return new ProductA();
}
}
public class ProductBFactory implements ProductFactory{
@Override
public Product createProduct() {
return new ProductB();
}
}
//产品类
public interface Product {
String getName();
}
public class ProductA implements Product {
@Override
public String getName() {
return "Product A";
}
}
public class ProductB implements Product {
@Override
public String getName() {
return "Product B";
}
}
// 使用 ProductAFactory 创建产品 A
ProductFactory productAFactory = new ProductAFactory();
Product productA = productAFactory.createProduct();
System.out.println("Product A: " + productA.getName());
// 使用 ProductBFactory 创建产品 B
ProductFactory productBFactory = new ProductBFactory();
Product productB = productBFactory.createProduct();
System.out.println("Product B: " + productB.getName());
抽象工厂模式在处理不同组相关项目时非常有用,它可以避免代码依赖于这些项目的特定类型。您可能事先不知道这些类型,或者希望为将来添加更多类型留出空间。这样,您的代码可以更加灵活和可扩展。
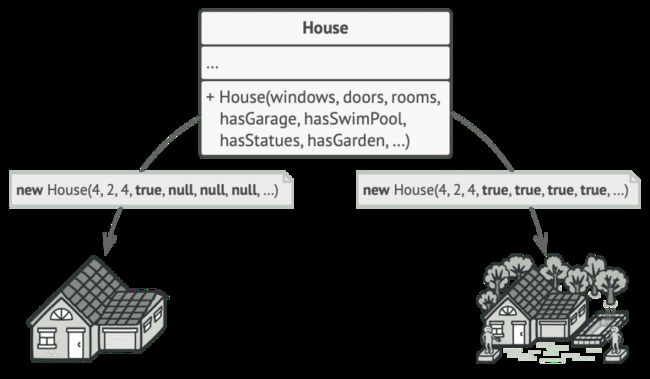
4 Builder
Builder是一种创建型设计模式,它允许您以逐步构建的方式创建复杂的对象。通过使用Builder模式,您可以使用相同的构建代码来生成不同类型和表示形式的对象。这种灵活性使得对象的构建过程更加可控和可定制。
以下是Java代码示例,
@Builder
@Getter
@Setter
public class Beer {
//必填属性
private String name;
private double drinkSize;
private double alcoholPercentage;
private double price;
// 其他属性
private String brewery; // 生产啤酒的酿酒厂
private String countryOfOrigin; // 啤酒原产国
private String description; // 对啤酒特点的简要描述
private String packaging; // 包装类型(瓶装、罐装、生啤等)
private String servingTemperature; // 推荐的饮用温度
private String foodPairing; // 适合搭配该啤酒的食物
}
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/beers")
public class BeerController {
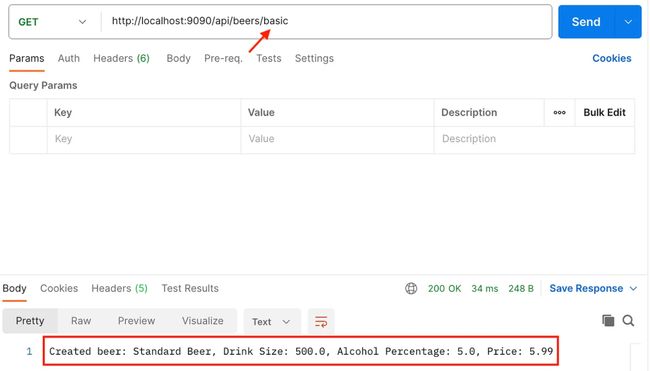
@GetMapping("/basic")
public String createStandardBeer() {
Beer beer = Beer.builder()
.name("Standard Beer")
.drinkSize(500)
.alcoholPercentage(5.0)
.price(5.99)
.build();
return "Created beer: " + beer.getName() +
", Drink Size: " + beer.getDrinkSize() +
", Alcohol Percentage: " + beer.getAlcoholPercentage() +
", Price: " + beer.getPrice();
}
@GetMapping("/premium")
public String createPremiumBeer() {
Beer beer = Beer.builder()
.name("Sample Beer")
.drinkSize(330)
.alcoholPercentage(5.0)
.price(10.99)
.brewery("Crafty Brews")
.countryOfOrigin("United States")
.description("A refreshing lager with a smooth taste.")
.packaging("Bottle")
.servingTemperature("4-6°C")
.foodPairing("Pairs well with grilled chicken and salads.")
.build();
return "Created beer: " + beer.getName() +
", Drink Size: " + beer.getDrinkSize() +
", Alcohol Percentage: " + beer.getAlcoholPercentage() +
", Price: " + beer.getPrice() +
", Brewery: " + beer.getBrewery() +
", Country of Origin: " + beer.getCountryOfOrigin() +
", Description: " + beer.getDescription() +
", Packaging: " + beer.getPackaging() +
", Serving Temperature: " + beer.getServingTemperature() +
", Food Pairing: " + beer.getFoodPairing();
}
}
优点
-
减少构造函数中的参数数量并提供可读的方法调用。
-
允许在完整状态下实例化对象。
-
简化了不可变对象的构建过程。
缺点
-
它会增加代码行数,但提供了设计灵活性和改进的代码可读性。
-
需要为每种产品类型创建单独的ConcreteBuilder类。
5 原型
原型是一种创建型设计模式,它允许您复制现有对象,而不依赖于它们的具体类。
以下是Java代码示例,
designpatterns
└── creational
└── prototype
├── controller
│ └── TreeController.java
├── model
│ ├── Tree.java
│ ├── PlasticTree.java
│ └── PineTree.java
└── PrototypeDemoApplication.java
//抽象类
@Getter
@Setter
public abstract class Tree implements Cloneable {
private String type;
public abstract void copy();
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone();
}
}
//具体类-松树
public class PineTree extends Tree {
public PineTree() {
setType("Pine Tree");
}
@Override
public void copy() {
//实现
}
}
//具体类-塑料树
public PlasticTree() {
setType("Plastic Tree");
}
@Override
public void copy() {
//实现
}
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/trees")
public class TreeController {
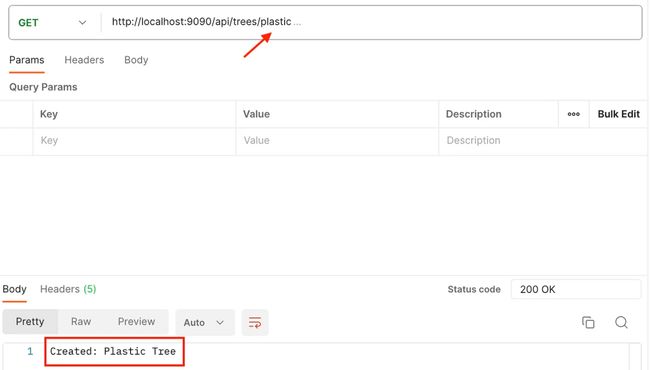
@GetMapping("/plastic")
public String createPlasticTree() {
Tree plasticTree = new PlasticTree();
return "Created: " + plasticTree.getType();
}
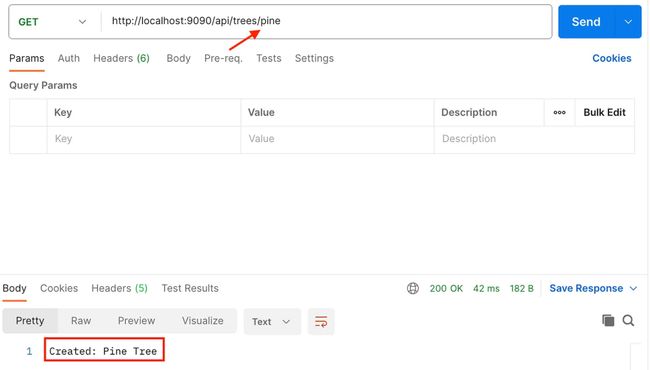
@GetMapping("/pine")
public String createPineTree() {
Tree pineTree = new PineTree();
return "Created: " + pineTree.getType();
}
}
当需要创建的新对象与现有对象仅存在轻微差异时,原型模式非常有用。通过提前设置具有正确设置的实例,我们可以在需要更多相似对象时进行复制,从而节省了创建对象的时间和资源。