shell C语言编程
文章目录
-
- 1、编译优化
-
- makefiel
- 2、文件基本操作编程
-
- 使用Linux系统调用编写一个完成文件拷贝的C程序。比较拷贝得到的文件与源文件的大小和内容(命令diff,cmp)。
- 编写C程序完成:创建一个新文件,输入一段数据,然后随机移动指针接着插入一段数据。完成后,查看该文件的大小和内容。怎样获取当前文件的读写指针位置?
- 3、编写拷贝命令,实现文件或目录的复制
- 4、gdb 调试工具
1、编译优化
//代码
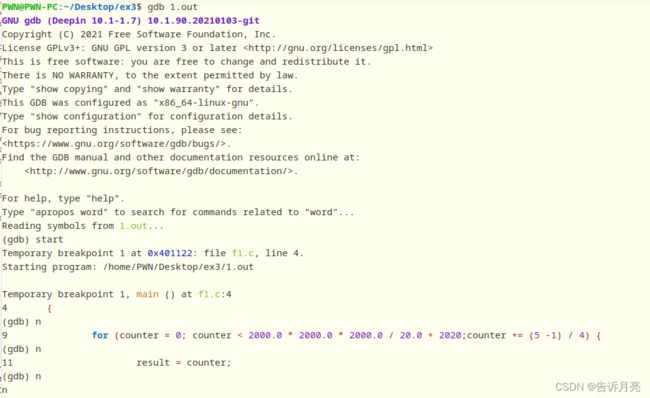
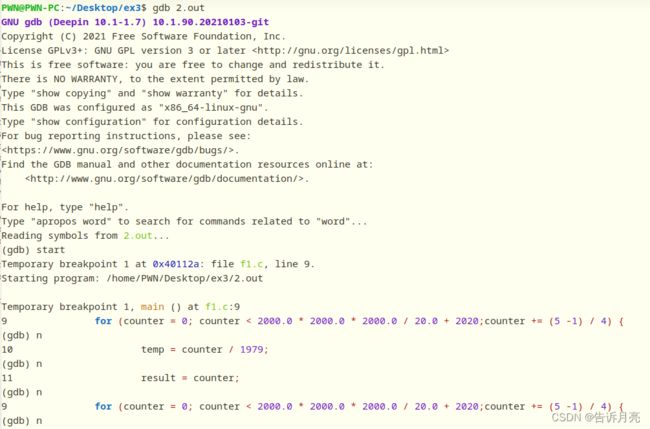
#include gdb调试:
未优化
优化分析:
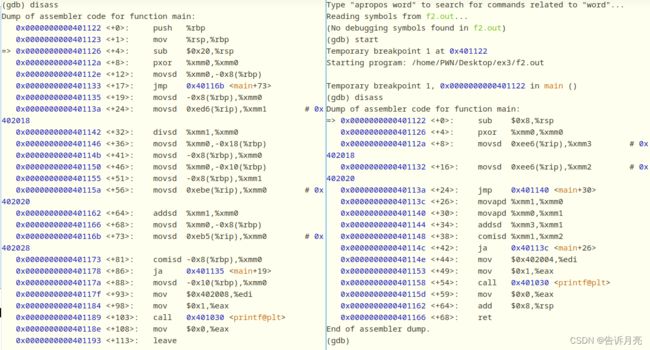
- 代码分析
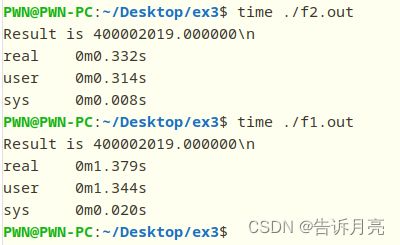
区别:-O优化会改变文件大小,会更小一点。优化后的代码执行时间会更短;优化后的代码会把数据全部存入xmm寄存器,计算时直接从寄存器读取数据;未优化的代码会把一些数据放在栈中来读取。栈中读取和寄存器读取,显然寄存器会更快。
makefiel
一个工程中的源文件不计数,其按类型、功能、模块分别放在若干个目录中,makefile定义了一系列的规则来指定,哪些文件需要先编译,哪些文件需要后编译,哪些文件需要重新编译,甚至于进行更复杂的功能操作,因为makefile就像一个Shell脚本一样,其中也可以执行操作系统的命令。makefile带来的好处就是——“自动化编译”,一旦写好,只需要一个make命令,整个工程完全自动编译,极大的提高了软件开发的效率。
2、文件基本操作编程
使用Linux系统调用编写一个完成文件拷贝的C程序。比较拷贝得到的文件与源文件的大小和内容(命令diff,cmp)。
代码
#include
#include
#include
#include
int main(){
int f1,f1_l,f2; //f1:文件a.txt的句柄;f2:文件b.txt的句柄;f1_l:a.txt文件内容的长度。
char buf[1024]={};//这个用于暂时存储被复制的文件内容
//打开源文件,读取文件内容
f1=open("a.txt",O_RDWR);
f1_l=read(f1,buf,1024);
//这里打开目标文件,如果没有就创建一个,且权限为777,然后将内容复制到目标文件
f2=open("b.txt",O_RDWR | O_CREAT,0777);
write(f2,buf,f1_l);
close(f1);
close(f2);
}
执行结果:
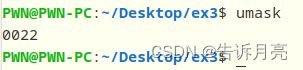
用ls去查看,发现文件大小没有不同,只是两者权限不同。权限设置的是777,但是由于用户的默认权限掩码,
0022,所以创建出来的权限就是0777-0022=0755。
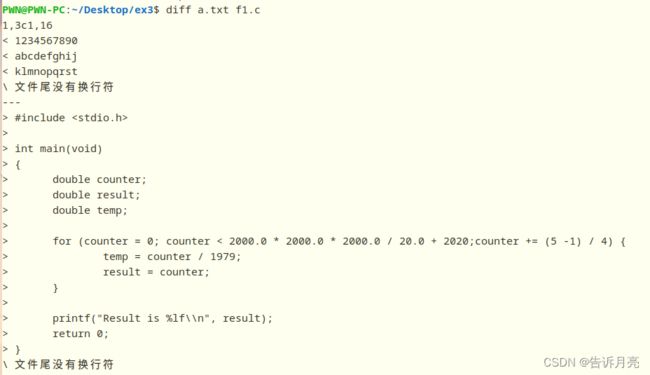
用diff去比较,
diff会针对文本内容逐行进行对比,如果有不同就会显示出这有差别的两行,这里看到文本内容上并没有什么差别。
用cmp去对比,
cmp会逐个字符去比较,会告诉有差异的字符的位置,第几行第几个字符。不加参数的情况下它只会显示出第一个有差异的位置。-l参数会帮助显示出所有有差异的位置。这里也没有不同。
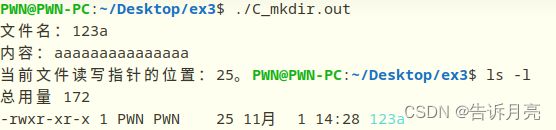
编写C程序完成:创建一个新文件,输入一段数据,然后随机移动指针接着插入一段数据。完成后,查看该文件的大小和内容。怎样获取当前文件的读写指针位置?
代码
#include 获取字符串长度的话就是lseek,SEEK_CUR锁定到当前位置,偏移量为0,就可以得到当前位置了。这里有尝试用tell函数,但是编译时显示没有定义这样一个函数。不知道是我的gcc太老了还是啥。
这里文件的大小就是总的字符串长度。
3、编写拷贝命令,实现文件或目录的复制
#include //这个代码网上转载
#include