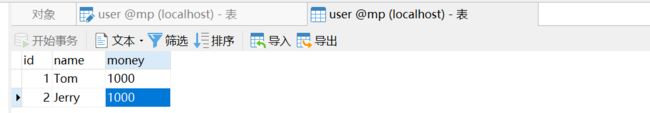
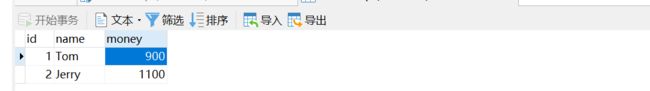
请你谈谈spring事务的理解-1?
1 事务的概念
事务:是数据库操作的最小工作单元,是作为单个逻辑工作单元执行的一系列操作;这些操作作为一个整体一起向系统提交,要么都执行、要么都不执行;事务是一组不可再分割的操作集合(工作逻辑单元) ;通俗点说就是为了达到某个目的而做的一系列的操作要么一起成功 (事务提交),要么一起失败(事务回滚)。
2 事务的四大特性
1(Atomicity)原子性 :事务是最小的执行单位,不允许分割。原子性确保动作要么全部完成,要么完全不起作用;
2(Consistency)一致性:一致性代表了底层数据存储的完整性, 事务系统通过保证事务的原子性,隔离性和持久性来满足这一要求执行事务前后,数据保持一致;
3(Isolation)隔离性: 并发访问数据库时,一个事务不被其他事务所干扰。
4(Durability)持久性: 一个事务被提交之后,对数据库中数据的改变是持久的,即使数据库发生故障。
3 事务的隔离级别

脏读:事务A读取了事务B中尚未提交的数据。如果事务B回滚,则A读取使用了错误的数据。
不可重复读:对于数据库中的某个数据,一个事务范围内多次查询却返回了不同的数据值。这是由于在查询期间,这个数据被另一个事务修改并提交了。【更新操作】
幻读: 在事务A多次读取构成中,事务B对数据进行了新增操作,导致事务A多次读取的数据不一致。【增删】
第一类事物丢失: (称为回滚丢失):A和B同时在执行一个数据, 然后B事物已经提交了,然后A事物回滚了,这样B事物的操作就因A事物回滚而丢失了。
第二类事物丢失: (提交覆盖丢失):也称为覆盖丢失,就是A和B一起执行一个数据,两个同时取到一个数据,然后B事物首先提交,但是A事物又提交,这样就覆盖了B事物。
Read uncommitted
读未提交,顾名思义,就是一个事务可以读取另-个未提交事务的数据,会产生脏读。
Read committed
读提交,顾名思义,就是一个事务要等另一个事务提交后才能读取数据,会产生不可重复读。
Repeatable read
重复读,就是在开始读取数据(事务开启)时,不再允许修改操作,可能会产生幻读。
Serializable
Serializable是最高的事务隔离级别,在该级别下,事务串行化顺序执行,可以避免脏读、不可重复读与幻读。但是这种事务隔离级别效率低下,比较耗数据库性能,一般不使用。
4 spring怎么配置事务
package com.zs.pojo;
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@ToString
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private String money;
}
package com.zs.mapper;
@Repository
public class UserDao {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public void out(String fromName, Integer money) {
String sql = "update user set money = money - ? where name = ? ";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql, money, fromName);
}
public void in(String toName, Integer money) {
String sq1 ="update user set money = money + ? where name = ?";
jdbcTemplate.update(sq1, money, toName) ;
}
}
package com.zs.service;
@Service
public class UserService {
@Autowired
private UserDao userDA0;
public void transfer(String fromName, String toName, Integer money) {
userDA0.out(fromName, money);
int x = 10;
if (x == 10)
throw new RuntimeException("出错啦! ");
userDA0.in(toName, money);
}
}
spring-dao.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.zs"/>
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mp?useSSL=true&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="root"/>
</bean>
<bean class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
</beans>
package com.zs.test;
public class TestBean {
@Test
public void test() {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-dao.xml");
UserService userService = (UserService) context.getBean(UserService.class);
userService.transfer("Tom", "Jerry", 100);
}
}
测试中,出现的问题:
int x = 10;
if (x == 10)
throw new RuntimeException("出错啦! ");
int x = 1;
if (x == 10)
throw new RuntimeException("出错啦! ");
5 xml编程式事务配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.zs"/>
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mp?useSSL=true&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="root"/>
</bean>
<!-- 配置事务管理器 -->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<!-- 配置事务模板对象 -->
<bean id="transactionTemplate" class="org.springframework.transaction.support.TransactionTemplate">
<property name="transactionManager" ref="transactionManager"/>
</bean>
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
</beans>
package com.zs.config;
@ComponentScan("com.zs")
@Configuration
public class AppConfig {
@Bean
public TransactionTemplate transactionTemplate(DataSourceTransactionManager transactionManager) {
TransactionTemplate transactionTemplate = new TransactionTemplate();
transactionTemplate.setTransactionManager(transactionManager);
return transactionTemplate;
}
@Bean
public DataSourceTransactionManager transactionManager(DataSource dataSource){
DataSourceTransactionManager transactionManager = new DataSourceTransactionManager();
transactionManager.setDataSource(dataSource);
return transactionManager;
}
@Bean
public JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate(DataSource dataSource){
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = new JdbcTemplate();
jdbcTemplate.setDataSource(dataSource);
return jdbcTemplate;
}
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource() {
DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource();
dataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mp?useSSL=true&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8");
dataSource.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
dataSource.setUsername("root");
dataSource.setPassword("root");
return dataSource;
}
}
package com.zs.service;
@Service
public class UserService {
@Autowired
private UserDao userDAO;
@Autowired
private TransactionTemplate transactionTemplate;
public void transfer(String fromName, String toName, Integer money) {
transactionTemplate.execute(status -> {
userDAO.out(fromName, money);
int a = 1 / 0;
userDA0.in(toName, money);
return null;
});
}
}
6 AspectJ申明式事务XML配置方式
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.zs"/>
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mp?useSSL=true&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="root"/>
</bean>
<!-- 配置事务管理器 -->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<!--基于AspectJ申明式事务XML配置方式-->
<!-- 定义一个增强-->
<tx:advice id="txAdvice"
transaction-manager="transactionManager">
<!--增强(事务)的属性的配置-->
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="transfer" isolation="DEFAULT" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
<!--aop配置定义切面和切点的信息-->
<aop:config>
<!--定义切点:哪些类的哪些方法应用增强-->
<aop:pointcut
expression="execution(* com.zs.service..*.*(..))"
id="mypointcut"/>
<!--定义切面: -->
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="mypointcut" />
</aop:config>
</beans>
package com.zs.service;
@Service
public class UserService {
@Autowired
private UserDao userDA0;
public void transfer(String fromName, String toName, Integer money) {
userDA0.out(fromName, money);
int a = 1 / 0;
userDA0.in(toName, money);
}
}
7 申明式事务注解配置方式
package com.zs.config;
@ComponentScan("com.zs")
@EnableTransactionManagement // 开启注解事务
public class AppConfig {
@Bean
public DataSourceTransactionManager transactionManager(DataSource dataSource){
DataSourceTransactionManager transactionManager = new DataSourceTransactionManager();
transactionManager.setDataSource(dataSource);
return transactionManager;
}
@Bean
public JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate(DataSource dataSource){
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = new JdbcTemplate();
jdbcTemplate.setDataSource(dataSource);
return jdbcTemplate;
}
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource() {
DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource();
dataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mp?useSSL=true&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8");
dataSource.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
dataSource.setUsername("root");
dataSource.setPassword("root");
return dataSource;
}
}
package com.zs.service;
@Service
public class UserService {
@Autowired
private UserDao userDA0;
@Transactional
public void transfer(String fromName, String toName, Integer money) {
userDA0.out(fromName, money);
int a = 1 / 0;
userDA0.in(toName, money);
}
}
package com.zs.test;
public class TestBean {
@Test
public void test() {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
UserService userService = context.getBean(UserService.class);
userService.transfer("Tom", "Jerry", 100);
}
}
8 事务的传播特性
所谓事务传播机制,也就是在事务在多个方法的调用中是如何传递的,是重新创建事务还是使用父方法的事务?父方法的回滚对子方法的事务是否有影响?这些都是可以通过事务传播机制来决定的。
事务传播行为常量都是以PROPAGATION_ 开头,形如PROPAGATION_XXX。


1)REQUIRED
定义:如果有事务则加入事务,如果没有事务,则创建一个新的(默认值)
- 操作1:将BlogServiceImpl和BlogServiceImpl2的事务传播机制都修改为
@Transactional(propagation=Propagation.REQUIRED)
- 操作2:将BlogServiceImpl事务传播机制修改为@Transactional(propagation=Propagation.NOT_SUPPORTED),BlogServiceImpl2的仍为@Transactional(propagation=Propagation.REQUIRED)
- 总结:当BlogServiceImpl提供事务的时候,BlogServiceImpl2的方法执行使用当前已有事务,不再新建事务;当BlogServiceImpl不创建事务的时候,BlogServiceImpl2的方法执行发现没有事务可用,自己新建事务;
2)NOT_SUPPORTED
定义:Spring不为当前方法开启事务,相当于没有事务
- 操作:将BlogServiceImpl和BlogServiceImpl2的事务传播机制都
修改为@Transactional(propagation=Propagation.NOT_SUPPORTED)
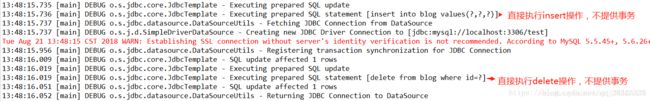
总结:NOT_SUPPORTED相当于没有Spring事务,每条执行语句单独执行,单独提交
3)REQUIRES_NEW
定义:不管是否存在事务,都创建一个新的事务,原来的事务挂起,新的方法执行完毕后,继续执行老的事务
- 操作:将BlogServiceImpl事务传播机制为@Transactional(propagation=Propagation.REQUIRED),BlogServiceImpl2的为@Transactional(propagation=Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW)
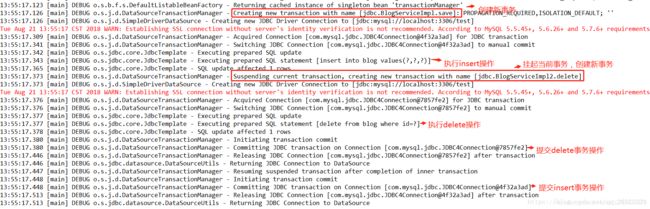
总结:REQUIRES_NEW为当前方法创建一个新的事务,并且当前事务先提交,然后再提交老的事务
4)MANDATORY
定义:必须在一个已有的事务中执行,否则报错
- 操作:将BlogServiceImpl事务传播机制修改为@Transactional(propagation=Propagation.NOT_SUPPORTED),BlogServiceImpl2的仍为@Transactional(propagation=Propagation.MANDATORY),查看是否报错

总结:MANDATORY必须在已有事务下被调用,否则报错;NOT_SUPPORTED执行数据库层面的事务操作,故当前测试中,insert方法成功执行,delete方法的抛错并不影响insert方法的执行
5)NEVER
定义:必须在一个没有的事务中执行,否则报错
-
操作:将BlogServiceImpl事务传播机制修改为@Transactional(propagation=Propagation.REQUIRED),BlogServiceImpl2的仍为@Transactional(propagation=Propagation.NEVER),查看是否报错
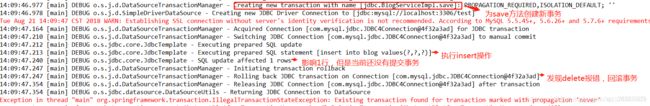
6)SUPPORTS
定义:如果其他bean调用这个方法时,其他bean声明了事务,则就用这个事务,如果没有声明事务,那就不用事务 -
操作1:将BlogServiceImpl事务传播机制修改为@Transactional(propagation=Propagation.REQUIRED),BlogServiceImpl2的仍为@Transactional(propagation=Propagation.SUPPORTS)
-
操作1:将BlogServiceImpl事务传播机制修改为@Transactional(propagation=Propagation.NOT_SUPPORTED),BlogServiceImpl2的仍为@Transactional(propagation=Propagation.SUPPORTS)

总结: SUPPORTS类型的事务传播机制,是否使用事务取决于调用方法是否有事务,如果有则直接用,如果没有则不使用事务7)NESTED
定义:如果当前存在事务,则在嵌套事务内执行。如果当前没有事务,则执行与REQUIRED类似的操作 -
操作1:将BlogServiceImpl事务传播机制修改为@Transactional(propagation=Propagation.REQUIRED),BlogServiceImpl2的仍为@Transactional(propagation=Propagation.NESTED)
-
操作2:将BlogServiceImpl事务传播机制修改为@Transactional(propagation=Propagation.NOT_SUPPORTED),BlogServiceImpl2的仍为@Transactional(propagation=Propagation.NESTED)
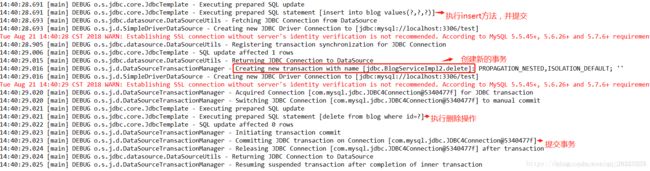
总结:save方法创建一个事务,则再调用delete方法时,直接在该事务的基础上创建一个嵌套事务,本质上还是同一个事务,做一次提交;save方法不创建事务,则调用delete方法时,直接创建一个新的事务,单独提交。 -
1)REQUIRED
当两个方法的传播机制都是REQUIRED时,如果一旦发生回滚,两个方法都会回滚 -
2)REQUIRES_NEW
当delete方法传播机制为REQUIRES_NEW,会开启一个新的事务,并单独提交事务,所以save方法的回滚并不影响delete方法事务提交 -
3)NESTED
当save方法为REQUIRED,delete方法为NESTED时,delete方法开启一个嵌套事务;
当save方法回滚时,delete方法也会回滚;反之,如果delete方法回滚,则并不影响save方法的提交