工程 (六) ——PointNet点云分类
目录
一、 基本原理
二、工程目录
三、代码解析
3.1 分类
3.2 语义分割
四、测试运行
4.1 分类
4.2 语义分割
一、 基本原理
相比与pointnet,pointnet++是对点云逐层运用RNN最邻近收缩进行均匀降采样,加上上一层的特征传入PointNet
为不受坐标的影响,需要有Normalize步骤减去中心位置,以不受绝对距离的影响。比如一个人在1m和在20m都是一个人。
网络框架如下,pointnet++可以进行点云分类和语义分割的操作。
二、工程目录
- test和train:这一系列文件是pointnet++不同功能的测试和验证文件
- visualizer:是对点云分割结果的可视化
- data:放数据集的文件夹
- data_utils:对数据集的解析文件
- log:日志文件及各种功能网络模型的相关代码及预训练权重
可以看到三个功能是分类、区域分割和语义分割,打开一个文件
checkpoint:预训练权重文件
logs:训练日志文件
pointnet2_utils.py:网络相关的代码组件
pointnet2_cls_msg.py:网络模型文件与models下的一样
- models:各种网络模型
三、代码解析
3.1 分类
首先打开model/pointnet2_cls_ssg.py的一个分类网络模型的文件,代码解析如下,可以看到分类网络主要通过三个特征提取层PointNetSetAbstraction之后再通过全链接来达到分类的目的。
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from pointnet2_utils import PointNetSetAbstraction
class get_model(nn.Module): #网络结构
def __init__(self,num_class,normal_channel=True):
super(get_model, self).__init__()
in_channel = 6 if normal_channel else 3
self.normal_channel = normal_channel
# 三次特征提取特征层
self.sa1 = PointNetSetAbstraction(npoint=512, radius=0.2, nsample=32, in_channel=in_channel, mlp=[64, 64, 128], group_all=False)
self.sa2 = PointNetSetAbstraction(npoint=128, radius=0.4, nsample=64, in_channel=128 + 3, mlp=[128, 128, 256], group_all=False)
self.sa3 = PointNetSetAbstraction(npoint=None, radius=None, nsample=None, in_channel=256 + 3, mlp=[256, 512, 1024], group_all=True)
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(1024, 512) #全链接层
'''
BatchNorm1d小批量数据归一化方法
1.加快网络的训练和收敛的速度
2.控制梯度爆炸和梯度消失
3.防止过拟合
'''
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm1d(512)
'''
nn.dropout()是为了防止或减轻过拟合而使用的函数,它一般用在全连接层
Dropout就是在不同的训练过程中随机扔掉一部分神经元。
也就是让某个神经元的激活值以一定的概率p
让其停止工作,这次训练过程中不更新权值,也不参加神经网络的计算。
'''
self.drop1 = nn.Dropout(0.4)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(512, 256)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm1d(256)
self.drop2 = nn.Dropout(0.4)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(256, num_class)
def forward(self, xyz): #前向传播
*********************************
class get_loss(nn.Module): #损失函数
*********************************PointNetSetAbstraction 的代码在pointnet2_untils.py中的PointNetSetAbstraction类中。
文件中有3个类
PointNetSetAbstraction,PointNetSetAbstractionMsg,PointNetFeaturePropagation分别代表不用网络模型所用到的层结构。文件中的其他函数为类中的相关函数
# PointNet网络,将每个区域的所有点变成一个特征 在输入网络之前,会把每个区域的坐标变成围绕中心点的相对坐标
class PointNetSetAbstraction(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, npoint, radius, nsample, in_channel, mlp, group_all):
super(PointNetSetAbstraction, self).__init__()
self.npoint = npoint
self.radius = radius
self.nsample = nsample
self.mlp_convs = nn.ModuleList()
self.mlp_bns = nn.ModuleList()
last_channel = in_channel
for out_channel in mlp:
self.mlp_convs.append(nn.Conv2d(last_channel, out_channel, 1))
self.mlp_bns.append(nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel))
last_channel = out_channel
self.group_all = group_all
def forward(self, xyz, points):
"""
Input:
xyz: input points position data, [B, C, N]
points: input points data, [B, D, N]
Return:
new_xyz: sampled points position data, [B, C, S]
new_points_concat: sample points feature data, [B, D', S]
"""
xyz = xyz.permute(0, 2, 1)
if points is not None:
points = points.permute(0, 2, 1)
if self.group_all:
new_xyz, new_points = sample_and_group_all(xyz, points) #下采样特征点
else:
new_xyz, new_points = sample_and_group(self.npoint, self.radius, self.nsample, xyz, points)
# new_xyz: sampled points position data, [B, npoint, C]
# new_points: sampled points data, [B, npoint, nsample, C+D]
new_points = new_points.permute(0, 3, 2, 1) # [B, C+D, nsample,npoint]
for i, conv in enumerate(self.mlp_convs):
bn = self.mlp_bns[i]
new_points = F.relu(bn(conv(new_points)))
new_points = torch.max(new_points, 2)[0]
new_xyz = new_xyz.permute(0, 2, 1)
return new_xyz, new_points使用sample_and_group以达到选取中心点分局部区域的目的
def sample_and_group(npoint, radius, nsample, xyz, points, returnfps=False):
"""
Input:
npoint:
radius:
nsample:
xyz: input points position data, [B, N, 3]
points: input points data, [B, N, D]
Return:
new_xyz: sampled points position data, [B, npoint, nsample, 3]
new_points: sampled points data, [B, npoint, nsample, 3+D]
"""
B, N, C = xyz.shape
S = npoint
fps_idx = farthest_point_sample(xyz, npoint) # [B, npoint, C] FPS法采样N个中心点
new_xyz = index_points(xyz, fps_idx)
idx = query_ball_point(radius, nsample, xyz, new_xyz) #根据N个中心点生成对应的局部区域
grouped_xyz = index_points(xyz, idx) # [B, npoint, nsample, C]
grouped_xyz_norm = grouped_xyz - new_xyz.view(B, S, 1, C) #坐标归一化
if points is not None:
grouped_points = index_points(points, idx)
new_points = torch.cat([grouped_xyz_norm, grouped_points], dim=-1) # [B, npoint, nsample, C+D]
else:
new_points = grouped_xyz_norm
if returnfps:
return new_xyz, new_points, grouped_xyz, fps_idx
else:
return new_xyz, new_points相关的采样点等函数代码如下
def square_distance(src, dst):
"""
Calculate Euclid distance between each two points.
src^T * dst = xn * xm + yn * ym + zn * zm;
sum(src^2, dim=-1) = xn*xn + yn*yn + zn*zn;
sum(dst^2, dim=-1) = xm*xm + ym*ym + zm*zm;
dist = (xn - xm)^2 + (yn - ym)^2 + (zn - zm)^2
= sum(src**2,dim=-1)+sum(dst**2,dim=-1)-2*src^T*dst
Input:
src: source points, [B, N, C]
dst: target points, [B, M, C]
Output:
dist: per-point square distance, [B, N, M]
"""
B, N, _ = src.shape
_, M, _ = dst.shape
dist = -2 * torch.matmul(src, dst.permute(0, 2, 1))
dist += torch.sum(src ** 2, -1).view(B, N, 1)
dist += torch.sum(dst ** 2, -1).view(B, 1, M)
return dist
def index_points(points, idx):
"""
Input:
points: input points data, [B, N, C]
idx: sample index data, [B, S]
Return:
new_points:, indexed points data, [B, S, C]
"""
device = points.device
B = points.shape[0]
view_shape = list(idx.shape)
view_shape[1:] = [1] * (len(view_shape) - 1)
repeat_shape = list(idx.shape)
repeat_shape[0] = 1
batch_indices = torch.arange(B, dtype=torch.long).to(device).view(view_shape).repeat(repeat_shape)
new_points = points[batch_indices, idx, :]
return new_points
# FPS法采样N个中心点
def farthest_point_sample(xyz, npoint):
"""
Input:
xyz: pointcloud data, [B, N, 3]
npoint: number of samples
Return:
centroids: sampled pointcloud index, [B, npoint]
"""
device = xyz.device
B, N, C = xyz.shape
centroids = torch.zeros(B, npoint, dtype=torch.long).to(device) #采样点矩阵(B,npoint) npoint剩下的点
distance = torch.ones(B, N).to(device) * 1e10 #采样点到所有点之间的距离(B,N)
farthest = torch.randint(0, N, (B,), dtype=torch.long).to(device) #最远点
batch_indices = torch.arange(B, dtype=torch.long).to(device) #batch_size数组
#寻找最远点
for i in range(npoint): #把剩下的点进行循环
centroids[:, i] = farthest #更新最远点
centroid = xyz[batch_indices, farthest, :].view(B, 1, 3) #取出最远点的坐标
dist = torch.sum((xyz - centroid) ** 2, -1) #计算到最远点的欧式距离
mask = dist < distance
distance[mask] = dist[mask] #更新最远点
farthest = torch.max(distance, -1)[1] #返回最远点索引
return centroids
# 根据N个中心点生成对应的局部区域 这里使用到两个超参数 ,一个是每个区域中点的数量K,另一个是query的半径r。
def query_ball_point(radius, nsample, xyz, new_xyz):
"""
Input:
radius: local region radius
nsample: max sample number in local region
xyz: all points, [B, N, 3]
new_xyz: query points, [B, S, 3]
Return:
group_idx: grouped points index, [B, S, nsample]
"""
device = xyz.device
B, N, C = xyz.shape
_, S, _ = new_xyz.shape
group_idx = torch.arange(N, dtype=torch.long).to(device).view(1, 1, N).repeat([B, S, 1])
sqrdists = square_distance(new_xyz, xyz)
group_idx[sqrdists > radius ** 2] = N
group_idx = group_idx.sort(dim=-1)[0][:, :, :nsample]
group_first = group_idx[:, :, 0].view(B, S, 1).repeat([1, 1, nsample])
mask = group_idx == N
group_idx[mask] = group_first[mask]
return group_idx #返回若干个区域3.2 语义分割
语义分割与分类的不同是除了将点云下采样得到特征向量后,还需要将点集上采样回原始点集数量,网络结构如下
class get_model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes):
super(get_model, self).__init__()
# 4次下采样提取特征层
self.sa1 = PointNetSetAbstraction(1024, 0.1, 32, 9 + 3, [32, 32, 64], False)
self.sa2 = PointNetSetAbstraction(256, 0.2, 32, 64 + 3, [64, 64, 128], False)
self.sa3 = PointNetSetAbstraction(64, 0.4, 32, 128 + 3, [128, 128, 256], False)
self.sa4 = PointNetSetAbstraction(16, 0.8, 32, 256 + 3, [256, 256, 512], False)
# 4次上采样恢复点云
self.fp4 = PointNetFeaturePropagation(768, [256, 256])
self.fp3 = PointNetFeaturePropagation(384, [256, 256])
self.fp2 = PointNetFeaturePropagation(320, [256, 128])
self.fp1 = PointNetFeaturePropagation(128, [128, 128, 128])
self.conv1 = nn.Conv1d(128, 128, 1)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm1d(128)
self.drop1 = nn.Dropout(0.5)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv1d(128, num_classes, 1)PointNetSetAbstraction 与分类的代码功能一样,对于语义分割多了上采样层
PointNetFeaturePropagation使用了分层的差值方法,代码如下
class PointNetFeaturePropagation(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channel, mlp):
super(PointNetFeaturePropagation, self).__init__()
self.mlp_convs = nn.ModuleList()
self.mlp_bns = nn.ModuleList()
last_channel = in_channel
for out_channel in mlp:
self.mlp_convs.append(nn.Conv1d(last_channel, out_channel, 1))
self.mlp_bns.append(nn.BatchNorm1d(out_channel))
last_channel = out_channel
def forward(self, xyz1, xyz2, points1, points2):
"""
Input:
xyz1: input points position data, [B, C, N]
xyz2: sampled input points position data, [B, C, S]
points1: input points data, [B, D, N]
points2: input points data, [B, D, S]
Return:
new_points: upsampled points data, [B, D', N]
"""
xyz1 = xyz1.permute(0, 2, 1)
xyz2 = xyz2.permute(0, 2, 1)
points2 = points2.permute(0, 2, 1)
B, N, C = xyz1.shape
_, S, _ = xyz2.shape
if S == 1:
interpolated_points = points2.repeat(1, N, 1)
else:
dists = square_distance(xyz1, xyz2)
dists, idx = dists.sort(dim=-1)
dists, idx = dists[:, :, :3], idx[:, :, :3] # [B, N, 3]
dist_recip = 1.0 / (dists + 1e-8)
norm = torch.sum(dist_recip, dim=2, keepdim=True)
weight = dist_recip / norm
interpolated_points = torch.sum(index_points(points2, idx) * weight.view(B, N, 3, 1), dim=2)
if points1 is not None:
points1 = points1.permute(0, 2, 1)
new_points = torch.cat([points1, interpolated_points], dim=-1)
else:
new_points = interpolated_points
new_points = new_points.permute(0, 2, 1)
for i, conv in enumerate(self.mlp_convs):
bn = self.mlp_bns[i]
new_points = F.relu(bn(conv(new_points)))
return new_points四、测试运行
4.1 分类
test_classification.py代码如下
"""
Author: Benny
Date: Nov 2019
"""
from data_utils.ModelNetDataLoader import ModelNetDataLoader
import argparse
import numpy as np
import os
import torch
import logging
from tqdm import tqdm
import sys
import importlib
BASE_DIR = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))
ROOT_DIR = BASE_DIR
sys.path.append(os.path.join(ROOT_DIR, 'models'))
def parse_args(): #初始化设置
'''PARAMETERS'''
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser('Testing')
parser.add_argument('--use_cpu', action='store_true', default=False, help='use cpu mode')
parser.add_argument('--gpu', type=str, default='0', help='specify gpu device')
parser.add_argument('--batch_size', type=int, default=24, help='batch size in training')
parser.add_argument('--num_category', default=40, type=int, choices=[10, 40], help='training on ModelNet10/40')
parser.add_argument('--num_point', type=int, default=1024, help='Point Number')
parser.add_argument('--log_dir', type=str, required=True, help='Experiment root')
parser.add_argument('--use_normals', action='store_true', default=False, help='use normals')
parser.add_argument('--use_uniform_sample', action='store_true', default=False, help='use uniform sampiling')
parser.add_argument('--num_votes', type=int, default=3, help='Aggregate classification scores with voting')
return parser.parse_args()
def test(model, loader, num_class=40, vote_num=1): #5.测试
mean_correct = []
classifier = model.eval()
class_acc = np.zeros((num_class, 3))
for j, (points, target) in tqdm(enumerate(loader), total=len(loader)):
if not args.use_cpu:
points, target = points.cuda(), target.cuda()
points = points.transpose(2, 1)
vote_pool = torch.zeros(target.size()[0], num_class).cuda()
for _ in range(vote_num):
pred, _ = classifier(points)
vote_pool += pred
pred = vote_pool / vote_num
pred_choice = pred.data.max(1)[1]
for cat in np.unique(target.cpu()):
classacc = pred_choice[target == cat].eq(target[target == cat].long().data).cpu().sum()
class_acc[cat, 0] += classacc.item() / float(points[target == cat].size()[0])
class_acc[cat, 1] += 1
correct = pred_choice.eq(target.long().data).cpu().sum()
mean_correct.append(correct.item() / float(points.size()[0]))
class_acc[:, 2] = class_acc[:, 0] / class_acc[:, 1]
class_acc = np.mean(class_acc[:, 2])
instance_acc = np.mean(mean_correct)
return instance_acc, class_acc
def main(args):
def log_string(str):
logger.info(str)
print(str)
'''HYPER PARAMETER''' #1.选择设备
os.environ["CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES"] = args.gpu
'''CREATE DIR''' #2.创建日志保存路径
experiment_dir = 'log/classification/' + args.log_dir
'''LOG'''
args = parse_args()
logger = logging.getLogger("Model")
logger.setLevel(logging.INFO)
formatter = logging.Formatter('%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s')
file_handler = logging.FileHandler('%s/eval.txt' % experiment_dir) #将命令保存到这个文件
file_handler.setLevel(logging.INFO)
file_handler.setFormatter(formatter)
logger.addHandler(file_handler)
log_string('PARAMETER ...')
log_string(args)
'''DATA LOADING''' #3.数据加载
log_string('Load dataset ...')
data_path = 'data/modelnet40_normal_resampled/'
test_dataset = ModelNetDataLoader(root=data_path, args=args, split='test', process_data=False)
testDataLoader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(test_dataset, batch_size=args.batch_size, shuffle=False, num_workers=10)
'''MODEL LOADING''' #4.加载模型
num_class = args.num_category
model_name = os.listdir(experiment_dir + '/logs')[0].split('.')[0] #获取网络结构文件
print(model_name)
model = importlib.import_module(model_name) #加载网络
classifier = model.get_model(num_class, normal_channel=args.use_normals)
if not args.use_cpu:
classifier = classifier.cuda()
checkpoint = torch.load(str(experiment_dir) + '/checkpoints/best_model.pth') #加载模型权重
classifier.load_state_dict(checkpoint['model_state_dict'])
with torch.no_grad():
instance_acc, class_acc = test(classifier.eval(), testDataLoader, vote_num=args.num_votes, num_class=num_class) #进行测试
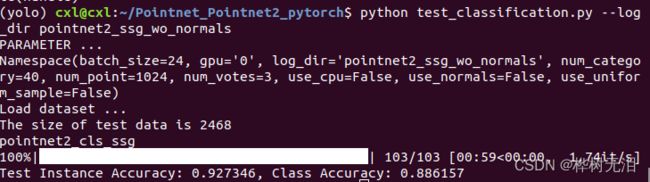
log_string('Test Instance Accuracy: %f, Class Accuracy: %f' % (instance_acc, class_acc))
if __name__ == '__main__':
args = parse_args()
main(args)分类官方使用的是ModelNet数据集,将下载好的 ModelNet40数据集放在./data/路径下
# ModelNet40
## Select different models in ./models
## e.g., pointnet2_ssg without normal features
python train_classification.py --model pointnet2_cls_ssg --log_dir pointnet2_cls_ssg
python test_classification.py --log_dir pointnet2_cls_ssg
## e.g., pointnet2_ssg with normal features
python train_classification.py --model pointnet2_cls_ssg --use_normals --log_dir pointnet2_cls_ssg_normal
python test_classification.py --use_normals --log_dir pointnet2_cls_ssg_normal
## e.g., pointnet2_ssg with uniform sampling
python train_classification.py --model pointnet2_cls_ssg --use_uniform_sample --log_dir pointnet2_cls_ssg_fps
python test_classification.py --use_uniform_sample --log_dir pointnet2_cls_ssg_fps--log_dir 后面跟的是网络模型的名称,也就是model文件夹下的文件。
4.2 语义分割
分割用的3D indoor数据集
Download 3D indoor parsing dataset (**S3DIS**) [here](http://buildingparser.stanford.edu/dataset.html) and save in `data/s3dis/Stanford3dDataset_v1.2_Aligned_Version/`.
```
cd data_utils
python collect_indoor3d_data.py
```
Processed data will save in `data/s3dis/stanford_indoor3d/`.
### Run
```
## Check model in ./models
## e.g., pointnet2_ssg
python train_semseg.py --model pointnet2_sem_seg --test_area 5 --log_dir pointnet2_sem_seg
python test_semseg.py --log_dir pointnet2_sem_seg --test_area 5 --visual