【达梦数据库】数据更新、DM索引(超详细)
文章目录
- 一、数据更新
-
- 1)插入数据(insert into)
-
- 1. 值插入(insert into ... values...)
- 2. 查询插入(insert into...select...)
- 2)修改数据(update...set...)
- 3)删除数据(delete from...)
- 4)另:merge into语句
- 二、DM索引
-
- 1)创建索引(create index...on)
-
-
- 说明:
- 何时使用索引?
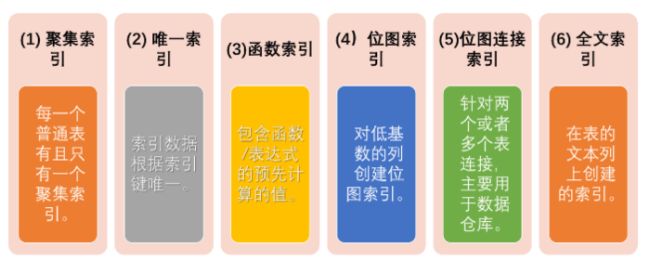
- 几种常见的索引
-
- 1. 在单个字段上建立普通索引
- 2. 在多个字段上建立唯一索引(unique)
- 3. 在单个字段上建立函数索引
- 4. 在低基数字段上建立位图索引
-
- 2)修改索引(alter index...)
- 3)删除索引 (drop index...)
一、数据更新
1)插入数据(insert into)
数据插入语句insert用于往已定义好的表中插入单个或成批的数据。
insert语句有2种形式:
-
值插入:构造一行或者多行,并将它们插入到表中
-
查询插入:通过返回一个查询结果集以构造要插入表的一行或多行。
1. 值插入(insert into … values…)
构造一行或者多行,并将它们插入到表中
insert into <表名>[(<列名>{<列名>})]
values (<插入值>{,<插入值>}; // 一个值
|<插入值>{,<插入值>}){(,<插入值>{,<插入值>})}; // 多个值
说明:
<列名> 指明表或视图的列的名称。在插入的记录中,这个列表中的每一列都被values子句赋一个值。
-
如果在此列表中省略了表的一个列名,则达梦用先前定义好的默认值插入到这一列中。
-
如果此列表被省略,则在values子句中必须为表中的所有列指定值。
<插入值> 指明在列表中对应的列的插入的列值,如果列表被省略了,插入的列值按照基表中列的定义顺序排列。
举例:
- 在EMPLOYEE中插入一条记录。
set schema dmhr; // 设置当前模式,以下的语句都在这个模式下执行
insert into employee(employee_id, employee_name, email, phone_num, hire_date, job_id, department_id)
values(12002, '张三', '[email protected]', '15312348552', '1981-02-20', 52,1105);
- 在EMPLOYEE中插入多行记录。
set schema dmhr; // 设置当前模式,以下的语句都在这个模式下执行
insert into employee(employee_id, employee_name, email, phone_num, hire_date, job_id, department_id)
values(12002, '张三', '[email protected]', '15312348552', '1969-02-20', 52,1105),
(12004,'李四', '[email protected]', '15312348554','1972-02-20',53, 1001);
2. 查询插入(insert into…select…)
将查询结果集插入指定数据表。
insert into <表名>[(<列名>{<列名>})]
select <列名> {,<列名>} from 源数据表名[where条件]
例:使用select子句将employee中部门为“市场部”的人员信息存储到一个新表em-ployee_sale中。
create table em-ployee_sale
as
select employee_id, employee_name, email, hire_date, job_id from employee where false;
insert into em-ployee_sale
(employee_id, employee_name, email, hire_date, job_id)
select t.employee_id, t.employee_name, email, hire_date, job_id
from employee t, department n
where t.department_id = n.department_id and n.department_name='市场部';
2)修改数据(update…set…)
update <表名>|<视图名>
set <列名> = <值表达式> | default>
{,<列名>=<值表达式> | default>}
[where<条件表达式>];
<表名>:指明被修改数据的表的名称。
<视图名>:指明被修改数据的视图的名称,实际上是对视图的基表更新数据。
<列名>:表或视图中被更新列的名称,如果set子句中省略列的名称,列的值保持不变。
<值表达式>:指明赋予相应列的新值。
<条件表达式>:指明限制被更新的行必须符合指定的条件,如果省略此子句,则修改表或视图中所有的行。
举例:
- 将EMPLOYEE中所有人员的工资增加补助500元。
update employee set salary=salary+500;
- 将employee中市场部人员的工资在市场部员工平均工资的基础上增加10%
update employee set salary=salary +
(select avg(salary)*0.1 from employee t, department n where t.department_id=n.department_id and n.department_name='市场部')
where department_id in (select department_id from department where department_name='市场部');
- (同时修改多个字段数据) 将job表中测试工程师的最低工资标准和最高工资标准提高5%。
update job set min_salary=min_salary*1.05, max_salary=max_salary*1.05
where job_title='测试工程师';
3)删除数据(delete from…)
delete from <表名> [where <条件表达式>]
<表名>: 指明被删除数据的表名称。
<条件表达式>: 指明限制被更新的行必须符合指定的条件,如果省略此子句,则修改表或视图中所有的行。
举例:
- 删除表job中的所有数据。
delete from job;
select * from job; // 查看job表是否删除
- 删除job_history表中市场专员人员的工作历史记录。
delete from job_history
where job_id=(select job_id from job where job_title='市场专员');
4)另:merge into语句
使用merge into语句可合并update和insert语句。
通过MERGE语句,根据一张表(或视图)的连接条件对另外一张表(或视图)进行查询,连接条件匹配上的进行update(可能含有delete),无法匹配的执行insert。其中,数据表包括普通表、分区表、加密表、压缩表和list表。
merge into <目标表引用>[<表别名>] using <from 源表引用> on (<目标表和源表的连接条件判断表达式>)
<[<merge_update_clause>] | [<merge_insert_clause>]>
-
on(<条件判断表达式>) : 表示目标表和源表的连接条件,如果目标表有匹配连接条件的记录则执行更新该记录,如果没有匹配到则执行插入源表数据。
-
merge_insert_clause: 当目标表和源表的JOIN条件为false时,执行该语句。同时会触发目标表上的insert触发器,也会进行约束检查。可指定插入条件,插入条件只能在源表上设置。
-
merge_update_clause和merge_insert_clause既可以同时指定,也可以只出现其中任何一个。
-
需要有对源表的select权限,对目标表的UPDATE/INSERT权限,如果UPDATE子句有DELETE,还需要有delete权限。
-
update子句不能更新在ON连接条件中出现的列。
-
如果匹配到,源表中的匹配行必须唯一,否则报错。
-
insert_action不能包含目标表列。
-
插入的where条件只能包含源表列。
举例:
- 把表T1中C1值为2的记录行中的C2列更新为表T2中C3值的记录中C4列的值,同时把表T2中C3列为4的记录行插入到了表T1中。
create table t1(c1 int, c2 varchar(20));
create table t2(c3 int, c4 varchar(20));
insert into t1 values(1,'T1_1');
insert into t1 values(2,'T1_2');
insert into t1 values(3,'T1_3');
insert into t2 values(2,'T2_2');
insert into t2 values(4,'T2_4');
merge into t1 using T2 on(t1.c1=t2.c3)
when matched then update set t1.c2=t2.c4
when not matched then insert(c1,c2) values(t2.c3,t2.c4);
- 把表T1中C1值为2,4的记录行中的C2列更新为表T2中C3值的记录中C4列的值,同时把表T2中C3列为5的记录行插入到了表T1中。由于update带了delete子句,且表T1中C1列值为2和4的记录行被更新过,而C1为4的行符合删除条件,最终该行会被删除掉。
create table t1(c1 int, C2 varchar(20));
create table t2(c3 int, C4 varchar(20));
insert into T1 values(1,'T1_1');
insert into T1 values(2,'T1_2');
insert into t1 values(3,'T1_3');
insert into t1 values(4,'T1_4');
insert into t2 values(2,'T2_2');
insert into t2 values(4,'T2_4');
insert into t2 values(5,'T2_5');
merge into t1 using t2 on(t1.c1=t2.c3)
when matched then update set t1.c2=t2.c4 where t1.c1>2
delete where t1.c1=4
when not matched then insert(c1,c2) values(t2.c3,t2.c4);
二、DM索引
1)创建索引(create index…on)
说明:
-
索引是与表相关的一种结构,能更快地定位数据,使对应于表的SQL语句执行得更快。
-
索引需要存储空间。
-
创建或删除一个索引,不会影响基本表、数据库应用或其他索引。
-
当插入、更改和删除相关的表的行时,DM会自动管理索引。
-
索引可以提高数据的查询效率,但也需要注意,索引会降低某些命令的执行效率,如insert、update、delete的性能,因为DM不仅要维护基表数据还要维护索引数据。
何时使用索引?
-
如果需要经常性地检索大表中的少量的行,就为查询键创建索引
-
为了改善多个表的连接的性能,可为连接列创建索引
-
主键和唯一键自动具有索引,在外键上很多情况下也创建索引
-
小表不需要索引
几种常见的索引
create [or replace][cluster|not partial][unique|bitmap | spatial]
index <索引名> on [<模式名>.]<表名>(<索引列定义>{,<索引列定义>})
[global][<storage子句>][nosort][online];
说明︰
-
on关键字:表示在哪个表的哪个字段上建立索引,字段的类型不能是多媒体类型。
-
<索引名>:指明被创建索引的名称,索引名称最大长度128字节;
-
在字段后面指定索引排序方式,ASC表示递增排序,DESC表示递减排序,默认为递增排序。
-
storage关键字:设置索引存储的表空间,默认与对应表的表空间相同。
-
unique:指明该索引为唯一索引;
-
bitmap:指明该索引为位图索引;
-
spatial:指明该索引为空间索引;
-
not partial:指明该索引为非聚簇索引,缺省即为非聚簇索引;
-
若缺省索引类型参数则默认创建普通索引。
1. 在单个字段上建立普通索引
例:以SYSDBA用户给purchasing模式的VENDOR表的vendorid字段建立普通索引,索引名为S1。
create index s1 on purchasing.vendor(vendorid);
2. 在多个字段上建立唯一索引(unique)
例:以SYSDBA用户给purchasing模式的vendor表的accountno和name字段建立唯一索引,索引名为S2。
create unique index s2 on purchasing.vendor(accountno, name)
3. 在单个字段上建立函数索引
例:以SYSDBA用户给dmhr模式下的city表的city_id字段建立lower()函数索引,索引名为city_lower。
create index city_lower on dmhr.city(lower(city_id));
select * from dmhr.city where lower(city_id)='wh'; // 利用函数索引查看数据
4. 在低基数字段上建立位图索引
低基数字段:字段取值比较少的字段。
关于索引的说明:
-
位图连接索引名称的长度限制为事实表名的长度+索引名称长度+6 <128。
-
仅支持普通表、LIST表和HFS表。
-
where条件只能是列与列之间的等值连接,并且必须含有所有表。
-
位图连接索引表(命名为BMJ$_索引名)仅支持select操作,不支持insert、delete、update、alter、drop等操作。
例:以SYSDBA用户给dmhr模式下的employee表的job_id字段建立位图索引。
create bitmap index dmhr.empjob_idx on dmhr.employee(job_id);
// 利用位图索引查询数据
select employee_id, employee from dmhr.employee where job_id=21;
2)修改索引(alter index…)
alter index [<模式名>.]<索引名><修改索引定义子句>
<修改索引定义子句>::=
rename to[<模式名>.]<索引名>|<invisible|visible>
<unusable>
|<rebuild>[nosort][online]
|<monitoring|nomonitoring>usage;
说明:
-
<模式名>:重命名索引
-
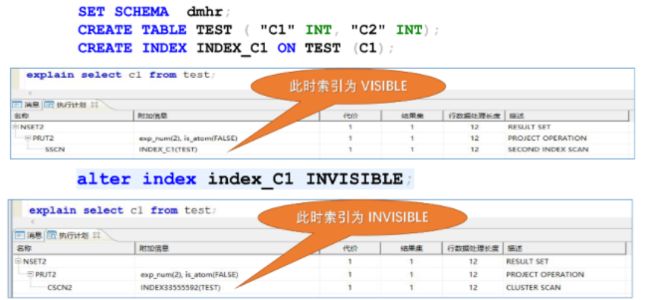
invisible:查询语句的执行不使用该索引,该索引相关计划不会生成,用别的计划代替。
-
visible(默认):会生成索引相关的计划。
-
unusable:索引将被置为无效状态,系统将不再维护此索引。
-
rebuild:重建索引,将置索引的状态为生效状态。
-
nosort:重建时不需要排序。
-
online:重建时使用异步创建逻辑,在过程中可以对索引依赖的表做增删改操作。
-
monitoring usage:对指定索引进行监控。
-
nomonitoring usage:对指定索引取消监控。
例1:以SYSDBA用户重命名S1索引为S3。
alter index purchasing.S1 rename to purchasing.S3;
例2:VISIBLE与INVISIBLE举例。
set schema dmhr;
create table test("C1" int, "C2" int);
create index index_c1 on test(c1);
alter index index_c1 invisible;
例3:使用unusable将索引置为无效状态。
create table test("C1" int, "C2"int);
create index index_C1O on test(C1);
alter index index_C1 unusable; // 此时系统将不维护index_c1,与此相关的计划均失效。
注意,若索引是用于保证数据唯一性的,那么此时表仅能查询,不能更新。
例4:使用rebuild将索引置为生效状态。
alter index index_c1 rebuild;
3)删除索引 (drop index…)
drop index [if exists][<模式名>.]<索引名>;
说明︰
-
删除索引的用户应拥有DBA权限或是该索引所属基表的拥有者。
-
索引是数据表的外在部分,删除索引不会删除表的任何数据,也不改变表的使用方式,只是会影响表数据的查询速度。
-
删除不存在的索引会报错。若指定if exists关键字,删除不存在的索引,不会报错。
举例:具有DBA权限的用户删除purchasing模式下的S1索引。
drop index purchasing.s1;
select vendorid, name from purchasing.vendor where vendorid>10;