检查Python中的变量是否为字符串
我们将通过示例介绍两种不同的方法来检查 Python 中的变量是否为字符串。
检查Python中的变量是否为字符串
在 Python 中,每个变量都有一个数据类型。 数据类型表示变量内部存储的数据类型。
数据类型是编程语言最重要的特征,用于区分我们可以存储的不同类型的数据,例如字符串、整型和浮点型。
在处理许多编程问题时,在某些情况下,我们可能会遇到需要查找某个变量的数据类型以对其执行某些任务的问题。
Python为我们提供了两个函数 isinstance() 和 type() ,用于获取任意变量的数据类型。 如果我们想确保变量存储特定的数据类型,我们可以使用 isinstance() 函数。
让我们来看一个示例,其中我们将创建两个变量,一个具有字符串数据类型,另一个具有 int 数据类型。 我们将测试这两个变量并检查 isinstance() 函数是否可以检测数据类型。
代码示例:
# python
testVar1 = "This is a string"
testVar2 = 13
if isinstance(testVar1, str):
print("testVar1 is a string")
else:
print("testVar1 is not a string")
if isinstance(testVar2, str):
print("testVar2 is a string")
else:
print("testVar2 is not a string")
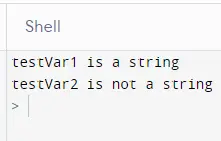
输出:
从输出中可以看出,该函数可以准确地检测任何变量的数据类型。
使用第二个函数 type() 尝试相同的场景。
代码示例:
# python
testVar1 = "This is a string"
testVar2 = 13
if type(testVar1) == str:
print("testVar1 is a string")
else:
print("testVar1 is not a string")
if type(testVar2) == str:
print("testVar2 is a string")
else:
print("testVar2 is not a string")
输出:
我们可以使用 type() 来检测任何变量的数据类型并相应地执行函数。