c++ 基础入门
问题集合:
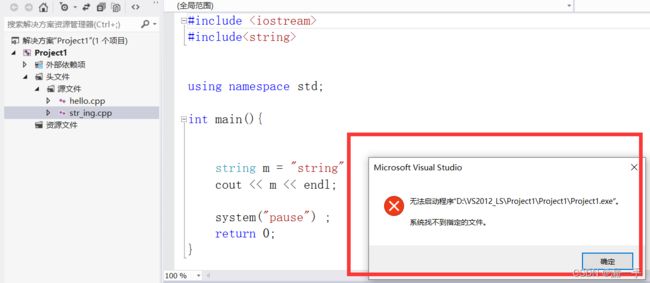
问题一:提示 无法启动程序,系统找不到指定文件
原因是 :在源文件中的两个.cpp文件中都包含了main()函数,但一个项目中只能包含一个main()函数。
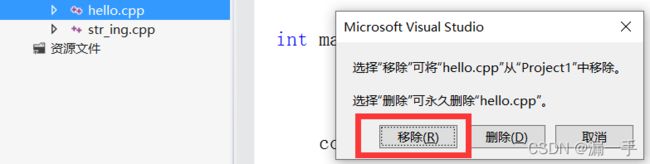
解决办法:移除掉不用的.cpp文件即可;
当需要某个文件时,再将其添加回来即可;
创建第一个程序
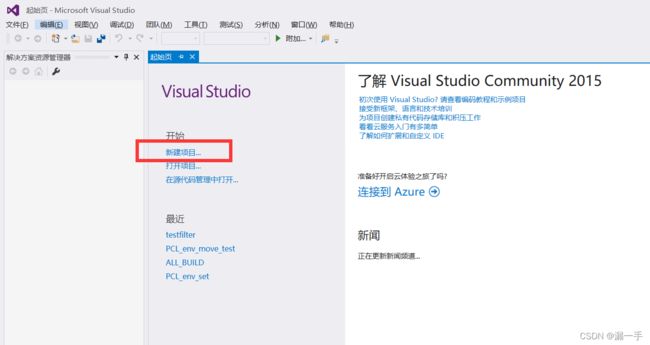
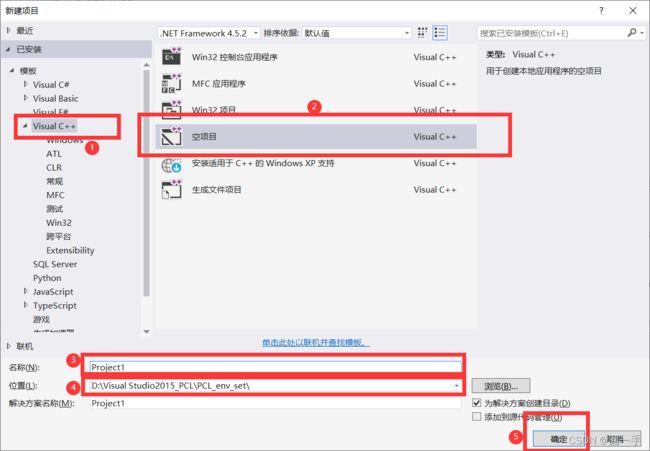
第一步:新建项目;
第二步:
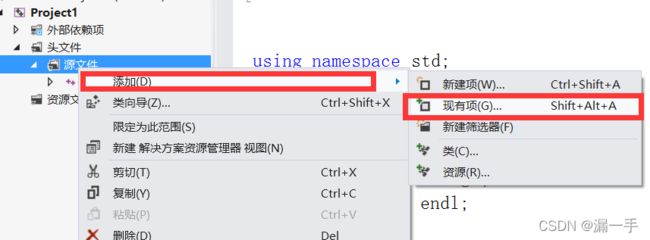
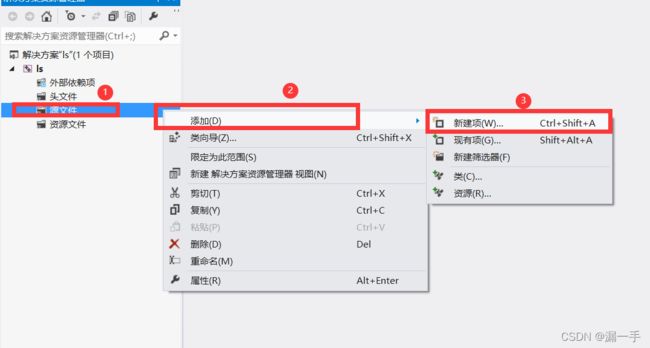
第三步:在源文件右侧点击选择添加,新建项;
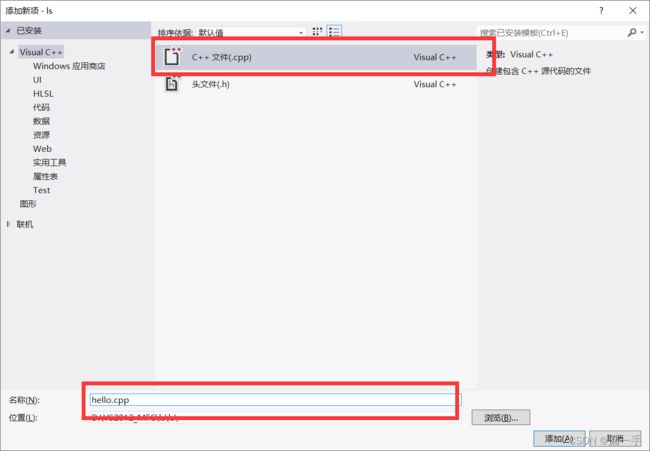
第四步:输入新建项的名称;
第五步:将以下代码写入;
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main(){
cout << "hello world" << endl;
system("pause") ;
return 0;
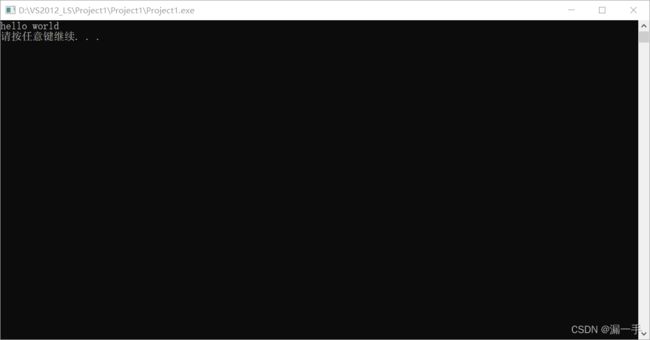
} 第六步: Crtl + F5 运行程序
第一个c++程序结束
C++基础知识
1. 注释
单行注释使用双斜杠 “//”
// “注释内容”
多行注释
/*
注释内容
*/
注释快捷键
crtl+k+c
取消注释快捷键
ctrl+k+u
2. 变量
c++中变量必须指定数据类型和初始值,语法如下;
int a = 03. 常量
常量就是不可改变的量,两种定义方式
//第一种,宏常量
//语法为 #define 常量名 常量数值
#define you 250
//第二种,const修饰的变量
//语法为: const 变量类型 变量名 = 变量值
const int i = 666
4.关键字
就是在c++中有含义的字母或者单词,有点像封建社会皇帝的名字,普通人不能使用
5.命名规则
起名字时的注意事项,有以下几点
1.不能是关键字 ;2.第一个字必须为字母或下划线;3.由 字母、数字、下划线组成;4.区分大小写
6.数据类型
//整形
int a =10
//浮点型
double = 3.14
//字符型
char x = "a"
//字符串型
char x[] = "abc"
//布尔类型
bool x = true;
bool y = flase;7.运算符
略
8.程序流程结构
待更新...
9.数组
略
10.函数
函数定义及调用
#include
using namespace std;
//函数的定义
/* 返回值类型 函数名(参数列表)
{
函数体语句
return表达式
}
*/
int add(int a, int b)
{
int num =a+b;
return num;
}
//函数调用
int main()
{
int x = 10;
int y = 10;
int sum = add(x,y);
cout<<"x y 的和为"< #include
using namespace std;
//函数定义
int add(int num1, int num2) //定义中的num1,num2称为形式参数,简称形参
{
int sum = num1 + num2;
return sum;
}
int main() {
int a = 10;
int b = 10;
//调用add函数
int sum = add(a, b);//调用时的a,b称为实际参数,简称实参
cout << "sum = " << sum << endl;
a = 100;
b = 100;
sum = add(a, b);
cout << "sum = " << sum << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
} 常见函数样式
#include
using namespace std;
//函数常见样式
//无参无返
//无参有返
//有参有返
//有参无返
//1、 无参无返
void test01()
{
//void a = 10; //无类型不可以创建变量,原因无法分配内存
cout << "this is test01" << endl;
//test01(); 函数调用
}
//2、 有参无返
void test02(int a)
{
cout << "this is test02" << endl;
cout << "a = " << a << endl;
}
//3、无参有返
int test03()
{
cout << "this is test03 " << endl;
return 10;
}
//4、有参有返
int test04(int a, int b)
{
cout << "this is test04 " << endl;
int sum = a + b;
return sum;
}
int main()
{
int a = 10;
int b = 5;
test01(); //调用test01
test02(a);//调用test02
int q = test03(); //调用test03
int p = test04(a,b); //调用test04
test04(a,b);
cout<<"test03="< 函数分文件编写:
就是将函数声明,函数的定义,函数的调用分别对应写在头文件、 函数定义文件、main函数中
如果不分开写应该是这样的:
#include
using namespace std;
//函数定义
void swap(int a, int b)
{
int temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
cout << "a = " << a << endl;
cout << "b = " << b << endl;
};
//函数调用
int main()
{
int x = 10;
int y = 5;
swap(x,y);
system("pause");
return 0;
} 如果分开写,头文件写函数声明
//函数声明的头文件
//头文件的命名必须是函数名
#include
using namespace std;
void swap(int a, int b);
函数定义文件编写:
//#include
//using namespace std;
#include "swap.h"
void swap(int a, int b)
{
int temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
cout << "a = " << a << endl;
cout << "b = " << b << endl;
};
main函数调用
#include "swap.h"
int main()
{
int x = 10;
int y = 5;
swap(x,y);
system("pause");
return 0;
}