六、freeRTOS_信号量的使用
目录
1. 信号量的理论讲解
1.1 信号量的常规操作
2. 信号量的常规使用
1. 信号量的理论讲解
本节源码:`15_freertos_example_semaphore`,在`12_freertos_example_sync_exclusion`上修改。
前面介绍的队列(queue)可以用于传输数据:在任务之间、任务和中断之间。
有时候我们只需要传递状态,并不需要传递具体的信息,比如:
- 我的事做完了,通知一下你
- 卖包子了、卖包子了,做好了1个包子!做好了2个包子!做好了3个包子!
- 这个停车位我占了,你们只能等着
在这种情况下我们可以使用信号量(semaphore),它更节省内存。
本章节涉及如下内容:
- 怎么创建、删除信号量
- 怎么发送、获得信号量
- 什么是计数型信号量?什么是二进制信号量?
1.1 信号量的常规操作
信号量这个名字很恰当:
- 信号:起通知作用
- 量:还可以用来表示资源的数量
- 当"量"没有限制时,它就是"计数型信号量"(Counting Semaphores)
- 当"量"只有0、1两个取值时,它就是"二进制信号量"(Binary Semaphores)
- 支持的动作:"give"给出资源,计数值加1;"take"获得资源,计数值减1
计数型信号量的典型场景是:
- 计数:事件产生时"give"信号量,让计数值加1;处理事件时要先"take"信号量,就是获得信号量,让计数值减1。
- 资源管理:要想访问资源需要先"take"信号量,让计数值减1;用完资源后"give"信号量,让计数值加1。
信号量的"give"、"take"双方并不需要相同,可以用于生产者-消费者场合:
- 生产者为任务A、B,消费者为任务C、D
- 一开始信号量的计数值为0,如果任务C、D想获得信号量,会有两种结果:
- 阻塞:买不到东西咱就等等吧,可以定个闹钟(超时时间)
- 即刻返回失败:不等
- 任务A、B可以生产资源,就是让信号量的计数值增加1,并且把等待这个资源的顾客唤醒
- 唤醒谁?谁优先级高就唤醒谁,如果大家优先级一样就唤醒等待时间最长的人
2. 信号量的常规使用
本节源码:`15_freertos_example_semaphore`,在`12_freertos_example_sync_exclusion`上修改。
信号量同步功能
static int sum = 0;
static volatile int flagCalcEnd = 0;
static volatile int flagUARTused = 0;
static SemaphoreHandle_t xSemCalc;
static SemaphoreHandle_t xSemUART;
void Task1Function(void * param)
{
volatile int i = 0;
while (1)
{
for (i = 0; i < 10000000; i++)
sum++;
//printf("1");
xSemaphoreGive(xSemCalc);
vTaskDelete(NULL);
}
}
void Task2Function(void * param)
{
while (1)
{
//if (flagCalcEnd)
flagCalcEnd = 0;
xSemaphoreTake(xSemCalc, portMAX_DELAY);
flagCalcEnd = 1;
printf("sum = %d\r\n", sum);
}
}
void TaskGenericFunction(void * param)
{
while (1)
{
xSemaphoreTake(xSemUART, portMAX_DELAY);
printf("%s\r\n", (char *)param);
xSemaphoreGive(xSemUART);
vTaskDelay(1);
}
}
/*-----------------------------------------------------------*/
int main( void )
{
TaskHandle_t xHandleTask1;
#ifdef DEBUG
debug();
#endif
prvSetupHardware();
printf("Hello, world!\r\n");
xSemCalc = xSemaphoreCreateCounting(10, 0);
xSemUART = xSemaphoreCreateBinary();
xSemaphoreGive(xSemUART);
xTaskCreate(Task1Function, "Task1", 100, NULL, 1, &xHandleTask1);
xTaskCreate(Task2Function, "Task2", 100, NULL, 1, NULL);
//xTaskCreate(TaskGenericFunction, "Task3", 100, "Task 3 is running", 1, NULL);
//xTaskCreate(TaskGenericFunction, "Task4", 100, "Task 4 is running", 1, NULL);
/* Start the scheduler. */
vTaskStartScheduler();
/* Will only get here if there was not enough heap space to create the
idle task. */
return 0;
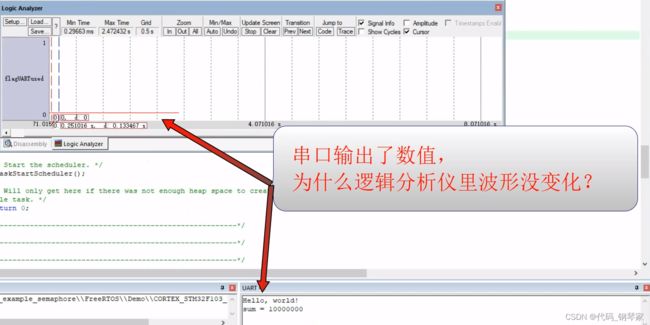
}运行结果
使用计数型的信号量xSemCalc = xSemaphoreCreateCounting(10, 0); 基本实现了同步功能,串口输出了数值。
信号量互斥功能
static int sum = 0;
static volatile int flagCalcEnd = 0;
static volatile int flagUARTused = 0;
static SemaphoreHandle_t xSemCalc;
static SemaphoreHandle_t xSemUART;
void Task1Function(void * param)
{
volatile int i = 0;
while (1)
{
for (i = 0; i < 10000000; i++)
sum++;
//printf("1");
xSemaphoreGive(xSemCalc);
vTaskDelete(NULL);
}
}
void Task2Function(void * param)
{
while (1)
{
//if (flagCalcEnd)
flagCalcEnd = 0;
xSemaphoreTake(xSemCalc, portMAX_DELAY);
flagCalcEnd = 1;
printf("sum = %d\r\n", sum);
}
}
void TaskGenericFunction(void * param)
{
while (1)
{
xSemaphoreTake(xSemUART, portMAX_DELAY);
printf("%s\r\n", (char *)param);
xSemaphoreGive(xSemUART);
vTaskDelay(1);
}
}
/*-----------------------------------------------------------*/
int main( void )
{
TaskHandle_t xHandleTask1;
#ifdef DEBUG
debug();
#endif
prvSetupHardware();
printf("Hello, world!\r\n");
xSemCalc = xSemaphoreCreateCounting(10, 0);
xSemUART = xSemaphoreCreateBinary();
xSemaphoreGive(xSemUART);
//xTaskCreate(Task1Function, "Task1", 100, NULL, 1, &xHandleTask1);
//xTaskCreate(Task2Function, "Task2", 100, NULL, 1, NULL);
xTaskCreate(TaskGenericFunction, "Task3", 100, "Task 3 is running", 1, NULL);
xTaskCreate(TaskGenericFunction, "Task4", 100, "Task 4 is running", 1, NULL);
/* Start the scheduler. */
vTaskStartScheduler();
/* Will only get here if there was not enough heap space to create the
idle task. */
return 0;
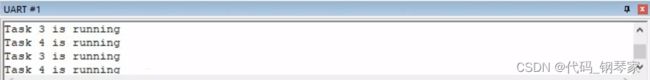
}运行结果
Task3、Task4使用二进制信号量xSemUART = xSemaphoreCreateBinary();,实现了互斥功能,串口输出了数值。