【Few-Shot Segmentation论文阅读笔记】Part-aware prototype for few-shot semantic Segmentation, ECCV, 2020
Abstract
问题:
现有Few-shot segmentation方法的缺点包括:
- 只能处理有限的问题:one-way few-shot segmentation, 比较难向multi-way进行扩展
- Single prototype 表征能力有限,无法涵盖object的全部regions
目标:
针对上述问题,本文引入semi-supervised framework,将其作为semi-supervised few-shot semantic segmentation问题,从两方面入手enrich the prototype representations of each semantic class:
- 将holistic class prototype representation分解为一组part-aware prototypes,进而capture diverse and fine-grained(细粒度的) object features,以更好地涵盖和表示object regions。
- 利用大量的unlabeled images作为支持集的补充,从unlabeled和labeled图片中钟提取prototypes, 丰富其prototype的表征能力。
方法:
为了实现上述目标,本文提出了算法Part-aware prototype network (PPNet), 该算法有三部分组成:
- An embedding network: 用来提取support set (unlabeled + labeled images)和query set的feature maps.
- A prototypes generation network: 为每个类别生成一组具有可以区分性的part-aware prototypes.
- A part-aware mask generation network: 生成semantic mask prediction on a query image.
结果:
- 在PASCAL-5i和COCO-20i两个数据集上取得了更好的效果,优于现有方法
- 本文提出的算法,可以既可以应用到one-way few-shot segmentation,也可以应用到multi-way few-shot segmentation问题。
代码地址: https://github.com/Xiangyi1996/PPNet-PyTorch
Comments:
优点:
- 本文是第一个将unlabeled data应用于few-shot segmentation task的文章
(the first to leverage the unlabeled data in the few-shot segmentation task)
- 本文提出了一种灵活的,基于prototype的小样本语义分割算法,在one-way和multi-way小样本语义分割问题上都取得了更好的结果
- 本文提出了一种part-aware prototype representation for semantic class, 能够提取更细粒度的特征用于语义分割
- 为了capture intra-class variation, 利用unlabeled data进行半监督学习,计算prototype by GNN.
缺点:
- 虽然作者说自己的算法优于过去的算法,但实际上,在one-way one-shot segmentation问题上,效果并不好,而且作者也没有给出原因。
1. Problem Setting 问题定义
本文采用meta-learning strategy, 定义M为meta-learner, 存在a family of few-shot segmentation tasks,记为: ={}, 是从an underlying task distribution 中采用得到的。
每个Task T (也叫episode), 其数据集由support set + query set组成,
- Support set: 本文中包括两部分,labeled + unlabled数据,记为
。
- 对于c-way k-shot问题而言,即:每个task涉及到C个类别,每个类别涉及K个样本
- Labeled set:
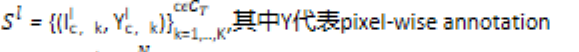
- Unlabeled set:
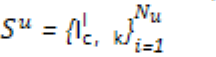
- Labeled set:
- Query set: 记为

- 注意:
- Q中的image also from the class set:
- 在训练集上有标签,测试集上无标签
- Q中的image also from the class set:
训练集和测试集:

注意: 和
没有交集!
2. The proposed methods
Main Idea: capture the intra-class (类内) variation and fine-grained features of semantic classes by a set of part-aware prototypes for each class, and additionally utilizing unlabeled data to enrich their representations.
模型组成:三个网络 + 一个Semantic branch组成:
- Embedding network:提取feature maps for support and query images
- Prototype generation network:从labeled和unlabeled support images中提取a set of part-aware prototypes.
- 组成模块:part generation module + part refinement module
- Part-aware mask generation network:用于生成the final semantic prediction for the query images.
- Semantic branch: 用于generate mask predictions over the global semantic class space

2.1 Embedding network, 记为
目的:计算feature maps
结构:Following prior work [36, 35],使用ResNet[12];使用dilated convolution,enlarge the receptive field and preserve spatial details.
计算过程:

2.2 Prototypes Generation network
目的:为每个类别生成对应的一组part-aware prototypes.
输入:![]() 和
和, k代表当前类别
输出:a set of part-aware prototypes
组成模块:
- Prototype generation network: 基于labeled数据集生成a set of initial part-ware prototypes, 并为其添加global context of the semantic class
 |
- Part Refinement with unlabeled data: 通过引入unlabeled support images来enrich the prototypes,使其能够更好地捕获intra-class variations of each semantic class.
 |
2.3 Part-aware mask generation network

2.4 Model Training with Semantic Regularization

3. Experiment
数据集: PASAL-5i [3] + COCO-20i [33, 20]
3.1 Experimental Configuration
Network:
- ResNet[12] pretrained on ILSVC [25]作为feature extractor
- 输入图像被resize为[417, 417]
- 使用horizontal random flipping来做data augmentation
- Part-aware prototype network: =5, =100, =0, =0.8, =0.2
Training Setting:
SGD, initial learning rate = 5e-4, weight decay = 1e-4, momentum = 0.9, 最大迭代次数=24K
Decay the learning rate 10 times in 10K, 20K respectively.
的权重=0.5
Baseline & Evaluation Metrics:
PANet[33]作为baseline method
对比方法:[3, 37, 22, 33, 35], [27, 20, 36], [29]
评估标准:mean-IoU (本文关注), binary-IoU
3.2 Experiments on PASCAL-5i [11] + [3, 37]
共有20个类别,分为4folds,每个fold有5个类别。
定量结果分析:Table 1 和 Tabel 2
- Table 1: 1-way 1-shot & 1-way 5-shot
- Table 2: multi-way setting (2-way 1-shot and 2-way 5-shot)
 |
定性分析:Fig 3 (1-way 1-shot setting)
 |
5.3 Experiments on Coco-20i [33, 20]
分为4-fold, 每组20类。
本文的划分有两种,分别记为:
- Split-A, 参考[33], 本文关注这个
- Split-B, 参考[20]
模型在three folds上训练,另外一个fold作为验证集,进行交叉验证
定量结果:

3.4 Ablation Study
在COCO-20i上使用split-A, 进行1-way 1-shot learning
- Part-aware prototypes (PAP): 说明global semantic is important for part-level representation
- Semantic branch (SEM): can improve the convergence and the final performance significantly.
- Unlabeled data (UD): GNN is useful
- Hyper-parameters: =5, =6, =0.5

4. Introduction & Related Work
基于DL的语义分割问题往往依赖于大量的标注数据,但是获取标注数据是非常耗时耗力的,常用的解决方法:
- Weak supervision [15], 2017, ICLR: Kipf, T.N., Welling, M.: Semi-supervised classification with graph convolutional networks. In: International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR) (2017)
目前,小样本语义分割问题受到了广泛的关注:
Matching-based methods:
- 相关方法:
- [21], 2018: Rakelly, K., Shelhamer, E., Darrell, T., Efros, A.A., Levine, S.: Few-shot segmen- tation propagation with guided networks. arXiv preprint (2018)
- [37], 2018 SG-One: Zhang, X., Wei, Y., Yang, Y., Huang, T.: Sg-one: Similarity guidance network for one-shot semantic segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv (2018)
- [36], 2019, CVPR: Zhang, C., Lin, G., Liu, F., Yao, R., Shen, C.: Canet: Class-agnostic segmentation networks with iterative refinement and attentive few-shot learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition(CVPR) (2019)
- [35], 2019, ICCV: Zhang, C., Lin, G., Liu, F., Guo, J., Wu, Q., Yao, R.: Pyramid graph networks with connection attentions for region-based one-shot semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision(ICCV) (2019)
- [20], 2019, ICCV: Nguyen, K., Todorovic, S.: Feature weighting and boosting for few-shot segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vi- sion(ICCV) (2019)
- [3], 2017, BMCV: Boots, Z.L.I.E.B., Shaban, A., Bansal, S.: One-shot learning for semantic segmen- tation. British Machine Vision Conference(BMVC) (2017)
- [22], 2018: Rakelly, K., Shelhamer, E., Darrell, T., Efros, A., Levine, S.: Conditional networks for few-shot semantic segmentation (2018)
- 上述方法缺点:only focus on one-way few-shot segmentation, and computationally expensive to generalize to the multi-way setting.
Prototype-based methods: conduct pixel-wise matching on query images with holistic prototypes of semantic classes.
- 相关方法:
- [7], BMCV, 2018: Dong, N., Xing, E.: Few-shot semantic segmentation with prototype learning. In: British Machine Vision Conference(BMVC) (2018)
- [27], 2019: Siam, M., Oreshkin, B.: Adaptive masked weight imprinting for few-shot segmen- tation. arXiv preprint arXiv (2019)
- [33], 2019: Wang, K., Liew, J.H., Zou, Y., Zhou, D., Feng, J.: Panet: Few-shot image semantic segmentation with prototype alignment. arXiv preprint arXiv (2019)
- 上述方法缺点:仅仅使用a single holistic representation, 很难cope with diverse appearance in objects with different parts poses and subcategories.
- Optimization-based methods:
- 相关方法:
- [29], 2019, Tian, P., Wu, Z., Qi, L., Wang, L., Shi, Y., Gao, Y.: Differentiable meta-learning model for few-shot semantic segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv (2019)
- 相关方法:
类别1和类别2的方法具有的共同缺点是:只利用了a small support set来提取信息,限制了其捕获rich and fine-grained feature variant的能力。
其他的Related Work:
- Few-Shot Classification
- Metric learning based methods: [34], 2018, AAAI; [28], 2017, NIPS; [32], 2016, NIPS
- Optimization learning based methods: [23], 2016; [8], 2017
- Graph-neural network based methods: [9], 2017; [8], 2017
- 引入Semi-supervised learning的方法:
- [24], 2018
- [10], 2019, NIPS
- [1], 2019
- Graph Neural Networks
- [10], [26],
- [14]: semi-supervised + GNN
- [31]: GNN + attention
- [9]: GNN + few-shot image classification
Conclusion
本文提出了PPNet模型,首次在few-shot segmentation问题中引入semi-supervised framework,利用unlabled data来capture intra-class variation of the prototypes, 并结合GNN为每一类产生多个part-aware prototypes,取得了更好地结果。