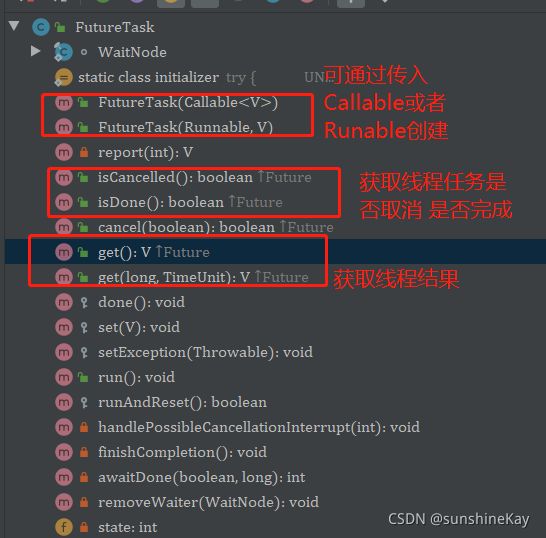
- javaweb中@Component和@Mapper和@Service和@RestController这几个注解要加在哪?为什么?
瑞金彭于晏
mavenjavaspringbootspring
在JavaWeb开发中特别是在使用Spring框架(包括SpringBoot)时,@Component、@Mapper、@Service、@RestController这些注解扮演着非常重要的角色,它们用于定义组件的类型,并帮助Spring框架进行自动装配和依赖注入。下面分别解释这些注解应该加在哪里以及为什么:1.@Component加在哪里:@Component可以加在任何类上,表示这个类是一个
- Java Stream 去重的多种方法
坎布里奇
javajavapython开发语言
在JavaStream中实现去重有多种方法,具体取决于需求和场景。以下是常见的几种方法及示例:1.使用distinct()方法适用于对象已正确实现equals()和hashCode(),基于对象整体去重并保留顺序:ListuniquePersons=persons.stream().distinct().collect(Collectors.toList());2.根据对象的属性去重方法一:使用C
- java数组
TwitCoder
java算法
目录一、数组概念二、数组的声明与初始化三、数组操作示例四、数组属性与注意事项五、内存结构分析六、常见操作七、二维数组八、稀疏数组一、数组概念数组是Java中用于存储相同类型数据的有序集合,具有以下特性:类型一致性:所有元素必须属于同一数据类型有序性:元素按顺序排列,通过索引访问长度固定:创建后无法改变容量二、数组的声明与初始化声明数组//推荐写法int[]numbers;初始化方式:动态初始化nu
- Java开发-面试题-0014-@Component, @Controller, @Repository,@Mapper,@Service有何区别
CodeZeng1998
面试题java开发语言springboot
更多内容欢迎关注我(持续更新中,欢迎Star✨)Github:CodeZeng1998/Java-Developer-Work-Note技术公众号:CodeZeng1998(纯纯技术文)生活公众号:好锅(Lifeismorethancode)其他平台:CodeZeng1998、好锅@Component,@Controller,@Repository,@Mapper,@Service有何区别:@Co
- PySpark安装及WordCount实现(基于Ubuntu)
uui1885478445
ubuntulinux运维
在Ubuntu上安装PySpark并实现WordCount,需要以下步骤:安装PySpark:安装Java:PySpark需要Java运行环境。你可以使用以下命令安装OpenJDK:sudoaptupdatesudoaptinstalldefault-jredefault-jdk安装Scala:PySpark还需要Scala,可以使用以下命令安装:sudoaptinstallscala安装Pyth
- JavaScript 全面教程:从基础到高级实践
幼儿园扛把子\
javascript开发语言ecmascript
JavaScript全面教程:从基础到高级实践目录JavaScript全面教程:从基础到高级实践2.JavaScript基础语法2.1变量与数据类型2.1.1变量声明2.1.2数据类型2.2条件语句与循环2.2.1条件语句2.2.2循环2.3函数2.3.1函数定义2.3.2参数默认值3.对象与数组3.1对象3.2数组4.高级特性与最佳实践4.1作用域与闭包4.1.1闭包示例4.2事件循环(Even
- VUE前端实现防抖节流 Lodash
2501_91133275
前端vue.jsjavascript
写在前面:兄弟们,我手里有个长期项目,考虑接私活的可以看看我GitHub!https://github.com/ccy-233/coder2retire方法一:采用Lodash工具库Lodash是一个一致性、[模块化]、高性能的JavaScript实用工具库。(1)采用终端导入Lodash库$npmi-gnpm$npmi--savelodash(2)应用示例:搜索框输入防抖在这个示例中,我们希望用
- 一篇文章带你学完Java所有的时间与日期类
MHP小喇叭
java开发语言
目录一、传统时间与日期类1.Date类构造方法获取日期和时间信息的方法设置日期和时间信息的方法2.Calendar类主要特点和功能常用方法1.获取当前日历对象2.获取日历中的某个信息3.获取日期对象4.获取时间毫秒值5.修改日历的某个信息6.为某个信息增加或者减少值3.SimpleDateFormat类主要用途构造函数模式字符串将日期格式化成日期与时间字符串将时间毫秒值格式化成字符串解析日期示例要
- IDEA Reformat Code 避免将多行参数或多行方法链调用合并成一行
阿湯哥
intellij-ideajavaide
在IntelliJIDEA中,如果你希望在进行代码格式化(ReformatCode)时,避免将多行参数或多行方法链调用合并成一行,可以通过以下步骤进行设置:1.打开设置在IntelliJIDEA中,点击File菜单,然后选择Settings(Windows/Linux)或Preferences(macOS)。2.进入代码格式化设置在设置窗口中,导航到Editor->CodeStyle->Java(
- CVE-2017-5645(使用 docker 搭建)
JM丫
网络安全
介绍:是一个与ApacheLog4j2相关的安全漏洞,属于远程代码执行,它可能允许攻击者通过构造恶意的日志信息在目标系统上执行任意代码Log4j2介绍Log4j2是Apache的一个日志记录工具,属于Java应用的日志框架,它是Log4j的升级版,性能更好,功能更多.它被广泛的适用于Java应用程序中,帮助开发者记录程序运行的时候的日子信息,是Java生态系统中最重要的一个日志框架之一漏洞编号:C
- 【前端入门】应该了解和知道的几个国内外前端开发资源网站
爱上大树的小猪
前端
与大家分享一下几个国内外前端开发资源网站国际资源MDNWebDocs(MozillaDeveloperNetwork)用途:MDN是Web技术领域最全面的文档库之一,涵盖了HTML、CSS、JavaScript以及浏览器API等。链接:https://developer.mozilla.orgW3Schools用途:适合初学者学习Web技术,提供从基础到进阶的教程,同时还有在线练习环境。链接:ht
- Python(1)Python全方位指南:定义、应用与零基础入门实战
一个天蝎座 白勺 程序猿
Python入门到精通python开发语言
背景:为什么Python成为开发者必备技能?Python自1991年发布以来,凭借“简单高效”的设计理念,成为全球增长最快的编程语言。根据TIOBE2023年榜单,Python稳居前三,其核心竞争力包括:开发效率高:代码量仅为Java的1/5,C++的1/10。跨领域通吃:从Web开发到AI训练,覆盖90%以上技术场景。企业级应用:YouTube用Python处理视频推荐,NAS
- IntelliJ IDEA 2023.3.1安装指南从下载到配置的完整教程(附资源下载)
心灵宝贝
intellij-ideajavaide
安装IntelliJIDEA2023.3.1非常简单,以下是详细的安装步骤,适用于Windows、macOS和Linux系统。1.下载IntelliJIDEAIntelliJIDEA下载链接:https://pan.quark.cn/s/3ad975664934选择适合你的操作系统的版本:Ultimate版:功能全面,支持所有开发语言和框架(需付费)。Community版:免费版,适合Java和K
- 计算机毕业设计springboot教务管理系统 0k1c1源码+系统+程序+lw文档+部署
呦呦网络
springbootjavamysql
计算机毕业设计springboot教务管理系统0k1c1源码+系统+程序+lw文档+部署计算机毕业设计springboot教务管理系统0k1c1源码+系统+程序+lw文档+部署本源码技术栈:项目架构:B/S架构开发语言:Java语言开发软件:ideaeclipse前端技术:Layui、HTML、CSS、JS、JQuery等技术后端技术:JAVA运行环境:Win10、JDK1.8数据库:MySQL5
- c++与c语言的区别是什么?
pythoncainiao221
c++c语言开发语言
1、类型不同C语言是面向过程的,而C++是面向对象的。2、函数库不同C语言的标准的函数库很松散,而C++对于大多数的函数都是集成的很紧密。3、结构不同C语言中结构只有成员变量,而在C++中结构中,可以有成员变量和成员函数。它们的区别是c++是在C语言基础上发展起来的,根据开发过程中遇到的需求,它引入了很多新的特性。如果你不走C/C++方向,直接学习Java就可以了,相同的待遇下,选择简单的更好。当
- JAVASE(七)关键字this和static,类的结构详解(二)
永无魇足
javajava
目录一、关键字this和static1.关键字this2.关键字static二、代码块1.定义2.实例代码块和静态代码块一、关键字this和static1.关键字thisthis代表当前对象。(1)当方法里面的局部变量和成员变量同名的时候,就可以使用this。如:publicclassHuman{Stringname;Stringgender;publicHuman(Stringname,Stri
- JetBrains IntelliJ IDEA 2024 for Mac v2024.3 中文 Java开发工具
Olive_Sweet
javaintellij-ideamacos
介绍JetBrainsIntelliJIDEA2024mac,是一款Java开发工具,IntelliJIDEA凭借无与伦比的Java和Kotlin支持脱颖而出。从一开始就支持尖IDEA2024.3中文版开发工具端语言功能,保持领先地位。IntelliJIDEA对您的代码了如指掌,利用这些知识在每个上下文中提供相关建议,实现极快的导航和智能体验。效果下载百度网盘:https://pan.baidu.
- 02、数据结构与算法 - 基础:数组 - 吊打面试官
星星学霸
数据结构与算法-吊打面试官python开发语言java算法数据结构
更多系列教程,每天更新更多教程关注:xxxueba.com星星学霸本篇博客我们介绍数据结构的鼻祖------数组,可以说数组几乎能表示一切的数据结构,在每一门编程语言中,数组都是重要的数据结构,当然每种语言对数组的实现和处理也不相同,但是本质是都是用来存放数据的的结构,这里我们以Java语言为例,来详细介绍Java语言中数组的用法。Java中数组的介绍在Java中,数组是用来存放同一种数据类型的集
- Android wifi的开关Settings值异常分析
峥嵘life
androidAndroid系统Android网络androidpython开发语言
Androidwifi的开关Settings值异常分析文章目录Androidwifi的开关Settings值异常分析一、前言二、异常分析1、adb或者串口获取Settings的wifi开关值2、代码获取wifi开关值3、根据日志分析代码(1)logcat对应的wifi开启日志的代码①WifiServiceImpl.java②WifiSettingsStore.java3、wifi_on不同的具体原
- 如何减少跨团队交付摩擦?——基于 DevOps 与敏捷的最佳实践
网罗开发
实战实战源码devops运维
网罗开发(小红书、快手、视频号同名) 大家好,我是展菲,目前在上市企业从事人工智能项目研发管理工作,平时热衷于分享各种编程领域的软硬技能知识以及前沿技术,包括iOS、前端、HarmonyOS、Java、Python等方向。在移动端开发、鸿蒙开发、物联网、嵌入式、云原生、开源等领域有深厚造诣。图书作者:《ESP32-C3物联网工程开发实战》图书作者:《SwiftUI入门,进阶与实战》超级个体:CO
- Android开源库——RxJava和RxAndroid
松仔log
#Android开源库android开源rxjava
RxJava和RxAndroid是什么?RxJava是基于JVM的响应式扩展,用于编写异步代码RxAndroid是关于Android的RxJava绑定RxJava和RxAndroid使用依赖implementation'io.reactivex.rxjava3:rxjava:3.1.0'implementation'io.reactivex.rxjava3:rxandroid:3.0.2'使用过程
- java实现卷积神经网络CNN(附带源码)
Katie。
Java实战项目java
Java实现卷积神经网络(CNN)项目详解目录项目概述1.1项目背景与意义1.2什么是卷积神经网络(CNN)1.3卷积神经网络的应用场景相关知识与理论基础2.1神经网络与深度学习概述2.2卷积操作与卷积层原理2.3激活函数与池化层2.4全连接层与损失函数2.5前向传播、反向传播与梯度下降项目需求与分析3.1项目目标3.2功能需求分析3.3性能与扩展性要求3.4异常处理与鲁棒性考虑系统设计与实现思路
- kettle ETL 配置
云连山
数字化etl
pdi-ce-9.1.0.0-324配置-CSDN博客3、配置中文字符3.1)spoon支持中文字符,spoon.bat启动文件加-Dfile.encoding=utf-8REM%SPOON_START_OPTION%"%_PENTAHO_JAVA%"%JAVA_ADD_OPENS%%OPT%-jarlauncher\launcher.jar-lib..\%LIBSPATH%%_cmdline%%
- 深度解析前端面试八股文:核心知识点与高效应对策略
赵大仁
前端面试职场和发展
深度解析前端面试八股文:核心知识点与高效应对策略1.引言前端面试是每位开发者迈向职业进阶的重要环节,涉及HTML、CSS、JavaScript、性能优化、浏览器原理、网络、安全、框架(Vue/React)等核心知识点。本文不仅会覆盖前端面试的高频八股文,还会结合生动的案例,让你在面试时能够脱离死记硬背,从理解中突破!2.HTML&CSS高频考点2.1HTML语义化问题:什么是HTML语义化?为什么
- 字符流在处理不同编码文件时的工作原理
啊sen丶
java开发语言
在Java中,字符流是专门用于处理文本数据的IO流,它基于字符(char)操作,能够自动处理字符编码的转换。字符流的核心在于它可以根据指定的字符集(如UTF-8、GBK、ISO-8859-1等)将字节数据解码为字符数据,或者将字符数据编码为字节数据。这种机制使得字符流在处理不同编码的文件时非常灵活,能够有效避免因编码不一致导致的乱码问题。一、字符流的工作原理字符流在内部使用Charset(字符集)
- Java中的参数传递机制:值传递与引用传递的真相
啊sen丶
java开发语言
在Java编程中,参数传递机制是每个开发者都必须理解的基本概念之一。然而,关于Java的参数传递机制,常常存在一些误解。很多人会问:“Java是按值传递还是按引用传递?”本文将通过详细的解释和代码示例,帮助你彻底理解Java的参数传递机制。一、值传递与引用传递的基本概念(一)值传递(PassbyValue)值传递是指在调用方法时,将实际参数的值复制一份传递给方法。在方法内部对参数的修改不会影响到原
- AJAX PHP:深入理解与实际应用
wjs2024
开发语言
AJAXPHP:深入理解与实际应用引言随着互联网技术的不断发展,前端与后端交互变得更加频繁。AJAX(AsynchronousJavaScriptandXML)和PHP(HypertextPreprocessor)作为两种流行的技术,在实现动态网页和应用程序方面扮演着重要角色。本文将深入探讨AJAXPHP的工作原理、应用场景以及实际开发中的注意事项。AJAXPHP概述AJAXAJAX是一种基于Ja
- python代码重构技巧_Python代码重构指南,老师Bryan Beecham完结
weixin_39916479
python代码重构技巧
本套课程由BryanBeecham,全球知名敏捷开发教练主讲的:Python代码重构指南。重构是软件改进的核心,它使软件拥有更好的结构和性能,也使代码更易于理解、修改和扩展。尽管重构并不是新事物,但是软件开发人员仍然会苦恼于如何正确地进行重构。随着敏捷运动的发展,DevOps之类的概念不断追求高质量和精心设计的代码,以实现更快的部署和反馈。不过,现有的很多关于重构的教程都基于Java语言,关于Py
- Spring Boot 多级缓存实战:基于 Redis+Redisson 构建高并发解决方案
Isaac_Gao
缓存springbootredis
SpringBoot多级缓存实战:基于Redis+Redisson构建高并发解决方案本文适合人群:中高级Java开发工程师、系统架构师、对高并发场景优化感兴趣的技术人员一、为什么需要多级缓存?在百万级并发的电商系统中,我们曾遇到这样的性能瓶颈:本地缓存导致各节点数据不一致单纯依赖Redis造成带宽瓶颈缓存雪崩导致DB被打挂多级缓存架构通过结合本地缓存与分布式缓存的优势,实现了:热点数据纳秒级访问分
- Java代码优化提升系统性能
种豆走天下
java开发语言
优化可以涉及许多方面,例如算法优化、内存管理、线程管理、I/O性能等。以下是一些常见的优化建议和技巧:1.优化算法和数据结构选择合适的算法:优化性能的首要步骤是选择正确的算法。例如,使用二分查找代替线性查找,或者使用合适的排序算法来替代简单的冒泡排序。选择合适的数据结构:数据结构的选择对系统的性能有很大影响。例如,如果需要频繁的插入和删除操作,使用LinkedList而不是ArrayList可能会
- java杨辉三角
3213213333332132
java基础
package com.algorithm;
/**
* @Description 杨辉三角
* @author FuJianyong
* 2015-1-22上午10:10:59
*/
public class YangHui {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//初始化二维数组长度
int[][] y
- 《大话重构》之大布局的辛酸历史
白糖_
重构
《大话重构》中提到“大布局你伤不起”,如果企图重构一个陈旧的大型系统是有非常大的风险,重构不是想象中那么简单。我目前所在公司正好对产品做了一次“大布局重构”,下面我就分享这个“大布局”项目经验给大家。
背景
公司专注于企业级管理产品软件,企业有大中小之分,在2000年初公司用JSP/Servlet开发了一套针对中
- 电驴链接在线视频播放源码
dubinwei
源码电驴播放器视频ed2k
本项目是个搜索电驴(ed2k)链接的应用,借助于磁力视频播放器(官网:
http://loveandroid.duapp.com/ 开放平台),可以实现在线播放视频,也可以用迅雷或者其他下载工具下载。
项目源码:
http://git.oschina.net/svo/Emule,动态更新。也可从附件中下载。
项目源码依赖于两个库项目,库项目一链接:
http://git.oschina.
- Javascript中函数的toString()方法
周凡杨
JavaScriptjstoStringfunctionobject
简述
The toString() method returns a string representing the source code of the function.
简译之,Javascript的toString()方法返回一个代表函数源代码的字符串。
句法
function.
- struts处理自定义异常
g21121
struts
很多时候我们会用到自定义异常来表示特定的错误情况,自定义异常比较简单,只要分清是运行时异常还是非运行时异常即可,运行时异常不需要捕获,继承自RuntimeException,是由容器自己抛出,例如空指针异常。
非运行时异常继承自Exception,在抛出后需要捕获,例如文件未找到异常。
此处我们用的是非运行时异常,首先定义一个异常LoginException:
/**
* 类描述:登录相
- Linux中find常见用法示例
510888780
linux
Linux中find常见用法示例
·find path -option [ -print ] [ -exec -ok command ] {} \;
find命令的参数;
- SpringMVC的各种参数绑定方式
Harry642
springMVC绑定表单
1. 基本数据类型(以int为例,其他类似):
Controller代码:
@RequestMapping("saysth.do")
public void test(int count) {
}
表单代码:
<form action="saysth.do" method="post&q
- Java 获取Oracle ROWID
aijuans
javaoracle
A ROWID is an identification tag unique for each row of an Oracle Database table. The ROWID can be thought of as a virtual column, containing the ID for each row.
The oracle.sql.ROWID class i
- java获取方法的参数名
antlove
javajdkparametermethodreflect
reflect.ClassInformationUtil.java
package reflect;
import javassist.ClassPool;
import javassist.CtClass;
import javassist.CtMethod;
import javassist.Modifier;
import javassist.bytecode.CodeAtt
- JAVA正则表达式匹配 查找 替换 提取操作
百合不是茶
java正则表达式替换提取查找
正则表达式的查找;主要是用到String类中的split();
String str;
str.split();方法中传入按照什么规则截取,返回一个String数组
常见的截取规则:
str.split("\\.")按照.来截取
str.
- Java中equals()与hashCode()方法详解
bijian1013
javasetequals()hashCode()
一.equals()方法详解
equals()方法在object类中定义如下:
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
return (this == obj);
}
很明显是对两个对象的地址值进行的比较(即比较引用是否相同)。但是我们知道,String 、Math、I
- 精通Oracle10编程SQL(4)使用SQL语句
bijian1013
oracle数据库plsql
--工资级别表
create table SALGRADE
(
GRADE NUMBER(10),
LOSAL NUMBER(10,2),
HISAL NUMBER(10,2)
)
insert into SALGRADE values(1,0,100);
insert into SALGRADE values(2,100,200);
inser
- 【Nginx二】Nginx作为静态文件HTTP服务器
bit1129
HTTP服务器
Nginx作为静态文件HTTP服务器
在本地系统中创建/data/www目录,存放html文件(包括index.html)
创建/data/images目录,存放imags图片
在主配置文件中添加http指令
http {
server {
listen 80;
server_name
- kafka获得最新partition offset
blackproof
kafkapartitionoffset最新
kafka获得partition下标,需要用到kafka的simpleconsumer
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.
- centos 7安装docker两种方式
ronin47
第一种是采用yum 方式
yum install -y docker
- java-60-在O(1)时间删除链表结点
bylijinnan
java
public class DeleteNode_O1_Time {
/**
* Q 60 在O(1)时间删除链表结点
* 给定链表的头指针和一个结点指针(!!),在O(1)时间删除该结点
*
* Assume the list is:
* head->...->nodeToDelete->mNode->nNode->..
- nginx利用proxy_cache来缓存文件
cfyme
cache
user zhangy users;
worker_processes 10;
error_log /var/vlogs/nginx_error.log crit;
pid /var/vlogs/nginx.pid;
#Specifies the value for ma
- [JWFD开源工作流]JWFD嵌入式语法分析器负号的使用问题
comsci
嵌入式
假如我们需要用JWFD的语法分析模块定义一个带负号的方程式,直接在方程式之前添加负号是不正确的,而必须这样做:
string str01 = "a=3.14;b=2.71;c=0;c-((a*a)+(b*b))"
定义一个0整数c,然后用这个整数c去
- 如何集成支付宝官方文档
dai_lm
android
官方文档下载地址
https://b.alipay.com/order/productDetail.htm?productId=2012120700377310&tabId=4#ps-tabinfo-hash
集成的必要条件
1. 需要有自己的Server接收支付宝的消息
2. 需要先制作app,然后提交支付宝审核,通过后才能集成
调试的时候估计会真的扣款,请注意
- 应该在什么时候使用Hadoop
datamachine
hadoop
原帖地址:http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-301743-id-3925358.html
存档,某些观点与我不谋而合,过度技术化不可取,且hadoop并非万能。
--------------------------------------------万能的分割线--------------------------------
有人问我,“你在大数据和Hado
- 在GridView中对于有外键的字段使用关联模型进行搜索和排序
dcj3sjt126com
yii
在GridView中使用关联模型进行搜索和排序
首先我们有两个模型它们直接有关联:
class Author extends CActiveRecord {
...
}
class Post extends CActiveRecord {
...
function relations() {
return array(
'
- 使用NSString 的格式化大全
dcj3sjt126com
Objective-C
格式定义The format specifiers supported by the NSString formatting methods and CFString formatting functions follow the IEEE printf specification; the specifiers are summarized in Table 1. Note that you c
- 使用activeX插件对象object滚动有重影
蕃薯耀
activeX插件滚动有重影
使用activeX插件对象object滚动有重影 <object style="width:0;" id="abc" classid="CLSID:D3E3970F-2927-9680-BBB4-5D0889909DF6" codebase="activex/OAX339.CAB#
- SpringMVC4零配置
hanqunfeng
springmvc4
基于Servlet3.0规范和SpringMVC4注解式配置方式,实现零xml配置,弄了个小demo,供交流讨论。
项目说明如下:
1.db.sql是项目中用到的表,数据库使用的是oracle11g
2.该项目使用mvn进行管理,私服为自搭建nexus,项目只用到一个第三方 jar,就是oracle的驱动;
3.默认项目为零配置启动,如果需要更改启动方式,请
- 《开源框架那点事儿16》:缓存相关代码的演变
j2eetop
开源框架
问题引入
上次我参与某个大型项目的优化工作,由于系统要求有比较高的TPS,因此就免不了要使用缓冲。
该项目中用的缓冲比较多,有MemCache,有Redis,有的还需要提供二级缓冲,也就是说应用服务器这层也可以设置一些缓冲。
当然去看相关实现代代码的时候,大致是下面的样子。
[java]
view plain
copy
print
?
public vo
- AngularJS浅析
kvhur
JavaScript
概念
AngularJS is a structural framework for dynamic web apps.
了解更多详情请见原文链接:http://www.gbtags.com/gb/share/5726.htm
Directive
扩展html,给html添加声明语句,以便实现自己的需求。对于页面中html元素以ng为前缀的属性名称,ng是angular的命名空间
- 架构师之jdk的bug排查(一)---------------split的点号陷阱
nannan408
split
1.前言.
jdk1.6的lang包的split方法是有bug的,它不能有效识别A.b.c这种类型,导致截取长度始终是0.而对于其他字符,则无此问题.不知道官方有没有修复这个bug.
2.代码
String[] paths = "object.object2.prop11".split("'");
System.ou
- 如何对10亿数据量级的mongoDB作高效的全表扫描
quentinXXZ
mongodb
本文链接:
http://quentinXXZ.iteye.com/blog/2149440
一、正常情况下,不应该有这种需求
首先,大家应该有个概念,标题中的这个问题,在大多情况下是一个伪命题,不应该被提出来。要知道,对于一般较大数据量的数据库,全表查询,这种操作一般情况下是不应该出现的,在做正常查询的时候,如果是范围查询,你至少应该要加上limit。
说一下,
- C语言算法之水仙花数
qiufeihu
c算法
/**
* 水仙花数
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#define N 10
int main()
{
int x,y,z;
for(x=1;x<=N;x++)
for(y=0;y<=N;y++)
for(z=0;z<=N;z++)
if(x*100+y*10+z == x*x*x
- JSP指令
wyzuomumu
jsp
jsp指令的一般语法格式: <%@ 指令名 属性 =”值 ” %>
常用的三种指令: page,include,taglib
page指令语法形式: <%@ page 属性 1=”值 1” 属性 2=”值 2”%>
include指令语法形式: <%@include file=”relative url”%> (jsp可以通过 include