cpp-httplib 避免阻塞主线程, c++封装httplib,httplib面向对象开发
目录
- 说明/前言
- 原生的httplib会阻塞你的主线程
- 解决httplib阻塞主线程的问题
- BashController - 面向对象风格使用httplib
-
-
- 自定义controller --- TestController.h文件
- 使用controller功能的main.cpp文件
- get请求测试结果
- post请求测试结果
-
- HttpServer.h
说明/前言
~~~~~~~~ - cpp-httplib是一个简单易用, 跨平台, 开发快速, 仅头文件的c++ http库, 只需要把一个头文件包含到你的代码里, 就可以用很少的代码完成一个http server, 但它仍有一些不足之处, 比如会阻塞你的主线程(cpp-httplib的github地址)
~~~~~~~~ - 在不影响cpp-httplib原生代码的基础上, 对其进行了进一步的封装, 且完全和httplib解耦
~~~~~~~~ - 封装类为header-only, 直接inlude使用(封装的具体代码在文章最后的HttpServer.h中)
~~~~~~~~ - 避免了httplib原生使用方式阻塞主线程的问题
~~~~~~~~ - 在支持原生开发方式的基础上, 增加了BashController类,模仿java的spring mvc的开发方式, 以解耦代码, 支持较大型的web项目
~~~~~~~~ - 正文主要讲述使用方式, 封装的具体代码在文章最后, 可以直接复制使用
~~~~~~~~ - 跨平台, 可在linux和window中使用, 但原生的cpp-httplib对mingw支持不太好, windows下尽量使用msvc编译
~~~~~~~~ - 关于httplib更高级的用法, 请直接到(cpp-httplib的github地址)参考
~~~~~~~~ - 确保你的编译器最低支持c++14
原生的httplib会阻塞你的主线程
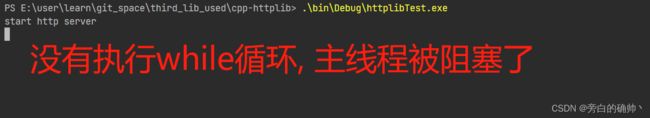
~~~~~~~~ cpp-httplib是一个简单易用, 跨平台, 开发快速, 仅头文件的c++ http库. 只需要把一个头文件包含到你的代码里, 就可以用很少的代码完成一个http server, 就像下面这样. 但是, 它会阻塞当前线程, 导致while循环中的cout不执行, 看下面的代码
#include ~~~~~~~~ 阻塞的原因是因为, 在httplib的listen函数中有一个while循环, 其中不停的执行accept()函数, 用来监听端口对应的文件描述符, 所以, 只要你开一个子线程, 让listen函数在子线程中执行, 就不会阻塞主线程了
~~~~~~~~ 但其实你不用太关心原因, 甚至不用操心线程, 因为这些我都给你封装好了 _
解决httplib阻塞主线程的问题
~~~~~~~~ 把HttpServer.h复制到httplib的同级目录下, 在你的程序中include它, 通过HttpServer.h使用httplib, 就不会阻塞你的主线程了 , 如下:(HttpServer.h代码较多, 放到文章最后了)
~~~~~~~~ HttpServer.h的代码在文章的最后, 你可以直接复制使用
#include BashController - 面向对象风格使用httplib
~~~~~~~ - HttpServer.h不但能自动为你的httplib::Server对象创建子线程, 还提供了一种类似于java spring mvc风格的http服务器开发方式, 以解耦你的代码. 让你的程序更加清晰明了.
~~~~~~~ - 你只需要继承BashController, 并按下面的方式编写的你服务器响应代码.
自定义controller — TestController.h文件
自定义controler, 解耦代码
#pragma once
#include "Httpserver.h"
class TestController : public httplib::BaseController
{
// 注意: 必须重写bind()函数, 并在内部填写映射关系, 否则会抛出异常
void bind() override
{
// BindController可以绑定httplib中所有参数为(const httplib::Request& req, httplib::Response& resp)的方法
server->Get("/get", BindController(&TestController::getApi, this));
server->Post("/post", BindController(&TestController::postApi, this));
}
// 注意:Request和Response这两个参数必须是引用类型
void getApi(const httplib::Request& req, httplib::Response& resp)
{
std::string jsonData = "{\"type\": \"get\", \"code\": 2001}";
resp.set_content(jsonData, "application/json");
}
// 注意:Request和Response这两个参数必须是引用类型
void postApi(const httplib::Request& req, httplib::Response& resp)
{
std::string data = req.body;
std::cout << "接收请求数据: \n" << data << std::endl;
std::string jsonData = "{\"type\": \"post\", \"code\": 2001}";
resp.set_content(jsonData, "application/json");
}
};
使用controller功能的main.cpp文件
当你把自定义的controllor写到头文件中, 只在main中include它们时, 你的main函数会非常简洁和清晰, 像下面这样:
#include // include你自定义的controllor
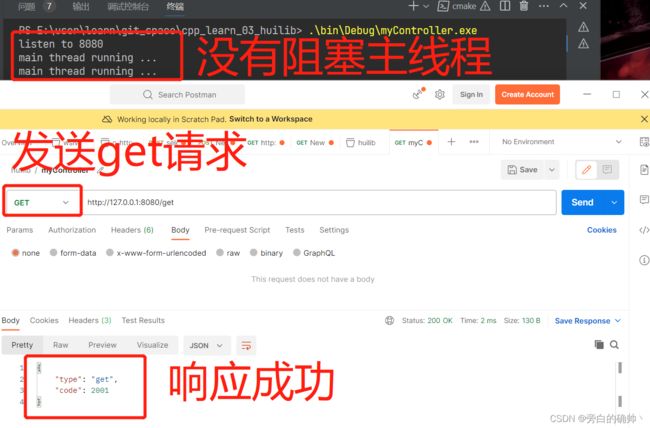
#include get请求测试结果
post请求测试结果
HttpServer.h
~~~~~~~~ 具体的封装代码, 把它放在httplib.h的同级目录下, 就可以按文章中提到的方式使用他们了
// 将HttpServer.h放到httplib.h文件的同级目录下
#pragma once
#include