SpringMvc源码分析(三) 请求执行过程之获取MethodHandler
1.请求是如何关联到DispatcherServlet的
DispatcherServlet是Servlet的实现,遵循Servlet生命周期的规则。
Servlet的生命周期即其出生到死亡的过程中分别会调用Servlet里的以下方法:
加载和实例化:可以参考SpringMvc源码分析一
init方法:初始化,在整个 servlet 生命周期中,init() 方法只会被调用一次,即服务器启动后第一次请求时会调用一次,后续请求不再调用。
service方法:每次请求都会调用该service方法。
destory方法:重启加载或者重启容器时会调用该方法。
当前端向Tomcat服务器发起请求时,被Tomcat容器里管理的DispatcherServlet接收到Tomcat监听到的请求信息,第一次调用init方法初始化,然后再调用Service方法。
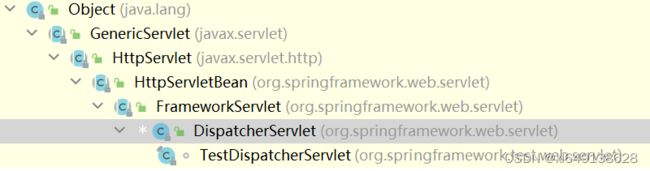
以下是DispatcherServlet的继承实现树
先分析init方法,根据DispatcherServlet类的继承实现树,其实际调用的时HttpServletBean里的init方法
public final void init() throws ServletException {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Initializing servlet '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
// Set bean properties from init parameters.
PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties);
if (!pvs.isEmpty()) {
try {
BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this);
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(getServletContext());
bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, getEnvironment()));
initBeanWrapper(bw);
bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isErrorEnabled()) {
logger.error("Failed to set bean properties on servlet '" + getServletName() + "'", ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
//重点关注此处
// Let subclasses do whatever initialization they like.
initServletBean();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Servlet '" + getServletName() + "' configured successfully");
}
}在该方法中initServletBean方法是一个未实现的方法。其实际实现的方法在FrameworkServlet类的initServletBean中
@Override
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
getServletContext().log("Initializing Spring FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "'");
if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
this.logger.info("FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "': initialization started");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
//重点关注此处
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext();
initFrameworkServlet();
}
catch (ServletException | RuntimeException ex) {
this.logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
throw ex;
}
if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
this.logger.info("FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "': initialization completed in " +
elapsedTime + " ms");
}
}
分析FrameworkServlet类里的initWebApplicationContext方法。
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
WebApplicationContext rootContext =
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
// A context instance was injected at construction time -> use it
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent -> set
// the root application context (if any; may be null) as the parent
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
}
}
}
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance was injected at construction time -> see if one
// has been registered in the servlet context. If one exists, it is assumed
// that the parent context (if any) has already been set and that the
// user has performed any initialization such as setting the context id
wac = findWebApplicationContext();
}
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance is defined for this servlet -> create a local one
wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
}
if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {
// Either the context is not a ConfigurableApplicationContext with refresh
// support or the context injected at construction time had already been
// refreshed -> trigger initial onRefresh manually here.
//重点关注此处
onRefresh(wac);
}
if (this.publishContext) {
// Publish the context as a servlet context attribute.
String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName();
getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Published WebApplicationContext of servlet '" + getServletName() +
"' as ServletContext attribute with name [" + attrName + "]");
}
}
return wac;
}上面源码中的onRefresh最后调用的是DispatcherServlet类里的initStrategies方法。
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) {
initStrategies(context);
} protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
//初始化文件处理解析器
initMultipartResolver(context);
initLocaleResolver(context);
initThemeResolver(context);
//对DispatcherServlet类中的handlerMappings(处理器映射)属性赋值
initHandlerMappings(context);
//对DispatcherServlet类中的handlerAdapters(适配器映射)属性赋值
initHandlerAdapters(context);
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
//初始化视图解析器
initViewResolvers(context);
initFlashMapManager(context);
}
观察DispatcherServlet继承树里的结构 ,其继承了HttpServlet类,调用DispatcherServlet对象的Service方法时,实际调用的是HttpServlet类里的service方法。
在HttpServlet类里的代码中我们可以看到根据不同的前端请求方式比如GET,POST等不同的请求方式执行了不同的方法。
public void service(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res)
throws ServletException, IOException
{
HttpServletRequest request;
HttpServletResponse response;
if (!(req instanceof HttpServletRequest &&
res instanceof HttpServletResponse)) {
throw new ServletException("non-HTTP request or response");
}
request = (HttpServletRequest) req;
response = (HttpServletResponse) res;
service(request, response);
}
}
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp)
throws ServletException, IOException
{
String method = req.getMethod();
if (method.equals(METHOD_GET)) {
long lastModified = getLastModified(req);
if (lastModified == -1) {
// servlet doesn't support if-modified-since, no reason
// to go through further expensive logic
doGet(req, resp);
} else {
long ifModifiedSince = req.getDateHeader(HEADER_IFMODSINCE);
if (ifModifiedSince < lastModified) {
// If the servlet mod time is later, call doGet()
// Round down to the nearest second for a proper compare
// A ifModifiedSince of -1 will always be less
maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified);
doGet(req, resp);
} else {
resp.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_MODIFIED);
}
}
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_HEAD)) {
long lastModified = getLastModified(req);
maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified);
doHead(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_POST)) {
doPost(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_PUT)) {
doPut(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_DELETE)) {
doDelete(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_OPTIONS)) {
doOptions(req,resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_TRACE)) {
doTrace(req,resp);
} else {
//
// Note that this means NO servlet supports whatever
// method was requested, anywhere on this server.
//
String errMsg = lStrings.getString("http.method_not_implemented");
Object[] errArgs = new Object[1];
errArgs[0] = method;
errMsg = MessageFormat.format(errMsg, errArgs);
resp.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_IMPLEMENTED, errMsg);
}
}
因为是DispatcherServlet类型的对象调用的service方法,而FrameworkServlet类、HttpServlet类都实现了doGet、doPost等方法,根据动态绑定机制的原理,因为FrameworkServlet比HttpServlet类的继承管理离DispatcherServlet更近,所以调用的是FrameworkServlet里的doGet,doPost方法。在这些方法内部中我们发现都调用了processRequest方法
@Override
protected final void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
processRequest(request, response);
}
继续分析FrameworkServlet类中的processRequest方法。
protected final void processRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
//开始时间
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Throwable failureCause = null;
//获取上一个LocalContext,这里叫上一个,
//是因为此方法是从ThreadLocal中获取的,获取当前线程的LocaleContext
LocaleContext previousLocaleContext = LocaleContextHolder.getLocaleContext();
//构建一个本地国际化上下文,SimpleLocaleContext
LocaleContext localeContext = buildLocaleContext(request);
//获取当前绑定到线程的RequestAttributes
RequestAttributes previousAttributes = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
// 构建ServletRequestAttributes
ServletRequestAttributes requestAttributes = buildRequestAttributes(request, response, previousAttributes);
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptor(FrameworkServlet.class.getName(), new RequestBindingInterceptor());
//将localeContext和requestAttributes放入当前线程中
initContextHolders(request, localeContext, requestAttributes);
try {
//核心处理
doService(request, response);
}
catch (ServletException | IOException ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw new NestedServletException("Request processing failed", ex);
}
finally {
resetContextHolders(request, previousLocaleContext, previousAttributes);
if (requestAttributes != null) {
requestAttributes.requestCompleted();
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
if (failureCause != null) {
this.logger.debug("Could not complete request", failureCause);
}
else {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
logger.debug("Leaving response open for concurrent processing");
}
else {
this.logger.debug("Successfully completed request");
}
}
}
//发布事件
publishRequestHandledEvent(request, response, startTime, failureCause);
}
}
在FrameworkServlet类中的该方法中调用了doService方法,但是DispatcherServlet类中存在doService方法,所以调用的是DispatcherServlet类的的doService方法。
@Override
protected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
String resumed = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).hasConcurrentResult() ? " resumed" : "";
logger.debug("DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'" + resumed +
" processing " + request.getMethod() + " request for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "]");
}
// 保留请求属性的快照,以防出现include,
// 能够在include之后恢复原始属性
// Keep a snapshot of the request attributes in case of an include,
// to be able to restore the original attributes after the include.
Map attributesSnapshot = null;
if (WebUtils.isIncludeRequest(request)) {
attributesSnapshot = new HashMap<>();
Enumeration attrNames = request.getAttributeNames();
while (attrNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String attrName = (String) attrNames.nextElement();
if (this.cleanupAfterInclude || attrName.startsWith(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PREFIX)) {
attributesSnapshot.put(attrName, request.getAttribute(attrName));
}
}
}
// Make framework objects available to handlers and view objects.
request.setAttribute(WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, getWebApplicationContext());
request.setAttribute(LOCALE_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.localeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.themeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_SOURCE_ATTRIBUTE, getThemeSource());
if (this.flashMapManager != null) {
FlashMap inputFlashMap = this.flashMapManager.retrieveAndUpdate(request, response);
if (inputFlashMap != null) {
request.setAttribute(INPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, Collections.unmodifiableMap(inputFlashMap));
}
request.setAttribute(OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, new FlashMap());
request.setAttribute(FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE, this.flashMapManager);
}
try {
//请求分发
doDispatch(request, response);
}
finally {
if (!WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Restore the original attribute snapshot, in case of an include.
if (attributesSnapshot != null) {
//恢复属性
restoreAttributesAfterInclude(request, attributesSnapshot);
}
}
}
}
在上面的源码中需要重点关注doDispatch(request, response)以下是分发方法的源码
在该源码中需要关注以下代码
1.getHandler(processedRequest) 获取处理器链的方法
2.getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler()) 获取处理器链封装到适配器
3.mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response) 请求前预处理
4.ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler())调用适配器的处理方法
5.mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv)请求执行后处理
6.processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException)
请求后置处理
2.请求是如何获取到处理器执行链
本文分析的是获取处理器的过程,所以主要讲述方法一和方法二
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
//检查当前请求是不是一个文件上传的请求(),
//是返回MultipartHttpServletRequest类型对象
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
// 确认当前请求的处理器,根据不同的请求返回不同的处理器
// Determine handler for the current request.
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
//获取当前处理器的适配器
// Determine handler adapter for the current request.
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler.
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Last-Modified value for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "] is: " + lastModified);
}
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
// Actually invoke the handler.
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
}
catch (Throwable err) {
// As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well,
// making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios.
dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err);
}
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler,
new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err));
}
finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
}
}
else {
// Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.
if (multipartRequestParsed) {
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
}
2.1获取处理器执行链分析
方法一:getHandler获取处理器
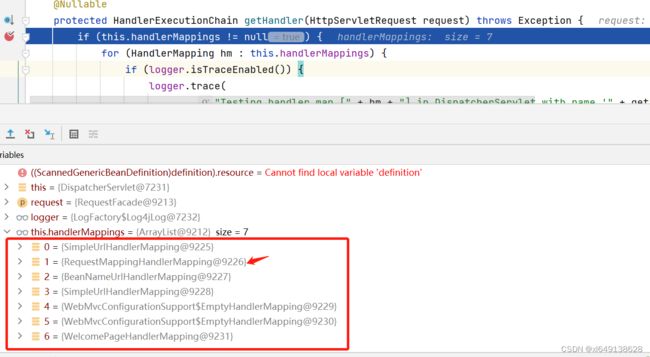
找到DispatcherServlet类里的getHandler方法,代码中handlerMappings属性中获取到HandlerMapping类型的对象。实际上该对象是RequestMappingHandlerMapping类的一个实例。
注意:为什么是有7种映射但是返回的是RequestMappingHandlerMapping的映射就不分析了。
因为这些方法一个一个分析比较麻烦。只需要知道通过debug最终返回的是一个RequestMappingHandlerMapping类型的对象就可以了。因为需要分析的类太多了。
获取到RequestMappingHandlerMapping类型的对象后,该对象的执行逻辑hm.getHandler方法来获取方法执行器链
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
if (this.handlerMappings != null) {
for (HandlerMapping hm : this.handlerMappings) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(
"Testing handler map [" + hm + "] in DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
HandlerExecutionChain handler = hm.getHandler(request);
if (handler != null) {
return handler;
}
}
}
return null;
}
HandlerMapping里的getHandler是一个未实现的方法,实际实现的方法在AbstractHandlerMapping类中的getHandler方法。
public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
//获取处理器
Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request);
//如果没有使用默认的处理器
if (handler == null) {
handler = getDefaultHandler();
}
//如果连默认的处理器也没有返回空
if (handler == null) {
return null;
}
// Bean name or resolved handler?
// 如果返回的是handler是String类型的去Spring上线文中根据bean名获取处理器Bean对象
if (handler instanceof String) {
String handlerName = (String) handler;
handler = obtainApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
//获取处理器执行器链
HandlerExecutionChain executionChain = getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request);
//处理跨域相关的执行器配置,由拦截器配置
if (CorsUtils.isCorsRequest(request)) {
CorsConfiguration globalConfig = this.globalCorsConfigSource.getCorsConfiguration(request);
CorsConfiguration handlerConfig = getCorsConfiguration(handler, request);
CorsConfiguration config = (globalConfig != null ? globalConfig.combine(handlerConfig) : handlerConfig);
//获取跨域相关的执行器链,该执行器链由拦截器实现
executionChain = getCorsHandlerExecutionChain(request, executionChain, config);
}
return executionChain;
}
在这个方法中存在比较重要的三个方法,本文分别针对这些方法做分析
方法1:getHandlerInternal(request)
方法2: getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request)
方法3:getCorsHandlerExecutionChain(request, executionChain, config)
2.1.1 查找内部的处理器
分析 getHandlerInternal方法,发现AbstractHandlerMapping类中的getHandlerInternal方法是一个抽象方法。因为AbstractHandlerMapping和AbstractHandlerMethodMapping是RequestMappingHandlerMapping的父类,所以其实现方法在AbstractHandlerMethodMapping中实现的。
@Override
protected HandlerMethod getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
//1.获取请求的url
String lookupPath = getUrlPathHelper().getLookupPathForRequest(request);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Looking up handler method for path " + lookupPath);
}
this.mappingRegistry.acquireReadLock();
try {
//2.查找url对应的handlerMethod
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = lookupHandlerMethod(lookupPath, request);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
if (handlerMethod != null) {
logger.debug("Returning handler method [" + handlerMethod + "]");
}
else {
logger.debug("Did not find handler method for [" + lookupPath + "]");
}
}
//3.如果handlerMethod不为空则创建一个新的handlerMethod返回
return (handlerMethod != null ? handlerMethod.createWithResolvedBean() : null);
}
finally {
this.mappingRegistry.releaseReadLock();
}
}
关注AbstractHandlerMethodMapping类中的lookupHandlerMethod方法
@Nullable
protected HandlerMethod lookupHandlerMethod(String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
List matches = new ArrayList<>();
//根据路径查找,在urlLookup属性中查找,该属性是一个Map,
//该属性中的值是在register方法中赋值的,register方法的调用可以在我写的上篇文章
//SpringMvc源码分析(二) 请求执行前的准备过程:
//@Controller/@RequestMapping注解解析为RequestMappingInfo的过程可以看到
//返回的类型是List类型的数据
List directPathMatches = this.mappingRegistry.getMappingsByUrl(lookupPath);
if (directPathMatches != null) {
//如果有匹配的结果生成一个新的RequestMappingInfo对象放入到matches对象中
addMatchingMappings(directPathMatches, matches, request);
}
if (matches.isEmpty()) {
// 如果通过url没找到,则遍历所有的 mappings 匹配,匹配类似于 /hello/{name} 的url
// mappings也是一个map,key是RequestMappingInfo, value是HandlerMethod
// No choice but to go through all mappings...
addMatchingMappings(this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().keySet(), matches, request);
}
//找到最佳的匹配并返回对应的handlerMethod
if (!matches.isEmpty()) {
Comparator comparator = new MatchComparator(getMappingComparator(request));
matches.sort(comparator);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Found " + matches.size() + " matching mapping(s) for [" + lookupPath + "] : " + matches);
}
Match bestMatch = matches.get(0);
if (matches.size() > 1) {
if (CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) {
return PREFLIGHT_AMBIGUOUS_MATCH;
}
Match secondBestMatch = matches.get(1);
if (comparator.compare(bestMatch, secondBestMatch) == 0) {
Method m1 = bestMatch.handlerMethod.getMethod();
Method m2 = secondBestMatch.handlerMethod.getMethod();
throw new IllegalStateException("Ambiguous handler methods mapped for HTTP path '" +
request.getRequestURL() + "': {" + m1 + ", " + m2 + "}");
}
}
handleMatch(bestMatch.mapping, lookupPath, request);
//返回handerMethod
return bestMatch.handlerMethod;
}
else {
return handleNoMatch(this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().keySet(), lookupPath, request);
}
}
最佳匹配的规则如下图的源码所示:
优先级分别为:
请求方式>路径>参数等等
protected Comparator getMappingComparator(final HttpServletRequest request) {
return (info1, info2) -> info1.compareTo(info2, request);
}
public int compareTo(RequestMappingInfo other, HttpServletRequest request) {
int result;
// Automatic vs explicit HTTP HEAD mapping
if (HttpMethod.HEAD.matches(request.getMethod())) {
result = this.methodsCondition.compareTo(other.getMethodsCondition(), request);
if (result != 0) {
return result;
}
}
result = this.patternsCondition.compareTo(other.getPatternsCondition(), request);
if (result != 0) {
return result;
}
result = this.paramsCondition.compareTo(other.getParamsCondition(), request);
if (result != 0) {
return result;
}
result = this.headersCondition.compareTo(other.getHeadersCondition(), request);
if (result != 0) {
return result;
}
result = this.consumesCondition.compareTo(other.getConsumesCondition(), request);
if (result != 0) {
return result;
}
result = this.producesCondition.compareTo(other.getProducesCondition(), request);
if (result != 0) {
return result;
}
// Implicit (no method) vs explicit HTTP method mappings
result = this.methodsCondition.compareTo(other.getMethodsCondition(), request);
if (result != 0) {
return result;
}
result = this.customConditionHolder.compareTo(other.customConditionHolder, request);
if (result != 0) {
return result;
}
return 0;
}
此时我们就找到了该请求对应的MethodHandler了。
2.1.2 获取处理器执行链
在AbstractHandlerMapping类 getHandler(HttpServletRequest request)方法中调用的getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request)方法通过handler和request获取到了该请求的执行器链。分析getHandlerExecutionChain方法。
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandlerExecutionChain(Object handler, HttpServletRequest request) {
HandlerExecutionChain chain = (handler instanceof HandlerExecutionChain ?
(HandlerExecutionChain) handler : new HandlerExecutionChain(handler));
//获取请求路径
String lookupPath = this.urlPathHelper.getLookupPathForRequest(request);
for (HandlerInterceptor interceptor : this.adaptedInterceptors) {
if (interceptor instanceof MappedInterceptor) {
MappedInterceptor mappedInterceptor = (MappedInterceptor) interceptor;
// 判断当前请求路径是否满足interceptor里配置的路径
if (mappedInterceptor.matches(lookupPath, this.pathMatcher)) {
chain.addInterceptor(mappedInterceptor.getInterceptor());
}
}
else {
chain.addInterceptor(interceptor);
}
}
return chain;
}1. Interceptors:用于配置SpringMVC的拦截器,有两种设置方式: 通过子类的extendInterceptors钩子方法进行设置 ;通过子类的extendInterceptors钩子方法进行设置。Interceptors并不会直接使用,而是通过initInterceptors方法按类型分配到mappedInterceptors和adaptedInterceptors中进行使用,Interceptors只用于配置。
2. mappedInterceptors:此类Interceptor在使用时需要与请求的url进行匹配,只有匹配成功后才会添加到getHandler的返回值HandlerExecutionChain里。它有两种获取途径:从interceptors获取或者注册到spring的容器中通过detectMappedInterceptors方法获取。
3. adaptedInterceptors:这种类型的Inerceptor不需要进行匹配,在getHandler中会全部添加到返回值HandlerExecutionChain里面。它只能从interceptor中获取。
AbstractHandlerMapping的创建其实就是初始化这三个Interceptor
在AbstractHandlerMapping类中存在initApplicationContext方法。
protected void initApplicationContext() throws BeansException {
//扩展拦截器
extendInterceptors(this.interceptors);
//在adaptedInterceptors容器中加入MappedInterceptor类型的拦截器
detectMappedInterceptors(this.adaptedInterceptors);
initInterceptors();
}在上面的源码中
1. extendInterceptors是模板方法,用于给子类提供一个添加(或者修改)Interceptors的入口,不过在现有springMVC的实现中并没有使用。
2. detectMappedInterceptors方法用于将SpringMVC容器及父容器中的所有MappedInterceptor类型的Bean添加到mappedInterceptors属性。
3. initInterceptors方法的作用是初始化Interceptor,具体内容其实是interceptors属性里所包含的对象按类型添加到mappedInterceptors或者adaptedInterceptors:
DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration类中的方法可以通过实现WebMvcConfigurer中的addInterceptors方法并往其中添加实现HandlerInterceptor接口的拦截器,然后将实现WebMvcConfigurer接口的类纳入Spring容器管理来实现自定义拦截器
源码一:往WebMvcConfigurerComposite里的delegate添加自定义拦截器
@Autowired(required = false)
public void setConfigurers(List configurers) {
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(configurers)) {
this.configurers.addWebMvcConfigurers(configurers);
}
} 源码二:往registry添加从delegate取到的自定义拦截器
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
for (WebMvcConfigurer delegate : this.delegates) {
delegate.addInterceptors(registry);
}
}2.1.3获取跨域处理执行链
AbstractHandlerMapping类中的getCorsHandlerExecutionChain方法的作用是通过读取跨域配置往拦截器链中添加拦截器
protected HandlerExecutionChain getCorsHandlerExecutionChain(HttpServletRequest request,
HandlerExecutionChain chain, @Nullable CorsConfiguration config) {
if (CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) {
HandlerInterceptor[] interceptors = chain.getInterceptors();
chain = new HandlerExecutionChain(new PreFlightHandler(config), interceptors);
}
else {
//添加跨域拦截器
chain.addInterceptor(new CorsInterceptor(config));
}
return chain;
}
2.2封装处理器链适配器
方法二:getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler()) 获取处理器适配器。
protected HandlerAdapter getHandlerAdapter(Object handler) throws ServletException {
if (this.handlerAdapters != null) {
//循环所有的适配器,获取符合要求的适配器
for (HandlerAdapter ha : this.handlerAdapters) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Testing handler adapter [" + ha + "]");
}
//判断适配器是否支持该方法处理器,此处符合要求的适配器是
//RequestMappingHandlerAdapter
if (ha.supports(handler)) {
return ha;
}
}
}
throw new ServletException("No adapter for handler [" + handler +
"]: The DispatcherServlet configuration needs to include a HandlerAdapter that supports this handler");
}