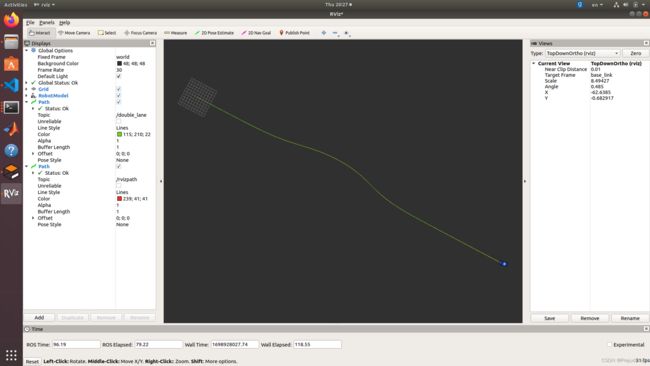
Pure-Pursuit 跟踪双移线 Gazebo 仿真
Pure-Pursuit 跟踪双移线 Gazebo 仿真
主要参考学习下面的博客和开源项目
自动驾驶规划控制(A*、pure pursuit、LQR算法,使用c++在ubuntu和ros环境下实现)
https://github.com/NeXTzhao/planning
Pure-Pursuit 的理论基础见今年六月份的笔记
对参考轨迹进行调整,采用双移线轨迹
#include 编程方面进行了一些简单的优化,轨迹跟踪的算法在 poseCallback 中实现,和博主有所区别
#include 这里和 CarSim-Simulink 联合仿真的代码类似
function [sys,x0,str,ts] = MY_MPCController3(t,x,u,flag)
% 该函数是写的第3个S函数控制器(MATLAB版本:R2011a)
% 限定于车辆运动学模型,控制量为速度和前轮偏角,使用的QP为新版本的QP解法
% [sys,x0,str,ts] = MY_MPCController3(t,x,u,flag)
%
% is an S-function implementing the MPC controller intended for use
% with Simulink. The argument md, which is the only user supplied
% argument, contains the data structures needed by the controller. The
% input to the S-function block is a vector signal consisting of the
% measured outputs and the reference values for the controlled
% outputs. The output of the S-function block is a vector signal
% consisting of the control variables and the estimated state vector,
% potentially including estimated disturbance states.
switch flag,
case 0
[sys,x0,str,ts] = mdlInitializeSizes; % Initialization
case 2
sys = mdlUpdates(t,x,u); % Update discrete states
case 3
sys = mdlOutputs(t,x,u); % Calculate outputs
case {1,4,9} % Unused flags
sys = [];
otherwise
error(['unhandled flag = ',num2str(flag)]); % Error handling
end
% End of dsfunc.
%==============================================================
% Initialization
%==============================================================
function [sys,x0,str,ts] = mdlInitializeSizes
% Call simsizes for a sizes structure, fill it in, and convert it
% to a sizes array.
sizes = simsizes;
sizes.NumContStates = 0;
sizes.NumDiscStates = 4; % this parameter doesn't matter
sizes.NumOutputs = 1;
sizes.NumInputs = 5;
sizes.DirFeedthrough = 1; % Matrix D is non-empty.
sizes.NumSampleTimes = 1;
sys = simsizes(sizes);
x0 =[0.00001;0.00001;0.00001;0.00001];
global U; % store current ctrl vector:[vel_m, delta_m]
U=[0];
global cx;
cx = 0:0.01:160;
global cy;
shape=2.4;%参数名称,用于参考轨迹生成
dx1=25;dx2=21.95;%没有任何实际意义,只是参数名称
dy1=4.05;dy2=5.7;%没有任何实际意义,只是参数名称
Xs1=27.19;Xs2=56.46;%参数名称
for i = 1:length(cx) %全局路径c(y)生成 路径初始化
z1=shape/dx1*(cx(i)-Xs1)-shape/2;
z2=shape/dx2*(cx(i)-Xs2)-shape/2;
cy(i) = dy1/2*(1+tanh(z1))-dy2/2*(1+tanh(z2));
end
% Initialize the discrete states.
str = []; % Set str to an empty matrix.
ts = [0.05 0]; % sample time: [period, offset]
%End of mdlInitializeSizes
%==============================================================
% Update the discrete states
%==============================================================
function sys = mdlUpdates(t,x,u)
sys = x;
%End of mdlUpdate.
%==============================================================
% Calculate outputs
%==============================================================
function sys = mdlOutputs(t,x,u)
global U; %store chi_tilde=[vel-vel_ref; delta - delta_ref]
global cx;
global cy;
pi = 3.1415926;
tic
fprintf('Update start, t=%6.3f\n',t);
x = u(1);
y = u(2);
yaw_angle =u(3)*pi/180;%CarSim输出的Yaw angle为角度,角度转换为弧度
v = u(4) / 3.6;
k = 0.1; % look forward gain 前向预测距离所用增益
Lfc = 3; % 基础预瞄距离
L = 2.7; % [m] wheel base of vehicle
Ld = k * v + Lfc;
N = length(cx);
ind = N;
for i = N : -1 : 1
distance = sqrt((cx(i)-x)^2 + (cy(i)-y)^2);
if distance < Ld
ind = i + 1;
break;
end
end
if ind > N
ind = N;
end
tx = cx(ind);
ty = cy(ind);
Ld = sqrt((tx-x)^2 + (ty-y)^2);
alpha = atan((ty-y)/(tx-x))-yaw_angle; %该处定义向左转为alpha=beta-Fai,所以向右转就输出-alpha
delta = atan(2*L * sin(alpha)/Ld); %前轮转角
U = delta;
sys= U; % vel, steering, x, y
toc
% End of mdlOutputs.
注意处理接近终点的情况,不加限制的话容易出现绕着终点转圈的现象
限制后整体的跟踪效果尚可,但在终点处仍旧会出现异常的偏航,仍有较大的优化空间