JS 数据结构:链表
单链表
每个节点中只包含一个指针域的链表称为单链表。
头结点—其指针域指向表中第一个结点的指针(头结点不是必须的,只是习惯上加上头结点,而头结点的数据域一般记录的是该链表的相关数据,如:链表长度)。
单链表由头指针唯一确定,因此单链表可以用头指针的名字来命名。
例如:若头指针为head,则可把链表称为“表head”。
![]()
话不多说,直接来看看链表的相关操作吧!!!
定义结点结构体
class Node {
constructor(value) {
this.value = value;
this.next = null;
}
}
class Head {
constructor() {
this.count = 0;
this.next = null;
}
}
插入
这一部分可以说是链表操作的精华部分,理解这一部分代码很关键哦!
尾插
尾插法就是在链表尾部插入新节点,那么要做的第一步当然是找到链表的尾结点了,找到后直接尾结点指针指向新节点就好啦,是不是很简单!!!
function insert(head, value) {
const node = new Node(value);
if (head.next == null) {//若链表为空尾结点即为头结点
head.next = node;
} else {
let tem = head.next;
while (tem.next != NULL) {//链表不为空则不断往后遍历
tem = tem.next;
}
tem.next = node;
}
}
头插
头插法就是在链表的头部插入新节点,而头结点的指针就是指向链表第一个节点的指针,所以将新节点指针域指向头结点原来指向的节点,再将头结点指向新节点即可。啊这,晕了?没关系,来,上图。
function head_insert(head, value) {
const node = new Node(value);
node.next = head.next;
head.next = node;
}
![]()
如图所示,头插法需要两步完成:1.将新节点指针域指针指向图中首元结点。2.将头结点指针域指针指向新节点(完成这一步的时候图中打×的地方就断开了)。想一想这两步的顺序能否颠倒?答案是不能,至于为什么好好想一想吧!
前插
即为在指定元素前插入新节点
function pre_insert(head, value, element) {
const node = new Node(value);
if (head.next == null) {//如果链表为空
head.next = node;
} else {//链表不为空
let pre = head, tem = head.next;
while (tem != null) {
if (tem.value == element) {//找到目标节点
node.next = tem;
pre.next = node;
return;
}
tem = tem.next;
pre = pre.next;
}
}
console.log("指定元素不存在,插入失败!!!");
}
![]()
后插
在指定元素后插入新节点。
function back_insert(head, value, element) {
const node = new Node(value);
if (head.next == null) {
head.next = node;
} else {
let tem = head.next;
while (tem.next != null) {//遍历查找指定元素
if (tem.value == element) {
break;
}
tem = tem.next;
}
node.next = tem.next;
tem.next = node;
return;
}
console.log("指定元素不存在,插入失败!!!");
}
![]()
链表的插入只需要改变指针域指向的节点即可,单链表的后插要比前插简单一点。
删除
找到目标节点,使其前驱结点指向其指向的下一个节点即可。
function del(head, element) {//删除
let tem = head.next;//临时节点
if (head.next == null) {//链表为空
console.log("链表为空!!!");
return;
} else if (head.next.data == element) {//第一个节点为目标节点
head.next = tem.next;
return;
} else {//第一个节点不是目标节点
let pre = head;//tem前驱节点
while (tem != null) {
if (tem.value == element) {
pre.next = tem.next;
return;
}
pre = pre.next;
tem = tem.next;
}
console.log("链表中没有此元素!!!");
}
}
![]()
单链表的其它操作比较简单且容易理解,具体看完整代码和注释。
分解 & 合并
将两个链表合成一个,先找到第一个链表的尾节点,将第二个链表的第一个节点作为尾节点的后续节点插入就好了。分解则是逆过程。
//合并
function combine(head1, head2) {
let tem = head1.next;
if (tem == null) {//head1链表为空head1直接指向head2指向的节点
head1.next = head2.next;
return;
}
while (tem.next != null) {//若head1不为空,找head1尾节点,使其指向head2的首节点
tem = tem.next;
}
tem.next = head2.next;
}
//分解
function resolve(head, element) {
if (head.next == null) {
console.log("链表为空,分解失败!!!");
return null;
}
let head1 = new Head();//为新头节点分配内存空间
head1.next = null;
let tem = head.next;
while (tem != null) {//寻找目标节点
if (tem.value == element) {//将新头节点指向目标节点指向的节点,将目标节点的指针域置为空
head1.next = tem.next;
tem.next = null;
return head1;
}
tem = tem.next;
}
console.log("未找到标记点,分解失败!!!");
return null;
}
其它操作
//查询
function search(head, element) {
let number = 1;
let tem = head.next;
if (tem == null) {
console.log("链表为空!!!");
return;
}
while (tem != null) {//遍历
if (tem.value == element) {
console.log("所查找的元素为链表第" + number + "个节点!",);
return;
}
number++;
tem = tem.next;
}
console.log("目标元素不存在!!!");
}
//从大到小排序
function sorted(head) {
if (head.next == null) {
console.log("链表为空,排序失败!!!");
return;
}
let tem1 = head.next;
while (tem1 != null) {
let tem2 = tem1.next;
while (tem2 != null) {
if (tem1.value < tem2.value) {
let p = tem1.value;
tem1.value = tem2.value;
tem2.value = p;
}
tem2 = tem2.next;
}
tem1 = tem1.next;
}
}
// 返回链表的长度
function length(head) {
let len = 0;
let tem = head.next;
while (tem != null) {
len++;
tem = tem.next;
}
return len;
}
//输出链表
function print(head) {
if (head.next == null) {
console.log("链表为空,无法输出!!!");
return;
} else {
let tem = head.next;
while (tem != null) {
console.log(tem.value);
tem = tem.next;
}
return;
}
}
双向链表(Double linked list)
单链表的每个结点再增加一个指向其前趋的指针域 pre,这样形成的链表有两条不同方向的链,称之为双向链表。
特点:
- 双链表一般也由头指针head唯一确定。
- 每一结点均有:
数据域(value)
左链域(pre)指向前趋结点.
右链域(next)指向后继。
是一种对称结构(既有前趋势,又有后继) - 双链表的前插和后插难度是一样的。
缺点:
指针数的增加会导致存储空间需求增加;二是添加和删除数据时需要改变更多指针的指向。
节点
class Node {
constructor(value) {
this.value = value;
this.next = null;
this.pre = null;
}
}
双向链表的大部分操作与单链表非常类似,只是在操作的时候改变指针稍稍不同,这里只重点说明一下变化较大的操作。
插入
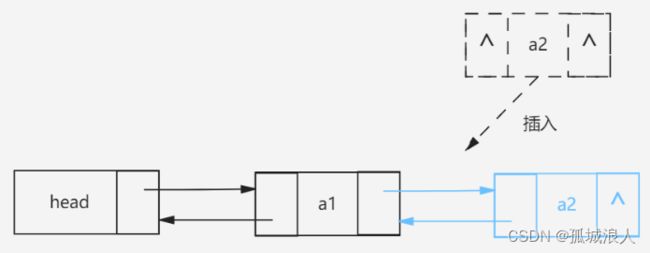
插入空链表或在链表尾部插入 这种情况相对来说比较简单。
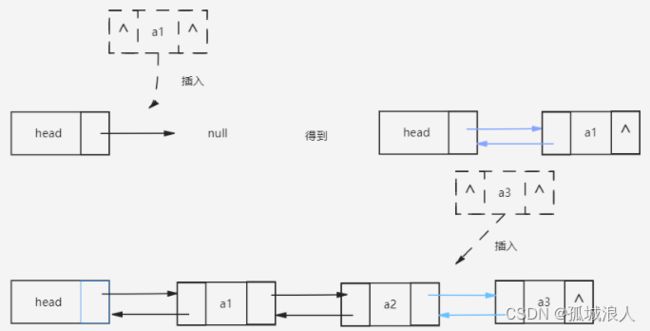
在链表中间插入需要移动的指针较多具体看图。
// 在指定位置插入
function insert(head, value, index = 0) {
if (index >= 0 && index <= head.count) {//指定位置是否合法
const node = new Node(value);
let num = 0, tem = head;
while (num != index && tem != null) {//找指定位置的前驱节点
tem = tem.next;
num++;
}
if (tem.next == null) {
node.pre = tem;
tem.next = node;
} else {
node.pre = tem;
node.next = tem.next;
tem.next.pre = node;
tem.next = node;
}
head.count++;
return node;
} else {
console.log('插入位置错误');
}
}
查询
单链表只能从头结点往后遍历查找,但双向链表可从链表任意位置开始查找。而我给出的示例中是同时从头尾开始向中间遍历查找,这样会加快便利的速度。我这里是在求链表长度的时候记录下尾结点。
//查询
function search(head, element, tail = null) {
let number = 1;
if (head.next == null) {
console.log("链表为空!!!");
return;
}
head = head.next;
if (tail) { // 如果传入尾节点就行二分查找
while (head != tail && tail.next != head) {
if (head.value == element) {
console.log("所查找的元素为链表第" + number + "个节点!");
return head;
} else if (tail.value == element) {
console.log("所查找的元素为链表倒数第" + number + "个节点!");
return tail;
}
number++;
head = head.next;
tail = tail.pre;
}
} else {// 从头开始遍历
while (head != null) {
if (head.value == element) {
console.log("所查找的元素为链表第" + number + "个节点!");
return head;
}
number++;
head = head.next;
}
}
console.log("目标元素不存在!!!");
}
![]()
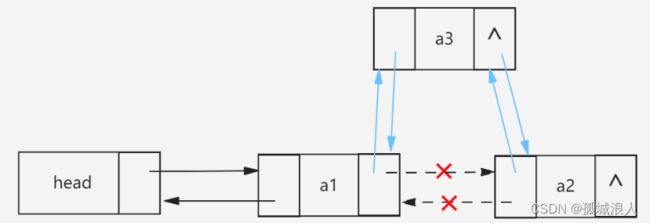
如图:tem利用节点next指针从前往后遍历,temp利用节点pre指针从后往前遍历,遍历结束条件为:
若有奇数个节点,则结束时tem一定等于temp;节点为偶数个时,结束时tem->next一定等于temp或者temp->pre一定等于tem。
删除
双链表删除要比单链表简单一些,因为它不需要额外的寻找指定节点的前驱结点。如上图:若要删除p节点,只需将head节点next指针指向rear节点,而rear节点pre指针指向head节点,最后再释放掉p节点所占内存就完成了删除操作。
//删除
function del(head, element = undefined, node = null) {
let tem = head.next;//临时节点
if (head.next == null) {//链表为空
console.log("链表为空!!!");
return;
}
if (element && !node) {// 传入的是一个值
while (tem != null) {// 循环找值
if (tem.value == element) {
tem.pre.next = tem.next;
if (tem.next) {
tem.next.pre = tem.pre;
}
head.count--;
return;
}
tem = tem.next;
}
} else if (!element && node) {// 传入的是要删除的节点对象
node.pre.next = node.next;
if (node.next) {
node.next.pre = node.pre;
}
head.count--;
return;
}
console.log("链表中没有此元素!!!");
}
其它操作
//输出函数
function print(head) {
if (head.next == null) {
console.log("链表为空,无法输出!!!");
return;
} else {
tem = head.next;
while (tem != null) {
console.log(tem.value);
tem = tem.next;
}
return;
}
}
//合并
function combine(head1, head2, tail = null) {
if (tail) {// 如果传入 head1 链表的尾节点
tail.next = head2.next;
head2.next.pre = tail;
head1.count += head2.count;
} else {// 如果未传入 head1 链表的尾节点
let tem = head1;
while (tem.next != null) {// 循环遍历找 head1 尾节点
tem = tem.next;
}
tem.next = head2.next;
head2.next.pre = tem;
head1.count += head2.count;
}
}
循环链表(Circular linked list)
整个链表形成一个环,从表中任一结点出发均可找到表中其它结点。
特点:
- 表中最后一个结点的指针指向第一个结点或表头结点(如有表头结点的话)
- 循环链表的运算与单链表基本一致。但两者判断是否到表尾的条件不同: 单链表:判断某结点的链域是否为空。循环链表:判断某结点的链域值是否等于头指针。
插入 & 删除
循环链表的插入与单链表极为相似,唯独在尾插、头插、删除‘尾节点‘和删除第一个节点的时候有点区别,因为需要移动’尾节点‘的指针。如下图是’尾插‘,删除’尾节点‘是逆过程。
其实本质上循环链表并没有严格意义上的尾节点,因为该链表就相当于一个环,所以‘尾插’就是严格意义上的在链表中间插入。

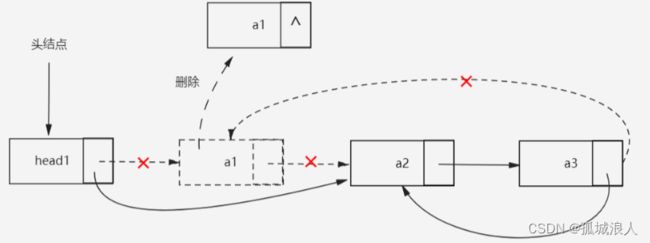
删除头结点如下图所示,头插是逆过程。
// 指定位置插入
function insert(head, value, index = 0) {
if (index >= 0 && index <= head.count) {//指定位置是否合法
const node = new Node(value);
let num = 0;
if (index === 0) {//处理头插
if (head.next == null) {// 链表为空的情况
head.next = node;
node.next = node;
} else {// 链表不为空的情况
let tem = head.next;
node.next = head.next;
while (tem.next != head.next) {// 找到尾节点
tem = tem.next;
}
head.next = node;
tem.next = node;
}
} else {//处理尾插和在链表中间插入
let tem = head;
while (num != index && tem != null) {//找指定位置的前驱节点
tem = tem.next;
num++;
}
node.next = tem.next;
tem.next = node;
}
head.count++;
return node;
} else {
console.log('插入位置错误');
}
}
// 删除某一元素
function del(head, element = undefined) {
let tem = head.next;//临时节点
if (head.next == null) {//链表为空
console.log("链表为空!!!");
return;
}
if (head.count === 1) {// 处理链表只有一个节点的情乱搞
if (head.next.value === element) {
head.next = null;
return;
}
} else {
while (tem.next != head.next) {// 循环找目标节点的前驱
if (tem.next.value === element) {
tem.next = tem.next.next;
while (tem.next != head.next) {// 循环找尾节点
tem = tem.next;
}
tem.next = head.next;// 使尾节点指针指向新的第一个节点
head.count--;
return;
}
tem = tem.next;
}
}
console.log("链表中没有此元素!!!");
}
合并
两循环链表的合并只需要将第一个链表的尾节点指向第二个链表的头节点,第二个链表的尾节点指向第一个链表的头节点即可。其实就是交换两链表的尾节点的指针值。如图所示:
![]()
// 合并链表
function combin(head, head1) {
let tem = head.next, tem1 = head1.next;;//临时节点
while (tem.next && tem.next != head.next) {// 找链表1的尾节点
tem = tem.next;
}
while (tem1.next && tem1.next != head1.next) {// 找链表2的尾节点
tem1 = tem1.next;
}
// 交换两尾节点的指针值
const temp = tem.next;
tem.next = tem1.next;
tem1.next = temp;
}
循环链表的其它操作与单链表和双向链表极为相似,就不在赘述其操作了。
链表的内容基本上就这么多了,希望能够就对你有所帮助。欢迎各位小伙伴在下方留言区留言评论或提问!我是孤城浪人,一名正在前端路上摸爬滚打的菜鸟,欢迎你的关注。