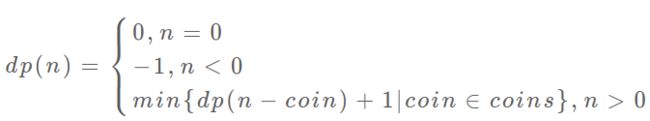leetcode刷题笔记
一、数组
1. 两数之和
给定一个整数数组 nums 和一个目标值 target,请你在该数组中找出和为目标值的 两个 整数。
你可以假设每种输入只会对应一个答案。但是,你不能重复利用这个数组中同样的元素。
示例:
给定 nums = [2, 7, 11, 15], target = 9
因为 nums[0] + nums[1] = 2 + 7 = 9
所以返回 [0, 1]
答案:
public static int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
if (nums == null || nums.length < 2) {
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException("nums length must greater than 2");
}
// 存储返回结果
int[] result = new int[2];
// 把nums和下标写入map
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>(nums.length);
for (int i=0; i<nums.length; i++) {
map.put(nums[i], i);
}
// 遍历nums, 看target - num = remain,remain
for (int j=0; j<nums.length; j++) {
int remain = target - nums[j];
if (map.containsKey(remain) && j != map.get(remain)) {
result[0] = nums[j];
result[1] = remain;
break;
}
}
return result;
}
总结:
1、这是leetcode中简单级别的题目
2、结题时,可以多次用for循环,但不要用for循环嵌套,用多次for循环的时间复杂度仍是O(n)
3、类似的题,可以把数组放到map中,key是数组的值,value是数组的下标。
4、注意,结果不能重复,可以根据下标值做比较。
5、开头注意入参的参数校验,这个是个加分项。
2、三数之和
给你一个包含 n 个整数的数组 nums,判断 nums 中是否存在三个元素 a,b,c ,使得 a + b + c = 0 ?请你找出所有满足条件且不重复的三元组。
注意:答案中不可以包含重复的三元组。
示例:
给定数组 nums = [-1, 0, 1, 2, -1, -4],
满足要求的三元组集合为:
[
[-1, 0, 1],
[-1, -1, 2]
]
public List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
// Step1、参数校验
if (nums == null || nums.length < 3) {
return result;
}
// Step2、给数组排序,O(nlog(n))
Arrays.sort(nums);
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length - 2; i++) {
// 若三个中最小的元素大于0,则结束
if (nums[i] > 0) {
break;
}
// 去重:用当前值与之前比较过的nums[i-1]比较,而不用nums[i]==nums[i+1]比较,否则会覆盖掉left
if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i-1]) {
continue;
}
int target = -nums[i];
int left = i + 1;
int right = nums.length -1;
while (left < right) {
if (nums[left] + nums[right] == target) {
result.add(new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(nums[i], nums[left], nums[right])));
left++;
right--;
// 去重
while (left < right && nums[left] == nums[left - 1]) {
left++;
}
// 去重
while (left < right && nums[right] == nums[right+1]) {
right--;
}
} else if (nums[left] + nums[right] < target) {
left++;
} else {
right--;
}
}
}
return result;
}
总结:排序+双指针
1、中等题目
2、对于求和找出满足条件的元素,可以先对数组排序Arrays.sort(nums); 时间复杂度O(nlog(n))
3、排序后的好处:
1)方便去重
2)排序后左边一定比右边小
4、数组转链表:new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(nums[i], nums[left], nums[right]));
另一种解法:
public class ThreeSum {
public static int[][] threeSum (int[] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
map.put(arr[i], i);
}
Set<String> set = new HashSet<>();
List<int[]> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int j = 0; j < arr.length; j++) {
for (int k = j+1; k < arr.length; k++) {
int tempSum = arr[j] + arr[k];
if (map.containsKey(0-tempSum)) {
int index = map.get(0-tempSum);
if (index != j && index != k) {
int[] subArr = new int[3];
subArr[0] = 0-tempSum;
subArr[1] = arr[j];
subArr[2] = arr[k];
Arrays.sort(subArr);
String str = subArr[0] + "," + subArr[1] + "," + subArr[2];
if (!set.contains(str)) {
set.add(str);
list.add(subArr);
}
}
}
}
}
if (list.size() == 0) {
return null;
}
int[][] resArr = new int[list.size()][];
for (int i = 0; i < resArr.length; i++) {
resArr[i] = list.get(i);
}
return resArr;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {-1, 0, 1, 2, -1, -4};
int[][] res = threeSum (arr);
for (int i = 0; i < res.length; i++) {
int[] subArr = res[i];
for (int j = 0; j < subArr.length; j++) {
System.out.print(subArr[j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
3、斐波那契数
斐波那契数,通常用 F(n) 表示,形成的序列称为斐波那契数列。该数列由 0 和 1 开始,后面的每一项数字都是前面两项数字的和。也就是:
F(0) = 0, F(1) = 1
F(N) = F(N - 1) + F(N - 2), 其中 N > 1.
给定 N,计算 F(N)。
示例 1:
输入:2
输出:1
解释:F(2) = F(1) + F(0) = 1 + 0 = 1.
示例 2:
输入:3
输出:2
解释:F(3) = F(2) + F(1) = 1 + 1 = 2.
示例 3:
输入:4
输出:3
解释:F(4) = F(3) + F(2) = 2 + 1 = 3.
提示:
0 ≤ N ≤ 30
public int fib2(int n) {
if (n==0 || n==1) {
return n;
}
int curSum = 1;
int preSum = 1;
for (int i = 3; i <= n; i++) {
int tmp = curSum;
curSum = curSum + preSum;
preSum = tmp;
}
return curSum;
}
总结:
1、简单级别
2、能用递归解决的,都可以用for循环。for循环的时间复杂度低于递归。
3、结题思路就是for循环,每次循环时,当前值是上次循环的值+上上次循环的值。
4、求两个string类型的值的和
快手面试高频考题
public class LongSum {
public static String sum (String str1, String str2) {
if (str1 == null || str2 == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("");
}
String res = new String();
String maxStr;
String minStr;
if (str1.length() > str2.length()) {
maxStr = str1;
minStr = str2;
} else {
maxStr = str2;
minStr = str1;
}
int nextBit = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < maxStr.length(); i++) {
char add1 = maxStr.charAt(maxStr.length() - i - 1);
char add2 = '0';
int index = minStr.length() - i - 1;
if (index < minStr.length() && index >= 0) {
add2 = minStr.charAt(index);
}
int curSum = Character.getNumericValue(add1) + Character.getNumericValue(add2) + nextBit;
if (curSum > 10) {
nextBit = 1;
curSum = curSum - 10;
} else {
nextBit = 0;
}
res = curSum + res;
}
return res;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String a = "127";
String b = "456";
System.out.println(sum(a, b));
}
}
二、链表
总结:对于链表,需要记住的套路:
一共两个类:节点类、链表类
1、节点类定义:
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
public Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
2、链表类定义:
class SingleLink {
Node head;
Node end;
public void addNode(Node node) {
if (head == null) {
head = node;
end = node;
return;
}
end.next = node;
end = node;
}
public int getSize() {
Node cur = head;
int i = 0;
while (cur != null) {
i++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return i;
}
public Node pop() {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
Node result = head;
if (head.next != null) {
head = head.next;
} else {
head = null;
}
return result;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return head == null;
}
public void print() {
Node cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.data + " ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
}
1、单链表反转
题目:反转一个单链表。
示例:
输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL
输出: 5->4->3->2->1->NULL
进阶:
你可以迭代或递归地反转链表。你能否用两种方法解决这道题?
答案:
public class SingleLink {
LinkNode head;
LinkNode end;
public void addNode(LinkNode node) {
if (head == null) {
head = node;
end = node;
return;
}
end.next = node;
end = node;
}
public void printLinkNode (LinkNode head) {
LinkNode cur = head;
while (cur.next != null) {
System.out.print(cur.data + "-->");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.print(cur.data);
}
// 单链表反转
public LinkNode revertLink(LinkNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
LinkNode cur = head;
LinkNode pre = null;
while (cur != null) {
// 保存当前的下一个节点
LinkNode next = cur.next;
// 把cur的指针指向pre
cur.next = pre;
// pre和cur指针后移
pre = cur;
cur = next;
}
return pre;
}
// 递归方式反转链表
public LinkNode diguiRevertLink(LinkNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
LinkNode cur = diguiRevertLink(head.next);
head.next.next = head;
head.next = null;
return cur;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SingleLink link = new SingleLink();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
LinkNode n = new LinkNode(i);
link.addNode(n);
}
link.printLinkNode(link.head);
System.out.println();
// LinkNode newHead = link.diguiRevertLink(link.head);
LinkNode newHead = link.revertLink(link.head);
link.printLinkNode(newHead);
}
}
class LinkNode {
int data;
LinkNode next;
public LinkNode(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
思考:凡是涉及到链表,先用笔把过程在纸上画出来,然后再写代码。
这里就是通过修改单链表的指针。
2、给定一个链表,反转相邻的两个节点
输入:1->2->3->4
输出:2->1->4->3
答案:
public class RevertNeighborNode {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SingleLink sl = new SingleLink();
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
sl.addNode(new LinkNode(i));
}
sl.printLinkNode(sl.head);
System.out.println();
LinkNode newHead = revertNeighborNode(sl.head);
sl.printLinkNode(newHead);
}
// 自己逻辑写的
public static void reverse (LNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("");
}
LNode cur = head;
LNode pre = null;
while (cur != null && cur.next != null) {
// 把cur和cur.next的data互换,指针不变
int tmp = cur.data;
cur.data = cur.next.data;
cur.next.data = tmp;
// 把cur和pre向后移动2位
pre = cur.next;
cur = cur.next.next;
}
}
public static LinkNode revertNeighborNode (LinkNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
LinkNode cur = head;
LinkNode pre = null;
while (cur != null && cur.next != null) {
LinkNode next = cur.next;
cur.next = next;
pre = cur;
cur = next;
// 把cur和pre的data互换位置
int temp = cur.data;
cur.data = pre.data;
pre.data = temp;
pre.next = cur;
// 指针向后移动1位
cur = cur.next;
pre = pre.next;
}
return head;
}
}
总结:需要边写边debug, 或者Print中间结果,帮助分析。
这里有个技巧:链表,不单可以修改指针,还可以在指针不变的情况下,仅修改链表中data值,以达到事半功倍的效果
3、给定一个链表,判断其中是否有环
答案:
public class Circle {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Circle c = new Circle();
Link l = new Link();
Node n1 = new Node(1);
l.addNodeFromTail(n1);
l.addNodeFromTail(new Node(2));
l.addNodeFromTail(new Node(3));
Node n = new Node(4);
l.addNodeFromTail(n);
// n.next = n1;
System.out.println(c.isCircle(l));
}
public boolean isCircle(Link link) {
Set<Node> set = new HashSet<>();
Node cur = link.head;
while (cur != null) {
if (set.contains(cur)) {
return true;
} else {
set.add(cur);
cur = cur.next;
}
}
return false;
}
}
注意:这里比较的是两个Node对象,而不是Node.data,因为链表的value可能重复。
4、链表合并(coupang)
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/*
合并K个升序链表
输入:lists = [[1,4,5],[1,3,4],[2,6]]
输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4,5,6]
解释:链表数组如下:
[
1->4->5,
1->3->4,
2->6
]
将它们合并到一个有序链表中得到。
1->1->2->3->4->4->5->6
*/
public class LinkOrder {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<SingleLink> l = new ArrayList<>();
SingleLink link1 = new SingleLink();
link1.addNode(new Node(1));
link1.addNode(new Node(4));
link1.addNode(new Node(5));
link1.print();
SingleLink link3 = new SingleLink();
link3.addNode(new Node(1));
link3.addNode(new Node(3));
link3.addNode(new Node(4));
link3.print();
SingleLink link2 = new SingleLink();
link2.addNode(new Node(2));
link2.addNode(new Node(6));
link2.print();
l.add(link1);
l.add(link3);
l.add(link2);
SingleLink sl = createOrderdeLink(l);
System.out.print("result: ");
sl.print();
}
public static SingleLink createOrderdeLink(List<SingleLink> list) {
if (list == null) {
return null;
}
SingleLink link = new SingleLink();
for (SingleLink llink : list) {
if (link.isEmpty()) {
while (!llink.isEmpty()) {
Node n = llink.pop();
if (n != null) {
link.addNode(n);
}
}
} else {
while (!llink.isEmpty()) {
Node n = llink.pop();
if (n != null) {
insertOrderedNodeInLink(n, link);
}
}
}
}
return link;
}
public static void insertOrderedNodeInLink (Node node, SingleLink slink) {
if (node == null || slink == null || slink.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
Node cur = slink.head;
while (cur != null) {
if (node.data >= cur.data && cur.next != null && cur.next.data >= node.data) {
node.next = cur.next;
cur.next = node;
break;
} else if (node.data >= cur.data && cur.next == null) {
cur.next = node;
break;
}
if (node.data < cur.data && cur.data == slink.head.data) {
node.next = cur;
slink.head = node;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
}
}
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
public Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
class SingleLink {
Node head;
Node end;
public void addNode(Node node) {
if (head == null) {
head = node;
end = node;
return;
}
end.next = node;
end = node;
}
public int getSize() {
Node cur = head;
int i = 0;
while (cur != null) {
i++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return i;
}
public Node pop() {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
Node result = head;
if (head.next != null) {
head = head.next;
} else {
head = null;
}
return result;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return head == null;
}
public void print() {
Node cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.data + " ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
}
5、在一个排序的链表中,存在重复的结点,请删除该链表中重复的结点,重复的结点不保留,返回链表头指针
public static Node removeDuplicated(Node head) {
TreeMap<Integer, Integer> map = new TreeMap<>();
SingleLink sl = new SingleLink();
Node cur = head;
Node pre = null;
while (cur != null) {
if (map.containsKey(cur.data)) {
map.put(cur.data, map.get(cur.data) + 1);
} else {
map.put(cur.data, 1);
}
cur = cur.next;
}
for (Entry<Integer, Integer> entry : map.entrySet()) {
if (entry.getValue() == 1) {
sl.addNode(new Node(entry.getKey()));
}
}
return sl.head;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SingleLink link = new SingleLink();
link.addNode(new Node(1));
link.addNode(new Node(2));
link.addNode(new Node(2));
link.addNode(new Node(3));
link.addNode(new Node(4));
link.addNode(new Node(4));
link.addNode(new Node(5));
link.print();
Node head = removeDuplicated(link.head);
Node cur = head;
while (cur!=null) {
System.out.print(cur.data + "-->");
cur = cur.next;
}
}
三、栈和队列
1、给定一个只包含大、中、小括号的字符串,判断字符串是否有效
示例:输入“() [] {}", 输出:true
输入"{[)]", 输出:false
输入”((([])))", 输出:true
思考:每次看到题,先不要着急做,先想清楚思路再做。
思路:如果是左括号,压入栈中;如果是右括号,取出栈顶元素,看是否匹配。如果有不匹配的,返回false, 如果都匹配,看最后栈是否为empty
public class StackTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
boolean result = test("((<(([])))>)");
System.out.print(result);
}
public static boolean test(String str) {
if (str == null) {
return false;
}
// 设置匹配规则
Map<Character, Character> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(']','[');
map.put('>','<');
map.put('}','{');
map.put(')','(');
// 初始化栈
Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<>();
// 处理字符串
char[] arr = str.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
// System.out.println("arr[i]:" + arr[i] + ", map.containsKey:" + map.containsKey(arr[i]));
if (map.containsKey(arr[i])) {
// 是右括号,则取出栈顶元素,跟当前元素比较
if (!stack.empty()) {
Character value = stack.pop();
// System.out.println("value:" + value);
if (value != null && value.equals(map.get(arr[i]))) {
continue;
} else {
return false;
}
} else {
return false;
}
} else {
// 是左括号,则写入栈
// System.out.println("push stack:" + arr[i]);
stack.push(arr[i]);
}
}
return stack.isEmpty();
}
}
总结:
1)网页写代码不能用编辑器debug时,可以通过System.out.println来替代
2)写代码前,一定可以先写明白思路,然后再下手写。想不明白思路不要写。
2、只用stack实现queue, 只用queue实现stack
背景知识:
1)栈:数组或链表实现,先进后出
2)队列:数组或双向链表实现,先进先出
思路:
1)用栈实现队列:依次写入数字:1,2,3,4,5
用两个栈:
栈1:进栈顺序:1,2,3,4,5; 出栈结果:5,4,3,2,1
栈2:进栈顺序:5,4,3,2,1;出栈结果:1,2,3,4,5 ,这样刚好跟写入栈1的顺序相同
题目:
请你仅使用两个栈实现先入先出队列。队列应当支持一般队列的支持的所有操作(push、pop、peek、empty):
实现 MyQueue 类:
void push(int x) 将元素 x 推到队列的末尾
int pop() 从队列的开头移除并返回元素
int peek() 返回队列开头的元素
boolean empty() 如果队列为空,返回 true ;否则,返回 false
说明:
你只能使用标准的栈操作 —— 也就是只有 push to top, peek/pop from top, size, 和 is empty 操作是合法的。
你所使用的语言也许不支持栈。你可以使用 list 或者 deque(双端队列)来模拟一个栈,只要是标准的栈操作即可。
进阶:
你能否实现每个操作均摊时间复杂度为 O(1) 的队列?换句话说,执行 n 个操作的总时间复杂度为 O(n) ,即使其中一个操作可能花费较长时间。
示例:
输入:
["MyQueue", "push", "push", "peek", "pop", "empty"]
[[], [1], [2], [], [], []]
输出:
[null, null, null, 1, 1, false]
解释:
MyQueue myQueue = new MyQueue();
myQueue.push(1); // queue is: [1]
myQueue.push(2); // queue is: [1, 2] (leftmost is front of the queue)
myQueue.peek(); // return 1
myQueue.pop(); // return 1, queue is [2]
myQueue.empty(); // return false
答案:
class MyQueue {
Stack<Integer> stack;
Stack<Integer> stack_bak;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public MyQueue() {
stack = new Stack<>();
stack_bak = new Stack<>();
}
/** Push element x to the back of queue. */
public void push(int x) {
stack.push(x);
}
/** Removes the element from in front of queue and returns that element. */
public int pop() {
// Step1、把stack中元素取出,放入到bak的stack里
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
stack_bak.push(stack.pop());
}
// Step2、对stack_bak执行pop
int result = stack_bak.pop();
// Step3、把stack_bak的元素取出,放回stack中
while (!stack_bak.isEmpty()) {
stack.push(stack_bak.pop());
}
return result;
}
/** Get the front element. */
public int peek() {
// Step1、把stack中元素取出,放入到bak的stack里
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
stack_bak.push(stack.pop());
}
// Step2、对stack_bak执行pop
int result = stack_bak.peek();
// Step3、把stack_bak的元素取出,放回stack中
while (!stack_bak.isEmpty()) {
stack.push(stack_bak.pop());
}
return result;
}
/** Returns whether the queue is empty. */
public boolean empty() {
return stack.isEmpty();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyQueue mq = new MyQueue();
mq.push(1);
mq.push(2);
mq.push(3);
// System.out.println(mq.pop());
System.out.println(mq.peek());
}
}
/**
* Your MyQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyQueue obj = new MyQueue();
* obj.push(x);
* int param_2 = obj.pop();
* int param_3 = obj.peek();
* boolean param_4 = obj.empty();
*/
2)用队列实现栈:
思路:每次向队列中放入数据前,先把队列中的元素都取出放入备用队列,然后放入新元素,再把备用队列中的数据取出放入队列。
举例:依次输入数字:1,2,3,4,5,取出为5,4,3,2,1
Step1:队列1:1
Step2:先取出队列1中的1,放入2;再把队列1中的数据1取出放入队列1,这样队列1中的元素变成了2,1
Step3:先取出队列1中的所有元素2,1放入备用队列,再把3放入队列中;在把备用队列中的2,1取出放入队列,这样队列中的元素变为3,2,1
以此类推。
答案:
class MyStack {
Deque<Integer> queue;
Deque<Integer> queue_bak;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public MyStack() {
queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue_bak = new LinkedList<>();
}
/** Push element x onto stack. */
public void push(int x) {
// Step1、先把现有队列中的数据取出,放入到bak队列中
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
queue_bak.push(queue.pop());
}
// Step2、把元素放入队列中
queue.push(x);
// Step3、把bak中的队列元素取出,放入到队列中
while (!queue_bak.isEmpty()) {
queue.push(queue_bak.pop());
}
}
/** Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element. */
public int pop() {
// Step1、把queue中的元素都放入bak队列
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
queue_bak.push(queue.pop());
}
// Step2、把bak队列执行pop
int result = queue_bak.pop();
// Step3、把bak队列的数据取出放入queue队列
while (!queue_bak.isEmpty()) {
queue.push(queue_bak.pop());
}
return result;
}
/** Get the top element. */
public int top() {
int size = queue.size();
int result = 0;
int i = 0;
for (int q : queue) {
i++;
if (i == size) {
result = q;
break;
}
}
return result;
}
/** Returns whether the stack is empty. */
public boolean empty() {
return queue.isEmpty();
}
}
/**
* Your MyStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyStack obj = new MyStack();
* obj.push(x);
* int param_2 = obj.pop();
* int param_3 = obj.top();
* boolean param_4 = obj.empty();
*/
总结:
1)写完代码,自己写测试用例测试下运行结果,然后再提交
2)写代码前,先写注释的思路,然后再写代码
四、堆(优先队列PriorityQueue)
1、实时判断数据流中第K大元素
题目:
设计一个找到数据流中第 k 大元素的类(class)。注意是排序后的第 k 大元素,不是第 k 个不同的元素。
请实现 KthLargest 类:
KthLargest(int k, int[] nums) 使用整数 k 和整数流 nums 初始化对象。
int add(int val) 返回当前数据流中第 k 大的元素。
示例:
输入:
["KthLargest", "add", "add", "add", "add", "add"]
[[3, [4, 5, 8, 2]], [3], [5], [10], [9], [4]]
输出:
[null, 4, 5, 5, 8, 8]
解释:
KthLargest kthLargest = new KthLargest(3, [4, 5, 8, 2]);
kthLargest.add(3); // return 4
kthLargest.add(5); // return 5
kthLargest.add(10); // return 5
kthLargest.add(9); // return 8
kthLargest.add(4); // return 8
提示:
1)返回第k大的元素,套路:可以让priority队列中最多保留这个几个元素
2)每次add,向数组中添加新元素,然后只保留最大的top k元素即可。
答案:
public class PriorityTest {
PriorityQueue<Integer> queue;
int k = 0;
public PriorityTest(int k, int[] arr) {
this.k = k;
queue = new PriorityQueue<>(k);
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
add(arr[i]);
}
}
public void printQueue() {
System.out.println("print queue:");
for (Integer i : queue) {
System.out.println(i);
}
System.out.println("---------------");
}
public int add(int element) {
// 如果超过了队列大小,新元素比队头元素大,则把队头(最小的元素)清除,然后加入新元素
if (queue.size() < k) {
queue.add(element);
} else {
if (queue.peek() < element) {
queue.poll();
queue.add(element);
}
}
return queue.peek();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int k = 3;
int[] arr = {4,5,8,2};
PriorityTest pt = new PriorityTest(k, arr);
System.out.println(pt.add(3));
System.out.println(pt.add(5));
System.out.println(pt.add(10));
System.out.println(pt.add(9));
System.out.println(pt.add(4));
}
}
总结:
1)top k的问题,可以用PriorityQueue来实现,默认取最大top k
2)如果程序结果不对,可以写print函数,然后调试结果,直到找到问题来修正。
进一步为:如果求最小top k,怎样解决?
答:可以自实现priorityqueue中的comparator中的compare函数
public MinTopK(int k, int[] arr) {
this.k = k;
queue = new PriorityQueue(k, new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o2-o1;
}
});
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
add(arr[i]);
}
}
五、Map和Set
1、有效的字母异位词,不限字母次序
示例1:
输入 s=“anagram”, t=“nagaram”
输出 true
示例2:
输入 s=“rat”, t=“car”
输出 false
示例3:
输入 s=“rat”, t=“art”
输出 true
答案:
public static boolean isYiweici(String str1, String str2) {
if (str1.length() != str2.length()) {
return false;
}
Map<Character, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
Map<Character, Integer> map2 = new HashMap<>();
Set<Character> set = new HashSet<>();
for (int i = 0; i < str1.length(); i++) {
if (map.containsKey(str1.charAt(i))) {
map.put(str1.charAt(i), map.get(str1.charAt(i)) + 1);
} else {
map.put(str1.charAt(i), 1);
}
set.add(str1.charAt(i));
if (map2.containsKey(str2.charAt(i))) {
map2.put(str2.charAt(i), map2.get(str2.charAt(i)) + 1);
} else {
map2.put(str2.charAt(i), 1);
}
set.add(str2.charAt(i));
}
for (Character c : set) {
if (map.get(c) != map2.get(c)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
用Set解,时间复杂度是O(n)
也可以把两个字符串分别排序,然后比较后equal,Arrays.sort是归并排序,时间复杂度O(n * log(n))
答案:
public class YiWeiCi2 {
public static boolean test(String str1, String str2) {
if (str1 == null || str2 == null) {
return false;
}
if (str1.length() != str2.length()) {
return false;
}
char[] arr1 = str1.toCharArray();
char[] arr2 = str2.toCharArray();
Arrays.sort(arr1);
Arrays.sort(arr2);
String s1 = new String(arr1);
String s2 = new String(arr2);
return s1.equals(s2);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(test("abc", "abca"));
Arrays.sort(args);
}
}
其他题目:两数之和和三数之和,见第一章 数组。
六、二叉树
背景知识:
1)二叉树是由链表演进而来,只是有2个next指针而已。
2)二叉搜索树:
- 1、左子树上所有节点的值均小于它根节点的值
- 2、右子树上所有节点的值均大于他的根节点的值
- 3、递归:左右子树也分别为二叉查找树
这样每次查找,根据与根的大小比较,可以减少一半的查找量,把时间复杂度从O(N)变成了O(log(n))
实战中很多二叉搜索树都是用红黑树来实现的
二叉树的遍历分深度优先遍历和广度优先遍历,其中深度优先遍历又分为前序遍历、中序遍历、后续遍历:
中序遍历:左、根、右。
前序遍历:根、左、右。
后续遍历:左、右、根。
广度优先也就是逐层遍历。
1、基础:二叉树的前序遍历、中序遍历、后续遍历(递归和非递归)
public class BTree {
int data;
BTree left;
BTree right;
public BTree(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
public void insertTree(BTree root, int data) {
if(data >= root.data) {
if(root.right == null) {
root.right = new BTree(data);
} else {
insertTree(root.right, data);
}
} else {
if(root.left == null) {
root.left = new BTree(data);
} else {
insertTree(root.left, data);
}
}
}
//get the height of Binary Tree
public int getTreeHeight() {
int height = 0;
if(this == null)
return -1;
int leftHeight = 0;
int rightHeight = 0;
if(left != null) {
leftHeight = left.getTreeHeight();
}
if(right != null) {
rightHeight = right.getTreeHeight();
}
height = (leftHeight <= rightHeight) ? rightHeight + 1 : leftHeight + 1;
return height;
}
//previous order loop:中、左、右
public void preOrder(BTree root) {
if(root == null) {
return ;
}
System.out.print(root.data + " ");
preOrder(root.left);
preOrder(root.right);
}
//middle order loop:左、中、右
public void middleOrder(BTree root) {
if(root == null)
return;
middleOrder(root.left);
System.out.print(root.data + " ");
middleOrder(root.right);
}
//behindOrder:左、右、中
public void behindOrder(BTree root) {
if(root == null)
return ;
behindOrder(root.left);
behindOrder(root.right);
System.out.print(root.data + " ");
}
//前序:中、左、右
public static void preOrder2(BTree node) {
if(node == null) {
return;
}
Stack<BTree> stack = new Stack<>();
while(!(node == null && stack.isEmpty())) {
//找到当前节点最深的左子树
if(node != null) {
System.out.print(node.data + " "); //访问节点
stack.push(node); //将当前左子树入栈
node = node.left;
} else { //当左子树到底时,开始访问右子树
node = stack.pop();
node = node.right;
}
}
}
// 中序:左,中,右
public static void middleOrder2(BTree node) {
if(node == null)
return ;
Stack<BTree> stack = new Stack<BTree>();
while(!(node == null && stack.empty())) {
while(node != null) { //先找到最深的左子树
stack.push(node);
node = node.left;
}
//找到最深左子树后开始访问
if(!stack.empty()) {
node = stack.pop();
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
node = node.right;
}
}
}
//后续:左,右,中
public static void behindOrder2(BTree node) {
Stack stack = new Stack(); //用来存放BTree节点和Integer的Stack
while(!(node == null && stack.isEmpty())) {
if(node != null) { //找到最深的左子树
stack.push(node); //将当前节点压入栈
stack.push(1); //并标记当前节点访问的次数
node = node.left;
} else { //找到最深左子树后
while(!stack.isEmpty()) {
int sign = (Integer)stack.pop(); //出栈标记
node = (BTree)stack.pop(); //出栈的BTree节点
if(sign == 1) { //当第一次访问时,找右节点,而不应该打印
stack.push(node);
stack.push(2);
node = node.right; //将节点指向右子树,并开始访问指向右子树的左子树
break;
} else if (sign == 2) { //当第二次出栈时,打印当前节点
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
node = null;
}
}
}
}
}
// 二叉树广度遍历(逐层遍历)
public void levelOrder(BTree node) {
if (node == null) {
return;
}
Queue<BTree> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(node);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
node = queue.poll();
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
if (node.left != null) {
queue.offer(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
queue.offer(node.right);
}
}
}
/*
* 8
* 5 10
* 4 6 9
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
BTree root = new BTree(8);
root.insertTree(root, 10);
root.insertTree(root, 5);
root.insertTree(root, 6);
root.insertTree(root, 4);
root.insertTree(root, 9);
root.preOrder(root);
}
}
非递归前序思路:
1)先打印当前节点
2)把当前节点放入stack
3)把当前节点的左节点作为当前节点,这样不断找左节点
4)如果没有左节点了,那么把stack中的节点pop出来,然后取出这个节点的右节点,继续递归。
非递归中序思路:
跟前序类似,只是先不打印当前节点,等左子树遍历完后,从stack取出后,再打印当前节点,然后再获取当前节点的右孩子,继续循环。
注意:中序有两个while嵌套
非递归后续思路:
1)先把当前节点放入stack(放入时,先放当前节点,然后再放个标志位1(表示该节点还没有被从栈取出过))
2)逐步找当前节点的左节点,然后放入栈中,直到找完所有的左节点
3)从栈中pop标志位和节点,如果标志位是1,则把当前节点再次放入stack, 并把标志位置为2也放入Stack,然后把当前节点置为其右节点,以此类推。
2、验证给定的二叉树是否为二叉搜索树
示例1:
输入:[3,1,5,null, 2]
输出:true
示例2:
输入:[5,1,4,null, null, 3,6]
输出:false
public class IsBinarySearchTree {
public boolean isBST (TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return false;
}
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
// 中序遍历
middleOrder (root, list);
int cur = list.get(0);
for (int i = 1; i < list.size(); i++) {
if (list.get(i) < cur) {
return false;
}
cur = list.get(i);
}
return true;
}
public void middleOrder (TreeNode root, List<Integer> list) {
if (root.left != null) {
middleOrder (root.left, list);
}
list.add(root.data);
if (root.right != null) {
middleOrder (root.right, list);
}
}
}
3、二叉搜索树两个节点的最近公共祖先
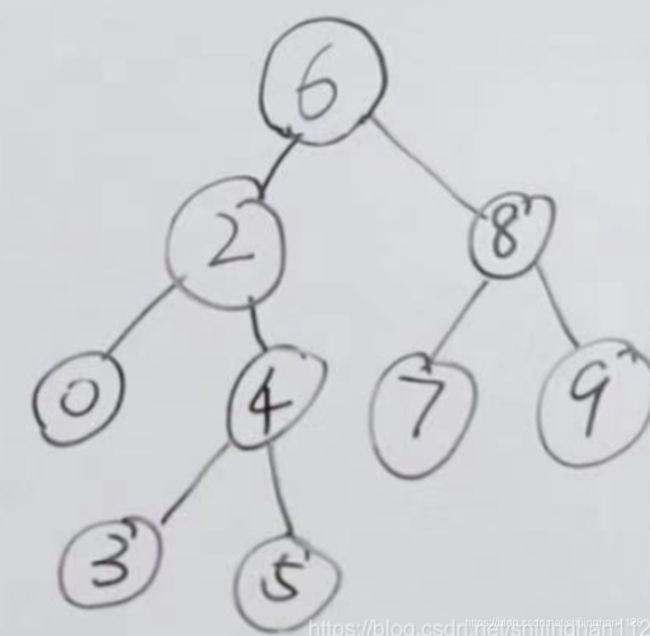
示例1:
输入: root=[6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5], p=2, q=8
输出:6
示例2:
输入:root=[6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5], p=2, q=4
输出:2
背景知识:二叉搜索树,left < root < right
思路:把p, q两个节点和根比较,如果一个比根大,一个比根小,则返回根;如果都比根小,则根变为左子树;如果都比根大,则变为右子树,以此类推。
答案:
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if (p == null || q == null || root == null) {
return null;
}
if (root.val < p.val && root.val < q.val) {
return lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
}
if (root.val > p.val && root.val > q.val) {
return lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
}
return root;
}
七、递归 & 分治法
背景知识:
递归:自己调自己,但要防止死循环。递归可以加个level参数。
1、求 n! = 1* 2* 3*… * n
答案:
public int jiecheng(int n) {
if (n <= 1) {
return n;
}
return n * jiecheng(n-1);
}
递归也是分治的一种思想。
分治:把大问题拆分成n个子问题分别求解
2、给定一个字符串:abcdefghij, 把每个字符变成大写。
解题思路:分治法:并行计算。
3、pow(x, n),即x的n次幂
// x的n次幂
public static int pom(int x, int n) {
if (n <= 1) {
return x;
}
return x * pom(x, n-1);
}
4、求众数:count(x) > n/2, x是数组中重复的元素,count(x)是x出现的次数,n是数组元素的个数
即找出数组中出现次数大于数组元素个数一半的元素
示例1:
输入:[1,3,3,2,3]
输出:3
示例2:
输入:[1,1,1,0,2]
输出:1
答案:
public static Integer zhongshu(int[] arr) {
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
int size = arr.length;
for (int i : arr) {
if (map.containsKey(i)) {
int value = map.get(i) + 1;
if (value > size/2) {
return i;
}
map.put(i, value);
} else {
map.put(i, 1);
}
}
return null;
}
八、面试答题四件套
在面试前,对前面的模板套路一定要形成机械记忆和条件反射!!!
1、搞清题目
弄清题目细节、边界条件、可能的极端错误情况
2、把所有可能的解法和面试官沟通一遍:不要把面试官当成监考老师,而是把他当成未来的同事,当成讨论问题。
1)每种解法的时间复杂度、空间复杂度
2)最优解
3、写代码
把思路写到注释里,这样可以帮助思路清晰的写出代码,且不易出错。
可以print调试结果
4、测试用例
1)正常用例
2)极端用例
3)想不到的用例
九、经典题
1、利用前序遍历和中序遍历构造二叉树【分治】
思路:
- 根据先序遍历,我们可以知道根节点就是给定数组的第一个元素pre[0],那么我们就可以在中序遍历中找出值等于pre[0]的位置,该位置的前半部分就是左子树,右半部分就是右子树
- 重复1,直到遍历完
经验总结:凡是跟树相关的,都可以考虑用递归法,把复杂的问题拆解成可以重复的子问题。
参考答案:https://www.cnblogs.com/du001011/p/11229211.html
2、给定一个整数数组 nums ,找到一个具有最大和的连续子数组(子数组最少包含一个元素),返回其最大和。【动态规划】
示例:
输入: [-2,1,-3,4,-1,2,1,-5,4]
输出: 6
解释: 连续子数组 [4,-1,2,1] 的和最大,为 6。
分析:最大子序列,属于动态规划。
只有i==j时,才是真正计算长度;i != j 时,只是传承之前的计算结果。
此类题可以先画出结果来。
技巧:dp后面的值,要包括前面的计算结果,最后返回dp最后面的元素
答案:
public class MaxSubSum {
public static int maxSubArray(int[] nums) {
int ans = 0;
int[] dp = new int[nums.length];
dp[0] = nums[0];
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i-1] + nums[i], nums[i]);
}
for (int j = 0; j < dp.length; j++) {
if (dp[j] > ans) {
ans = dp[j];
}
}
return ans;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {-2,1,-3,4,-1,2,1,-5,4};
System.out.print(maxSubArray(arr));
}
}
总结:用dp[]数组记录每一步的中间值,最后取最大值。
关键在于这个条件不好想:
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i-1] + nums[i], nums[i]);
套路:
Step1、找出base case, dp[0] = nums[0];
Step2、设定状态数组dp[]
Step3、遍历,找出规律
Step4、找出dp[]数组中的最大值
3、最大公共子序列【动态规划】
题目:
给定两个字符串str1和str2,返回两个字符串的最长公共子序列,例如:str1=“1A2C3D4B56",str2=“B1D23CA45B6A”,"123456"和"12C4B6"都是最长公共子序列,返回哪一个都行。
答案:
public class MaxSubXulie {
private static int subMax(String str1, String str2) {
// 1. 构造dp状态函数:二维数组
int[][] dp = new int[str1.length() + 1][str2.length() + 1];
/*
2. 循环添加状态:
1)横竖相等:
dp[i+1][j+1]=dp[i][j]+1
2)横竖不等:
dp[i+1][j+1]=max(dp[i+1][j], dp[i][j+1]
*/
for (int i = 0; i < str1.length(); i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < str2.length(); j++) {
if (str1.charAt(i) == str2.charAt(j)) {
dp[i+1][j+1] = dp[i][j] + 1;
} else {
dp[i+1][j+1] = Math.max(dp[i][j+1], dp[i+1][j]);
}
}
}
return dp[str1.length()][str2.length()];
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1= "1A2C3D4B56";
String str2 = "B1D23CA45B6A";
System.out.println(subMax(str1, str2));
}
}
总结:经典动态规划算法,用二维数组解决,其中的条件为条路,自己想比较不易。
十、解题套路总结
1、动态规划
动态规划:一般形式是求"最值"。
求解动态规划的核心问题是“穷举”,但动态规划的穷举有点特别,因为存在“重叠子问题”,穷举的话效率会非常差。所以需要用“备忘录”即“DB Table”来优化穷举的过程,避免重复的计算,这就是dp table的作用。
而且,动态规划问题一定会具备“最优子结构”,才能通过子问题的最值得到原问题的最值。
求解动态规划,穷举所有可行解,并不是一件容易事,只有列出正确的“状态转移方程”,才能正确地穷举。
1.1、动态规划求解三要素
三要素:重叠子问题、最优子结构、状态转移方程。
其中,写出状态转移方程是最困难的,这就是为什么大家觉得动态规划难的原因。
动态规划思维框架
1)明确base case
2)明确“状态”
3)明确“选择”
4)定义dp数组/函数的含义
"动态规划"框架:
// 初始化 base case
dp[0][0] = base;
for (状态1 in 状态1的所有值) {
for (状态2 in 状态2的所有值) {
for ... {
dp[状态1][状态2][...] = 求最值(选择1, 选择2, ...);
}
}
}
1.2、动态规划入门:斐波那契数列
递归算法:
public int fib (int n) {
if (n == 1 || n == 2) {
return 1;
}
return fib(n-1) + fib(n-2);
}
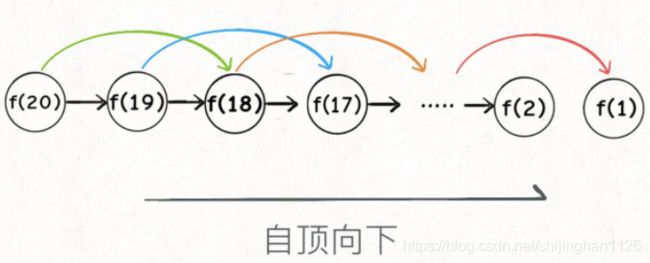
这样的代码简单,但低效。为什么低效,画出递归树就知道了:

要计算f(20), 需要先计算f(19), f(18), 而计算f(19),需要先计算f(18), f(17), 最后到f(1)和f(2), 返回结果。但这样存在大量的重复计算。
在递归里,子问题的个数,就是递归树中节点的个数,所以二叉树是指数级别的,上面算法的时间复杂度为O(2^n)。
所以,动态规划的第一个性质:重叠子问题。要解决,可以用“带备忘录”的递归:
public int fib(int n) {
if (n < 1) {
return 0;
}
// 备忘录初始化为0
int[] memo = memo(n+1, 0);
// 进行带备忘录的递归
return helper(memo, n);
}
public int helper(int[] memo, int n) {
// base case
if (n == 1 || n == 2) {
return 1;
}
// 已经计算过
if (memo[n] != 0) {
return memo[n];
}
memo[n] = helper(memo, n-1) + helper(memo, n-2);
return memo[n];
}

带“备忘录”的递归解法,相当于把一棵巨量的冗余的递归树做了“剪枝”,改造成了一棵不存在冗余的递归图,极大地减少了子问题的个数。
变成了这样:
所以,带备忘录的递归,时间复杂度从O(2^n) 降低到了 O(n)
带备忘录的递归解法和动态规划已经非常相似了,不同点在于备忘录的递归解法是“自顶向下”,而动态规划是“自底向上”。
什么是自顶向下呢?
从一个规模较大的问题比如f(20)向下分解,直到 f(1) 和 f(2)这两个base case,然后逐层返回。
什么是自底向上呢?
从问题最小规模的 f(1) 和 f(2) 往上推,直到找到 f(20), 这就是动态规划的思路。
这也是为什么动态规划一般都脱离了递归,而是由循环完成的计算。
采用动态规划来解:
public int fib (int n) {
if (n < 1) {
return 0;
}
if (n==1 || n==2) {
return 1;
}
int[] dp = new int[n + 1];
// base case
dp[0] = 1;
dp[1] = 1;
for (int i = 3; i <= n; i++) {
dp[i] = dp[i-1] + dp[i-2];
}
return dp[n];
}
有了上一步的备忘录,我们把备忘录独立出一张表,就叫做DP Table。
状态转移方程:

把f(n)想作一个状态n, 这个状态n是由状态 n-1 和 状态 n-2 相加转移而来,这叫做“状态转移”。
可以看出,上述算法中的 return f(n-1) + f(n-2) ,dp[i] = dp[n-1] + dp[n-2],及对备忘录的初始化操作,都是围绕这个方程式的不同表现形式,所以“状态转移方程”是解决动态规划问题的核心。而且可以看出,状态转移方程直接代表着暴力解法。
千万不要看不起暴力解,动态规划问题最困难的就是写出这个暴力解,即状态转移方程。只要写出暴力解,优化方法无非就是用备忘录或DP Table, 再无奥秘可言。
状态压缩
再说个优化细节,根据斐波那契数列的状态转移方程,当前的状态之和之前的两个状态有关,其实并不需要太长的一个DP Table来存储所有的状态,只要想办法存储之前的状态就可以了。
所以,可以进一步优化:
public int fib (int n) {
if (n < 1) {
return 0;
}
if (n == 1 || n == 2) {
return 1;
}
int pre = 1;
int cur = 1;
for (int i = 3; i <= n; i++) {
int sum = cur + pre;
pre = cur;
cur = sum;
}
return cur;
}
这个技巧就是“状态压缩”, 如果我们发现每次状态转移只要DP table中的一部分,那就可以尝试用状态压缩来缩小DP table的大小,只记录必要的数据,上述例子就把DP Table的大小从n压缩到2.
1.3、动态规划经典问题:凑零钱问题
题目:给你 k 种面值的硬币,面值分别为 c1, c2 … ck,每种硬币的数量无限,再给一个总金额 amount,问最少需要几枚硬币凑出这个金额,如果不可能凑出,算法返回 -1
// coins 中是可选硬币面值,amount 是目标金额
int coinChange(int[] coins, int amount);
例如 k = 3,面值分别为1,2,5,总金额 amount = 11。那么最少需要3枚硬币,即11=5+5+1
思路1:暴力递归
首先,很容易看出这是个经典的“背包”动态规划问题,因为他具有“最优子结构”,子问题间必须互相独立。
对于零钱问题,为什么说他符合最优子结构呢? 比如你想求 amount = 11 时的最少硬币数,如果你知道凑出amount = 10 的最少硬币数(子问题),你只需要把子问题的答案加一(再选一枚面值为1的硬币)就是原问题的答案。因为硬币是没有限制的,所以子问题之间没有互相制约,是互相独立的。
那么,有了“最优子结构”之后,怎样列出正确的状态转移方程呢?
Step1:确定 base case
很显然 amount = 0时,只需要 0 个硬币。
Step2:确定状态:也就是原问题和子问题中变化的变量
由于硬币的数量不限,硬币的面额也是题目给定的,只要目标金额不断地向base case靠近,所以唯一的“状态”就是目标金额 amount
Step3:确定“选择”:也就是导致“状态”发送变化的行为
目标金额为什么变化呢,因为你在选择硬币,没选择一枚硬币,就相当于减少了目标金额。所以说所有硬币的面值,就是你的“选择”。
Step4:明确dp函数/数组的定义
一般来说状态函数的参数就是状态转移中变化的量,也就是“状态”,函数的返回值就是题目要我们求的计算的量。就本题来说,状态只有一个,即目标金额。题目要求我们计算出凑出目标金额所需的最少的硬币数量。
我们可以这样定义 dp 函数:
dp(n)的定义:输入一个目标金额n, 返回凑出目标金额n的最少硬币数量。
伪代码:
def coinChange(coins: List[int], amount: int):
# 定义:要凑出金额 n,至少要 dp(n) 个硬币
def dp(n):
# 做选择,选择需要硬币最少的那个结果
for coin in coins:
res = min(res, 1 + dp(n - coin))
return res
# 题目要求的最终结果是 dp(amount)
return dp(amount)
def coinChange(coins: List[int], amount: int):
def dp(n):
# base case
if n == 0: return 0
if n < 0: return -1
# 求最小值,所以初始化为正无穷
res = float('INF')
for coin in coins:
subproblem = dp(n - coin)
# 子问题无解,跳过
if subproblem == -1: continue
res = min(res, 1 + subproblem)
return res if res != float('INF') else -1
return dp(amount)
待备忘录的递归:
def coinChange(coins: List[int], amount: int):
# 备忘录
memo = dict()
def dp(n):
# 查备忘录,避免重复计算
if n in memo: return memo[n]
# base case
if n == 0: return 0
if n < 0: return -1
res = float('INF')
for coin in coins:
subproblem = dp(n - coin)
if subproblem == -1: continue
res = min(res, 1 + subproblem)
# 记入备忘录
memo[n] = res if res != float('INF') else -1
return memo[n]
return dp(amount)
dp数组迭代法:
我们也可以自底向上使用dp table来消除重叠子问题。
dp数组的定义:当目标金额为 i 时,至少需要 dp[i] 枚硬币凑出。
int coinChange(vector<int>& coins, int amount) {
// 数组大小为 amount + 1,初始值也为 amount + 1
vector<int> dp(amount + 1, amount + 1);
// base case
dp[0] = 0;
// 外层 for 循环在遍历所有状态的所有取值
for (int i = 0; i < dp.size(); i++) {
// 内层 for 循环在求所有选择的最小值
for (int coin : coins) {
// 子问题无解,跳过
if (i - coin < 0) continue;
dp[i] = min(dp[i], 1 + dp[i - coin]);
}
}
return (dp[amount] == amount + 1) ? -1 : dp[amount];
}
用java实现的最终答案:
public class DPCoins {
public static int coinChange (int[] coins, int amount) {
if (coins.length == 0) {
return -1;
}
// dp[n]的值: 表示的凑成总金额为n所需的最少的硬币个数
// 数组int[] coins:表示硬币都有哪些面值
int[] dp = new int[amount + 1];
dp[0] = 0;
// i 表示达到最大金额前的中间金额
for (int i = 1; i <= amount; i++) {
int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int j = 0; j < coins.length; j++) {
// 当前金额 - 硬币面值 >=0 且 这一步所需硬币数比min少
int remain = i - coins[j];
if (remain >= 0 && dp[remain] < min) {
// 记录当前需要最少的硬币数,写入min
min = dp[remain] + 1;
}
}
// 每做完一步,记录个备忘录到dp[i]
dp[i] = min;
}
return dp[amount] == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? -1 : dp[amount];
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1,2,5};
System.out.print(coinChange(arr, 11));
}
}
1.4、动态规划进阶:一和零问题
题目:给你一个二进制字符串数组 strs 和两个整数 m 和 n 。
请你找出并返回 strs 的最大子集的大小,该子集中 最多 有 m 个 0 和 n 个 1 。
如果 x 的所有元素也是 y 的元素,集合 x 是集合 y 的 子集 。
示例 1:
输入:strs = ["10", "0001", "111001", "1", "0"], m = 5, n = 3
输出:4
解释:最多有 5 个 0 和 3 个 1 的最大子集是 {"10","0001","1","0"} ,因此答案是 4 。
其他满足题意但较小的子集包括 {"0001","1"} 和 {"10","1","0"} 。{"111001"} 不满足题意,因为它含 4 个 1 ,大于 n 的值 3 。
示例 2:
输入:strs = ["10", "0", "1"], m = 1, n = 1
输出:2
解释:最大的子集是 {"0", "1"} ,所以答案是 2 。
答案:
public static int zeroAndOne(String[] strArr, int maxM, int maxN) {
if (strArr == null || strArr.length == 0) {
return -1;
}
int stringNum = strArr.length;
int[][][] dp = new int[stringNum+1][maxM+1][maxN+1];
for (int i = 1; i <= stringNum; i++) {
int[] curCntArr = count(strArr[i-1]);
for (int j = 0; j <= maxM; j++) {
for (int k = 0; k <= maxN; k++) {
if (curCntArr[0] > j || curCntArr[1] > k) {
dp[i][j][k] = dp[i-1][j][k];
} else {
dp[i][j][k] = Math.max(dp[i-1][j][k], dp[i-1][j-curCntArr[0]][k-curCntArr[1]]+1);
}
}
}
}
return dp[stringNum][maxM][maxN];
}
private static int[] count(String str) {
int[] arr = new int[2];
int oneCnt = 0;
int zeroCnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
if (str.charAt(i) == '1') {
oneCnt++;
}
if (str.charAt(i) == '0') {
zeroCnt++;
}
}
arr[0] = zeroCnt;
arr[1] = oneCnt;
return arr;
}
解题思路:
第一步,要明确两点,[状态]和[选择]。
状态有三个, [背包对1的容量]、[背包对0的容量]和 [可选择的字符串];选择就是把字符串[装进背包]或者[不装进背包]。
明白了状态和选择,只要往这个框架套就完事儿了:
**for 状态1 in 状态1的所有取值:
for 状态2 in 状态2的所有取值:
for ...
dp[状态1][状态2][...] = 计算(选择1,选择2...)**
第二步,要明确dp数组的定义:
首先,[状态]有三个,所以需要一个三维的dp数组。
dp[i][j][k]的定义如下:
若只使用前i个物品,当背包容量为j个0,k个1时,能够容纳的最多字符串数。
经过以上的定义,可以得到:
base case为dp[0][..][..] = 0, dp[..][0][0] = 0。因为如果不使用任何一个字符串,则背包能装的字符串数就为0;如果背包对0,1的容量都为0,它能装的字符串数也为0。
我们最终想得到的答案就是dp[N][zeroNums][oneNums],其中N为字符串的的数量。
第三步,根据选择,思考状态转移的逻辑:
注意,这是一个0-1背包问题,每个字符串只有一个选择机会,要么选择装,要么选择不装。
如果你不能把这第 i 个物品装入背包(等同于容量不足,装不下去),也就是说你不使用strs[i]这一个字符串,那么当前的字符串数dp[i][j][k]应该等于dp[i - 1][j][k],继承之前的结果。
如果你可以把这第 i 个物品装入了背包(此时背包容量是充足的,因此要选择装或者不装),也就是说你能使用 strs[i] 这个字符串,那么 dp[i][j] 应该等于 Max(dp[i - 1][j][k], dp[i - 1][j - cnt[0]][k - cnt[1]] + 1)。 Max函数里的两个式子,分别是装和不装strs[i的字符串数量。(cnt 是根据strs[i]计算出来的。)
比如说,如果你想把一个cnt = [1,2]的字符串装进背包(在容量足够的前提下),只需要找到容量为
[j - 1][k - 2]时候的字符串数再加上1,就可以得到装入后的字符串数了。
由于我们求的是最大值,所以我们要求的是装和不装中能容纳的字符串总数更大的那一个。
1.5、动态规划经典:三步问题:上楼梯
三步问题。有个小孩正在上楼梯,楼梯有n阶台阶,小孩一次可以上1阶、2阶或3阶。实现一种方法,计算小孩有多少种上楼梯的方式。结果可能很大,你需要对结果模1000000007。
示例1:
输入:n = 3
输出:4
说明: 有四种走法
示例2:
输入:n = 5
输出:13
提示:
n范围在[1, 1000000]之间
答案:
public static int test(int n) {
int[] dp = new int[n+1];
dp[1] = 1; // 1
dp[2] = 2; // 1+1, 2
dp[3] = 4; // 1+2, 1+1+1, 3,2+1
if (n < 3 && n >= 0) {
return n;
}
for (int i = 4; i <= n; i++) {
dp[i] = (dp[i-1] + dp[i-2] + dp[i-3]) % 1000000007 % 1000000007;
}
return dp[n];
}
思路:
根据题意可以得出,当小孩站在第n阶台阶上的时候,他上来的方式有三种,一种是走一个台阶,一种是走两个台阶,一种是走三个台阶,因此小孩上到第n阶台阶总的方式便等于从第n-1阶台阶上来的方式 + 从第n-2阶台阶上来的方式 + 从第n-3阶台阶上来方式的和。例如在第四个台阶上,小孩可能从第1阶台阶上来,可能从第二节阶上上来,可能从第第三个台阶上上来,因此f(4)=f(3)+f(2)+f(1)=7。
因此可以得到递推公式
f(n)=f(n-1)+f(n-2)+f(n-3),n>3。
f(1)=1,f(2)=2,f(3)=3。
字节抖音高频题
1、无重复字符的最长子串(难度:中等)
给定一个字符串s ,请你找出其中不含有重复字符的 最长子串 的长度。
示例 1:
输入: s = “abcabcbb”
输出: 3
解释: 因为无重复字符的最长子串是 “abc”,所以其长度为 3。
示例 2:
输入: s = “bbbbb”
输出: 1
解释: 因为无重复字符的最长子串是 “b”,所以其长度为 1。
示例 3:
输入: s = “pwwkew”
输出: 3
解释: 因为无重复字符的最长子串是 “wke”,所以其长度为 3。
请注意,你的答案必须是 子串 的长度,“pwke” 是一个子序列,不是子串。
提示:
0 <= s.length <= 5 * 104
s 由英文字母、数字、符号和空格组成
public static int maxSubString(String str) {
if (str == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
int result = 0;
String subStr = new String();
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
Character cur = str.charAt(i);
int index = subStr.indexOf(cur);
if (index != -1) {
subStr = subStr.substring(index + 1, subStr.length());
}
subStr = subStr + cur;
result = Math.max(result, subStr.length());
}
return result;
}
关键点:注意dvfwva, 这样的字符串,结果是4不是3,所以发现v重复时,此时,当前字符串应该是fwv,而不仅是v。
思路:
这道题主要用到思路是:滑动窗口
什么是滑动窗口?
其实就是一个队列,比如例题中的 abcabcbb,进入这个队列(窗口)为 abc 满足题目要求,当再进入 a,队列变成了 abca,这时候不满足要求。所以,我们要移动这个队列!
如何移动?
我们只要把队列的左边的元素移出就行了,直到满足题目要求!
一直维持这样的队列,找出队列出现最长的长度时候,求出解!
时间复杂度:O(n)
套路:单链表反转
public void revertLink (ListNode head) {
// 先构建一个pre
ListNode pre = null;
// 把head作为cur
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur.next != null) {
// 先保留next
ListNode next = cur.next;
// 把cur指向pre
cur.next = pre;
// 把pre的值变成cur
pre = cur;
// 把cur的值变成next
cur = next;
}
}
2、反转链表中的每k个节点(难度:hard)
给你一个链表,每 k 个节点一组进行翻转,请你返回翻转后的链表。
k 是一个正整数,它的值小于或等于链表的长度。
如果节点总数不是 k 的整数倍,那么请将最后剩余的节点保持原有顺序。
进阶:
你可以设计一个只使用常数额外空间的算法来解决此问题吗?
你不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际进行节点交换。
示例 1:
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2
输出:[2,1,4,3,5]
示例 2:
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 3
输出:[3,2,1,4,5]
示例 3:
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 1
输出:[1,2,3,4,5]
示例 4:
输入:head = [1], k = 1
输出:[1]
提示:
列表中节点的数量在范围 sz 内
1 <= sz <= 5000
0 <= Node.val <= 1000
1 <= k <= sz
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
// 先构建一个虚拟节点
ListNode dummy = new ListNode();
dummy.next = head;
ListNode start = head;
ListNode end = head;
// 记录revert后的最后一个节点
ListNode tail = null;
int i = 0;
while (end != null) {
int cnt = 0;
while (cnt < k - 1) {
cnt++;
if (end.next == null) {
return dummy.next;
}
end = end.next;
}
// 在反转前先记录下反转链表的下一个指针
ListNode next = null;
if (end != null) {
next = end.next;
// 把end的下一个指针置为null, 避免反转多了
end.next = null;
}
// 记录第一个反转前的end元素,作为后续的头元素
if (i == 0) {
dummy.next = end;
} else {
if (tail != null) {
tail.next = end;
}
}
// 反转k个元素的单链表
tail = start;
revertLink(start);
if (tail != null) {
tail.next = next;
}
start = next;
end = next;
i++;
}
return dummy.next;
}
// 返回反转后链表的第一个head节点
public ListNode revertLink(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode cur = head;
ListNode pre = null;
while (cur != null) {
// 先保存当前节点的next节点
ListNode next = cur.next;
// 让cur指向pre
cur.next = pre;
// 用cur赋值给pre
pre = cur;
// 用next给cur赋值
cur = next;
}
return pre;
}
其中,revert链表划重点。
3、最长回文子串
最长回文子串
给你一个字符串 s,找到 s 中最长的回文子串。
示例 1:
输入:s = “babad”
输出:“bab”
解释:“aba” 同样是符合题意的答案。
示例 2:
输入:s = “cbbd”
输出:“bb”
提示:
1 <= s.length <= 1000
s 仅由数字和英文字母组成
public String longestPalindrome(String s) {
String result = new String();
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
char cur = s.charAt(i);
for (int j = i; j < s.length(); j++) {
if (s.charAt(j) == s.charAt(i)) {
String curStr = s.substring(i, j+1);
if (curStr.length() > result.length() && isHuiWen(curStr)) {
result = curStr;
}
}
}
}
return result;
}
public boolean isHuiWen(String str) {
int middle = str.length() / 2;
for (int i = 0; i < middle; i++) {
if (str.charAt(i) != str.charAt(str.length()-i-1)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
4、LRUCache
请你设计并实现一个满足 LRU (最近最少使用) 缓存 约束的数据结构。
实现 LRUCache 类:
LRUCache(int capacity) 以 正整数 作为容量 capacity 初始化 LRU 缓存
int get(int key) 如果关键字 key 存在于缓存中,则返回关键字的值,否则返回 -1 。
void put(int key, int value) 如果关键字 key 已经存在,则变更其数据值 value ;如果不存在,则向缓存中插入该组 key-value 。
如果插入操作导致关键字数量超过 capacity ,则应该 逐出 最久未使用的关键字。
函数 get 和 put 必须以 O(1) 的平均时间复杂度运行。
示例:
输入
[“LRUCache”, “put”, “put”, “get”, “put”, “get”, “put”, “get”, “get”, “get”]
[[2], [1, 1], [2, 2], [1], [3, 3], [2], [4, 4], [1], [3], [4]]
输出
[null, null, null, 1, null, -1, null, -1, 3, 4]
解释
LRUCache lRUCache = new LRUCache(2);
lRUCache.put(1, 1); // 缓存是 {1=1}
lRUCache.put(2, 2); // 缓存是 {1=1, 2=2}
lRUCache.get(1); // 返回 1
lRUCache.put(3, 3); // 该操作会使得关键字 2 作废,缓存是 {1=1, 3=3}
lRUCache.get(2); // 返回 -1 (未找到)
lRUCache.put(4, 4); // 该操作会使得关键字 1 作废,缓存是 {4=4, 3=3}
lRUCache.get(1); // 返回 -1 (未找到)
lRUCache.get(3); // 返回 3
lRUCache.get(4); // 返回 4
提示:
1 <= capacity <= 3000
0 <= key <= 10000
0 <= value <= 105
最多调用 2 * 105 次 get 和 put
class LRUCache1 {
class DLinkedNode {
int key;
int value;
DLinkedNode prev;
DLinkedNode next;
public DLinkedNode() {}
public DLinkedNode(int _key, int _value) {key = _key; value = _value;}
}
private Map<Integer, DLinkedNode> cache = new HashMap<Integer, DLinkedNode>();
private int size;
private int capacity;
private DLinkedNode head, tail;
public LRUCache1(int capacity) {
this.size = 0;
this.capacity = capacity;
// 使用伪头部和伪尾部节点
head = new DLinkedNode();
tail = new DLinkedNode();
head.next = tail;
tail.prev = head;
}
public int get(int key) {
DLinkedNode node = cache.get(key);
if (node == null) {
return -1;
}
// 如果 key 存在,先通过哈希表定位,再移到头部
moveToHead(node);
return node.value;
}
public void put(int key, int value) {
DLinkedNode node = cache.get(key);
if (node == null) {
// 如果 key 不存在,创建一个新的节点
DLinkedNode newNode = new DLinkedNode(key, value);
// 添加进哈希表
cache.put(key, newNode);
// 添加至双向链表的头部
addToHead(newNode);
++size;
if (size > capacity) {
// 如果超出容量,删除双向链表的尾部节点
DLinkedNode tail = removeTail();
// 删除哈希表中对应的项
cache.remove(tail.key);
--size;
}
} else {
// 如果 key 存在,先通过哈希表定位,再修改 value,并移到头部
node.value = value;
moveToHead(node);
}
}
private void addToHead(DLinkedNode node) {
node.prev = head;
node.next = head.next;
head.next.prev = node;
head.next = node;
}
private void removeNode(DLinkedNode node) {
node.prev.next = node.next;
node.next.prev = node.prev;
}
private void moveToHead(DLinkedNode node) {
removeNode(node);
addToHead(node);
}
private DLinkedNode removeTail() {
DLinkedNode res = tail.prev;
removeNode(res);
return res;
}
}