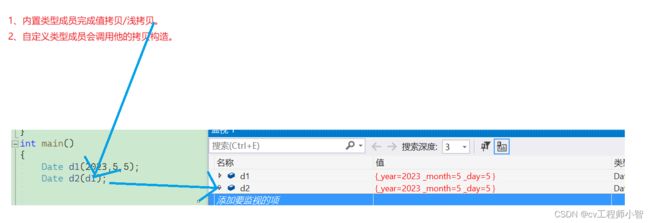
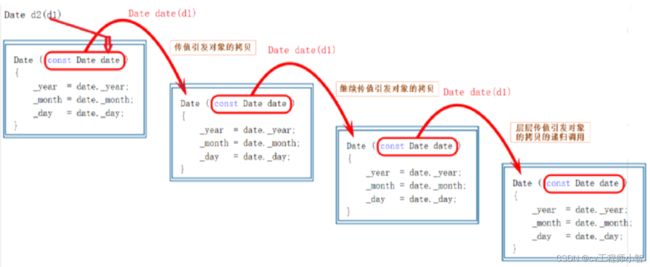
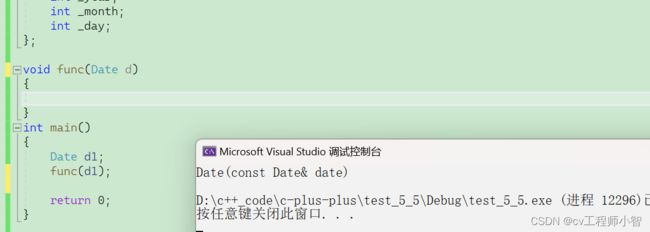
extern“c”被extern"c"修饰的代码会按照c语言的方式编译如果函数同时有声明和实现,要让函数声明被extern"C"修饰,函数实现可以不被修饰extern"C"voidfun(){cout<<"fun()"<
Datawhale 数学建模导论国赛B学习笔记
瓜瓜蛋
数学建模学习笔记
贪心算法贪心算法(Greedyalgorithm)(贪婪算法)基本思想:多机调度问题是一个多项式复杂程度的非确定性问题(Non-deterministicPolynomial),具有一定的复杂程度,当前没有有效的解决方法。相较于其它算法,贪心算法求解不从整体最优上加以考虑,。而是寻求某种意义上的局部最优解,从而做出当下最好的选择。因此,在求解并行机调度问题上,贪心算法容易获得近似最优解的答案,更有
C 语言中的数组与指针:深入剖析与实践应用
Kurbaneli
c语言算法
一、引言在C语言的学习旅程中,数组与指针是两个极为重要且强大的概念。它们不仅是C语言高效操作数据的基础,也是C语言能够广泛应用于系统编程、嵌入式开发等领域的关键因素之一。深入理解并熟练掌握数组与指针的使用,对于编写高质量、高性能的C语言程序至关重要。本文将详细介绍C语言中数组与指针的相关知识,并通过丰富的示例代码进行说明。二、数组的基本概念与使用数组的定义:数组是一种构造数据类型,它可以存储多个相
后端开发面经系列 -- 字节跳动C/C++一面面经
阿Q技术站
面经字节跳动面经c++面经字节跳动职场经验
字节跳动C/C++一面面经公众号:阿Q技术站来源:https://www.nowcoder.com/feed/main/detail/74bf25e202ea4fcba09c01dae530ff9b1、虚拟地址是怎么转化到物理地址的?页表的构成?mmu了解过吗?虚拟地址到物理地址的转换是通过操作系统中的内存管理单元(MemoryManagementUnit,MMU)来实现的。MMU是计算机系统中的
react原理面试题
前端react
以下是一些关于React原理的面试题:一、虚拟DOM(VirtualDOM)请简要解释React中的虚拟DOM是如何工作的?答案:当组件的状态发生变化时,React首先会在内存中创建一个新的虚拟DOM树来表示更新后的UI结构。然后,React会将这个新的虚拟DOM树与旧的虚拟DOM树进行比较(这个过程称为Diff算法)。Diff算法会找出两个虚拟DOM树之间的差异,例如哪些节点被添加、删除或者修改
C语言:多组输入a+b
爱学习的小孩啦
C_编程c语言开发语言
链接:登录—专业IT笔试面试备考平台_牛客网来源:牛客网计算a+b输入描述:输入包含多组数据,每组数据输入一行,包含两个整数输出描述:对于每组数据输出一行包含一个整数表示两个整数的和示例1输入1234输出37#includeintmain(){inta,b;//读取输入,直到文件结束while(scanf("%d%d",&a,&b)!=EOF){//计算两个整数的和intresult=a+b;//
字节后端面试面经综合分析
阿贾克斯的黎明
javajava开发语言go
目录一、字节豆包后端一面面经解析(一)自我介绍(二)实习项目拷打(三)手撕代码(四)C++多态相关问题(五)智能指针相关问题(六)malloc相关问题(七)mmap相关问题(八)多线程相关问题(九)MySQL存储引擎相关问题(十)Redis持久化相关问题(十一)前沿知识相关问题(十二)反问环节二、字节广告后端一面面经解析(一)自我介绍(二)实习项目拷打(三)文件系统相关问题(四)LinuxIO多路
2021年最新社招字节跳动 go 后端开发工程师一二三四五面面经
AI乔治
java面试架构Java架构面试程序人生编程语言
因为公司原因,所以就换了工作,第一目标就是字节,12月份找朋友内推的上海教育部门,朋友让我多准备准备,过了两周才开始一面。附上新鲜的一二三四五面面经。写在前面面试字节一定要提前复习,能提前多久就提前多久。尤其是算法,绝对是重中之重,因为我已经刷了3年LeetCode了,所以算法没怎么复习,三次面试一共6题也全写出来了,基本上都是原题。然后就是数据库、网络、消息中间件、架构等等。校招的话架构可以不用
【算法学习之路】4.简单数论(4)
零零时
算法学习之路算法学习c++开发语言数据结构数学高精度
简单数论(4)前言三.高精度1.什么是高精度2.解决办法精度乘除法一.精度乘法1.数据的存储2.步骤3.例题:高精度乘法二.精度除法1.例子2.步骤3.例题:高精度除法前言我会将一些常用的算法以及对应的题单给写完,形成一套完整的算法体系,以及大量的各个难度的题目,目前算法也写了几篇,滑动窗口的题单正在更新,其他的也会陆陆续续的更新,希望大家点赞收藏我会尽快更新的!!!三.高精度1.什么是高精度对运
C语言语法分析器
czme
c语言
C语言语法分析器是编译过程中的关键组件,用于检查C语言源程序的语法结构是否正确,并构建相应的语法树。以下是关于C语言语法分析器的一些介绍以及用简单示例说明其实现思路(以Python实现一个简易的C语言部分语法分析器为例,实际的C语言语法分析器非常复杂):1.语法分析器的作用在C语言编译流程中,词法分析器先把源程序的字符流分割成一个个单词,语法分析器则基于词法分析得到的单词序列,依据C语言的语法规则
每日一题——最长连续序列和uthash.h
tt555555555555
C语言算法题面经哈希算法数据结构算法
最长连续序列和uthash.hLeetCode128.最长连续序列(C语言实现)问题描述示例约束条件解题思路C语言实现代码代码说明测试结果`uthash.h`1.**`HASH_ADD_INT`**2.**`HASH_FIND_INT`**3.**`HASH_ITER`**4.**`HASH_DEL`**5.**`HASH_COUNT`**6.**`HASH_CLEAR`**总结LeetCode1
[C语言]初阶数据结构---链表习题
yycwhks
数据结构c语言链表
经典问题---链表带环问题最后一个节点的next指针,本来应该指向空指针,但是现在指向前面的节点(非NULL),这样就构成了带环链表例子1:判断链表是否带环(力扣)解题代码如下:/***Definitionforsingly-linkedlist.*structListNode{*intval;*structListNode*next;*};*/boolhasCycle(structListNod
矩阵求逆(JAVA)初等行变换
qiuwanchi
矩阵求逆(JAVA)
package gaodai.matrix;
import gaodai.determinant.DeterminantCalculation;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* 矩阵求逆(初等行变换)
* @author 邱万迟
*
JDK timer
antlove
javajdkschedulecodetimer
1.java.util.Timer.schedule(TimerTask task, long delay):多长时间(毫秒)后执行任务
2.java.util.Timer.schedule(TimerTask task, Date time):设定某个时间执行任务
3.java.util.Timer.schedule(TimerTask task, long delay,longperiod
JVM调优总结 -Xms -Xmx -Xmn -Xss
coder_xpf
jvm应用服务器
堆大小设置JVM 中最大堆大小有三方面限制:相关操作系统的数据模型(32-bt还是64-bit)限制;系统的可用虚拟内存限制;系统的可用物理内存限制。32位系统下,一般限制在1.5G~2G;64为操作系统对内存无限制。我在Windows Server 2003 系统,3.5G物理内存,JDK5.0下测试,最大可设置为1478m。
典型设置:
java -Xmx
JDBC连接数据库
Array_06
jdbc
package Util;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class JDBCUtil {
//完
Unsupported major.minor version 51.0(jdk版本错误)
oloz
java
java.lang.UnsupportedClassVersionError: cn/support/cache/CacheType : Unsupported major.minor version 51.0 (unable to load class cn.support.cache.CacheType)
at org.apache.catalina.loader.WebappClassL
用多个线程处理1个List集合
362217990
多线程threadlist集合
昨天发了一个提问,启动5个线程将一个List中的内容,然后将5个线程的内容拼接起来,由于时间比较急迫,自己就写了一个Demo,希望对菜鸟有参考意义。。
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
public c
JSP简单访问数据库
香水浓
sqlmysqljsp
学习使用javaBean,代码很烂,仅为留个脚印
public class DBHelper {
private String driverName;
private String url;
private String user;
private String password;
private Connection connection;
privat
Flex4中使用组件添加柱状图、饼状图等图表
AdyZhang
Flex
1.添加一个最简单的柱状图
? 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28
<?xml version=
"1.0"&n
Android 5.0 - ProgressBar 进度条无法展示到按钮的前面
aijuans
android
在低于SDK < 21 的版本中,ProgressBar 可以展示到按钮前面,并且为之在按钮的中间,但是切换到android 5.0后进度条ProgressBar 展示顺序变化了,按钮再前面,ProgressBar 在后面了我的xml配置文件如下:
[html]
view plain
copy
<RelativeLa
查询汇总的sql
baalwolf
sql
select list.listname, list.createtime,listcount from dream_list as list , (select listid,count(listid) as listcount from dream_list_user group by listid order by count(
Linux du命令和df命令区别
BigBird2012
linux
1,两者区别
du,disk usage,是通过搜索文件来计算每个文件的大小然后累加,du能看到的文件只是一些当前存在的,没有被删除的。他计算的大小就是当前他认为存在的所有文件大小的累加和。
AngularJS中的$apply,用还是不用?
bijian1013
JavaScriptAngularJS$apply
在AngularJS开发中,何时应该调用$scope.$apply(),何时不应该调用。下面我们透彻地解释这个问题。
但是首先,让我们把$apply转换成一种简化的形式。
scope.$apply就像一个懒惰的工人。它需要按照命
[Zookeeper学习笔记十]Zookeeper源代码分析之ClientCnxn数据序列化和反序列化
bit1129
zookeeper
ClientCnxn是Zookeeper客户端和Zookeeper服务器端进行通信和事件通知处理的主要类,它内部包含两个类,1. SendThread 2. EventThread, SendThread负责客户端和服务器端的数据通信,也包括事件信息的传输,EventThread主要在客户端回调注册的Watchers进行通知处理
ClientCnxn构造方法
&
【Java命令一】jmap
bit1129
Java命令
jmap命令的用法:
[hadoop@hadoop sbin]$ jmap
Usage:
jmap [option] <pid>
(to connect to running process)
jmap [option] <executable <core>
(to connect to a
Apache 服务器安全防护及实战
ronin47
此文转自IBM.
Apache 服务简介
Web 服务器也称为 WWW 服务器或 HTTP 服务器 (HTTP Server),它是 Internet 上最常见也是使用最频繁的服务器之一,Web 服务器能够为用户提供网页浏览、论坛访问等等服务。
由于用户在通过 Web 浏览器访问信息资源的过程中,无须再关心一些技术性的细节,而且界面非常友好,因而 Web 在 Internet 上一推出就得到
unity 3d实例化位置出现布置?
brotherlamp
unity教程unityunity资料unity视频unity自学
问:unity 3d实例化位置出现布置?
答:实例化的同时就可以指定被实例化的物体的位置,即 position
Instantiate (original : Object, position : Vector3, rotation : Quaternion) : Object
这样你不需要再用Transform.Position了,
如果你省略了第二个参数(
《重构,改善现有代码的设计》第八章 Duplicate Observed Data
bylijinnan
java重构
import java.awt.Color;
import java.awt.Container;
import java.awt.FlowLayout;
import java.awt.Label;
import java.awt.TextField;
import java.awt.event.FocusAdapter;
import java.awt.event.FocusE
struts2更改struts.xml配置目录
chiangfai
struts.xml
struts2默认是读取classes目录下的配置文件,要更改配置文件目录,比如放在WEB-INF下,路径应该写成../struts.xml(非/WEB-INF/struts.xml)
web.xml文件修改如下:
<filter>
<filter-name>struts2</filter-name>
<filter-class&g
redis做缓存时的一点优化
chenchao051
redishadooppipeline
最近集群上有个job,其中需要短时间内频繁访问缓存,大概7亿多次。我这边的缓存是使用redis来做的,问题就来了。
首先,redis中存的是普通kv,没有考虑使用hash等解结构,那么以为着这个job需要访问7亿多次redis,导致效率低,且出现很多redi
mysql导出数据不输出标题行
daizj
mysql数据导出去掉第一行去掉标题
当想使用数据库中的某些数据,想将其导入到文件中,而想去掉第一行的标题是可以加上-N参数
如通过下面命令导出数据:
mysql -uuserName -ppasswd -hhost -Pport -Ddatabase -e " select * from tableName" > exportResult.txt
结果为:
studentid
phpexcel导出excel表简单入门示例
dcj3sjt126com
PHPExcelphpexcel
先下载PHPEXCEL类文件,放在class目录下面,然后新建一个index.php文件,内容如下
<?php
error_reporting(E_ALL);
ini_set('display_errors', TRUE);
ini_set('display_startup_errors', TRUE);
if (PHP_SAPI == 'cli')
die('
爱情格言
dcj3sjt126com
格言
1) I love you not because of who you are, but because of who I am when I am with you. 我爱你,不是因为你是一个怎样的人,而是因为我喜欢与你在一起时的感觉。 2) No man or woman is worth your tears, and the one who is, won‘t
转 Activity 详解——Activity文档翻译
e200702084
androidUIsqlite配置管理网络应用
activity 展现在用户面前的经常是全屏窗口,你也可以将 activity 作为浮动窗口来使用(使用设置了 windowIsFloating 的主题),或者嵌入到其他的 activity (使用 ActivityGroup )中。 当用户离开 activity 时你可以在 onPause() 进行相应的操作 。更重要的是,用户做的任何改变都应该在该点上提交 ( 经常提交到 ContentPro
win7安装MongoDB服务
geeksun
mongodb
1. 下载MongoDB的windows版本:mongodb-win32-x86_64-2008plus-ssl-3.0.4.zip,Linux版本也在这里下载,下载地址: http://www.mongodb.org/downloads
2. 解压MongoDB在D:\server\mongodb, 在D:\server\mongodb下创建d
Javascript魔法方法:__defineGetter__,__defineSetter__
hongtoushizi
js
转载自: http://www.blackglory.me/javascript-magic-method-definegetter-definesetter/
在javascript的类中,可以用defineGetter和defineSetter_控制成员变量的Get和Set行为
例如,在一个图书类中,我们自动为Book加上书名符号:
function Book(name){
错误的日期格式可能导致走nginx proxy cache时不能进行304响应
jinnianshilongnian
cache
昨天在整合某些系统的nginx配置时,出现了当使用nginx cache时无法返回304响应的情况,出问题的响应头: Content-Type:text/html; charset=gb2312 Date:Mon, 05 Jan 2015 01:58:05 GMT Expires:Mon , 05 Jan 15 02:03:00 GMT Last-Modified:Mon, 05
数据源架构模式之行数据入口
home198979
PHP架构行数据入口
注:看不懂的请勿踩,此文章非针对java,java爱好者可直接略过。
一、概念
行数据入口(Row Data Gateway):充当数据源中单条记录入口的对象,每行一个实例。
二、简单实现行数据入口
为了方便理解,还是先简单实现:
<?php
/**
* 行数据入口类
*/
class OrderGateway {
/*定义元数
Linux各个目录的作用及内容
pda158
linux脚本
1)根目录“/” 根目录位于目录结构的最顶层,用斜线(/)表示,类似于
Windows
操作系统的“C:\“,包含Fedora操作系统中所有的目录和文件。 2)/bin /bin 目录又称为二进制目录,包含了那些供系统管理员和普通用户使用的重要
linux命令的二进制映像。该目录存放的内容包括各种可执行文件,还有某些可执行文件的符号连接。常用的命令有:cp、d
ubuntu12.04上编译openjdk7
ol_beta
HotSpotjvmjdkOpenJDK
获取源码
从openjdk代码仓库获取(比较慢)
安装mercurial Mercurial是一个版本管理工具。 sudo apt-get install mercurial
将以下内容添加到$HOME/.hgrc文件中,如果没有则自己创建一个: [extensions] forest=/home/lichengwu/hgforest-crew/forest.py fe
将数据库字段转换成设计文档所需的字段
vipbooks
设计模式工作正则表达式
哈哈,出差这么久终于回来了,回家的感觉真好!
PowerDesigner的物理数据库一出来,设计文档中要改的字段就多得不计其数,如果要把PowerDesigner中的字段一个个Copy到设计文档中,那将会是一件非常痛苦的事情。